AS business topic 3 CAIE
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
the marketing mix
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
The role of marketing
marketing is the management task of identifying and meeting the needs of customers profitably by getting the right product at the right price too the right place at the right time
it involves a number of related management functions:
market research
product design and packaging design
pricing, advertising, and distribution
customer service
Marketing objectives
the share of the market
total sales (value, volume, or both)
average number of items purchased by loyal customers
percentage of customers who return (customer loyalty)
customer satisfaction
brand identity
marketing objectives and how they are important and effective
to be effective:
they should be linked to corporate objectives which are well-defined and realistic goals that are set for the whole company, they should also be focused on helping the business achieve those overall targets
be determined by senior management as the key marketing objectives will impact on the markets and products a business trades
be realistic, motivating, achievable, measurable, and clearly communicated to other departments
why they’re important:
they provide a sense of focused direction for the marketing department
business success can be measured against the targets set by objectives
marketing objectives can be broken down into regional and product sales targets
marketing objectives form the basis of marketing strategy which is a plan of action giving details of how a business intends to achieve its marketing objectives by creating a competitive advantage
coordination of marketing with other departments
finance
the finance department will use the sales forecast of the marketing department to help construct cash flow forecasts and operational budgets
the finance department will have to ensure that the necessary capital is available to pay for the agreed marketing budget
Human Resources
sales forecasts will be used by Human Resources to help prepare a workforce plan
Human Resources must ensure the recruitment and selection of qualified and experienced workers
operations
market research data will play a key role in new product development
the operations department will use sales forecasts to plan the capacity needed, the purchase of the machines, and the raw material inventories required for the higher output level
Demand and supply
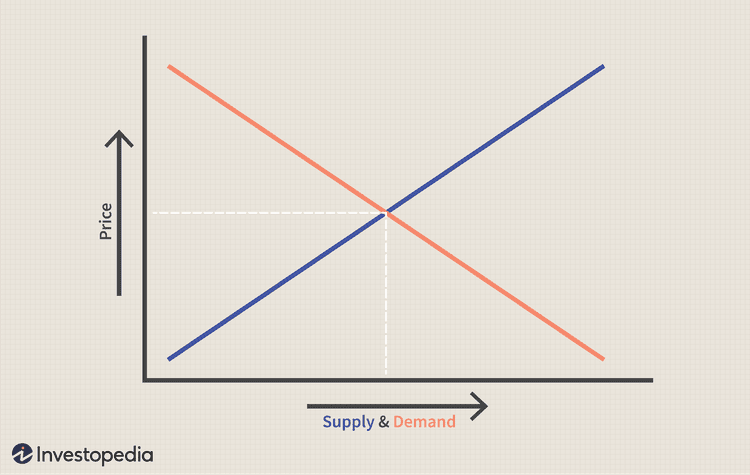
In free markets, the equilibrium price is determined when the demand equals supply.
equilibrium price is the price level where demand equals supply
demand is the quantity of. product that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price in a specific time period
supply is the quantity of a product that firms are prepared to supply at a given price in a specific time period
demand
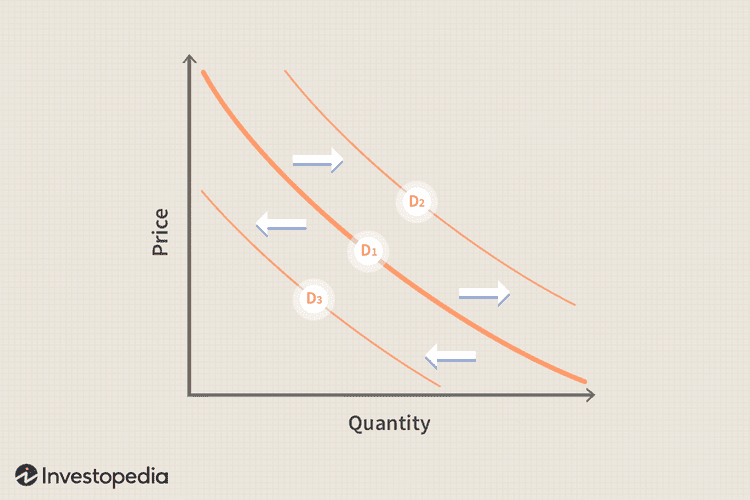
demand varies with price. for all normal goods the quantity bought rises with a price fall and falls with a price increase, which is shown by a typical demand curve
apart from price changes, the level of demand for a product can change as a result of a change in any of the following factors: consumer incomes, prices of substitute goods and complementary goods, population size and structure, fashion and taste, advertising and promotion spending, these are all determinants of demand
all of these changes can result in a new demand curve
supply
supply varies with price. Businesses will be more willing to supply more of a product id the price rises and will supply less of a product as the price falls which is shown by a typical supply curve
apart from changes in price, the level of supply of a product can vary due to a change in any of the following factors: costs of production, government taxes imposed in suppliers, government subsidies to suppliers, weather conditions and other natural factors, and advances in technology which lower the cost of production, these are all known as determinants of supply
all of these changes can result in a new supply curve

determining the equilibrium price
demand and supply can be shown on the same diagram, the price level at which demand equals supply is called the equilibrium price. If the price is higher than the equilibrium price then there will be unsold inventory (excess supply) and suppliers don’t want unsold products and so will lower the price. If the price is lower than the equilibrium price then inventories will run out leaving excess demands and so suppliers could make a higher profit by raising the price to equilibrium level
markets
the term market refers to the group of customers who are interested in a product and have the resources to purchase, the understanding of the term market can be broken down into:
The potential market for a product which is the total population interested in the product
the target market is known as the market segment of the total available market that the business that the business has decided to direct its product towards
the market segment is a subgroup of a whole market in which consumers have similar characteristics
How markets differ
an industrial market is the selling of product by businesses to other businesses known as business to business or B2B
a consumer market is the selling of products by businesses to the final end user also known as business to consumer B2C
there are also local, national, and international markets
customer (or market) orientation and product orientation
important distinctions can be made between businesses which focus on customer orientation and those which focus on product orientation
customer orientation is an outward looking approach approach that bases product decisions on consumer demand, as established by market research
product orientation is an inward looking approach that focuses on making products that can be made - or have been made for a long time - and then trying to sell them
the benefits of customer orientation are that the chances of newly developed products failing in the market are reduced and products based on consumers needs will have a longer lifespan and be more profitable than those that are sold using a product let approach, market research never ends.
Market size
the market size can be measured in two ways: the quantity of sales or the value of products sold by all businesses in the market over a given time period. It is important for 3 reasons:
it allows a marketing manager ti asses whether a market is worth entering or not
it allows a business to calculate its own share of the market
the growth or decline of the market over time can be measured
market size is the total value (or quantity) of sales of all producers within a market in a given time period
Market growth
market growth is the percentage change in the total size of a market (volume to value) over a period of time
the rate of market growth depends on several factors
a country’s rate of economic growth
changes in consumer incomes
development of new markets and products that reduce sales in existing markets and products
changes in consumer tastes
technological change
whether the market is saturated because most consumers already own the product
implications of a change in market growth
increased market growth
sales will increase if the businesses market share remains the same
it may be possible to increase prices and profit per unit
increased sales could lead to cost savings
more businesses might be attracted to the market, increasing the level of competition
reduced market growth
sales will increase more slowly even if the business’s market share remains the same
competitors might reduce prices to increase sales in a slow-growing or shrinking market
lower prices might result in lower profit per unit
businesses might consider expanding into faster-growing markets
market share
market share is calculated using the following formula
market share = sales of the business in time period/total market sales in time period x 100
if the market share of a business is increasing then the marketing of the products has been more successful relative to more of its competitors, the product with the highest market share is called the brand leader
implications of a change in market share
increase in market share
sales are rising faster than those of competing businesses in the same market which could lead to higher profits
retailers will be keen to stock and promote the best selling brands
the business producing the brand leader may be able to reduce the discount rate to retailers
the fact that an item or brand is market leader can be used in advertising and other promotional material
decrease in market share
sales are likely to fall unless there is rapid market growth
retailers will be less keen to stock and promote the product
larger discounts to retailers might have to be offered
the product may no longer be a brand leader
market growth could be measured by volume or value
classification of products
consumer products are goods or services sold to end users, they are usually classified into: convenience products which are purchased frequently and often bought on impulse with a large target market, shopping products which usually require some planning and research from products beforehand and they are not bought frequently, and specialty products which are bought infrequently and often are expensive with strong brand loyalty
industrial products are goods or services sold to businesses, they are usually classified into: materials and components which are needed for production to take place, capital items which are equipment, machinery, and vehicles, and services and supplies which are businesses services and utilities
the key differences with selling B2B rather than B2C
most industrial products are much more complex than many consumer products and so specialist sales employees and support services are more important
industrial buyers often have much more market power and are better informed than the regular consumer
industrial buyers will rarely buy on impulse
traditional mass media advertising and sales promotion techniques are not used in most industrial markets
mass marketing in consumer markets is a common strategy but not in industrial markets as there are normally less buyers
mass marketing and the advantages and disadvantages
mass marketing is the selling of standardised products or ranges of products in the same way to the whole market
advantages
a mass-market strategy with high sales of a standard product can lead to lower average costs of production
cost advantages can lead to lower prices to consumers which help to reinforce the position of the product in the market
mass marketing can result in extensive publicity for the business and its product which leads to clear brand identity
disadvantages
lack of differentiated products and differentiated marketing does not appeal to many consumers
the focus on low prices does not help to establish a premium brand image for the product
technological or other changes could lead to a fall in demand for the standardised product
niche marketing and the advantages and disadvantage
niche marketing identifies and exploits a small segment of a larger market by developing differentiated products to suit that segment
advantages
by using niche marketing, small businesses can survive and thrive in markets that are dominated by larger firms
an unexploited niche has no competitors
niche market products and exclusive marketing can be used by large firms to create status and image
disadvantages
small market niches do not allow economies of scale to be achieved
there is limited scope for business growth if the niche market has few customers
the business is vulnerable to market changes if it only operates in one niche market
if selling in a niche market is profitable then it is likely to attract competitors
market segmentation and methods of it
market segmentation is the identification of different groups of customers with common needs within a market and the marketing of different products or services to those customer groups
a consumer profile helps the marketing team to gather the right information, a consumer profile is a quantified picture of a business’s consumers, showing data about their age groups, income levels, location, gender, and social class
total markets can be segmented in a number of different wats but the most common are geographic differences, demographic differences, and psychographic factors
advantages and disadvantages of market segmentation
advantages
businesses can define their target market precisely and then design and produce goods which are specifically aimed at these groups
it enables identification of gaps in the market and groups of consumers which aren’t currently being targeted
differentiated marketing strategies can be focused on different target markets
small firms that are unable to compete in the whole market are able to specialise in one or two market segments
price discrimination between consumer groups can be used to increase revenue and profits
disadvantages
research and development and production costs might be high as a result of needing to make and market different product variation
promotional costs might be high as different advertisements and promotions might be needed for different segments
production and inventory holding costs will be higher
by focusing on one or two limited market segments it could lead to excessive specialisation
extensive market research is needed to identify market segments and their needs
customer relationship marketing (CRM)
customer relationship marketing is using marketing activities to build and establish good customer relationship sup that the loyalty of existing customers can be maintained
developing effective long-term relationships can be achieved by:
targeted marketing
customer service and support
communicate regularly with customers
using social media
costs and benefits of CRM
benefits
for businesses with an existing customer base, CRM has proved to be cost effective and higher sales from effective CRM nearly always exceeds its cost
it is a sustainable strategy creating long term customers
loyal customers often recommend the business to friends and family
it costs less per customer than trying to attract new customers
costs
IT systems and software are needed and employees need to be trained to respond to customer feedback
effective CRM campaigns may require the use of an external marketing agency at a high cost
CRM needs an existing customer base to be established before starting it
it may be costly to respond to each customers feedback
market research
market research is the process of collecting, recording and analysing data about customers, competitors, and the market
it can be used to measure customer reactions to: new products, different price levels, alternative forms of promotion, new types of packaging, and online distribution
purpose of market research - identifying main features of the market
key features include: overall size, growth, and competitors
businesses do market research so they can:
reduce the risks of new product launches
identify consumer characteristics
explain patterns in sales of existing products and market trends
predict future demand changes
assess the most popular designs, promotions, styles and packaging for a product
primary research and secondary research
primary research is the collection of first-hand data that is directly related to the needs of the business
secondary research is the use of existing data that was originally collected for another purpose
businesses often undertake secondary research first when entering a new market because:
it is lower cost and obtainable more quickly than primary data
it can be used to asses the main features of a market
usefulness of secondary research data
it can provide information about the population, economy, market conditions, and major trends in the market
it can help identify the key areas of market information that primary research needs to focus on
it provides evidence that can be used as a baseline against which primary data can be compared
large samples are often used which increases accuracy and reliability
many of the sources of secondary data can be accessed via the internet
if time or finance is limited then it might be the only option
there is so much of this data, which opens up new business possibilities if analysed carefully
there are many sources of secondary data which allows it to be double checked
limitations to the usefulness of secondary research data
data may be out of date as not all sources update every year
data is unlikely to have been collected for the specific needs of the business
not all secondary data is available to all potential users
secondary data might indicate the potential for a new market but primary data is needed to gather specific information
big data is so vast that it is not easy to analyse and to make useful for an individual business
sources of secondary data
the main sources of secondary data are:
government
local government
trade organisations
market research agencies
internal company records
company reports and accounts
usefulness of primary research data
to find out about completely new markets
to collect data for the specific purposes of the business
to gather qualitative data which helps to explain the quantitative data
to focus research on market reaction to specific changes made by the business
to gain information from a particular target group of consumers
when up-to-date data is essential
when data needs to be cross checked for accuracy
limitations to the usefulness of primary research data
the selection of a sufficiently large and representative sample greatly influences the accuracy of data
business start-ups may not be able to finance detailed primary research
newly formed businesses have no customers yet to gain important data from
it can be time-consuming to collect and analyse primary research Fata
sources of primary research data
questionnaires
interviews
observations
test marketing
focus groups
sampling and the need for it
sampling is the process of selecting a group of respondents from a larger population
in nearly all market research situations, it is impossible to seek evidence from the total population because either it is so extensive that contacting everyone in it would be too expensive or time consuming, or that it is impossible to identify everyone in the target market, so a sample of the total potential market will be chosen
a sample is a group of people taking part in a market research survey selected to be representative of the overall target market
limitations of sampling
sample may be too small
risk of sampling bias
researchers may not use the most appropriate methods of sampling
the reliability of market research data
secondary data can be unreliable because of the limitations already referred to earlier
there are 3 main reasons as to why primary data may be unreliable:
sampling bias which is when the sample does not accurately represent the population
questionnaire bias which may occur when questions tend to lead respondents towards one particular answer
other forms of bias which might include things such as the respondent not answering in a very truthful way
the analysis of quantitative data
averages include the mean, median, and mode
the mean is the value which is calculated by adding all of the results and dividing by the number of results. It is used as an indicator of likely sales levels per period of time and for making comparisons between sets of data. the advantages include that it includes all of the data in a calculation and is the most well known average. The disadvantages include that it is affected by one or two extreme results and is usually not a whole number.
the mode is the value that occurs out frequently in a set of data and can be used for inventory ordering purposes. the advantages are that it is easily observed and non calculation is necessary and that the result is a whole number and easily understood. the disadvantages are that it does not consider all of the data and there may be more than one modal result s
the median is the value of the middle item when data has been ordered or ranked and is can be used in wage negotiations and advertising. the advantages include that it is less influenced by extreme results than the mean. the disadvantages include that the calculation from grouped data is complicated, an even number of results means the value is approximated and it cannot be used for further statistical analysis
measures of spread include the range which is the difference between the higher and lowest value
the analysis of qualitative data
qualitative research aims to understand why consumer behave in a certain way or how consumerism might react to the launch of a new product. the answers to qualitative research are based on opinions, attitudes, and beliefs and so it cannot be analysed using statistical techniques s
the answers to these questions should be carefully recorded and should be categorised into types of response which is called coding
interpretation of information presented in tables, charts, and graphs
tables which allow easy reference to the data and can be used to present a mass of data in a precise way
pie graphs which are used where data needs to be presented so that the proportions of different sets of data in relation to the total are clearly shown, each section of the pie shows how relatively significant the part of the data is compared to the whole. the size of each section is determined by the angle at the centre of the circle and is calculated by: angle of section = value of one section/total value of all sections x 360 degrees
line graphs are most commonly used for showing changes in a variable and allows easy reference to rends in the data and shows fluctuations clearly
bar graphs use bands of equal width but varying length or height to represent relative value and allow easy comparison over time or between different items
the elements of the marketing mix
the marketing mix is the four key decision on product, price, promotion, and place that must be taken to enable the effective marketing of a product.
product - consumers require the right product, which might be an existing product, an update to an existing product or a newly developed product
price - the right price is important as id the price is too low then the consumers may lose confidence in the products quality but if the price is set too high then many consumers will be unable or unwilling to buy it
promotion - it must be effective at telling consumers about the products availability and convincing them that the brand is the one to choose
place - it refers how the product is distributed to the consumer through distribution channels and if the good or service is not available at the right time in the right place then it will not be bough in the quantities expected
product - goods and services
goods refers to products which have a physical existence
services are products which have no physical existence, bit satisfy consumer needs in other ways
tangible and intangible attributes of products
intangible attributes are the subjective opinions of customers about a product, which cannot be measured or compared easily
tangible attributes are the measurable features of a product, which can be easily compared with other products
marketing managers should try to understand what intangible attributes and tangible attributes when making purchase decisions, because this is why some consumers will pay more for a well known brand
a brand is an identifying symbol, name, image or trademark that distinguishes a product from its competitors
the importance of product development
new product development (NPD) is crucial to the success of some businesses
NPD is the design creation and marketing of new goods and services
it is important for:
changing consumer tastes and preferences
increasing competition
technological advancement
new opportunities for growth
risk diversification
improved brand image
use of excess capacity
for new products to succeed they must:
have desirable features that consumers are ready to pay for
be marketed effectively to consumers, who need to be informed bout it
be sufficiently different from other products to make it stand out and offer a unique selling point (USP)
the USP is the special feature of a product that makes it different from competitors products
product differentiation and USP
product differentiation is the unique qualities of a product that lead to a difference between to product and competitors’ products
the benefits of an effective USP are:
promotion that focuses on the differentiating feature of the product or service
opportunities to charge higher prices due to exclusive and unique features, design or customer service
free publicity foo media reporting on the USP of the product
higher sales compared to undifferentiated probes
customers being more willing to be identified with the brand because its different
product portfolio analysis
product portfolio analysis is analysing the range of existing products of a business to help allocate resources effectively between them
the two profit portfolio analysis techniques are: product life cycle and the Boston matrix analysis
Product life cycle
the product life cycle is the pattern of sales for a product from launch to withdrawal of the market
the introduction is when the product has just been launches after development and testing, sales are often quite low to begin with
the growth period is when sales start to grow, if the product is effectively promoted then this should happen but it cannot last forever
maturity or saturation is when sales fail to grow but they do not decline significantly either, the saturation of the consumer durables market is caused by consumers having already bought the particular product they want. consumer durables is a manufactured product that can be re-used and is expected to have a reasonable long life
decline is the stage when sales decline steadily and so either no extension strategy is used or it has not worked. an extension strategy is a marketing plan to extend the maturity stage of the product before a completely new one is launched
limitations of this is that it cannot be used to predict the future and is only based on past or current data
Boston matrix analysis
the Boston matrix is a method of analysing the product portfolio of a business in terms of market share and market growth, there are 4 sectors created by the matrix which can be analysed in the following way:
cash cow - low market growth, high market share; it is a well-established product in a mature market and is typically profitable with a high positive cash flow and sales are high relative to the market and promotional costs are likely to be low
star - high market growth, high market share; this is a successful product performing well in an expanding market, the promotion costs will be high as it is keen to maintain the market position
question mark - hight market growth, low market share; it consumes resources but generates little return and the future of the product may be uncertain
dog - low market growth, low market share; it offers little to the business in terms of existing sales and cash flow or future prospects because the market is not growing
impact and limitations of the Boston Matrix
the Boston matrix analysis is relevant when:
analysing the performance and current position of existing product portfolios
planning action to be taken with existing products
planning the introduction of new products
by identifying the position of all products of the business a full analysis of the portfolio is possible which can help focus on which products need marketing support or which need corrective action, which could include the following marketing decisions:
building - supporting question mark products with additional advertising or further distribution outlets
holding - continuing support for star products so that they maintain their good market position
milking - taking the positive cash flow from established products and investing it in other products in the portfolio
divesting - identifying the worst-performing dogs and stopping the production and supply of this produces
limitations
on its own, it cannot tell a manager what will happen next with any product
it is only a planning tool
it assumes higher rates of profit are related to high market share
impact of the product life cycle on marketing decisions
introduction
price - may be high (skimming) or low (penetration) compared to competitors’ prices
promotion - high levels of informative advertising are needed to make consumers aware of the products arrival on the market
place (distribution) - in restricted outlets, possibly high-class outlets if a skimming strategy is adopted
product - basic model with few variations
growth
price - if successful, an initial penetration pricing strategy could now lead to rising prices
promotion - consumers need encouraging to make repeat purchases and branding will help win consumer loyalty
place - in growing numbers of outlets in areas indicated by the strength of consumer demand
product - product improvements and developments to maintain consumer appeal
maturity
price - as competitors enter the market, prices for the product need to stay at competitive levels
promotion - brand imaging continues to stress the positive differences compared. to competitors products
place - highest geographical spread possible, including new distribution channels
product - new models, colours, accessories as part of extension strategies
decline
price - lower prices may be needed to sell of inventory, but if the product has a small niche following the prices could even rise
promotion - advertising is likely to be very limited and may just be used to inform of lower prices
place - unprofitable outlets for the product are eliminated
product - slowly withdraw product from certain markets and prepare to launch new products
price
price is the amount paid by the customers fora product and determining an appropriate price for a product is vital component of the marketing mix, it also has a big impact on the consumer demand for the product. the price level set for a product will also:
impact on the level of value added by the business to bought-in components
affect the revenue an profit made by a business due to its impact on demand
help establish the psychological brand image of a product
how to determine the right price:
cost of production
competitive conditions in the market
competitors prices
business and marketing objectives
price elasticity of demand
whether it is a new or existing product
cost based pricing methods - mark up pricing
mark-up pricing is adding a fixed mark-up for profit to the unit cost of buying in a product
cost based methods of pricing - cost-plus pricing
cost-plus pricing is the setting of a price by calculating a total unit cost for the product and then adding a fixed profit mark up
advantages
the price set covers all costs of production
it is easy to calculate for single-product firms where there is no doubt about fixed cost allocation
it is suitable for businesses that are price-makers due to market dominance
disadvantages
it is inaccurate for businesses with serval products where there is doubt over the allocation of fixed costs
it does not take market/competitive conditions into account
it tends to be inflexible
if sales fall, average costs often rise which could lead to the price being raised using this method
cost based methods of pricing - contribution-cost (or marginal-cost) pricing
contribution-cost pricing is the setting of prices based on the variable costs of making a product, in order to make a contribution towards fixed costs and profit
advantages
all variable costs are covered by the price and a contribution is made to the fixed costs
it is suitable for firms producing several products and fixed costs do not have to be allocated
it is flexible
disadvantages
fixed costs may not be covered
if prices vary too much, due to the flexibility advantage, then regular customers might be annoyed
cost based pricing - loss leaders
it involves the setting of very low products for some products which is expected to attract customers who will hopefully also buy products which make a positive contribution
competition based methods of pricing
dynamic pricing is offering of products at a price that changes according to the level of demand and the customers’ ability to pay
price discrimination is the charging of different groups of consumers different prices for the same good or service
advantages of competitor prices
it is almost essential for firms with little market power
it can be flexible to reflect market and competitive conditions
disadvantages of competitor prices
the price set may not cover all the costs of production
the price may have to vary frequently due to changing Markey and competitive conditions
advantages of price discrimination
it uses price elasticity to charge different prices to increase total revenue
disadvantages
there are administrative costs of having different price levels
customers may switch to lower-prices markets
consumers paying higher prices may object and look for alternatives
pricing methods for new products
penetration pricing - the setting of a relatively low price to achieve a high volume of sales
market skimming - the setting of a high price for a new product when a firm has a unique or highly differentiated product with low price elasticity of demand
psychological pricing
psychological pricing - is the setting of a price at a level which matches consumers’ views about a products perceived value
promotion methods
promotion is the use of advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, direct mail, trade fairs, sponsorships and PR to inform consumers and persuade them to buy
advertising is a type of promotion and is paid for communication to inform and persuade customers using media, newspapers, and cinema
direct promotion is another type of promotion and is a range of promotional activities aimed directly at target customers
sales promotion is a further type of promotion and uses incentives such as special offers or special deals directed at consumers or retailers to achieve short term sales increases and repeat purchases by consumers
the promotion mix is the combination of promotional techies that a firm uses to sell a product
promotion objectives
the success of promotion campaigns can be measured against these objectives and can include:
increasing sales by raising consumer awareness of a product
increasing consumer recall of existing products and its distinctive qualities
increasing purchases by existing consumer or attracting new consumers to the brand
demonstrating the superior specification or qualities of a product compared with those of competitors
creating or reinforcing the brand image or personality of the product
correcting misleading reports about the product or the business to reassure the public
improving the public image of the business through corporate advertising
encouraging retailers to hold inventories of the product and actively promote products to the final consumer
advertising promotion
advertisements are often classified into 2 types:
informative advertisement which are adverts which give information about a product to potential purchases
persuasive advertisements which are adverts trying to create a distinct image or brand identity for the product
advertising agencies
Businesses can use advertising agencies which are specialists that advise business on the most effective way to promote products. Advertising agencies can offer a complete promotional strategy. These agencies - for substantial fees - undertake the following stages in dividing a promotional plan:
research the market, establish consumer tastes and preferences, and identify the typical consumer profile
advise on the most cost-effective forms of advertising media to be used
use their own creative designs to design adverts appropriate for each medium
film or print the adverts to be used in the campaign
monitor public reactions to the campaign and feed this data back to the client
advertising methods - print advertising
this includes advertising in newspapers, magazines, and specialist publications
it can be directed at particular towns or regions or consumers who read particular special interest magazines
it provides hard copy, which can be cut out and kept by the consumer for future reference
it has its limitations
it is expensive to gain national coverage
evidence suggests that it is now much less effective with younger consumers than digital communications
advertising methods - broadcast advertising
this is advertising on TV and radio and in cinemas
adverts have visual appeal and can create a brand image through the actors used
national or even international coverage is possible
it can linger in the memory of consumers for a long time if visually dramatic
it has limitations:
it is expensive to buy media time
it is expensive to design and produce adverts
there is no permanent hard copy
advertising methods - outdoor advertising
this includes advertising on billboards and bus shelter posters
it is low cost compared to other media
it can be located in prime positions with many potential consumers passing by
it can be read/seen more than once
it does have its limitations
the best locations are the most expensive
it can be damaged or vandalised
many passers by will not notice this type of advertising
advertising methods - product placement advertising
products are featured in TV shows and films
the chosen shows or films will be targeted at a particular type of consumer
this creates a desirable image if the product ice associated with famous actors or shows
it is not explicit advertising
the limitations are:
the show, film, or actors may become less popular
it is very expensive if the show or film is well known
advertising methods - guerrilla advertising
this is where products are advertised at surprising and unconventional events to make the public take notice
it is low cost
it can be creative, inventive, and can appeal to young consumers
it encourages word-of-mouth communication between potential consumers
a staged event can receive free publicity from the media
the limitations are:
the message may be misunderstood
it may be considered irresponsible and lead to a negative backlash
it may be remembered for the wrong reasons
advertising methods - sponsorship
this involves payment by a business to become associated with an event, individual, or sports team, the advantages include:
the good publicity of being associated with big sporting and other events
global press and TV coverage of the largest events
the success of the team or individual can lead to a greatly increased interest in the brand
the limitations are:
it can be very expensive
failure of an event, team, or individual can reflect badly on the brand
which advertising method to use?
the advertising method chosen depends on:
cost
the consumer profile of the target audience - age, income levels, interests
the message and image to be communicated
other aspects of the marketing mix
legal constraints
sales promotion methods - price offers
Price offers are temporary reductions in price, commonly known as price discounting. The objective is to encourage existing customers to buy more and to attract new customers as the product now appears more competitive
limitations:
price reductions will reduce the gross profit on each item sold
there could be a negative impact on the brands reputation from the discounted price
sales promotion methods - money-off coupons
A money off coupon is a more versatile and better focused way of offering a price discount. Coupons can appear on the back of receipts, in newspaper adverts or on the existing pack of the product
limitations:
these could just encourage consumers to buy what they would have bought anyway
retailers may be surprised by the increase in demand and not hold enough inventory, leading to consumer disappointment
the number of consumers using coupons might be low if the price reduction is small
sales promotion methods - customer loyalty schemes
the purpose of a customer loyalty scheme is to encourage repeat purchases and discourage consumers from buying from competitors. Loyalty cards five the business lots of information about a consumers’ buying preferences, which helps in customer relationship marketing.
limitations:
the discount cuts the gross profit on each purchase
there are administration costs
most consumers now have many loyalty cards from different retailers so their loyalty impact is reduced
sales promotion methods - money refunds
money refunds are offered when the receipt is returned to the manufacturer
limitations
these involve the consumer completing and posting a form which might be a disincentive
the delay before a refund is received may act as a disincentive
sales promotion - buy one, get one free (BOGOF)
BOGOF encourages multiple purchases which reduces the demand for competitors’ products too
limitations
there could be substantial reduction in the gross profit margin
consumers may conclude that then normal price is too high
consumers may think goods are being sold off because they can’t be sold at normal prices which may impact on reputation
current sales may increase but future sales may fall as consumers are stocked up
sales promotion methods - point-of-sale displays
point-of-sale displays have the biggest impact on consumer behaviour when it is attractive, informative and well positioned in stores
limitations
the best display points are usually offered to the market leaders
new products may struggle for the best position in stores unless big discounts are offered to retailers
direct promotion methods - direct mail
direct mail is sent out by post
it is low cost and well-defined areas/regions can be targeted
it is easy to evaluate the success of a campaign by checking response rates
limitations
many potential consumers now prefer digital communication
the mailing may be viewed as junk mail and quickly thrown away
direct promotion methods - telemarketing
telemarketing includes all marketing activities conducted over. the telephone including selling, market researching, and promotion products
telemarketing can be outsourced to an agency which may charge for the cost of the script to be used and then on an hourly basis, or might charge for each cold call that leads to an interested potential customer being contacted again
this is lower cost than personal selling
it is easy to monitor the response/rejection rate
limitations:
many consumers object to cold calling
it is very easy for consumer to reject a telemarketing message
direct promotion methods - personal selling
With personal selling, a salesperson is employed to sell to each individual customer
sales success rates are often high with skilled direct-sales employees
it is often used for expensive industrial products, which is one of the key differences between consumer marketing and business marketing
it is effective with expensive and complex products that require specialist knowledge
limitations:
customers may complain about being pressured into buying, especially if the sales employees are paid a high bonus for each sale made
sales employees need to be well trained and should avoid selling to a reluctant consumer who later regrets the decision
this is a high-cost method of promotion and selling
digital promotion
Digital marketing methods and techniques are changing rapidly
digital promotion is the promotion of products using digital technologies, mainly on the internet but also including mobile phones. It is the fastest-growing from of promotion and new opportunities are constantly being created
methods of digital promotion
social media marketing - on social media apps
email marketing - newsletter campaigns, purchase confirmation emails, thank you emails, and email notifications about new products
online advertising - displaying pop-up banners or advertisements on other websites aiming at the same niche, Google AdSense is a way of doing this
smartphone marketing - this includes all things that can be used on a smartphone such as: emails, texts, apps, an social media
search engine optimisation (SEO) - businesses that use e-commerce locate their websites on search engines and need to use SEO to make sure their content appears among the first results of a search
Viral marketing - it makes use of all types of digital marketing, the essence of this is to make some form of content that spreads across the web and becomes viral
e-commerce - which is the buying and selling of goods and services by businesses and consumers through an electronica medium
benefits and limitations of digital promotion
benefits
worldwide coverage
relatively low cost
easy to track and measure results
personalisation
social media communication builds customer loyalty
content marketing
website convenience increases customer loyalty
content marketing
limitations
time consuming
skills and training
global competition
complaints and feedback
the role of packaging in promotion
packaging performs the following functions:
protects and contains the product both during transportation and in stores
give information
support the brand image of the product created by the promotional campaign
make the product attractive and help the consumer to recognise it
the role of branding in promotion
the aims of branding in promotion are:
aiding consumer recognition
making the product distinctive from competitors
giving the product an identity to personality that consumers can relate to
the benefits of effective branding are:
it increases the chance of brand recall by consumers
it clearly differentiated the product from the others
it allows for the established of a family of closely associated products with the same brand name
it reduces the responsiveness of consumer demand to a price cease
it increases consumer loyalty to brands
Place - channels of distribution
several different channels of distribution are available:
direct selling
single-intermediate channel
two-intermediary channel
a channel of distribution is the chain of intermediaries a product passes through from producer to final consumer
channels of distribution - direct selling
direct selling is the direct route from manufacturer to consumer
advantages
no mark-up or profit margin is taken by intermediaries
the producer has complete control over the marketing mix
it is quicker than other channels so may lead to fresher products
direct contact with consumers offers useful market research
disadvantages
all storage and inventory costs have to be paid by the producer
there are no retail putts so consumers cannot see and try before they buy
it may not be convenient for consumers
no after-sales service is offered by shops
it is expensive to deliver each item to consumers
channels of distribution - single-intermediary channel
a single-intermediary channel is where products go from manufacturer to retailer to consumer
advantages
retailers incur the cost of holding inventories
retailers display the products and offer after-sales service
retailers should be in locations that are convenient to consumers
producers focus on production, not on selling the products to consumers
disadvantages
the intermediary takes a profit mark-up, making the product more expensive to consumers
producers lose control over the marketing mix
the outlet is not exclusive as retailers sell competitors’ products too
producers pass on delivery costs to retailers
channels of distribution - two-intermediary channel
a two-intermediary channel is where products go from the manufacturer to the wholesaler to the retailer to consumer
advantages
wholesalers hold the goods and buy in bulk from producers
it reduces process; inventory costs
wholesalers pay got the costs of transport to retailers
wholesalers buy in large quantities and sell in small quantities
disadvantages
another intermediary takes a profit mark-up which makes the product more expensive to consumers
producers lose further control over the marketing mix
it slows down the distribution chain
online marketing (e-commerce)
online marketing (e-commerce) is the selling and marketing activities that use the internet, email and mobile communications to encourage direct sales via e-commerce
benefits
it is relatively inexpensive if the cost is compared to the number of consumers reached
companies can reach a worldwide audience for a small proportion of traditional promotion budgets
consumers interact with the websites and make purchases and leave important data about themselves
the internet is convenient for consumers to use if they have access to a computer
businesses can keep accurate records on the number of clicks or visitors, and quickly measure the success rate of different web promotions
computer and smartphone ownership is increasing in all countries of the world
selling products on the internet involves lower fixed costs than traditional retail stores
dynamic pricing is easier
limitations
some countries have low-speed internet connections and in poorer countries then computer ownership is not widespread
consumers cannot touch, feel smell, or try on tangible goods which may limit their willingness to buy something
product returns may increase if consumers are dissatisfied with their purchases
the cost and unreliability of postal service in some countries may reduce the cost advantage of internet selling
websites must be kept up-to-date and user-friendly which can be expensive
worries about internet security
factors that influence the choice of distribution channel
should the product be sold directly to customers or through retailers?
how long should the channel be?
in which locations should the product be made available?
should the internet be the main channel?
how much will it cost to keep the product inventory on store shelves and in warehouses?
how much control does the business want to have on the marketing mix?
how will the distribution channel integrate with other marketing mix components?
the choice of distribution channel is important because:
consumers can benefit from easy access to products
manufacturers need outlets for their products that give a wide geographical market coverage
retailers add a mark-up to cover their costs and make a profit
digital and physical distribution
digital distribution is the delivery or distribution of digital media content such as audio, video, TV, programmes, films, software, and video games
physical distribution is the activities that combine to achieve the efficient movement of finished products from the end of the production operation to the consumer