Descending motor control
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
The corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts are ____ ____ motor tracts that are part of ____ ____ control and ____ in the ____ ____ and ____ the _____ __
The corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts are lateral descending motor tracts that are part of volitional motor control and converge in the corona radiata and enter the internal capsule
40% of fibers from the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts are from the ____ ____ ___
Ascending somatic sensory fibers from the _____
40% of fibers from the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts are from the primary motor area (4)
Ascending somatic sensory fibers from the thalamus
In the midbrain, fibers of the corticospinal tract reside in the _____ ____ of the _____ ____ and innervate the ____ ____
in the brainstem they also innervate the ______ _____ and _____ ___
In the midbrain, fibers of the corticospinal tract reside in the middle 2/3rds of the cerebral peduncle and innervate the red nucleus
In the brainstem they also innervate the contralateral pontine and medullary nuclei
The corticospinal tract controls most of the ____ ____ especially the ____
Controls most of the manipulative movements especially the digits
The corticobulbar tract exits the _____ to connect with ____ ____ _____ ___
Cortical inputs to the _____ ____ of ____
Upper half is ____
Lower half is ____
The corticobulbar tract exits the brainstem to connect with motor based cranial nerves
Cortical inputs to the motor nucleus of VII
upper half is bilateral
lower half is contralateral
Rubrospinal tract originates from the ____ ____ of the ____ ___
Immediately descends through the _____ of the _____ side
Descends with the _____ _____
Terminates in ___, ___, ___ of the ____ ___
Descend only to the ____ and ____ ____ levels
Rubrospinal tract originates from the magnocellular portion of the red nucleus
Immediately descends through the brainstem of the contralateral side
Descends with the lateral corticospinal cord
Terminates in V, VI, and VII of spinal cord
Descends only to the cervical and high thoracic levels
The tectospinal tract has ____ axons that arise from cells in the _____ _____ ___
Axons descend to the _____ level
Terminate in ____, ____ and parts of ____
Mediates movements in response to _____ stimuli
Fibers terminate on _____ that regulate ____ ___
Regulate ____ of the ____ during tracking of ___ ____
The tectospinal tract has descending axons that arise from cells in the contralateral superior colliculus
Axons descend to the cervical level
Terminate in VII, VIII, and parts of VI
Mediates movements in response to auditory stimuli
Fibers terminate on motorneurons that regulate neck muscles
Regulate orientation of the head during tracking of moving objects
Medial descending tracts include the _____ and _____ _____ formation
These function to mediate _____ _____ control
Pontine and medullary reticular formation
These function to mediate postural motor control
The pontine (medial) reticulospinal tract _____ motorneurons to _____ muscles
descends ____
This receives input from the ____ ___, ____ ___, midbrain ____ centers and ____
Also receives significant input from ______ ___-
The pontine (medial) reticulospinal tract excites motor neurons to antigravity muscles
Descends uncrossed
This receives input from the cerebral cortex, red nucleus, midbrain locomotor centers, and cerebellum
Significant input from ascending afferents
the medullary (lateral) reticulospinal tract descends _____ and _____ motorneurons to _____ muscles
Cells are driven by input from the ____ ___ and _____ _____ Muscle function
the medullary (lateral) reticulospinal tract descends uncrossed and inhibits motorneurons to antigravity muscles
Cells are driven by input from the cerebral cortex and inhibit flexor muscle function
The vesitbulospinal tracts are located in the _____ _____ nucleus
Axons descend ____ in the _____ ____
Tract _____ motorneurons to _____ muscles
Primary input from the ____ _____ and ____
The vestibulospinal tracts are located in the lateral vestibular nucleus
Axons descend uncrossed in the lateral funiculus
Tract excited motorneurons to antigravity muscles
Primary input from the vestibular apparatus and cerebellum
The descending MLF descends _____ and innervates motorneurons to the _____
Involved in _____ and _____ orientation
Input from the ______ ____ and _____
Starts in the _____ _____ nucleus
The descending MLF descends ipsilaterally and innervates motorneurons to the neck
Involved in coordination and head orientation
input from the vestibular apparatus and cerebellum
Starts in the medial vestibular nucleus
Both the descending MLF and the vestibulospinal tracts are key in ____ and _____ regulation of ____
Key in static and dynamic regulation of posture
The medial tracts including the _____ and _____ tracts project _____ and are _____ ______ and ____ motorneuron pools to _____, _____ muscles to control ______, _____ mechanisms, and _____ tone
The medial tracts including the reticulospinal an vestibulospinal tracts project ipsilaterally and are tonically active and excite motorneuron pools to antigravity, extensory muscles to control posture, righting mechanisms, and muscle tone
The lateral tracts including the ______ and _____ tracts project _____ and exhibit _____ activity to _____ motorneurons and regulate _____ ___, _____, _____ ____ movements
The lateral tracts including the corticospinal and rubrospinal tracts project contralaterally and exhibit phasic activity to excite motorneurons and regulate finely controlled, manipulative, phasic volitional movements
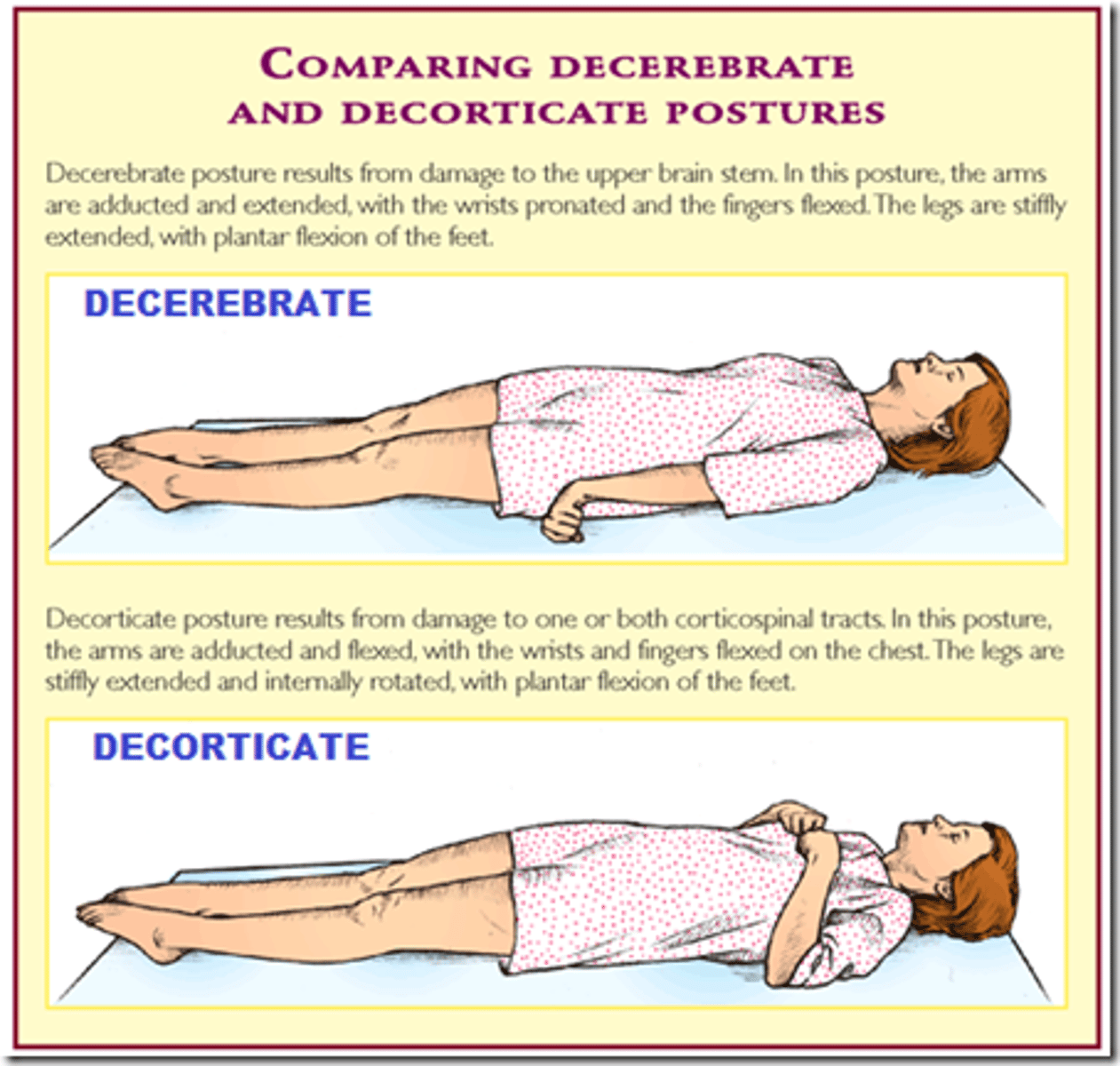
Decerebrate posture leaves the _____ ___ and _____ ____ intact but removes the descending _____ and ____ ____ input
results from ______ ______ lesions
Disruption to the ____ and _____ tracts
Interruption of _____ ____
_____ reflex patterns remain
____ and ______ muscle tone ____ dramatically
_____ and ______
____ muscles firing ______ _____
Decerebrate posture leaves the lower brainstem and spinal cord intact but removes the descending cerebral and red nucleus input
Results from upper brainstem lesions
Disruption to the cortico and rubrospinal tracts
Interruption of voluntary movements
Postural reflex patterns remain
DTR and extensor muscle tone increased dramatically
Hyperreflexia and spasticity
Postural muscles firing without inhibition
Decorticate posture results from ______ lesions
Exaggerated _____
Weakness of ____ ____ movements in ______ ___
Development of ____
_______ upper limb is ____ while _____ lower limb is _____
_____ baby
Decorticate posture results from cortical lesions
Exaggerated DTR (spasticity)
Weakness of very fine movements in distal extremities
Development of babinski
Contralateral upper limb flexed while contralateral lower limb extended
Mummy baby
Decerebrate vs decorticate posture?
Decerebrate = extensors upper and lower are firing
Decorticate = flexors up top, extensors down bottom