Restrictions on Free Trade
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a trade barrier?
a restriction placed by the government on the import of a foreign good.
What are the restrictions on free trade (protectionism)?
1. Tariffs, a tax on imported goods.
2. Quotas, a strict limit on the quantity of goods imported
3. Subsidies to domestic producers
4. Non-Tariff barriers such as environmental regulations
What is a tariff?
A tax paid on imports, they are also sometimes known as import or custom duties.
What is the impact of a tariff?
A tariff is a tax and so it will increase the price of the imported good and shift the world supply curve up. This will lead to an extension (increase) in domestic supply as domestic producers are willing to sell more at a higher price - remember they don’t have to pay the tariff. There will be a contraction(decrease) in domestic demand as consumers don’t want to pay a higher price.
If domestic consumers are demanding less and domestic producers are supplying more, there will be a reduction in imports.
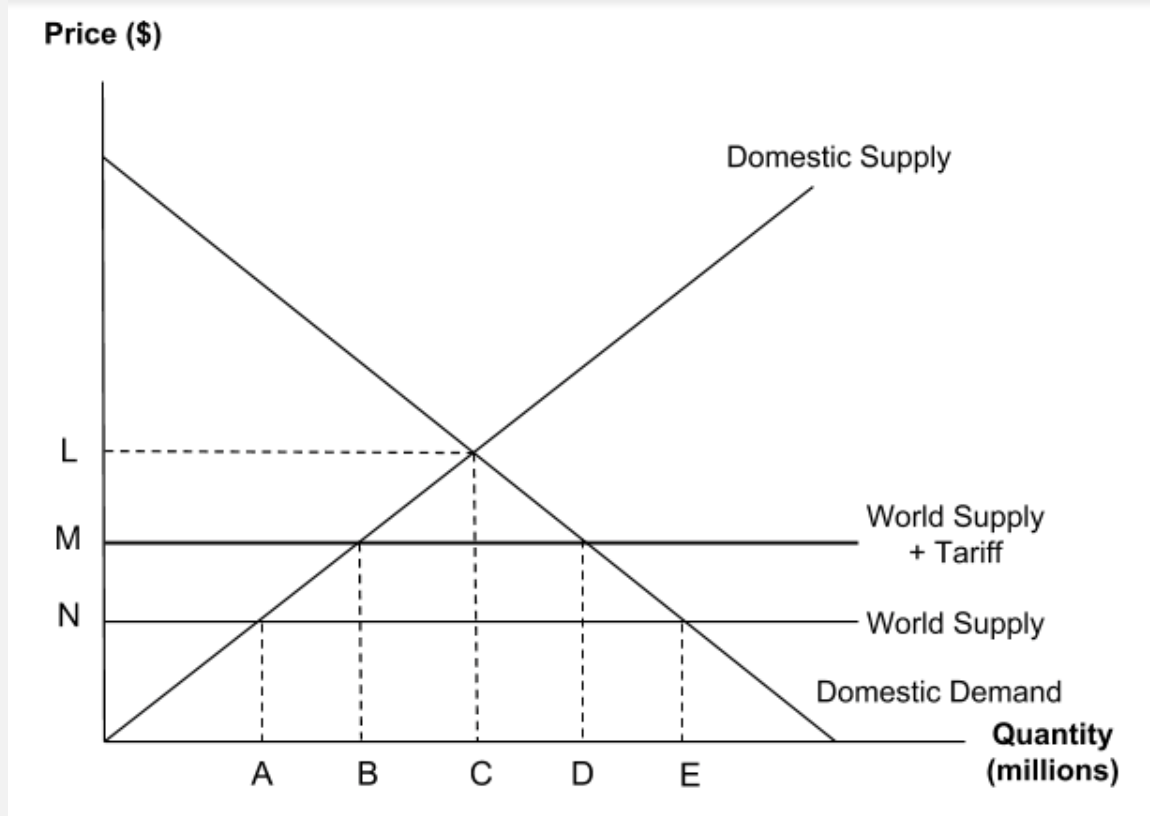
The diagram shows the market for a product with a tariff placed on imports.
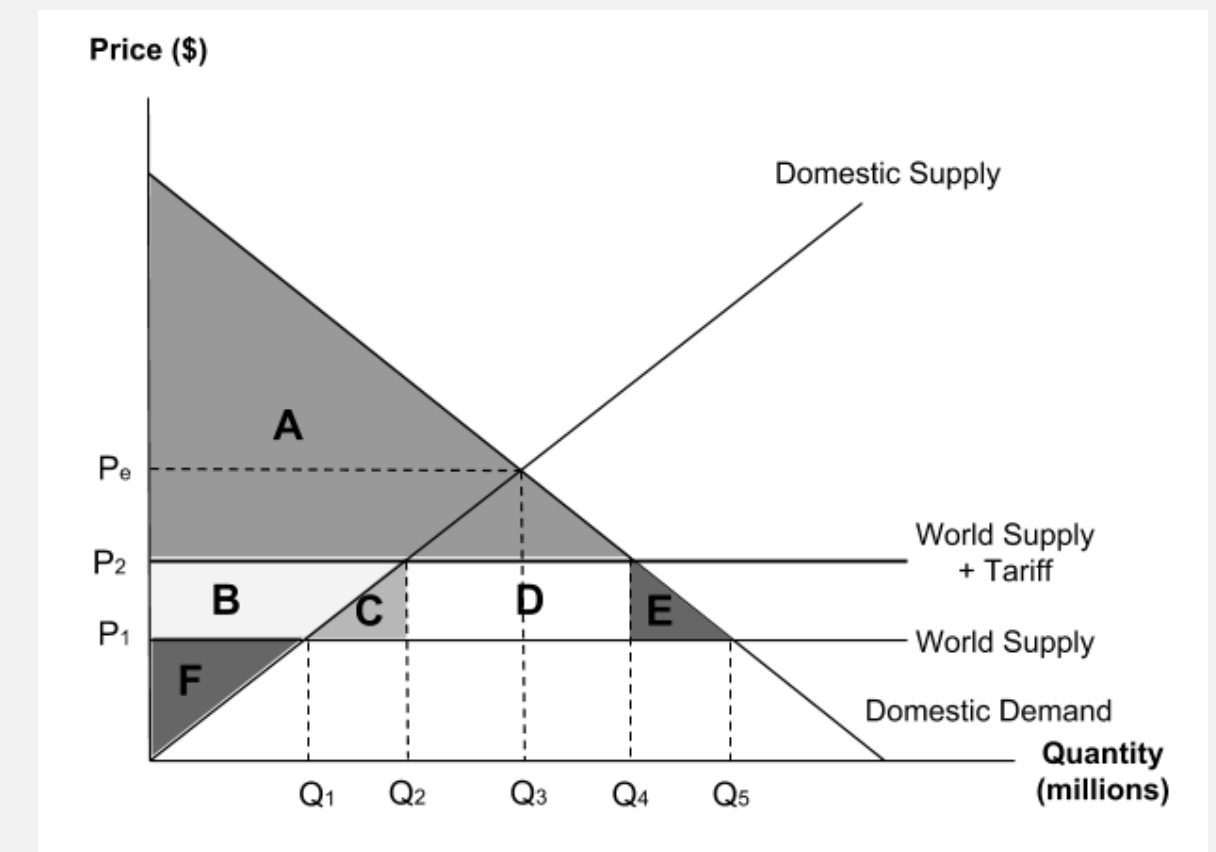
Which of the following shows the amount being supplied domestically before the tariff was introduced?
Slide along from the world supply price of N to the domestic supply curve and go down to the quantity axis to get a quantity of A.
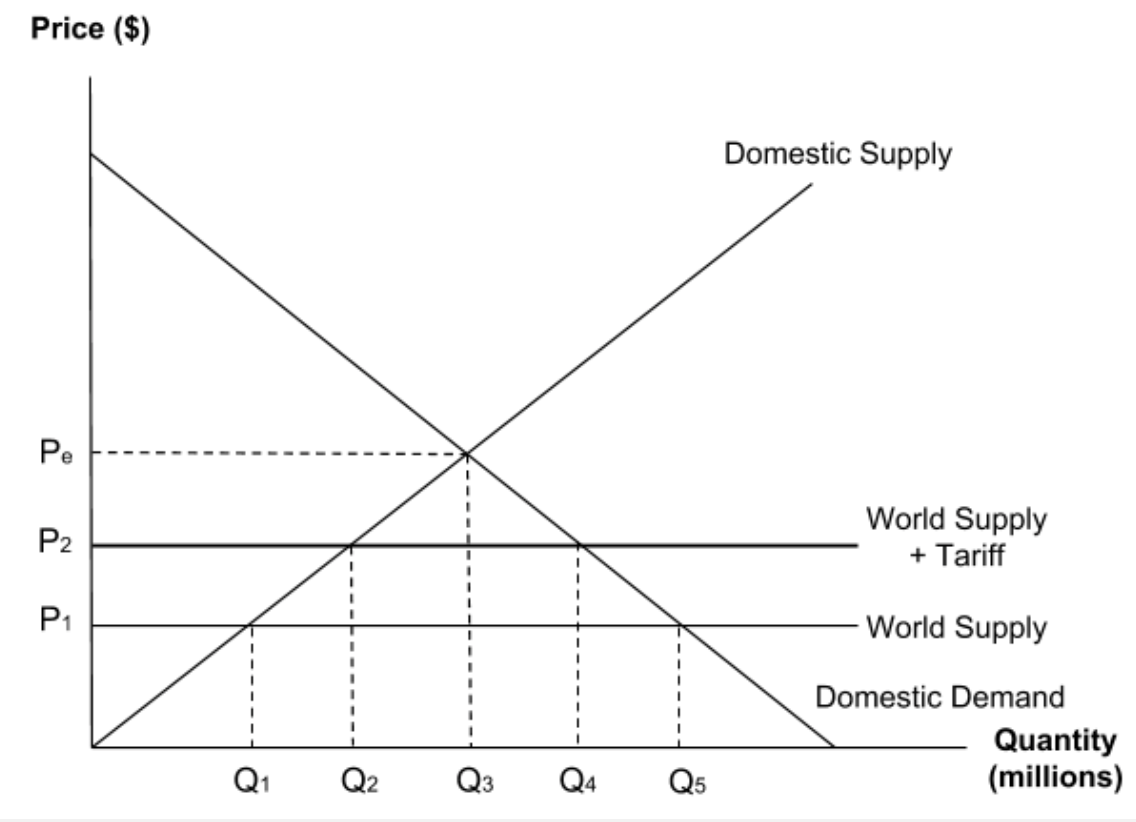
The diagram shows the market for a product with a tariff placed on imports.
Which of the following shows the change in domestic demand as the economy moves from free trade to having a tariff?
To find domestic demand before the tariff, go to the original world supply price P1 and then go all the way across to the domestic demand curve. Go down to get to Q5.
To find domestic demand after the tariff, go to the new tariff price P2 and then go all the way across to the domestic demand curve. Go down to get to Q4.
So, as a result of the tariff, demand has contracted from Q5 to Q4
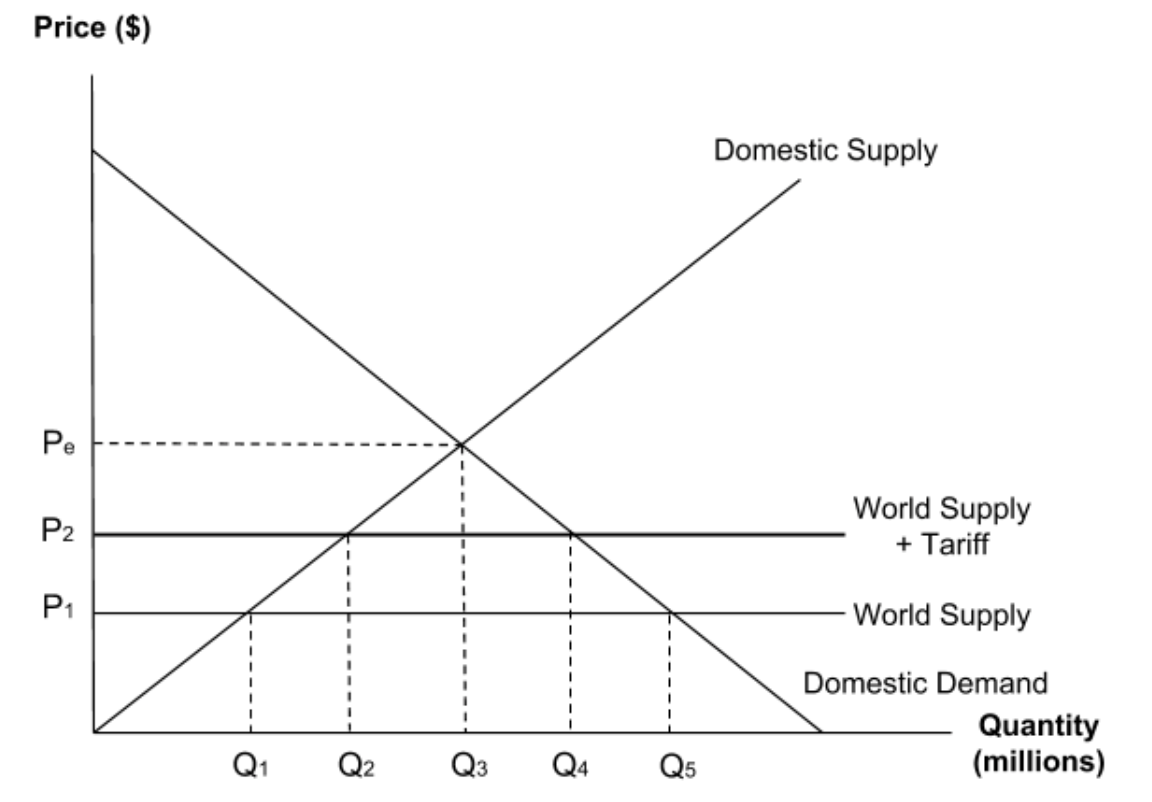
The diagram shows the market for a product with a tariff placed on imports.
Which of the following shows the change in domestic supply if the tariff in this market is removed?
To find domestic supply with the tariff, go to the world supply (+tariff) price P2 and then go all the way across to the domestic supply curve. Go down to get to Q2.
To find domestic supply after the tariff is removed, go to the world supply price P1 and then go all the way across to the domestic supply curve. Go down to get to Q1.
So, as a result of the removal of the tariff, domestic supply has contractedfrom Q2 to Q1
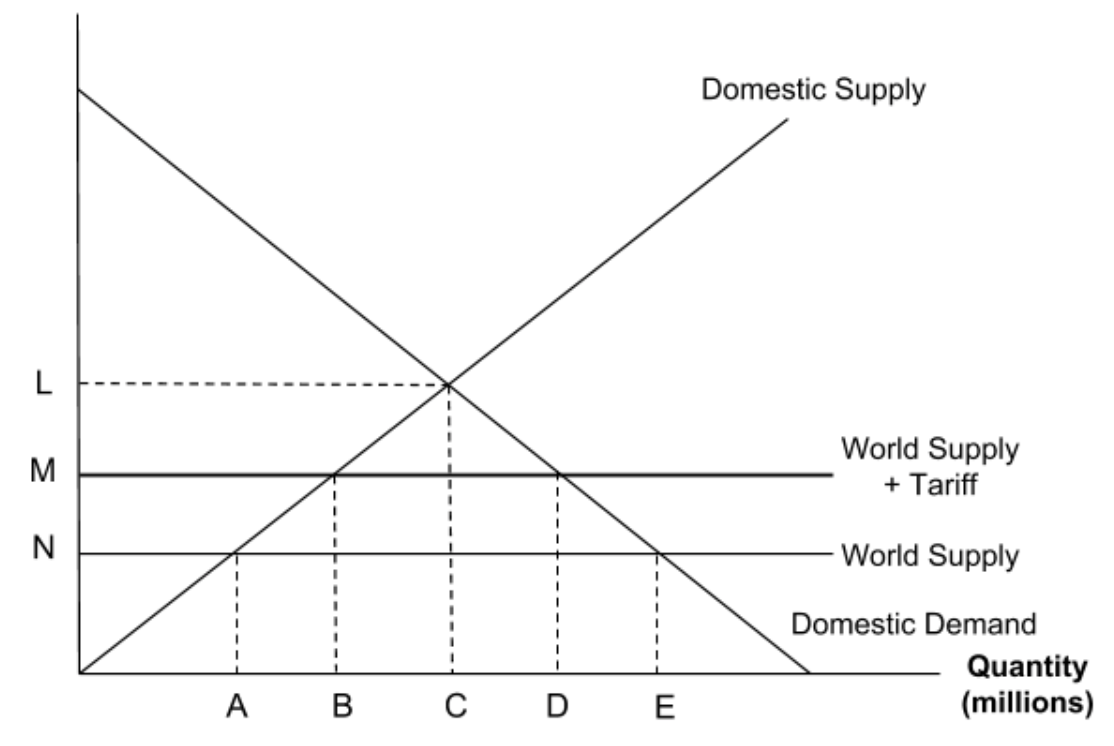
The diagram shows the market for a product with a tariff placed on imports.
Which of the following shows the quantity of goods which are being imported after the tariff?
Slide along from the world supply (+tariff) price of M to the domestic demandcurve and go down to the quantity axis to get a quantity of D.
Slide along from the world supply (+tariff) price of M to the domestic supplycurve and go down to the quantity axis to get a quantity of B.
So, at a price of M, American consumers are demanding D tons but American firms are only producing B. The difference between these must be imported, so DB.
What does a tariff diagram look like?
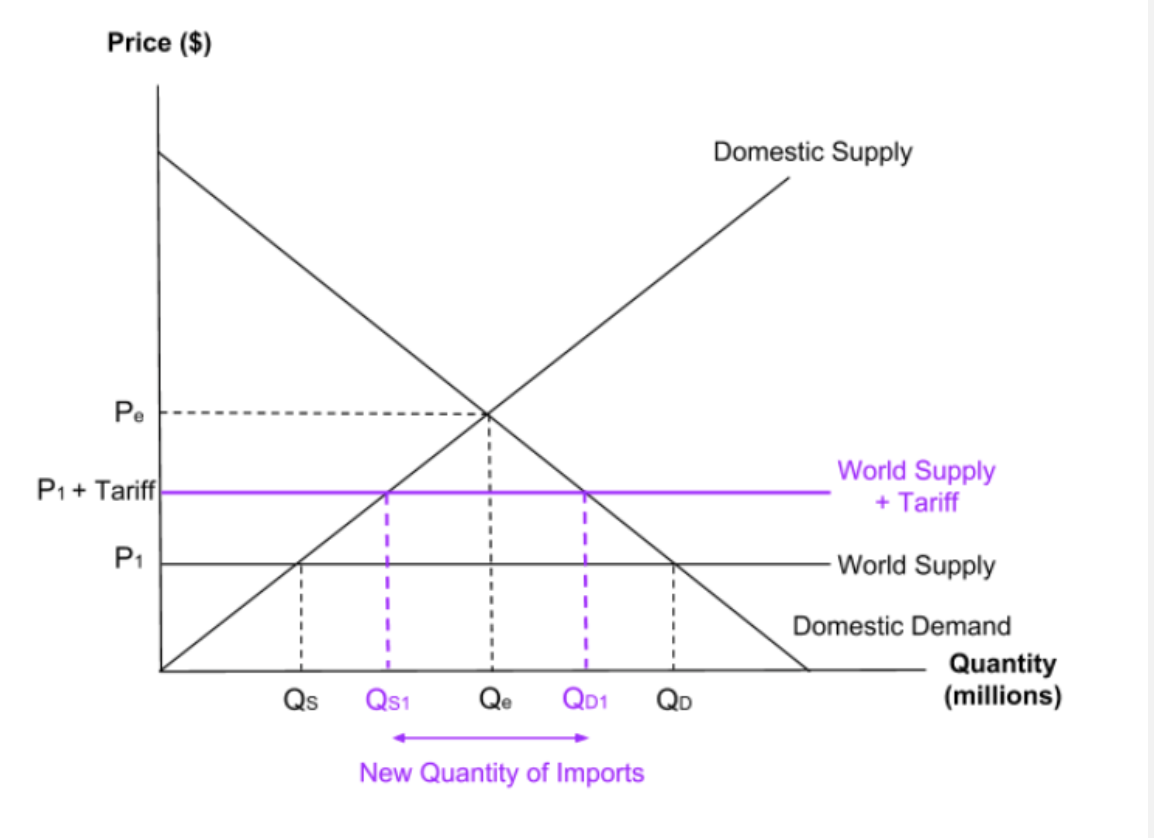
What does an imposition of a tariff do?
The imposition of a tariff will shift the world supply curve up. This will lead to an extension in domestic supply and a contraction in domestic demand. This will decrease the quantity of imports.
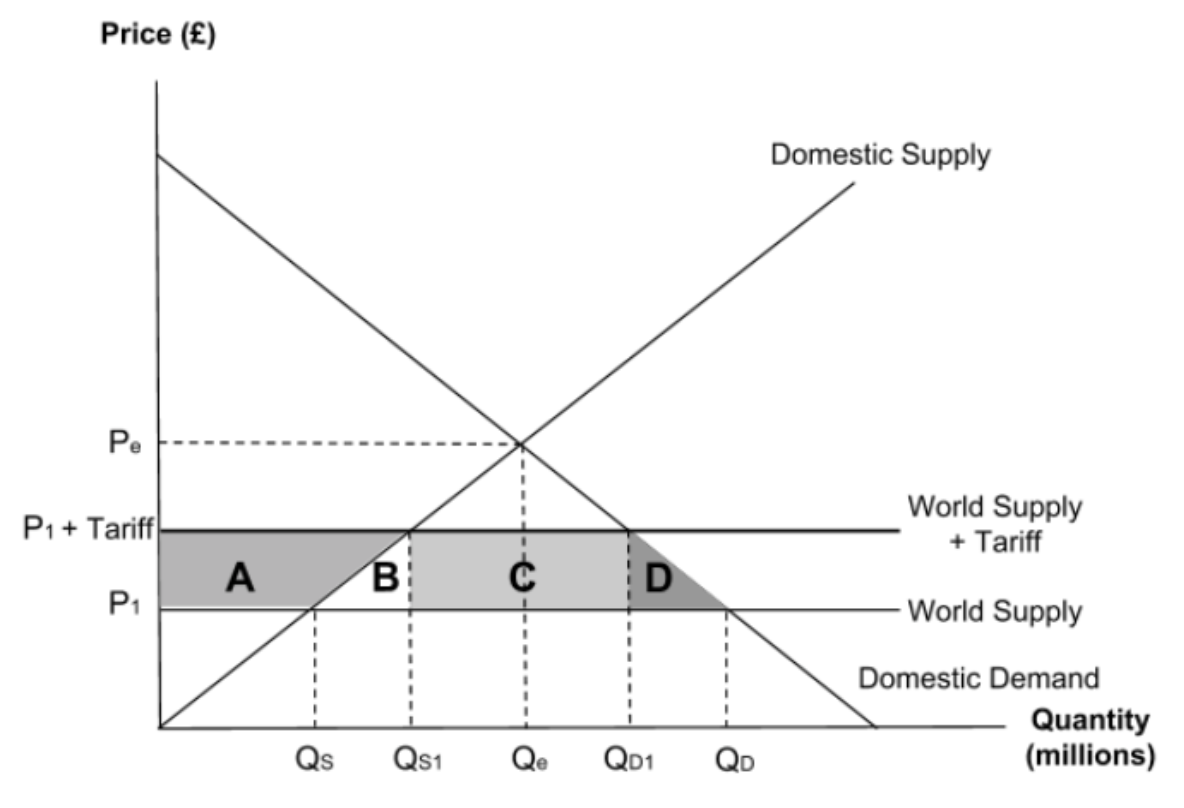
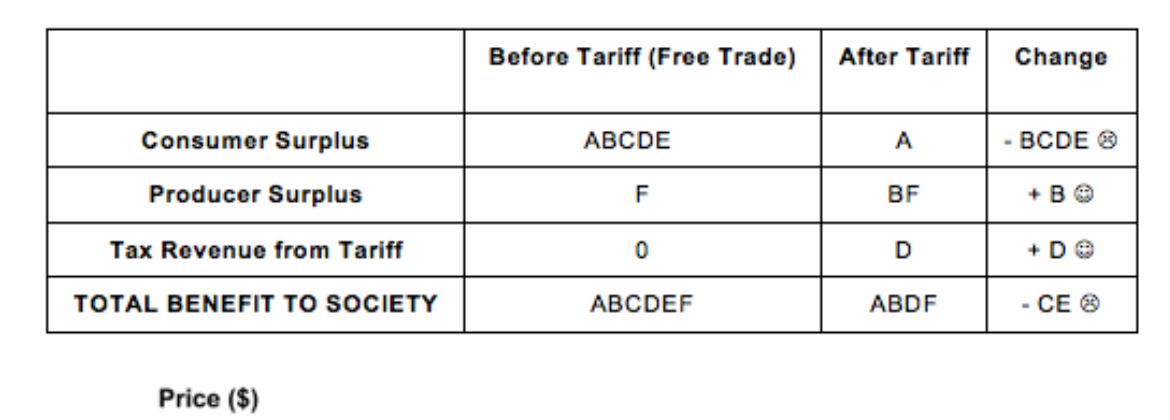
What do each of the lettered areas represent?
Area A represents the gain in producer surplus.
Area B and D represent the welfare loss.
Area C represents the government tax revenue from the tariff. It is the government that receives this money rather than the producer.
The length of the rectangle is Q2 to Q4 which is the quantity of goods that have been imported. The height of the rectangle is the tariff per unit as it shows the difference in price. Multiplying the tariff per unit by the quantity of imports will give the total tax revenue.
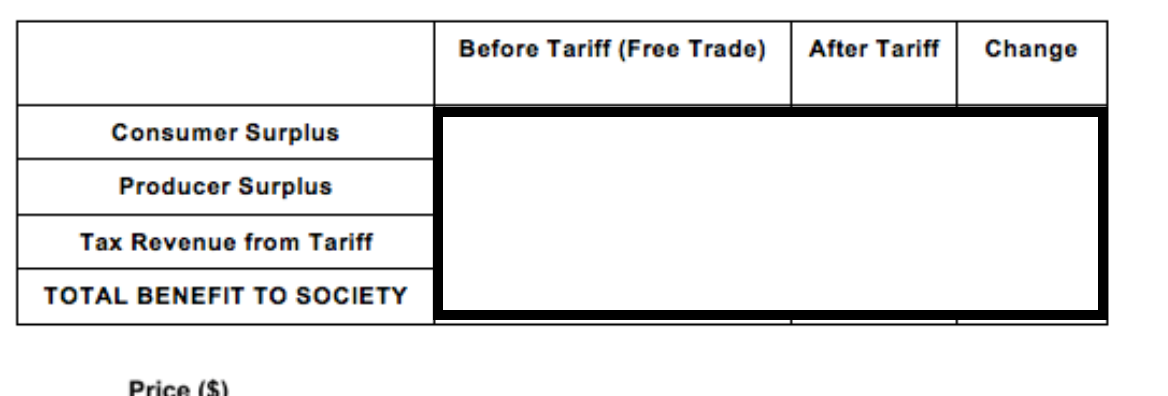
Complete the table using the diagram.
What is a quota?
a strict limit on the quantity of imports.
What is a subsidy?
when the government gives a grant to producers in order to increase supply.
What are non tariff barriers?
regulations regarding health and safety, environmental regulations and correct labelling of products to show a best before date.
What are the reasons for restricting trade?
to prevent dumping
protecting domestic employment by increasing demand for goods produced at home
protecting infant industries
health and safety
What is dumping?
when foreign firms aggressively cut their prices and force domestic producers out of the market
What is predatory pricing?
when a firm aggressively cuts prices below average variablecosts in order to force competitors out of the market.
How can a tariff prevent dumping?
a tariff will increase the price of imported goods so that foreign firms won’t be able to undercut domestic firms by charging a lower price.
How can trade barriers be used to protect domestic jobs?
A restriction on imports will increase demand for domestic goods. This will increase the derived demand for labour and increase employment.
Why are subsidies to domestic producers a type of restriction on free trade?
They increase demand for goods produced domestically
Subsidies to domestic producers will reduce the cost of production. This shifts supply to the right, which will decrease the price of domestic goods. This encourages consumers to switch from imports to domestic goods and leads to an extension along the demand curve.
What are internal economies of scale?
decrease in long run average costs due to an increase in the quantity produced.
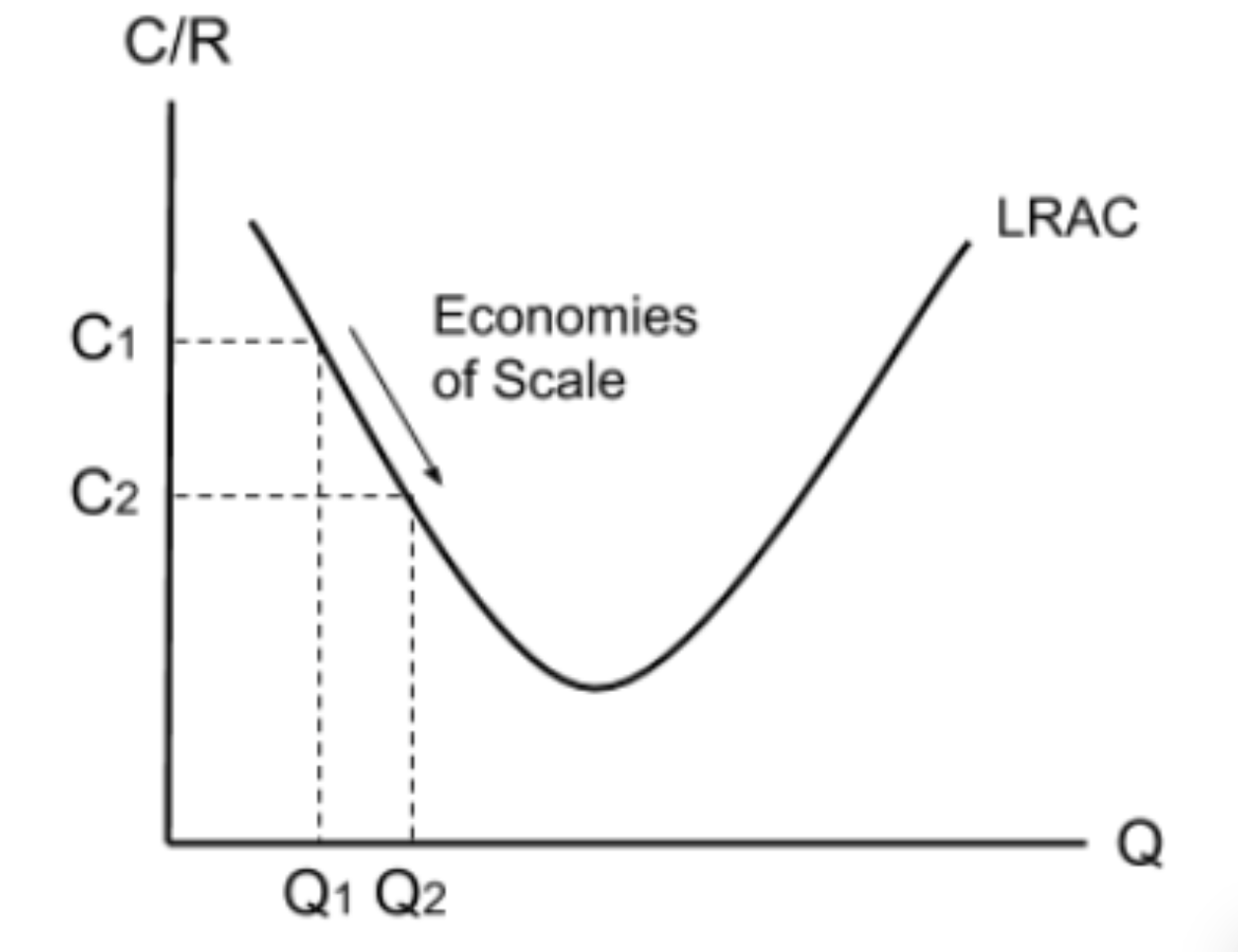
Why do infant industries need to be protected?
Infant industries do not benefit from economies of scale. This means that their cost of production is often higher than other countries. This means that they can’t compete with large industries from other countries. Subsidies to domestic producers can help reduce the price of their goods.
How do trade barriers support health and safety?
Trade barriers can be used to reduce imports of goods which do not meet health and safety regulations.