Excavation Safety
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Excavation
Is any man made cut, cavity or depression in an earth surface that is formed by earth removal
112%
The fatality rate for excavation work is ________ higher than the rate for general construction
Trench excavation
Is a narrow excavation where the depth of a trench is greater than its width, and the width measured at the bottom is not greater than 15 ft
5 ft (1.5m)
Trenches _________ deep or greater require a protective system, unless if the excavation is my entirely of stable rock. If less than ______, no protective system required.
20 ft (6.1m)
Trenches _________ or deeper required a protective system designed by a registered professional engineer.
Pre-planning
Protective systems
Safety measures
Inspections
Eliminate hazards and control risks by implementing precautions in excavations and trenches with:
Hazards of excavation work
Soil collapse
Falling objects
Underground utilities
Working surfaces
Confined space conditions
Soil
Is a mixture of rock, water, air and a variety of other substances
Voids
Soil is made up of rock in the form of small particles and spaced called _______.
Normally, some parts of the ______ are filled with water.
Types of soil collapse
Sliding
Bulge
Toppling
Boiling
Heave
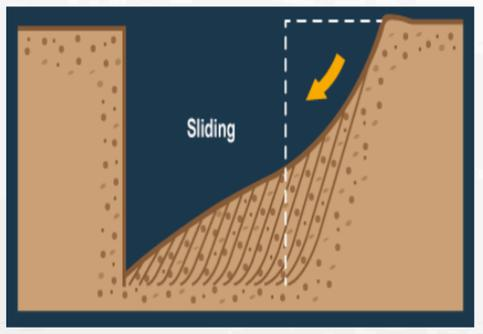
Sliding
Soil shifts downwards along a slip plane, often caused by excessive loading or water saturation weakening the soil structure.
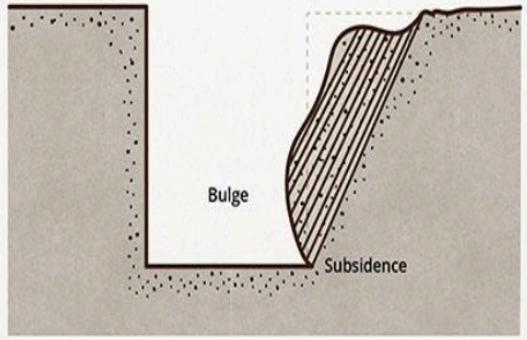
Bulge
Soil deforms outward, creating a protruding area, typically due to internal pressure or lateral forces from excavation or nearby construction.
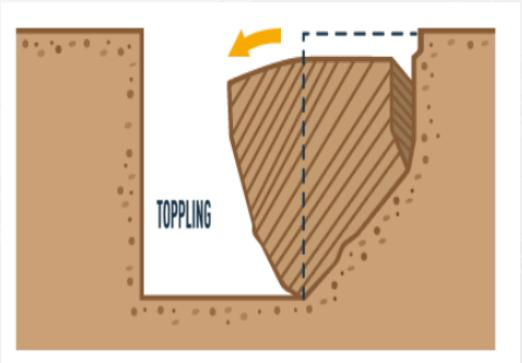
Toppling
Soil or rock tips over around a pivot point, commonly caused by undercutting or destabilizing forces at the base.
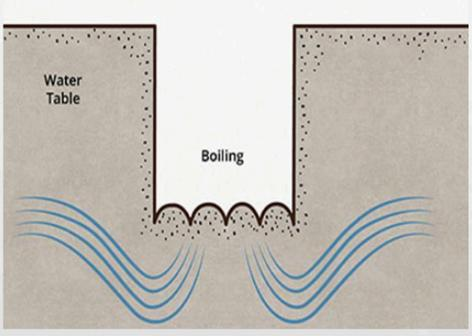
Boiling
Soil is displaced upward due to water pressure, often caused by high groundwater pressure or rapid infiltration disrupting soil stability.
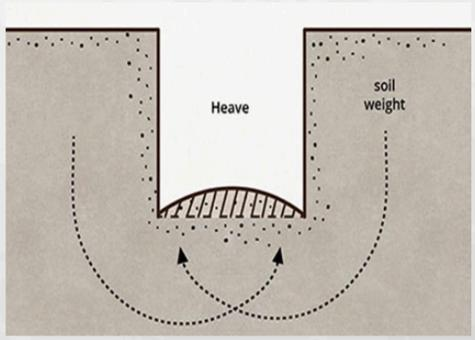
Heave
Soil rises and expands, usually due to moisture changes such as sweating and drying cycles or freezing and thawing, which affect soil volume.
Undercutting

Principal causes of soil collapse
Steep cutting angle
Super imposed load
Shock and vibration
Water pressure
Drying
Excavation
In general, ______ means loosening and taking out materials, living space above or below ground.
Earthworks phase
In civil engineering, this is usually performed during the ____________.
Level of risk for collapsing
Corresponding safety measures
Each type of soil has a certain ___________, and _____________.
Stable rock
Natural solid mineral matters
Examples are rock, hilly terrain
Type A
Cohesive soil with unconfined compressive strength of 1.5 tons per square foot or greater
Examples are clay, silt, sandy clay
Type B
Cohesive soil with strength greater than 0.5 tsf but less than 1.5 tsf
Examples are angular gravel (similar to crushed rock)
Type C
Cohesive soil strength 0.5 tsf or less
Examples are granular soil such as grave, sand and loamy sand
Vertical ; 90
Max Slope of stable rock (H:V)
¾ : 1; 53°
Max slope of Type A
1:1; 45°
Max slope of Type B
1- ½ : 1; 34°
Max slope of type C
Shoring
This involves the use of supports or structures to prevent the collapse of soil and provides the ability to excavation sites
Hydraulic shoring
Metal shoring
Adjustable shoring
Shoring systems can include:
Hydraulic shoring
Uses hydraulic pressure to support the excavation walls. This type can be adjusted as needed and is often used in deeper excavations.
Metal shoring
Uses steel plates and beams to provide support. It's durable and can be used in a variety of soil conditions.
Adjustable shoring
Consists of adjustable props and struts that can be modified to accommodate changes in the excavation depth
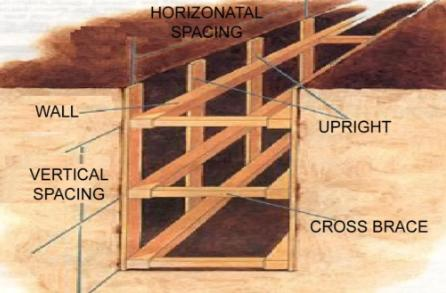
Timbering
This is an older method where wooden planks and beams are used to support the sides of an excavation.
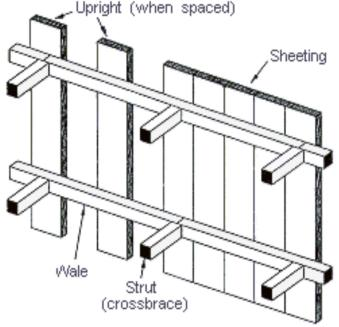
Timber sheeting
Timber bracing
Timbering involves:
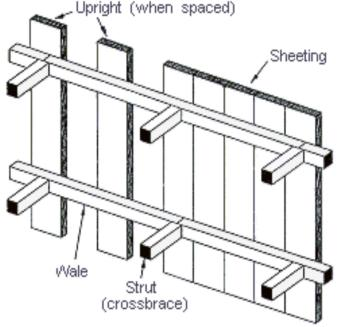
Timber sheeting
Wooden planks are placed vertically against the excavation walls to prevent soil from collapsing.
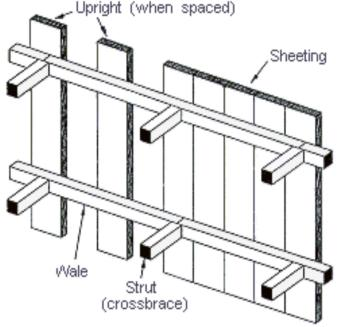
Timber bracing
Wooden beams are used to brace and support the timber sheeting or excavation walls.
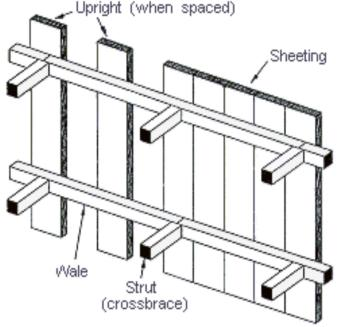
5 cm x 15 cm
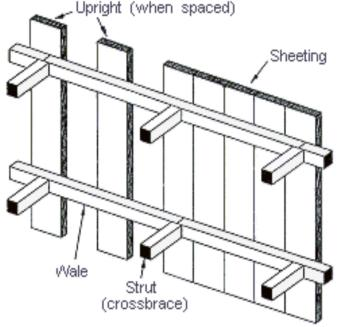
Sheeting
10 cm x 15 cm
Wales
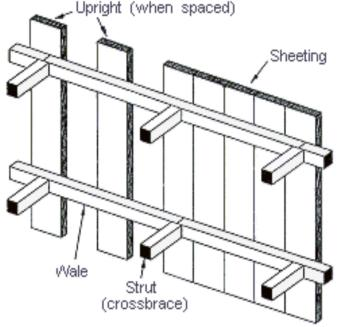
10 cm x 15 cm
Struts
OSHS RULE 1413: EXCAVATION
Before shoring or timbering, the walls of an excavation shall be stripped of loose rocks or other materials that might slide, roll, or fall on workers.
Every excavation over 1 m shall be kept free of water at all times.
1 m deep
Excavation over __________ shall be supported by adequate shoring and timbering. This shall not apply to such excavation if:
A worker is not required to enter for any purpose
Cut in solid rock
Walls are sloped to 45° from the vertical or cut to the angle of repose.
6.1 m
Shoring or timbering in excavation over ________ deep shall be designed by a structural engineer and approved by the proper authority.
Shielding/boxing
Refers to the use of protective systems designed to safeguard workers and equipment from the risks associated with soil collapse during excavation activities. Unlike shoring and timbering, which actively support and stabilize the excavation walls, ______ involves creating a protective barrier to prevent soil from falling into the excavation area.

Berms
A safe distance from the edge of excavation. Are constructed in order to prevent erosion and sedimentation, and in some cases as a means to provide for a safe working environment during excavation by controlling surface runoff.

Minimum berm
Not less than 1/3 of depth of excavation
Materials being excavated are stable
Shoring to carry the additional load
Barriers are provided to prevent rollback of excavated material
A berm of reduced width of not less than 1 m may be allowed if:
Prevention of falling materials
Barricades should be provided
Signs must be posted to prevent the public from going near the excavation

1 m
Provision for barricades
The top of the walls of an excavation more than 2 m deep shall be barricated to a height of at least_____.
Prevention of fall: surface crossing of trenches
Walkways or bridges must be provided
Minimum clear width of 20 in.
With standard rails
Extended a minimum of 24 in. past the surface edge

Working surface
Excavation shall be kept free of water at all times
In muddy areas, workers should be provided with boots to reduce the hazard of slipping
Underground facilities
Determine the location of underground facilities and take necessary steps to prevent damage to these facilities
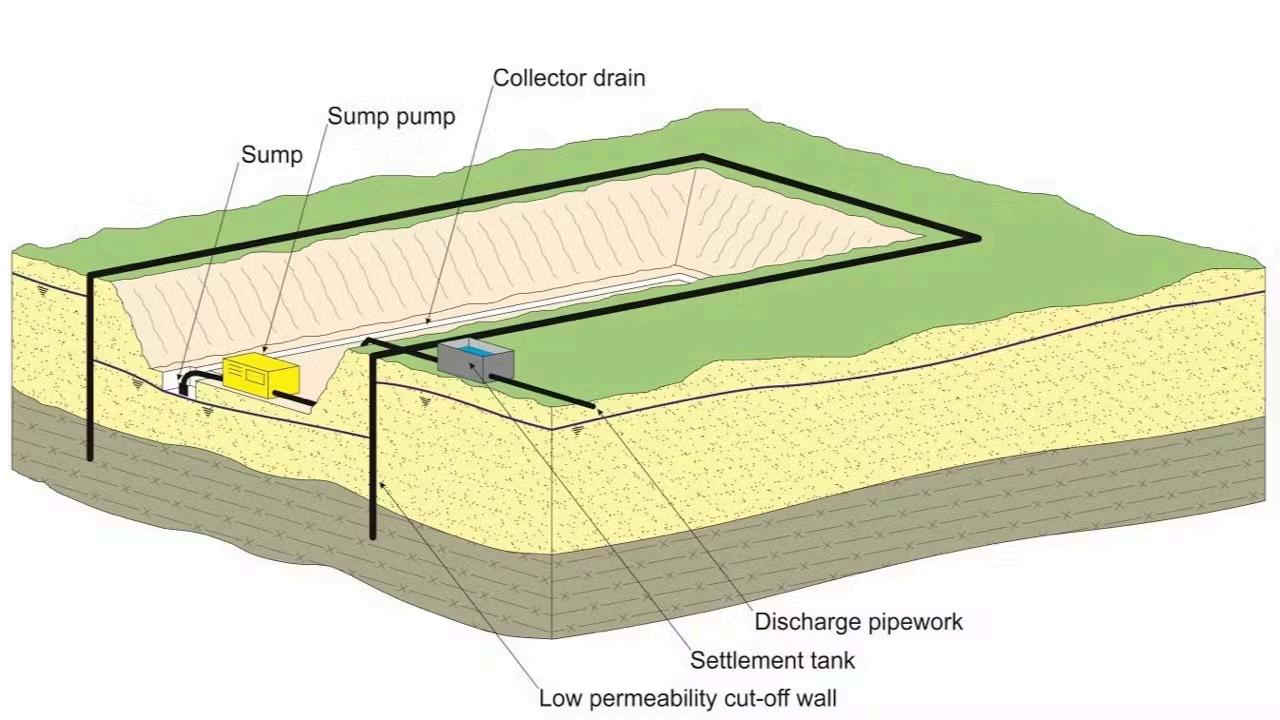
Groundwater
Causes extreme geotechnical problems in excavations such as sand running for most of construction projects such as tunneling
Two major methods for controlling groundwater
Pumping technique
Exclusion technique
Pumping technique
Involves digging a sump where groundwater collects, which is then simply drawn out using a pump
Exclusion technique
Achieved by constructing an impermeable or low permeability cut off wall to keep the groundwater out of the excavation
Groundwater control
Less than 19.5% oxygen
Oxygen deficient atmosphere
Natural gases from potential leaks or cut lines
Methane from decayed matter
Potential for other gases to be present include but not limited to:
4 ft deep or greater
Test for atmospheric hazards like low oxygen levels and presence of hazardous fumes and toxic gases is required when the excavation is ________
Working in excavation
Prior to opening
Check excavation permit
Protect all underground installations
Remove trees, boulders, stump add other surface emcumbrances and hazards before starting excavation.
Working in excavation
During operations
Wear goggles and hard hats
Store excavated materials at least 1 m from edge
Remove boulders or other materials that may roll
Do not stockpiles materials or store equipment near edge or excavation
Give special attention to side slops, adversely affected by weather, moisture content or vibration
In case of undercut, safely support overhanging materials
Safe working distance between workers
Control groundwater
Provide walkways, bridges, guardrails, barricades, warning flags/lights for pedestrian and vehicular traffic
Working on excavation
Equipment operations
Shore and brace sides of excavation to resist superimposed loads if necessary to operate equipment above or near excavation
Use stop logs, warning signs, or barricades if mobile equipment is utilized adjacent to excavations
Use horn or give signals to ensure safety
Working in excavation
Excavation and confined space
Check the atmosphere condition before entry
Do not work alone in a confined space
Provide lifeline
Provide ventilation or blower before entering
Provide emergency rescue equipment such as breathing apparatus, safety harness line, and basket stretcher
Working in excavation
During break time, workmen should never stand or take rest on high banks of soft material
Maintain guard rails, fences, or other barricades and warning lights from sunset to sundown
Do not leave tools, materials, or debris in walkway ramps or near the edge of excavation
Do not use guard rails as resting place
Competent person
An individual who is capable of identifying existing predictable hazards or working conditions that are unsanitary or dangerous (eg safety officers)
Inspection
Daily, before start of each shift:
Every part of an excavation over 2 m deep where workers work shall be inspected by the person in charge at least once a day
This must take performed by a competent person
After heavy rain
When there is any indication of change or movement in adjacent structures
When there is a change in size, location, or placement of spoil pile
When fissures, tension cracks, undercutting, water seepage, occur at the bottom