n/m Ch-2: Is Matter Around us Pure? (NCERT-Class-9)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
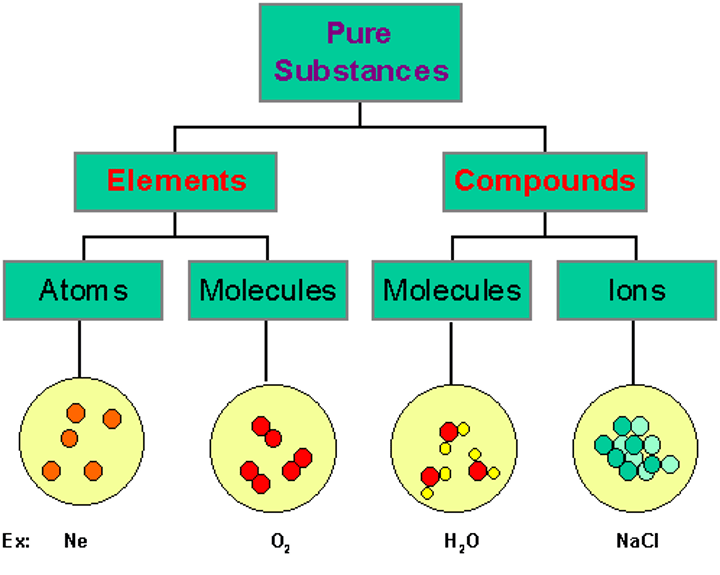
Pure substance
A substance that consists of a single type of particles.
Characteristics of a pure substance.
Constituent particles of a pure substance are the same in their chemical nature.
Can a substance be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical process?
No
Mixture
A substance that contains more than one substance.

What are the characteristics of a mixture?
The characteristics of a mixture are:
1. It has variable composition.
2. shows the properties of the constituent substances.
3. constituent particles of a mixture are different in their chemical nature.
What are the types of mixtures?
homogeneous and heterogeneous.

homogeneous mixture
A mixture that has a uniform composition throughout.
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that contains physically distinct parts and have non-uniform compositions.
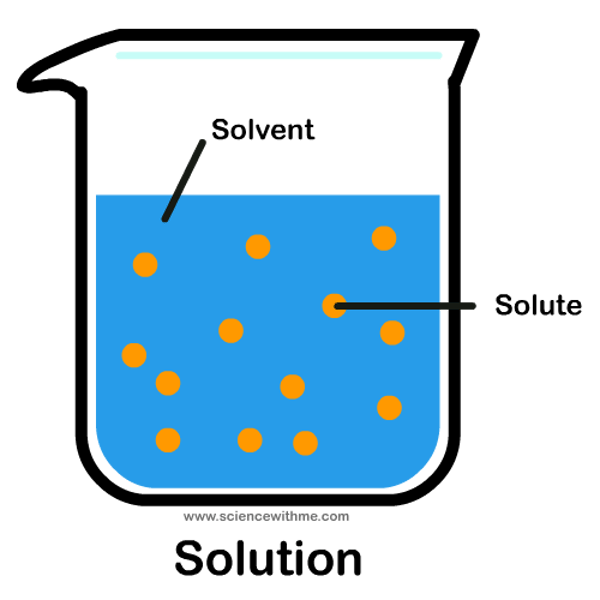
Solution
a homogenous mixture of two or more substances
Components of a solution
solute and solvent
Solvents
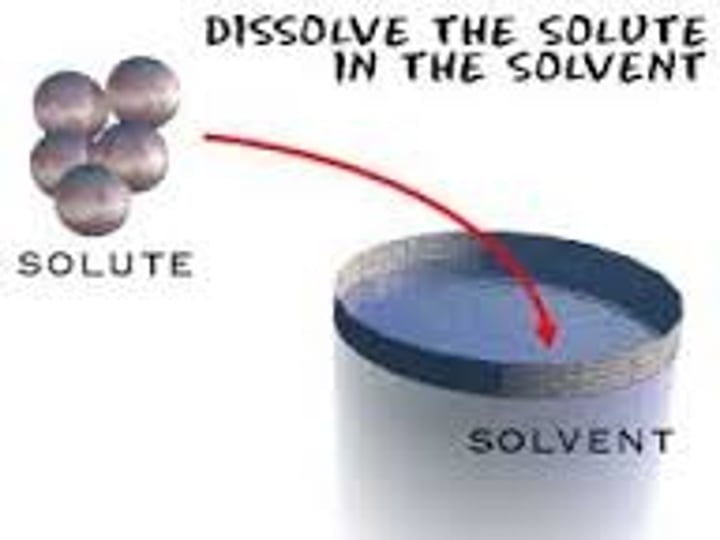
The component of the solution that dissolved the other component in it. (Usually present in a larger amount.)
Solutes
The component of the solution that is dissolved in the solvent. (Usually present in the lesser quantity.)
examples of solutions
1. Sugar in water - solid in liquid solution.
2. Iodine in alcohol, 'tincture of iodine.' - liquid in liquid solution.
3. Aerated drinks - gas in liquid solutions.
4. Air - gas in gas solution.
Properties of solutions
1. The solution is a homogenous mixture.
2. Particles smaller than 1 nm, cannot be seen with the naked eye.
3. Do not scatter a beam of light due to its small particle size.
4. Solute particles cannot be separated from the mixture by filtration.
5. Solution is stable, particles do not settle down when left undisturbed.
Alloys
Mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal that cannot be separated into their components by physical methods.
Why is an alloy considered a mixture?
It shows properties of its constituents and can have variable composition.
What are the type of solution based on the amount of solute present?
It can be called a dilute or concentrated or saturated solution.
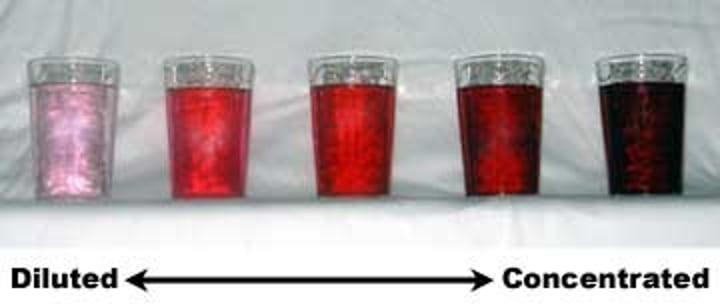
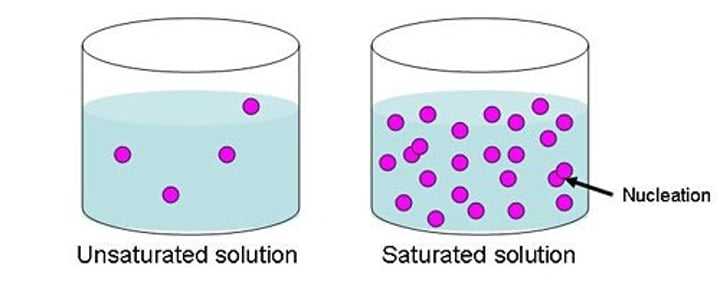
saturated solution
A solution that has dissolved as much solute as it is capable of dissolving at any particular temperature.
Solubility
The amount of solute present in the saturated solution at a given temperature.
unsaturated solution
The solution in which the amount of solute contained in the solution is less than the saturation level.
concentration of a solution
Amount of solute present in a given amount (mass or volume) of the solution.
Concentration of a solution =
Amount of solute / Amount of solution
Mass by mass concentration of a solution =
Mass of solute / mass of solution x 100%
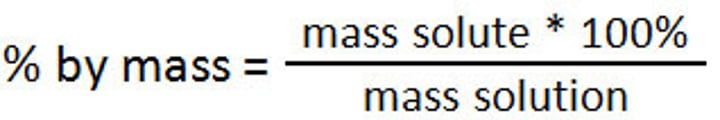
Mass by volume concentration of a solution =
Mass of solute / volume of solute x 100%
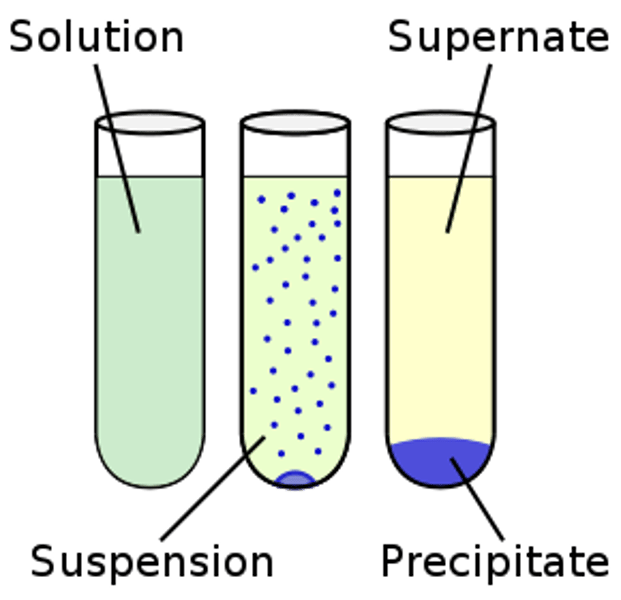
Suspensions
A heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the bulk of the medium.
properties of suspensions
1. They are heterogeneous.
2. Particles are big, can be seen with the naked eye.
3. Particles scatter a beam of light through it and makes its path visible.
4. Unstable, can be separated with the process of filtration.
What happens when the particles in a suspension settle down?
The suspension breaks and it does not scatter light anymore.
Colloids
Heterogeneous mixtures that appear to be homogenous due to their small particle size.

Tyndall effect
The scattering of a beam of light by colloidal particles.
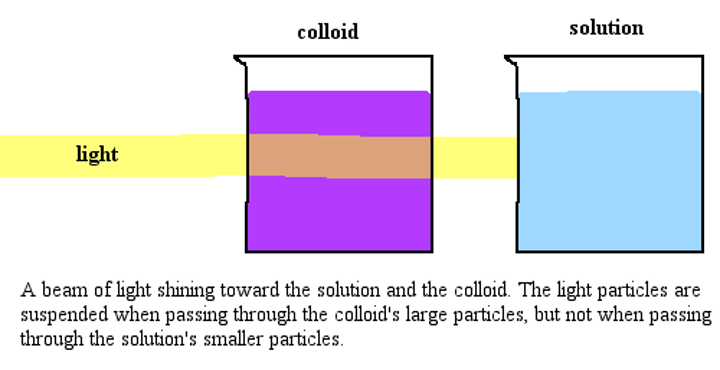
Examples of Tyndall effect
1. When sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest,
Mist acts as colloid dispersed in air.
2. When we see dust particles in a small beam of light,
Dust and particles act as colloid dispersed in ai.

properties of colloids
1. Heterogenous.
2. Particle size- bigger than that of a solution, smaller than that of a suspension and therefore cannot be seen with the naked eye.
3. Scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
4. Do not settle down when left undisturbed, quite stable.
components of a colloid
1. Dispersed phase (solute).
2. Dispersion medium (solvent).
dispersed phase
Solute-like component/dispersed particles in a colloid.
dispersion medium
Component in which dispersed phase is suspended in.
Colloids are classified according to
State of dispersing medium and dispersed phase
different types of colloids
1. Aerosol.
2. Foam.
3. Emulsion.
4. Sol.
5. Gel.
6. Solid Sol.
Aerosol
A type of colloid in which liquid drops or solid particles are spread throughout a gas.

Foam
A colloidal dispersion of a gas in a liquid.

Emulsion
A colloidal dispersion of a liquid in a liquid.

Sol
A colloidal dispersion of a solid in a liquid.
Gel
A colloidal dispersion of a liquid in a solid.

Solid sol
A solid dispersed within a solid. (certain metal alloys).
Why is separation necessary?
Separation makes it possible to study and use the individual components of a mixture.
How can heterogenous mixtures be separated?
Physical methods like handpicking, sieving, filtration.
How can we obtain coloured component (dye) from blue/black ink?
By Evaporation.
How do we separate volatile components from non-volatile ones?
By Evaporation.
What is a volatile component?
Something that can evaporate on heating.
How can we separate cream from milk?
By Centrifugation.
Principle of Centrifugation
When spun rapidly the denser particles are forced to the bottom and the lighter particles stay at the top.
applications of centrifugation
1. Used in diagnostic laboratories for blood and urine tests.
2. Used in fairies and homes to separate butter from cream.
3. Used in washing machines to squeeze out water from wet clothes.
How can we separate a mixture of two immiscible liquids?
by using a separating funnel.
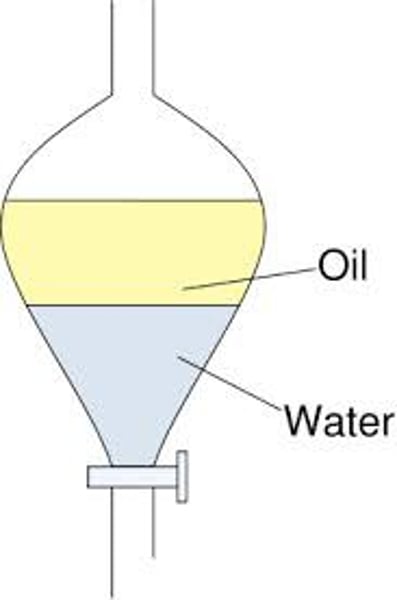
Applications of a separating funnel
1. To separate oil and water.
2. Iron from its ore.
The principle of a separating funnel
Immiscible liquids separate out in layers, depending on their densities.
How can we separate mixtures that contain a sublimate volatile component and a non sublimate impurity?
By sublimation.
Solids that sublime
Ammonium chloride,
Camphor,
Naphthalene,
Anthracene.
How do we separate dyes in black ink?
By using chromatography.
Chromatography
The separation of a mixture by passing it in solution through a medium in which the components move at different rates.
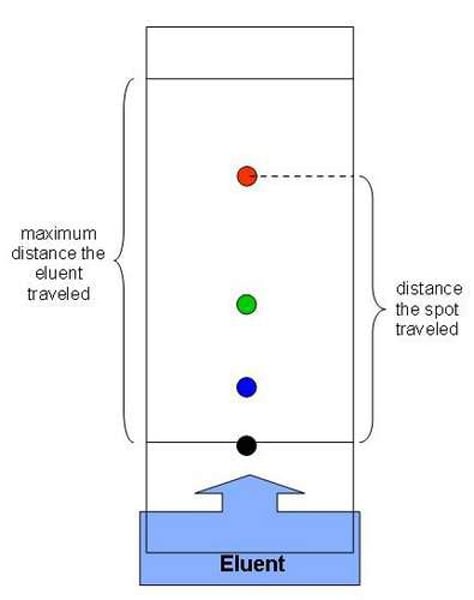
How do we separate solutes that dissolve in the same solvent?
by chromatography.
applications of chromatography
To separate
1. Colours in a die,
2. Pigments from natural colours,
3. Drugs from blood.
How can we separate a mixture of two miscible liquids?
By distillation
Distillation
The process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by selective boiling and condensation.
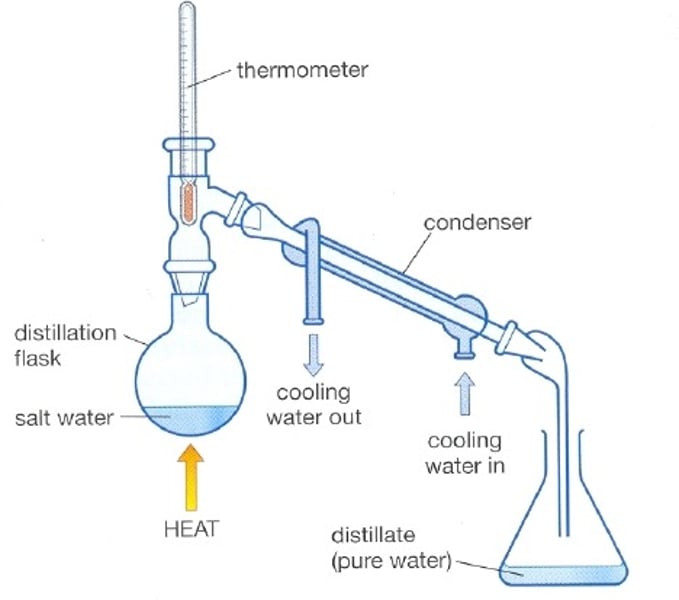
When is distillation used?
It is used for the separation of components of a mixture containing two miscible liquids that boil without decomposition and have sufficient difference in their boiling points.
When is fractional distillation used?
To separate a mixture of two or more miscible liquids for which the difference in their boiling points is less than 25K.
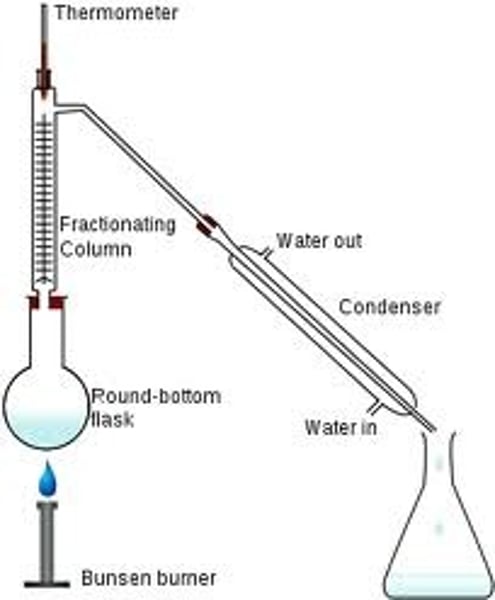
Differentiate between the apparatus used in fractional distillation and simple distillation.
Fractionating column is fitted in between the distillation flask and the condenser.
A simple fractionating column
Tube with glass beads,
glass beads provide a surface for the vapours to cool and condense repeatedly
How can we obtain different gases from air?
By distillation.
How can we obtain pure copper sulphate from an impure sample? How do we purify solids?
By Crystallization.
Crystallization
Process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution.
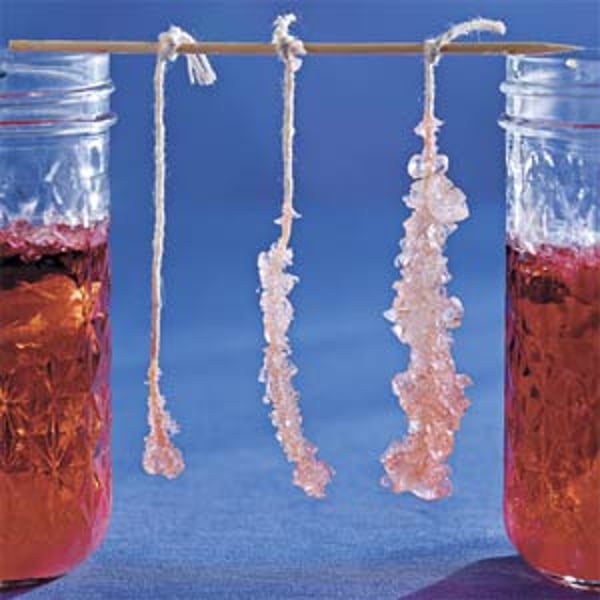

Why is crystallization preferred over evaporation?
1. Some solids decompose or some may get charred on heating to dryness.
2. Some impurities may remain dissolved even after evaporation.
application of crystallization
1. Purification of salt that we get from sea water.
2. Separation of crystals of alum from impure samples.
physical change
a change of matter from one form to another without a change in composition. There is no change in the chemical nature of the substance.

chemical change
A change that occurs when one or more substances change into entirely new substances with different chemical properties. Also known as a chemical reaction.

Who was the first scientist to use the term element?
Robert Boyle in 1661
Who was the first to establish an experimentally useful definition of an element? What was it?
Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94)
Element- the basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
Elements can be divided into
Metals, non-metals, metalloid
Metals
Substance composed of one or more metallic elements that is
shiny, hard, and malleable if solid.

Non-metals
Elements that are usually dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity.

Metalloids
Elements that have intermediate properties between those of metals and non-metals.
example - silicon.

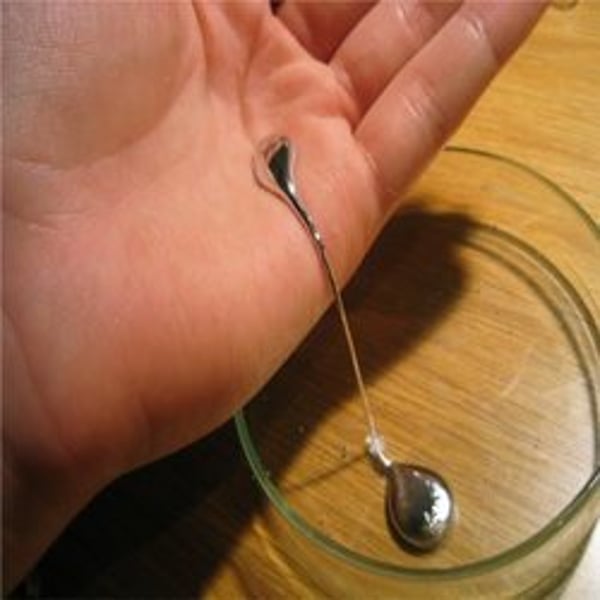
Elements that are liquid at room temperature are ------------.
mercury and bromine

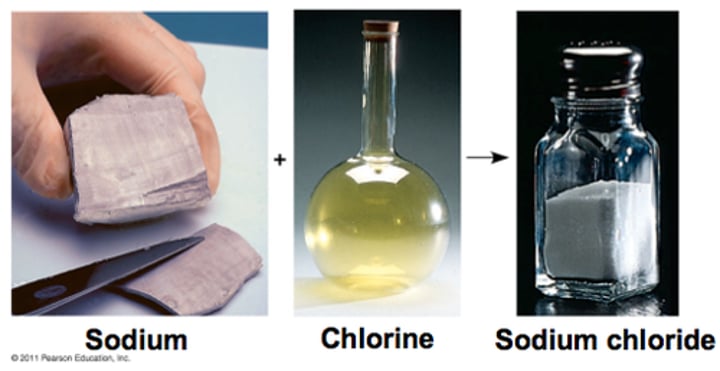
Compounds
A substance composed of two or more elects that chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion.
example - water (H2O).
Why is the sky blue?
The air molecules scatter blue light better than red light, so more blue light reaches our eyes.
Brownian motion
Zig-zag motion of colloidal particles is called Brownian motion.