Topic 8: Human Systems and Resource Use
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
crude brthrate
number of live births per 1000 people in a popoulation
crude death rate
number o deaths per 1000 people in a population
total fertility rate
average number of children that are born to a women over her life time
doubling time of a population
the duration it takes tfor a population size to double
natural increase rate
(crude birth rate - crude death rate) ÷ 10
BUT evaluative point is that migration is ignored
age/sex pyramid
a visual representation of the distribution of a population’s demographics of sex and age groups
demographic transition model
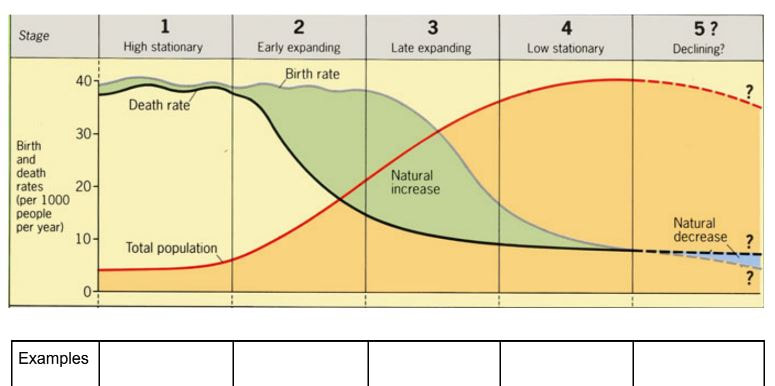
showing the population changes a country goes through ass wealth increases
exponential growth
a population that continues to grow beyond carrying capacity so limiting factors have no effect or are not present
overpopulation
where a population exceeds carrying capacity
policies that effect population sizes
education - especially for women, allows for improved job opportunities, family planning, sex education
healthcare policies - safe pregnancies, could have access to abortions, birth control
economic policies - poverty reductions, improve income equality
social welfare policies - child care support, parental leave, elderly care
migration policies - can restrict migration or promote it
environmental policies - green jobs like switching to different types of energy production, increases job opportunities for and improved standard of living
natural capital
the resources that are from naturen
natural income
the annual yield of natural capital
renewable resources
they can replenish t the same rate they are being used
non-renewable resources
they can not be replenished as they are a finite resource
natural income of goods
the resources that are sold for other people’s use
natural income of services
the natural occurrences in nature that protect or provide resources for other pares of the ecosystem
dynamic
the relationship between two given parts of an ecosystem and how they balance
use valuation
resources that have a price in society
non-use valuation
resources that have intrinsic value
sustainable yield
sustainable yield = ((total biomass / energy) at t + 1) - ((total biomass / energy) at t)
it is also equal to net primary productivity
solid domestic waste
everyday items that we discard
biodegradable
capable of being broken down by natural processes
circular economy
waste is reused instead of discarded
linear economy
waste is discarded at the end of its life and contributes to dumps and landfill
reduce
to consume less or use and item until the end of life
reuse
to use waste againre
recycle
to use waste for the creation of new products by using the materials from it
landfill
burying waste in a lined pit
e-waste
waste from technology such as parts or whole devices
incineration
controlled burning of waste
composting
decomposition of waste materials
what varies ecological footprints?
lifestyle choices - consumption, transport, housing
productivity of food production systems
land use and industry
ecological footprint
the area of land and/or water needed to sustain our needs and absorb our waste
what is the equation for the ecological footprint?
EF = (1÷Carrying capacity)
earthshore
the amount of land everyone should have if one were to divide all of the ecologically productive land by the population
carrying capacity
the maximum amount of a species that can live sustainably by the given area
remanufacturing
the object’s material is used to make a new object of the same type