M1 module 2 extra info
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Palpable landmarks in the back:
C7 spinous process
T3 spinous process
scapular spine
T7 spinous process
scapula inferior angle
T12 spinous process
L4 spinous process
iliac crest
posterior superior iliac spine
S2 spinous process
scapular movements:
Scapular Retraction = Scapular External Rotation = Scapular Adduction
Scapular Protraction = Scapular Internal Rotation = Scapular Abduction
two nerves in suboccipital region:
suboccipital nerve/dorsal ramus C1
greater occipital nerve/dorsal ramus C2
The suboccipital nerve emerges ___. The greater occipital nerve emerges ___.
above obliques capitis inferior muscle
below obliques capitis inferior muscle
course of vertebral artery:
branch of ___ artery
ascends through what openings in cervical spine:
dissected within:
enters what foramen to enter the head:
terminates into what vessel:
subclavian
transverse foramina of C6 → C1
suboccipital triangle
foramen magnum of skull
basilar artery at base of brain
superficial branch of transverse cervical artery:
anterior to ___ muscle
What nerve does this parallel?
What muscle will this help supply?
trapezius
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
trapezius
deep branch of transverse cervical artery:
medial border of ___
What nerve does this parallel?
What muscles does this help supply?
scapulae
dorsal scapular nerve (C5)
rhomboid minor & major, scapulae
The spinal cord relays ___ information from peripheral nerves to the bran stem and thalamus.
sensory (afferent)
The spinal cord relays ___ information from the cerebrum and brain stem to motor neurons.
motor (efferent)
What are dorsal and ventral roots?
dorsal: incoming axons of sensory neurons
ventral: exiting axons of motor neurons
What is a ganglion and a nucleus?
ganglion: collection of neuronal cell bodies outside CNS
nucleus: collection of neuronal cell bodies inside CNS
Dorsal roots are ___ and ___.
somatosensory
arriving
The ___ form a mesh-like substance that looks kind of like a spider web. It connects the arachnoid with the pia.
arachnoid trabeculae
The dorsal and ventral ___ refers to those parts of the spinal nerve distal to the dorsal root ganglion as it splits into dorsal and ventral branches. They are ___.
rami
mixed (motor and sensory)
Dorsal roots are ___ and ___.
somatosensory
arriving
Where are both dorsal and ventral roots located?
proximal to dorsal root ganglion
The ___ is a prominent blood vessel running in the ventral median fissure.
anterior spinal artery
A dorsal root and ventral root merge to form a ___. Joining of dorsal and ventral roots happens at, or just distal to, the ___, which contains the cell bodies of neurons that form the dorsal roots. That part of the spinal cord to which a single pair of dorsal and ventral roots attaches is termed a ___.
single spinal nerve
dorsal root ganglion
spinal segment
The ___ is the origin of spinal nerves that innervate the upper limbs. The ___ is the origin of spinal nerves that innervate lower limbs.
cervical enlargement (C4-T1)
lumbosacral enlargement (L2-S3)
How many nerves are in each spinal region?
cervical: 8 pairs
thoracic: 12 pairs
lumbar: 5 pairs
sacral: 5 pairs
1 vestigial coccygeal nerve (can be up to 3-4)
Filum terminale: difference between internus and externus
internus: inside dural sac
externus: outside dural sac
The most common cause for Cauda Equina Syndrome is:
disk herniation in lumbar spine
Neurons in the ___ receive sensory information and relay it to higher brain centers.
Lower motor neurons in the ___ receive motor signals from higher brain centers and relay those signals to muscle.
dorsal horn
ventral horn
The medial division of the ventral horn contains ___. Thus, it is found at ___
motor neurons that innervate the neck, trunk, intercostal and abdominal muscles
all levels of the spinal cord
The lateral division of the ventral horn contains ___. Thus, it is found at ___.
motor neurons that innervate the limbs
only the enlargements (cervical enlargement for the upper limbs; lumbosacral enlargement for the lower limbs)
What are the 2 major nuclear groups located in the gray matter intermediate zone?
intermediolateral nucleus (T1-L1/2)
sacral parasympathetic nucleus (S2-S4)
An ___ is a collective term for the three articulations between any two adjacent vertebrae, consisting of the ___.
intervertebral joint
intervertebral disc joint (a cartilaginous joint) and the two zygapophysial or facet joints (synovial joints)
The manubriosternal joint occurs between the:
medial clavicle and manubrium of sternum (+ 1st costal cartilage)
at sternal angle, T4-T5 level
The xiphisternal joint occurs between the:
body of the sternum and xiphoid process
A costotransverse joint is the articulation between ___.
the tubercle of a rib and the transverse process of the corresponding thoracic vertebra
T1 articulates with the ___ ribs, but the ___ rib only articulates with T1
1st and 2nd
1st
The point where the trachea bifurcates into the right and left main bronchi is called the ___.
carina
___ roots have no ganglion.
Ventral
Herniation of the 5th lumbar nerve root can result in numbness in the ___ and weakness through ___.
1st 3 toes of the lateral leg
dorsiflexion of the great toe and foot (difficulty walking on heels, foot drop)
S1 nerve root herniation can result in numbness of the ___ and ___.
back of the calf, lateral heel, and foot to toe
decreased achilles reflex
Does thick or thin skin have hair follices?
Thick skin does NOT have hair follicles, thin skin does.
List the curvature of the spinal cord segments:
cervical: lordotic
thoracic: kyphotic
lumbar: lordotic
sacral: kyphotic
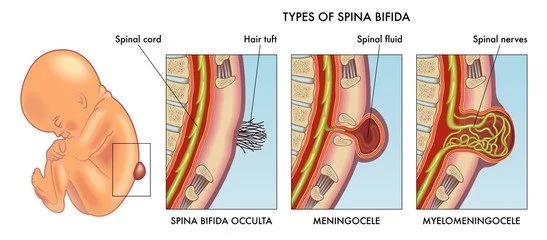
The vertebral arches form the posterior aspect of the vertebral canal and serve to protect the spinal cord. Failure of them to form correctly results in ___ and leaves the spinal cord and associated tissues vulnerable to injury.
spina bifida
The ___ is the sole remnant of the embryonic notochord, the initial longitudinal skeletal axis of the body.
nucleus pulposus
Each embryonic somite differentiates into three components:
myotome, dermatome, and sclerotome
The anterior tubercle of ___ is known as the carotid tubercle because deep pressure against it will stop or greatly slow flow in the common carotid artery.
C6