Body Systems + Cells
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Hypothalmus
detects increase in body temp. causes sweating
Homeostasis
maintains the bodys internal enviornment
Reproductive System Male
Testes, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, penis, urethra (maintain sex characteristics and perpetuate species)
Reproductive system female
ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina (maintain sex characteristics and perpetuate species)
Urinary System
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra (Chemical regulation of blood, forms and eliminates urine, maintains homeostasis/ pH and fluid/ mineral balance, Secretes hormones that help regulate production of RBC’s)
Digestive System
Alimentary canal: mouth, esophagus, pharynx, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum and anus
Associated glands: salivary, liver, pancreas (converts food into absorbable substance, eliminates waste)
Respiratory System
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs (O2→ CO2 exchange in blood, Helps regulate acid- base
balance of body fluids, Produces sound with air flowing out through the vocal cords)
Lymphatic/ Immune System
Lymph nodes, lymph vessels, thymus gland, spleen, thoracic duct (drains tissues excess fluid, transports fats, develops immunities, Returns fluid [lymph] to blood, Carries lipid from GI
tract to blood, Filters lymph)
Cardiovascular System
Heart, arteries, veins, capillaries (transport substances to and from cells, Heart pumps blood allowing gas exchange [CO2 & O2], Helps regulate pH balance, temperature, water content, White Blood cells help
fight diseases)
Endocrine system
Endocrine glands; hypothalamus, pituitary glands, pineal gland, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovary/testis (Regulate body activities by the chemical messengers)
Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord, cranial and peripheral nerves, sensory and motor structures (Generates Action Potentials (nerve impulses), Detects changes in body’s internal/external environment, Interprets & responds)
Muscular system
Muscles, fasciae, tendon sheaths, and bursae (movement, pushing food and blood, contracting heart, producing heat, posture)
Skeletal System
Bones, cartilage, membranous structures (movement, blood production, fat and mineral storage, protection)
Integumentary System
Skin, Hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (protection, insulation, regulation of temperature, eliminates wastes, creates vitamin D, detects sensation )
Tissues
Made of different cells
Epithelial (tissues)
Forms boundaries between different enviornments, protects, secretes, absorbs, filters (skin surface, glands, lining of hollow organs, ex: digestive tract)
Connective (tissues)
supports, connects, binds other tissues together (bones, tendons, fats and other soft padding tissues)
Muscle (tissues)
contracts to cause movement (skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles, smooth muscles)
Nervous (tissues)
connects sensory structures to motor structures, internal communication (brains, spinal cord, nerves)
Cells
Smallest unit of life, perform all activities needed to maintain life (metabolism, assimilation, digestion, excretion, reproduction)
Right Upper Quadrant
Liver, gallbladder, antrum + pylorusuodenum, head of pancreas, right kidney + adrenal gland, hepatic flexure + right half of transverse colon
Left Upper Quadrant
Largest part of spleen, left lobe of liver, body and tail of pancreas, left kidney + adrenal gland, splenic flexure of the colon, transverse + descending colon
Left Lower Quadrant
Descending colon, sigmoid colon, left ovary + fallopian tube, left ureter
Right Lower Quadrant
Cecum, appendix, Ascending colon, right ovary + fallopian tube, right ureter
Umbilical Holds…
Aorta, pancreas, small intestines
Suprapubic holds…
urinary bladder, uterus
Epigastrium
Stomach, duodenum, pancreas
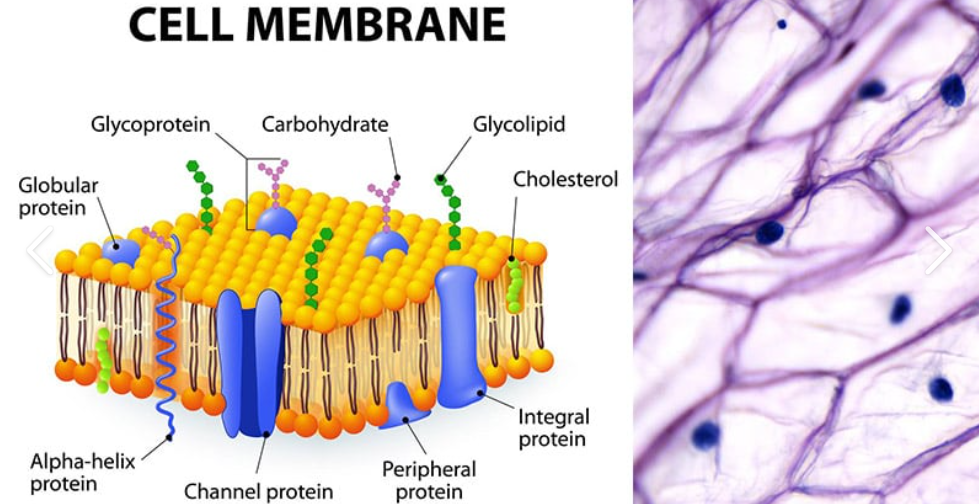
Plasma Membrane
Serves as external cell barrier, Proteins act as receptors for chemical messangers, transports proteins. regulates what enters and exits cell
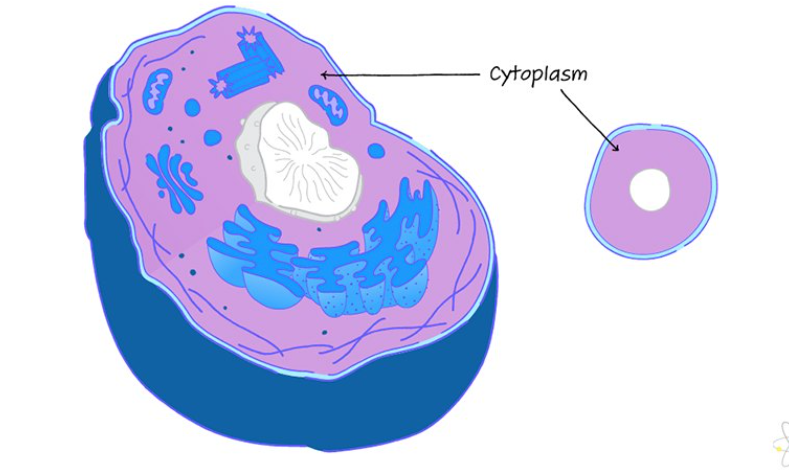
Cytoplasm + cytoskeleton
Hosts chemical reactions + gives cell shape
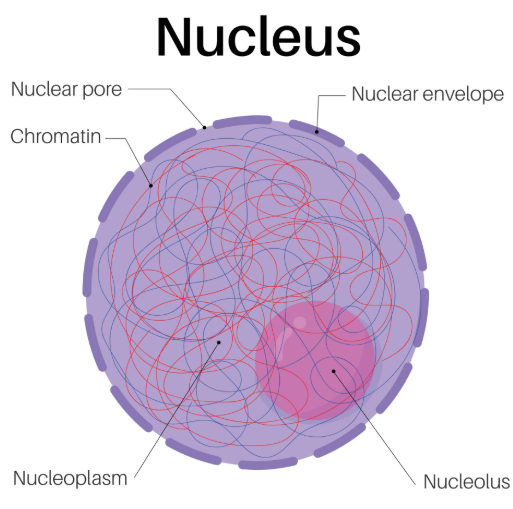
Nucleus
control center of cell, transmits genetic information, provides instruction for protein synthesis, houses chromatin
Nuclear membrane
regulates what comes in and out of the nucleus
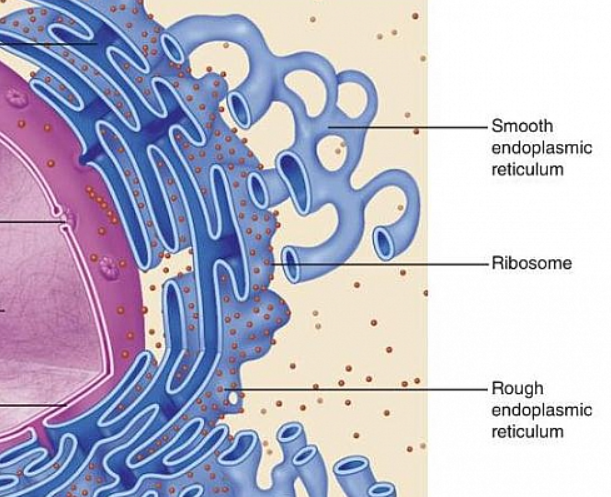
free ribosomes
Hosts protein synthesis, for inside the cell
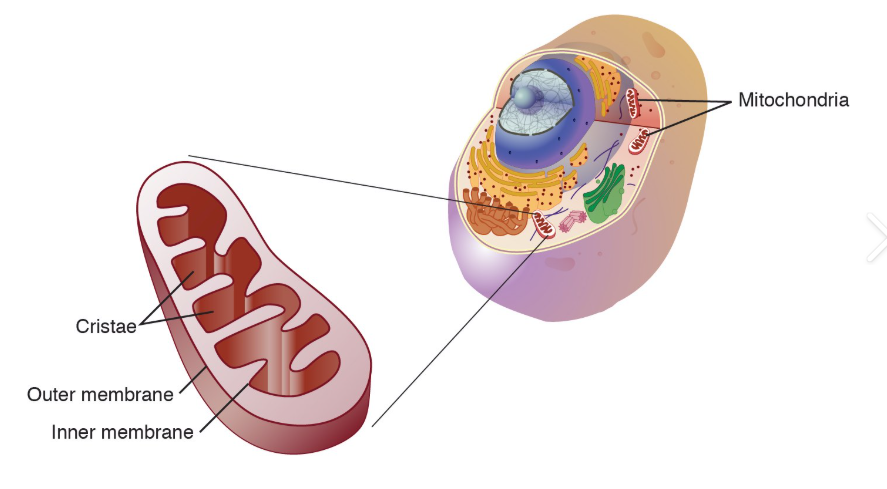
mitochondria
Hosts ATP synthesis, powers the cell
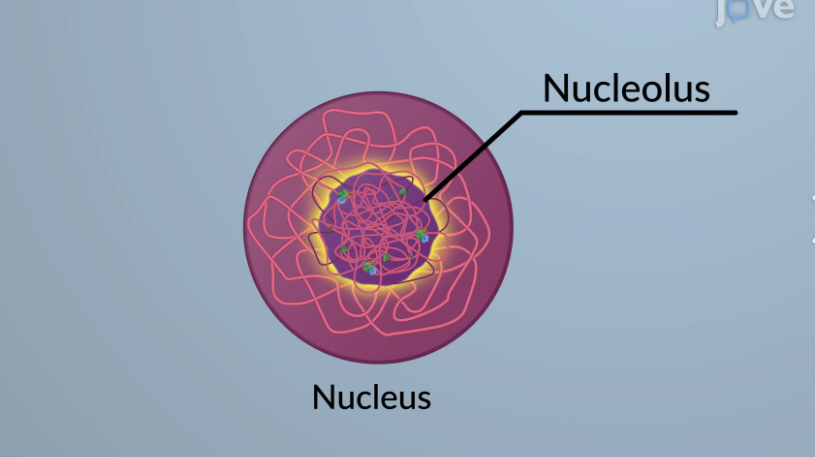
nucleolus
Hosts manufacturing of ribosome subunits, synthesizes ribosomes
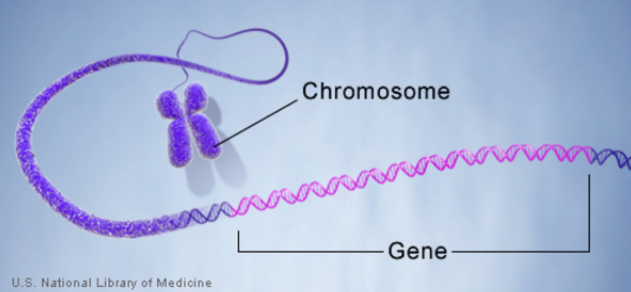
genes
Determines traits
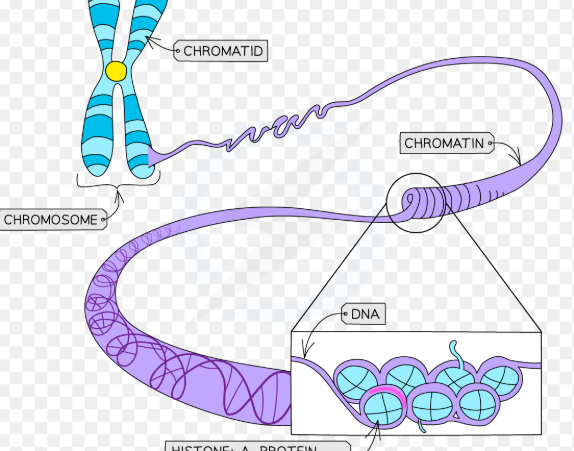
chromatin
Packages DNA
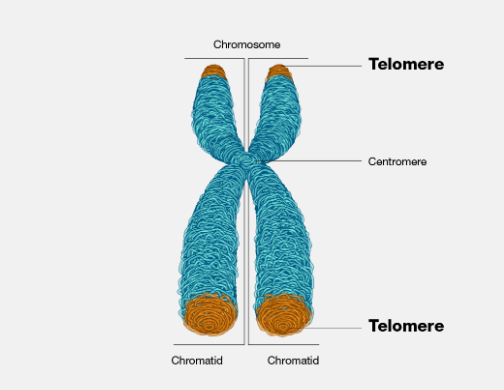
telomeres
Protects chromosome ends
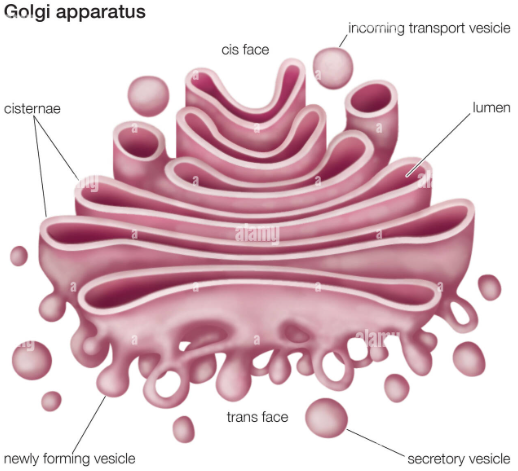
Golgi Apparatus
Packages, modifies, and segregates proteins secretion from the cell. Modifies carbohydrates on protein.
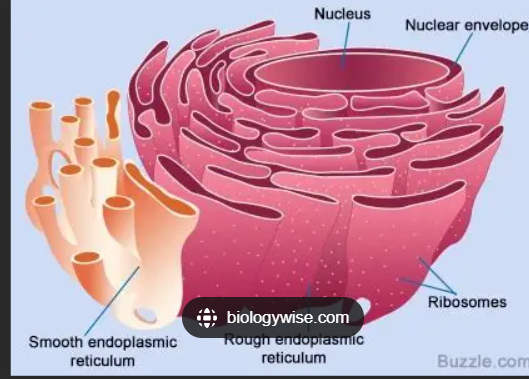
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Bounds proteins in vesicles for transport to the Golgi apparatus and other sites, External face synthesis phospholipids. protein synthesis for transport out of the cell
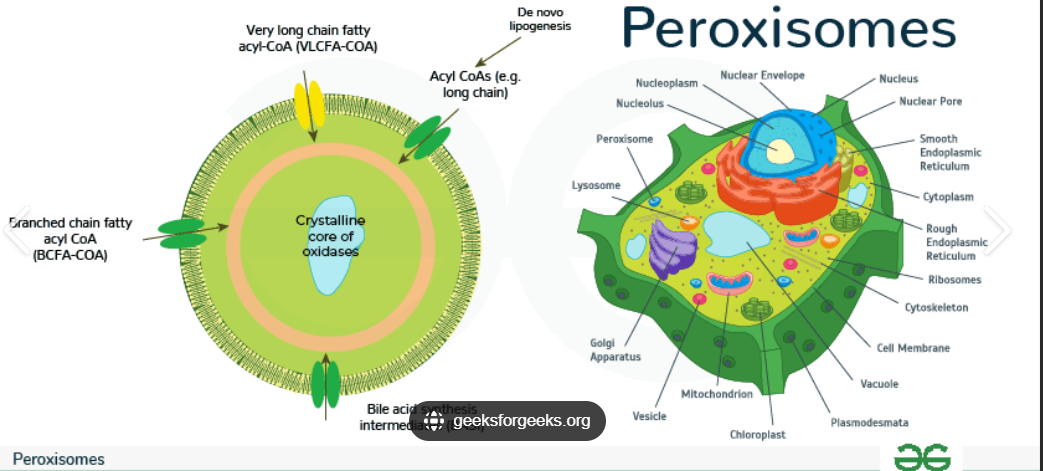
Peroxisome
Internal enzymes detoxify substances, enzyme (catalase) breaks down hydrogen peroxide
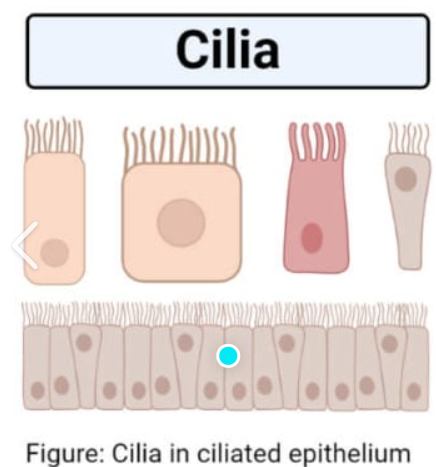
Cilia
Creates unidirectional current that propels substances across cell surface
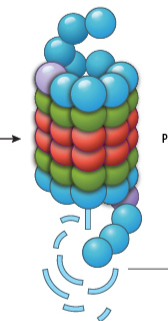
Proteasome
Degrades pre-existing proteins to provide amino acids for new proteins
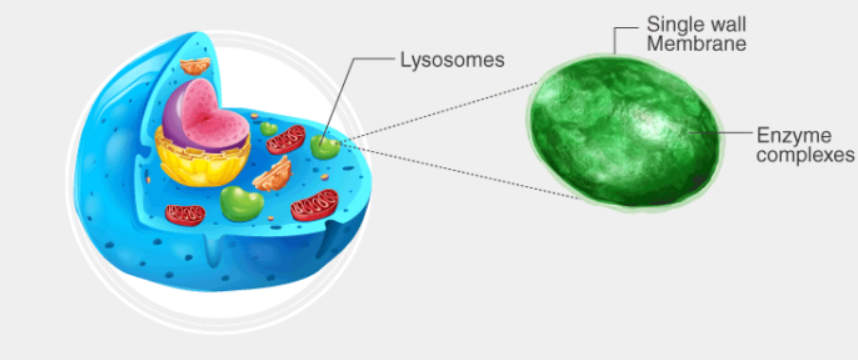
Lysosome
Hosts intracellular digestion, contains powerful digestive enzymes
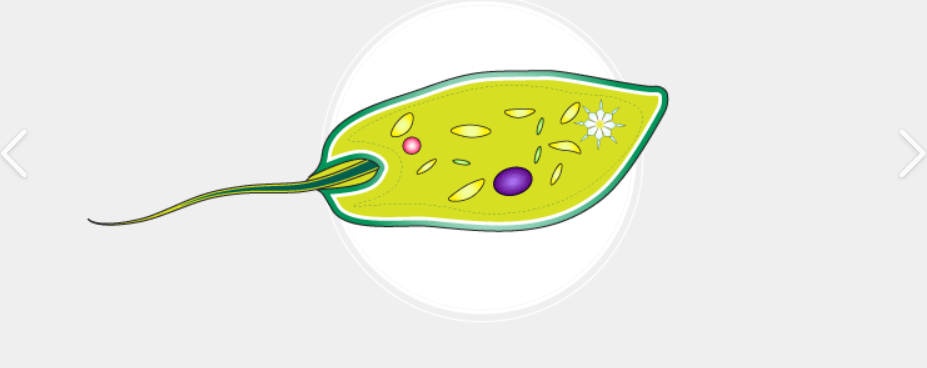
Flagella
Propels the cell as a whole
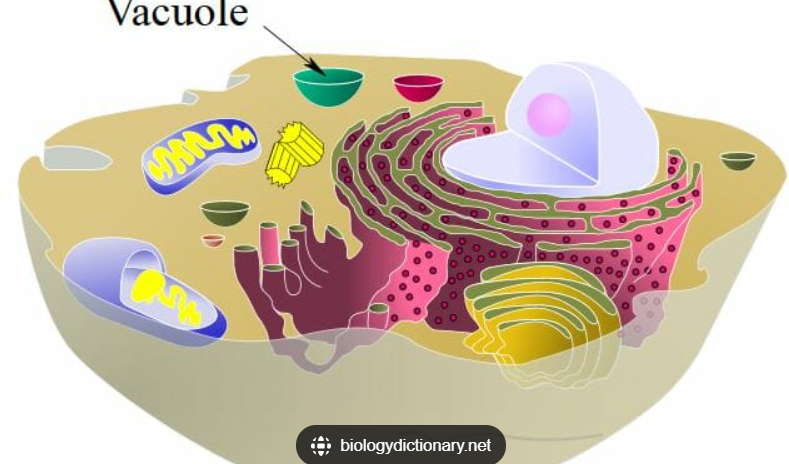
Vacuole
Stores, water, nutrients, and waste
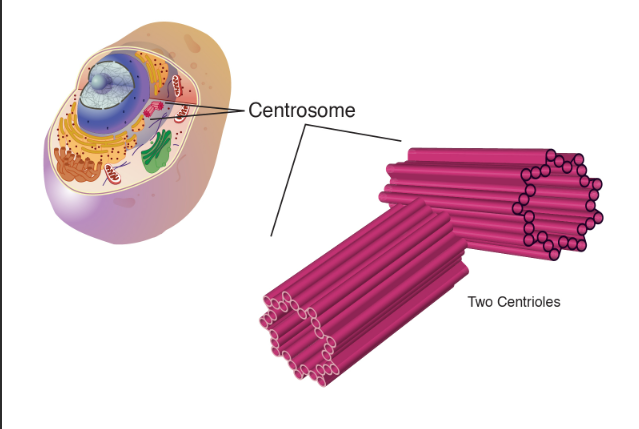
Centrosome
Organizes microtubules
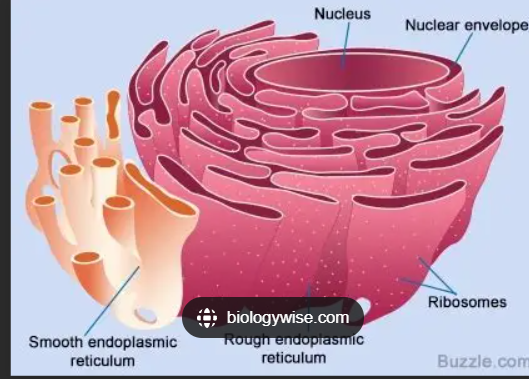
Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum
Hosts lipid and steroid synthesis, lipid metabolism, drug detoxification, makes hormones, Ca2+ storage.
Skeletal Muscle
Muscle attached to bones, pull on bones or skin causing body movements, VOLUNTARY movement,
skeletal muscle cells
AKA muscle fibers, long cylindrical cells, multinucleate, with peripheral nuclei, obvious striations
Cardiac Muscle
Muscles of the heart, only in walls of heart, propel blood through blood vessels to all parts of body, INVOLUNTARY control
Cardiac Muscle Cells
striated, with intercalated discs, cells are branched, usually uninucleate
Smooth Muscle
In the walls of hollow organs, propels substances along internal passageways, INVOLUNTARY control
Smooth Muscle Cells
spindle shaped (tapered on both ends like an almond), central nuclei, no striations, cells arranged closely to form sheets
Nervous Tissue
Neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands), supports cells, and protects neurons, in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Nervous Tissue Cells
Neurons are branching cells, axon, dendrites, cell body, looks like giant spider web
Neurons
Highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses
Neuroglia
Holds the neurons in place
Dendrites
Respond to stimuli
Axons
Transmits electrical impulses over substantial distances within the body
Simple Squamous Cell (epithelium)
single layer of flattened cells, disc shaped central nuclei, sparse cytoplasm, simplest of epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
In kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, serosae. Allow materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important, secretes lubricating substances in the serosae (linings of ventral body cavities)
Squamous
flattened and scale-like cells
Cuboidal
Box-like, as tall as they are wide
Columnar
Tall and column shaped
Lumen
Inside space of tubular structure
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
In kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface. They secrete and absorb
Simple Cuboidal Cell
single layer of cubelike cells, with large, spherical, central nuclei
Simple Columnar Epithelium
In nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract, gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands, ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes and some regions of uterus. Absorbtion and secretion of mucus, enzymes, etc. ciliated type propels mucus.
Simple Columnar Cells
singular layer of tall cells wih round/ oval nuclei, many cells bear microvilli, some bear cillia, layer may contain mucus secreting unicellular glands.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Ciliated: lines trachea and most upper respiratory tract, Nonciliated: in males sperm carrying ducts and ducts of large glands. Secretes substances, particularly mucus, propulsion of mucus by ciliary action.
Psuedostratified Columnar Epithelial Cell
single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching free surface, nuclei seen at different levels, may contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia.