AP Bio - Ch.40-43: Ecology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
population
group of individuals of the same species living in the same area
community
a group of populations
ecosystem
community of organisms and the physical factors that they interact with
habitat
the “area” / place. the physical embodiment of an animals ecological niches
dispersion
pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population
dispersal
the movement of individuals or gametes away from area of origin
clumped
pattern of dispersion involving aggregation. often associated with mating behaviors
uniform
pattern of dispersion involving spaced separation. often associated with territorial behavior
random
pattern of dispersion lacking a perceivable pattern. associated with neither attractive nor repulsive factors.
density
mass over volume. calculates number of individuals per unit area of volume
logistic
________ function can be used to determine population changes.
r — per Capita change
N — population change
t — time
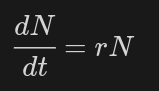
K
Carrying capacity (the maximum amount).
When N=K, population stops growing.
K-selection
Traits advantageous for high density environments
r-selection
Traits that maximize reproduction in small environments
Density-independent factors
Affect populations, but do not rely on population densities
eg. natural disasters
Density-dependent factors
Affect populations and rely on population densities
eg. scarcity of resources, disease
intraspecific competition
competition that exists within a population (same species)
interspecific competition
Ecological Interaction. (- / - )
Competition that exists within a community (different species)
Ecological Niches
Sum of the species (specific) use of biotic and abiotic resources in an environment
“preferences” that, if infringed by another competitor, results in intra/interspecific competition
depends on the species of the competitors (same species/difference species)
Sympatric populations
Populations that tend to have a greater variance in traits due to geographical overlap (increased competition)
Allopatric populations
Populations that have more consistent traits from being geographically more spread out
Ecological interactions
how organisms interact in an ecosystem
Made up of three main broad categories:
Competition ( - / - )
Exploitation ( + / - )
Positive Interaction ( + / + )
Parasitism
Ecological Interaction ( + / - )
ectoparasitism — feed off of host surface level
endoparasitism — feed off of host from within
Predation
Ecological Interaction ( + / - )
One organism preying upon another organism.
Herbivory
Ecological Interaction ( + / - )
The consumption of plant matierla by animals
Mutualism
Ecological Interaction ( + / + )
Symbiosis that is beneficial to both organisms involved.
Commensalism
Ecological Interaction ( + / 0 )
Association where one organism benefits off of the other, while the other doens’t necessarily get any benefits nor harm
Trophic positions
position an organism occupies within a food chain
Primary Producers
(Trophic position)
Autotrophs — convert their own energy from the sun
Primary Consumers
(Trophic position)
Herbivores (first to consume autotrophs)
Secondary Consumers
(Trophic position)
Carnivores that eat herbivores
Tertiary Consumers
(Trophic position)
Carnivores that consume other carnivores.
Detrivores
(Trophic position)
Decomposers — obtains nutrients from nonliving things