xylem and phloem
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
why do plants need transport systems
need substances like water, minerals and sugars
need to get rid of waste substances
multicellular so have a small surface area to volume ratio
have a high metabolic rate
exchanging substances by direct diffusion would take too long
what does the xylem transport
water and mineral ions up the plant
what does the phloem transport
sugars up and down the plant
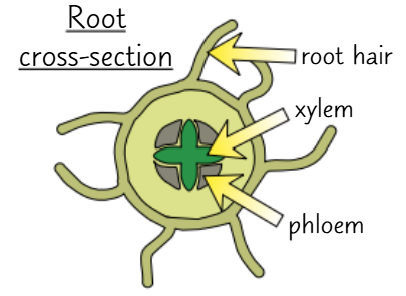
root cross section
xylem is in the centre surrounded by phloem to provide support for the root as it pushes through the soil
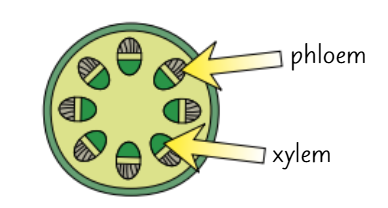
stem cross section
the xylem and phloem are near the outside to provide support for the root as it pushes through the soil
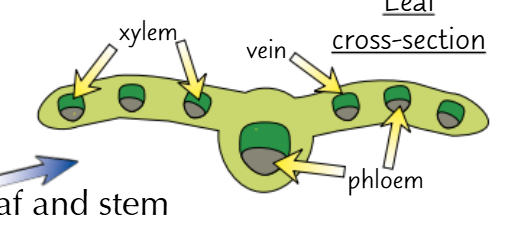
leaf cross section
xylem and phloem make up a network of veins which support the thin leaves
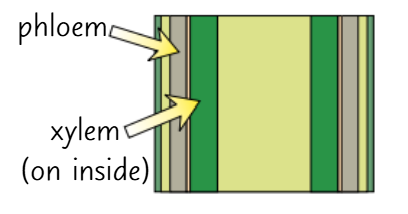
longitudinal cross section of a leaf
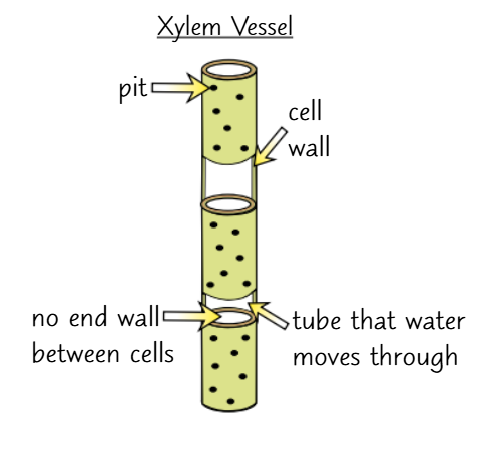
How are xylem vessels adapted for transporting water and mineral ions
xylem vessels are very long, tube like structures formed from cells joined end to end
there are no end walls on these cells, making an uninterrupted tube that allows water to pass up through the middle easily
their cells are dead so contain no cytoplasm
walls are thickened with a woody substance called lignin which helps to support the xylem vessels and stops them from collapsing inwards. Lignin can be deposited in xylem walls in different ways eg. in a spiral or as distinct rings
the amount of lignin increases as the cell gets older
water and ions move into and out of the vessels through small pits in the wall where there’s no lignin
what does phloem tissue contain
phloem fibres, phloem parenchyma, sieve tube elements and companion cells
are xylems or phloem used for support
just xylem
sieve tube elements
living cells that form the tube for transporting solutes through the plant
they are joined end to end to form sieve tubes
the ‘sieve’ parts are the end walls, which have lots of holes in them to allow solutes to pass through
although they are living cells, they have no nucleus, a thin layer of cytoplasm and few organelles
the cytoplasm of adjacent cells is connected through the holes in the sieve plates
cross section of phloem cells
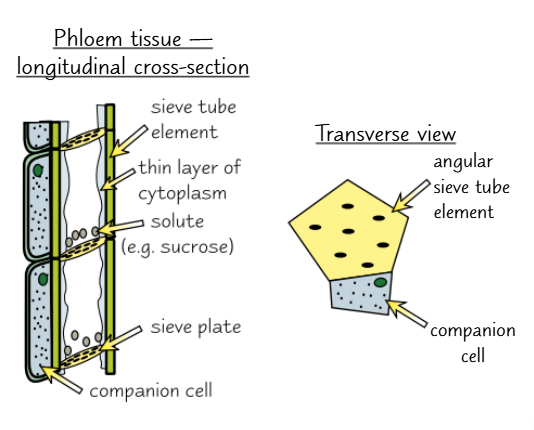
companion cells
lack of a nucleus are other organelles in a sieve tube means that they can’t survive on their own so each sieve tube has its own companion cell
they carrying out the living functions for both themself and their sieve cells. For example, they provide the energy for the active transport of solutes
how to dissect plant cells
use a scalpel to cut a cross-sections of the stem
cut the sections as thin as possible
use tweezers to gently place the cut sections in water until you come to use them. This stops them from drying out
transfer each section to a dish containing a stain eg, toluidine blue, and leave for one minute. TBO stains the lignin in the walls of the xylem vessels blue-green. This will let you see the position of the xylem vessels and examine their structure
rinse off the sections in water and mount each one onto a slide