2.0 Fructose and galactose metabolism
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Fructose and galactose are metabolized in the liver to produce
glucose,
lactate,
fatty acids
Unlike glucose, fructose and galactose do not have a dedicated catabolic pathway.
cells convert fructose/galactose→ glycolytic metabolites → incorporates them into glycolysis for pyruvate + ATP synthesis.
The catabolism of both fructose and galactose produces
the same number of ATP molecules as glucose.
Fructose is absorbed from the small intestine
and metabolized in the liver, primarily → glycogen.
However, fructose metabolism can also lead to the formation of
triglycerides
Fructose metabolism can follow either one of two pathways:
fructose (via fructokinase) → fructose 1 phosphate pathway
fructose (via hexokinase) → fructose 6 phosphate
The major pathway of fructose metabolism occurs in the liver,
where fructose molecules follow the fructose 1-phosphate pathway initiated by the enzyme fructokinase,
fructose 1-phosphate pathway transforms fructose → dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate,
which merge with the glucose metabolic pathway.
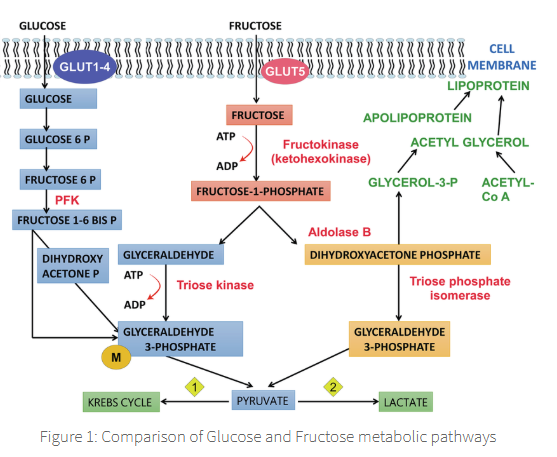
The utilization of fructose by fructokinase followed by the enzyme aldolase
bypasses the glucokinase + PFK-1 driven steps of glucose metabolism,
which are dependent on the hormone insulin
aldolase
rate limiting step of the reaction
This explains why fructose disappears from blood more rapidly than glucose
in diabetic subjects.
Within the skeletal muscle fructose can transform → fructose 6-phosphate via the enzyme hexokinase,
which can then be directly cycled into the glycolytic pathway.
However, hexokinase has a very low affinity to fructose compared to glucose,
so it is not a significant pathway for fructose metabolism unless elevated levels are expressed in plasma, such as during exercise.
Hereditary defects of fructose metabolism
Essential fructosuria:
Fructose 1,6 biphosphatase deficiency:
Hereditary fructose intolerance:
Essential fructosuria:
Occurring due to a deficiency of fructokinase.
A non-serious condition resulting in the loss of excess accumulated fructose in the urine.
hypoglycaemia
deficiency of glucose in the bloodstream
Fructose 1,6 biphosphatase deficiency: Subjects present with fasting hypoglycaemia.
Resulting in an accumulation of fructose 1,6 biphosphate, → the inhibition of glycogenolysis via suppression of the activity of phosphorylase.
Hereditary fructose intolerance:
Occurring due to a deficiency of aldolase B,
resulting in an accumulation of fructose-1-phosphate (F-1-P).
High levels of F-1-P → damage of liver + kidney tissues + the inhibition of glycogen phosphorylase,
resulting in the inhibition of glycogenolysis + fasting hypoglycaemia.