2. Disease of the Eyelashes and Eyelids: Allergic Eyelid Disease to Lumps and Bumps Eyelid Disease
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Allergic Eyelid Disease to Lumps and Bumps Eyelid Disease
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
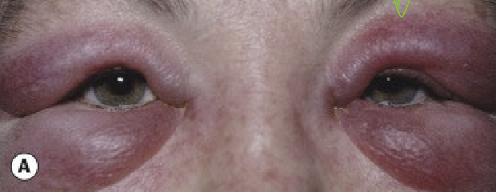
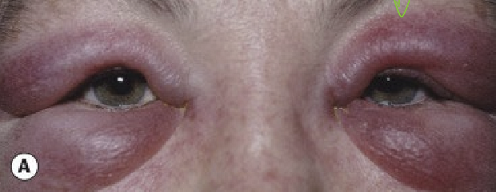
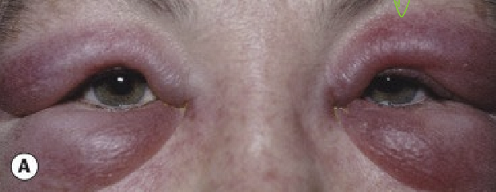
What are the presentations of allergic edema?
Bilateral periorbital edema with hyperemia
Conjunctival swelling (chemosis)
Pt complains of itchiness
What is the pathology for allergic edema?
Inflammatory reaction to pollen or insect bites.
What are the treatment for allergic eyelid disease/allergic edema?
Systemic antihistamines=oral medications
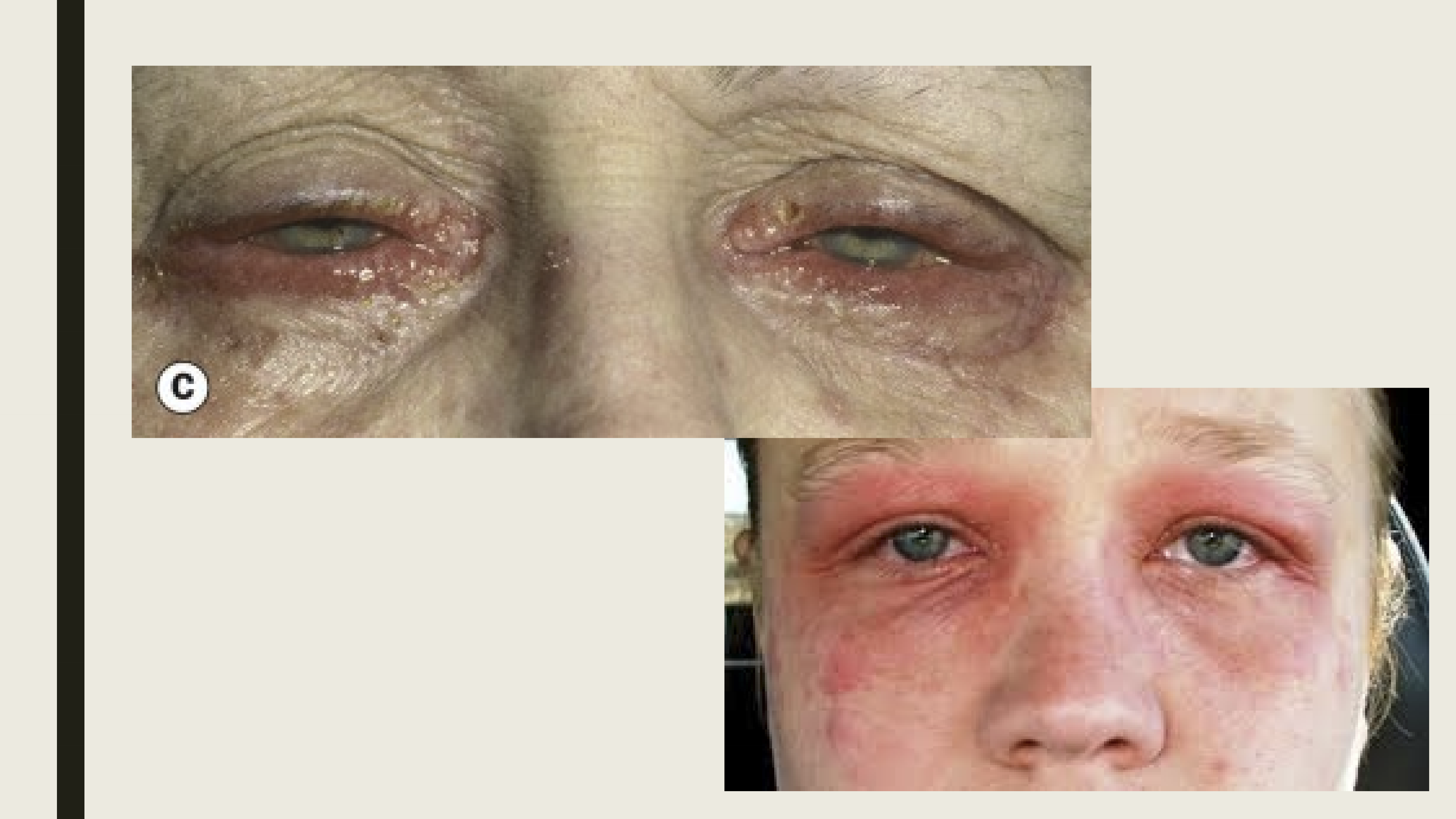
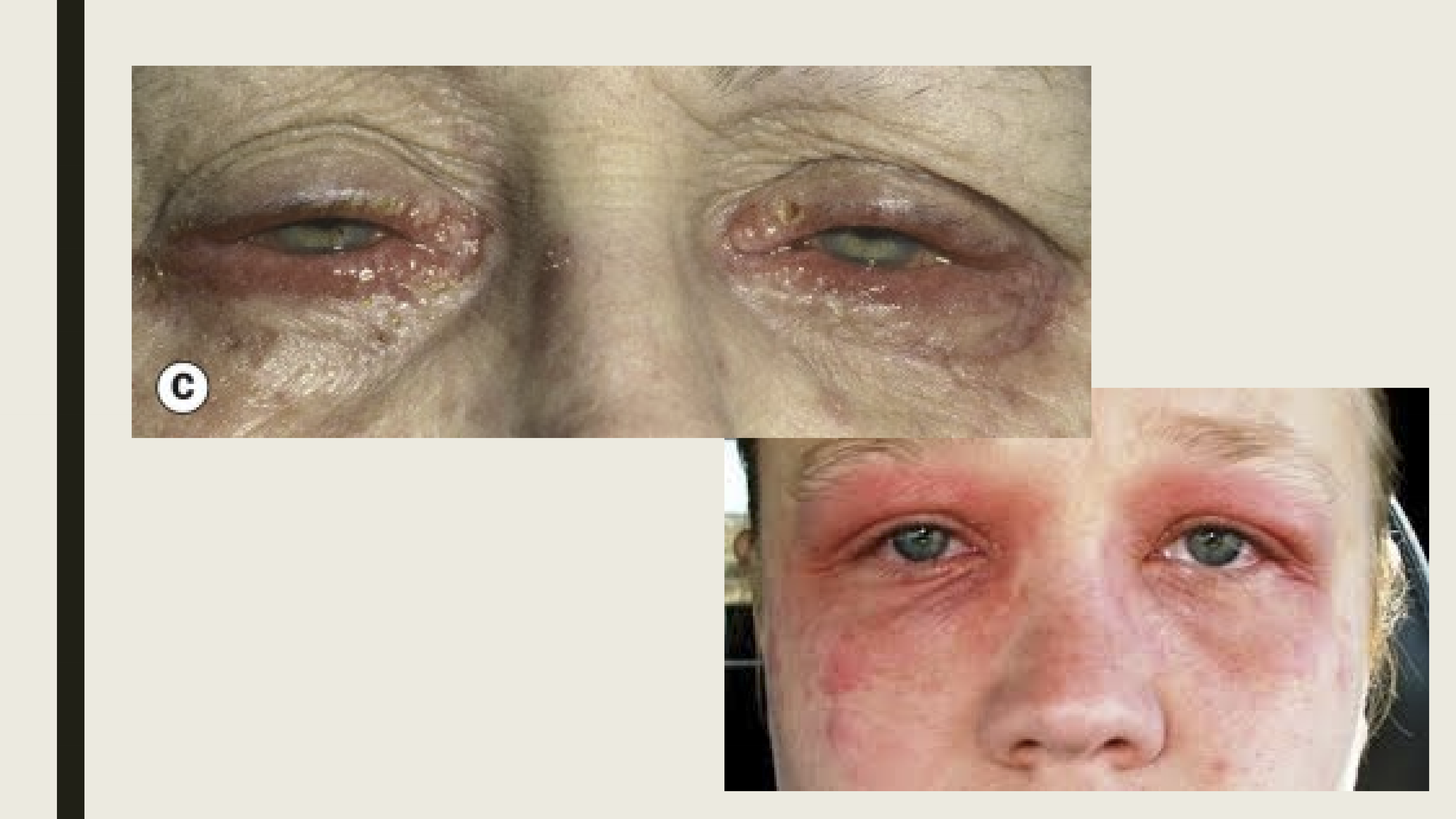
What is the pathophysiology of contact dermatitis?
A delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction triggered by allergens such as preservatives, medications, cosmetics, or metals.
What are the symptoms/presentation of contact dermatitis?
Eyelid itching with hyperemia
Lid edema and scaling of the eyelide
Conjunctival chemosis, hyperemia, and papillary reaction
PEE (Punctate corneal epithelial erosions)
What are the treatments for contact dermatitis?
Remove allergen exposure
Topical steroids, oral antihistabmines, cold compresses, and artificial tears
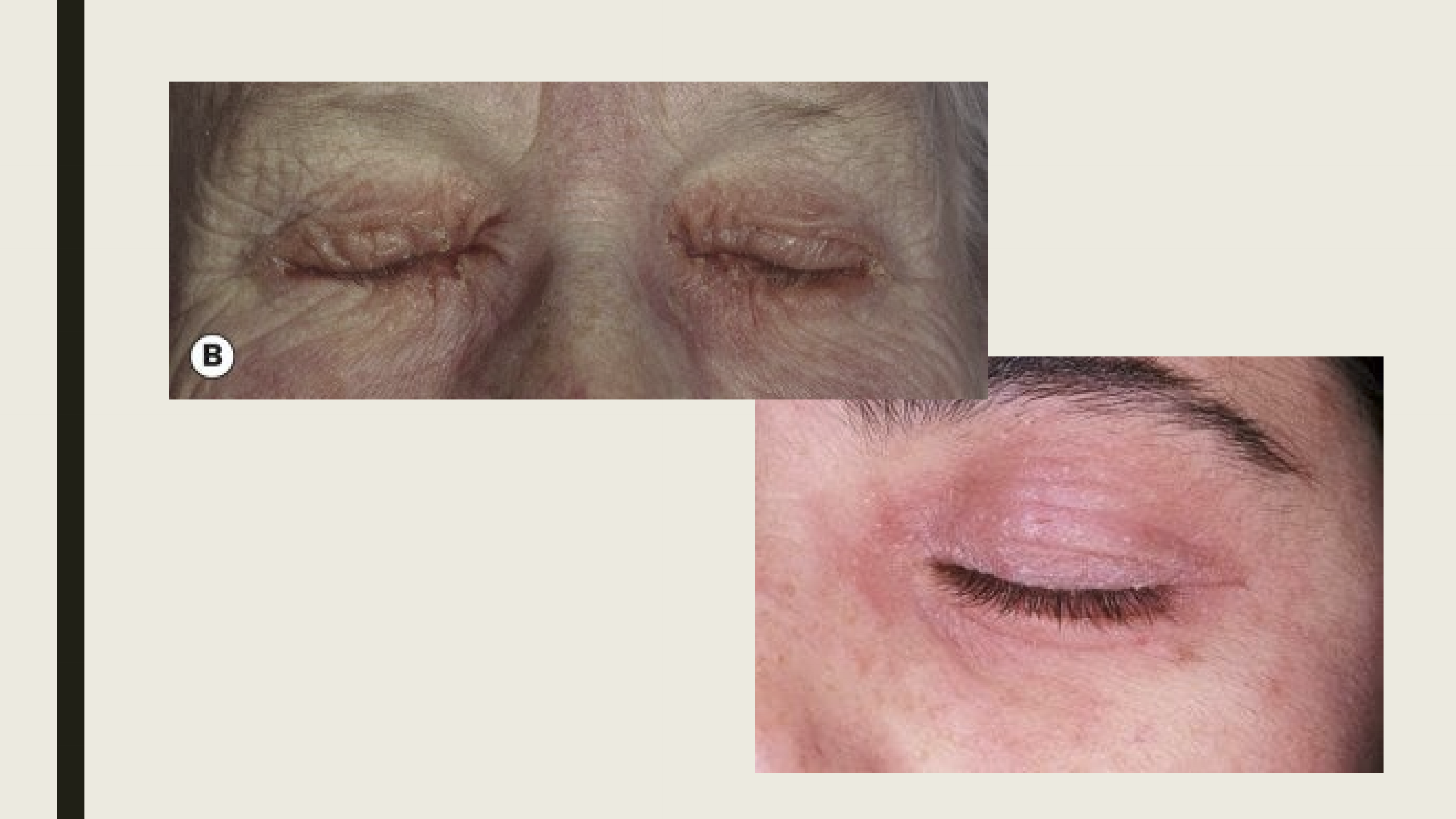
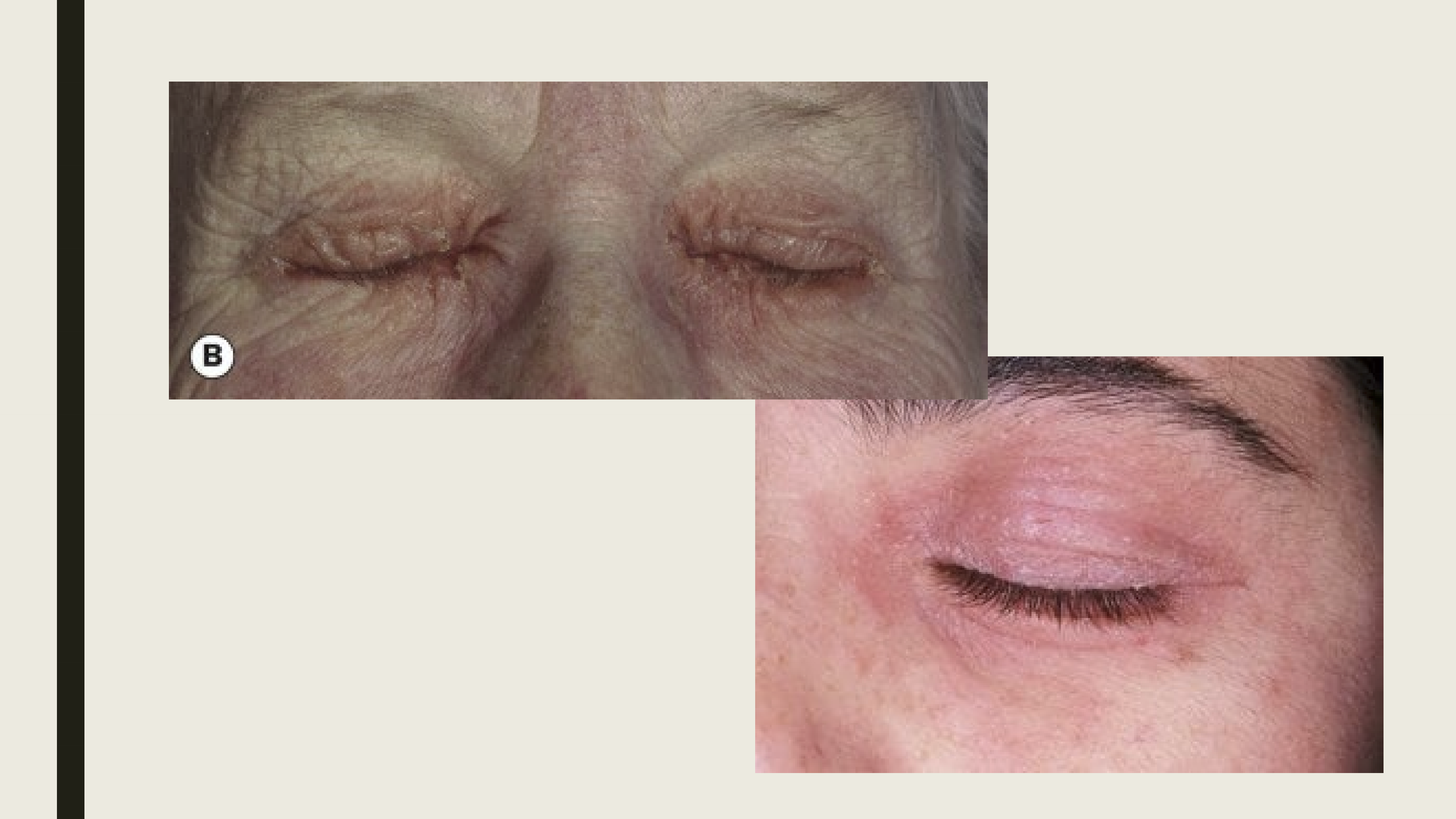
What is atopic dermatitis/eczema?
Idiopathic conditions associated with asthma and hayfever. It is commonly seen in children with vernal keratoconjunctivitis.
What are the presentations of atopic dermatitis/eczema?
Thickening and crusting of eyelids, typically associated with blepharitis and madarosis.
What are the treatments for atopic dermatitis/eczema?
Topical steriods
Emollients to hydrate skin
Treatment of associated blepharitis
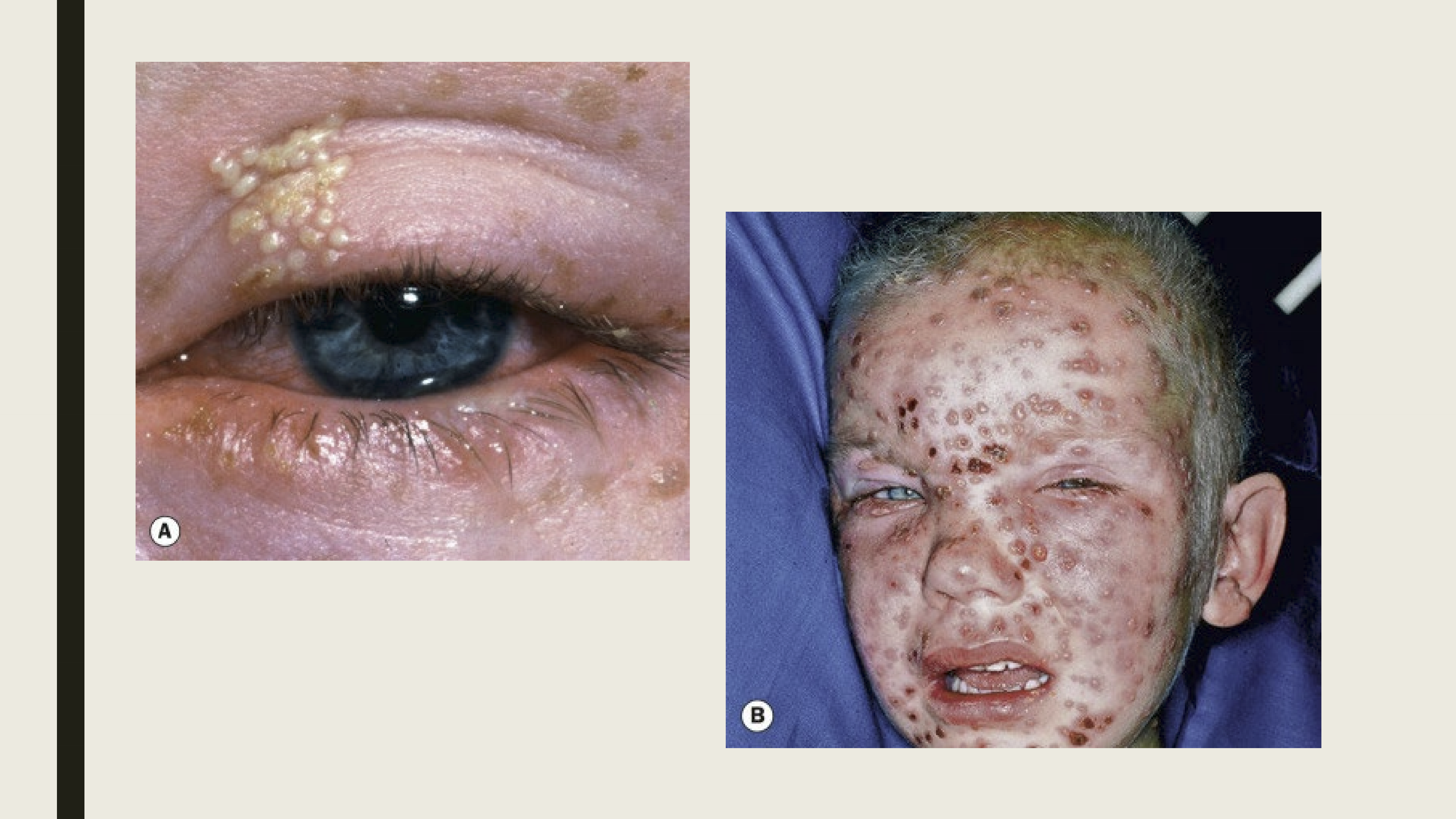
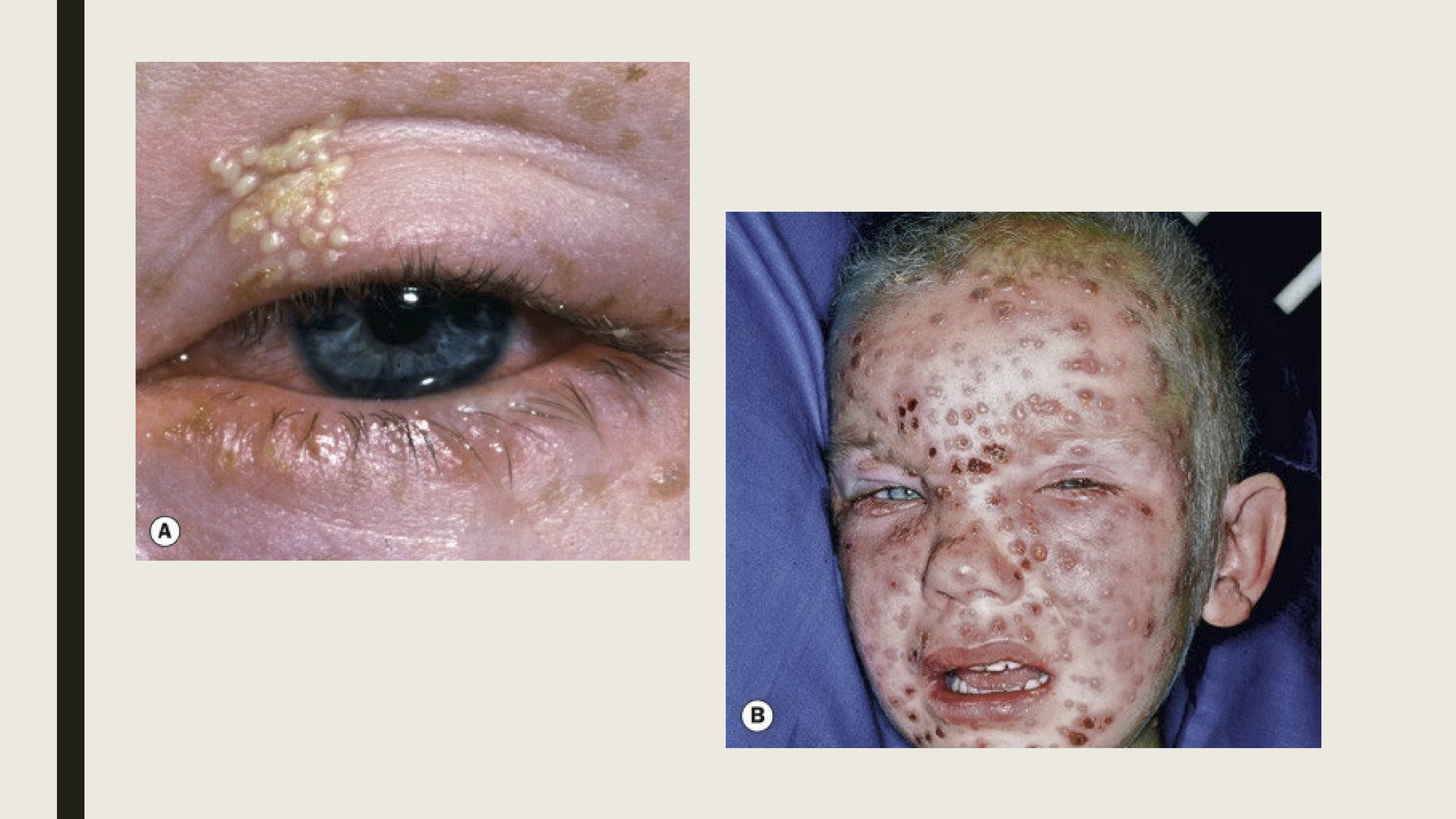
What are the presentations of Herpes Simplex in the eye?
Usually occurs in childhood
facial and lid tingling (last ~24 hours)
Eyelid or periorbital vesicles on the lid margin
Lid swelling
Follicular conjunctivitis, corneal dendrites
How is Herpes Simplex Virus 1 transmitted?
Via droplet transmission
What are the treatments for herpes simplex?
Oral medications or topical cream
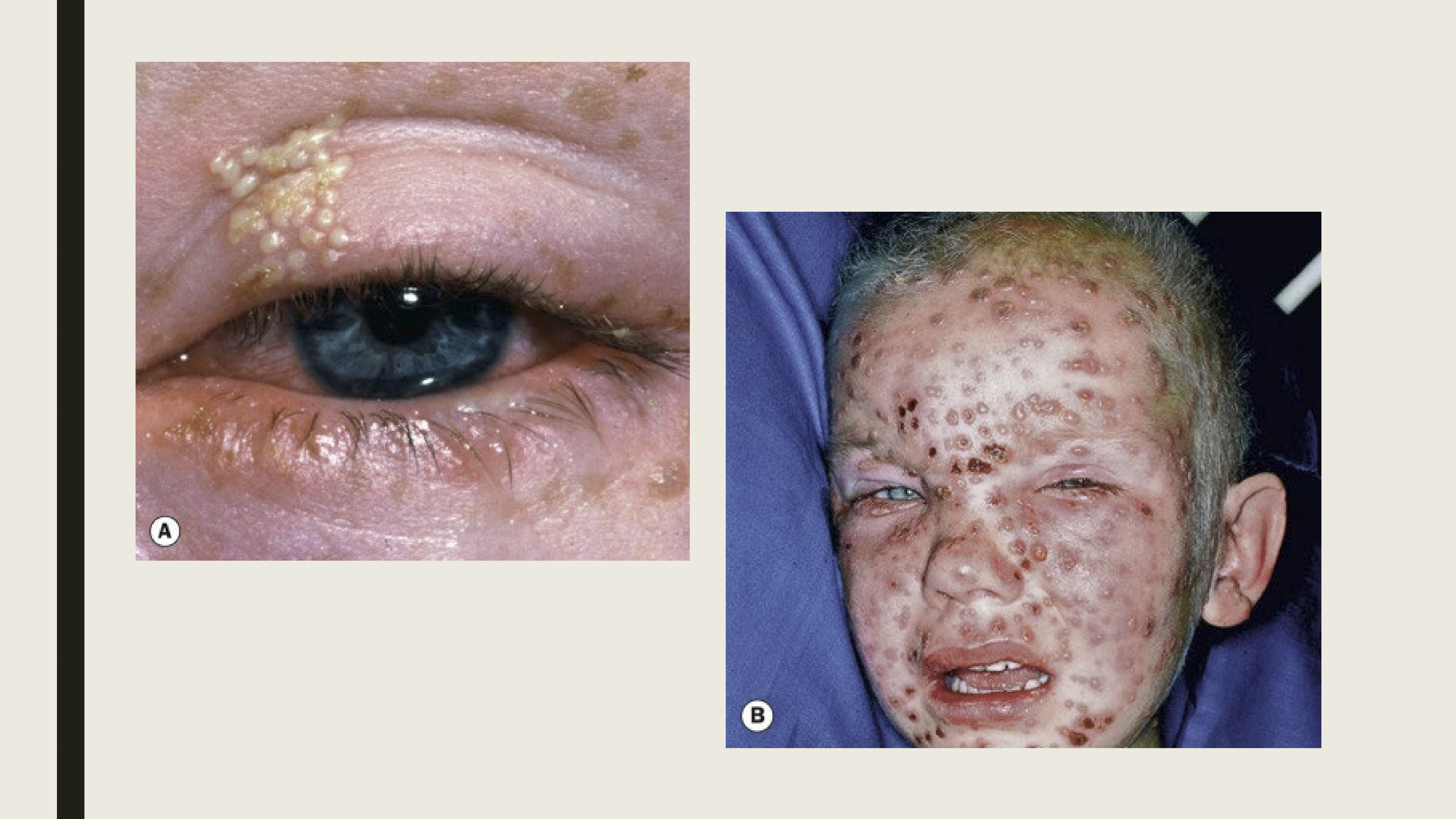
When is Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO) seen in patients?
It is commonly seen in elderly individuals and immunocompromised
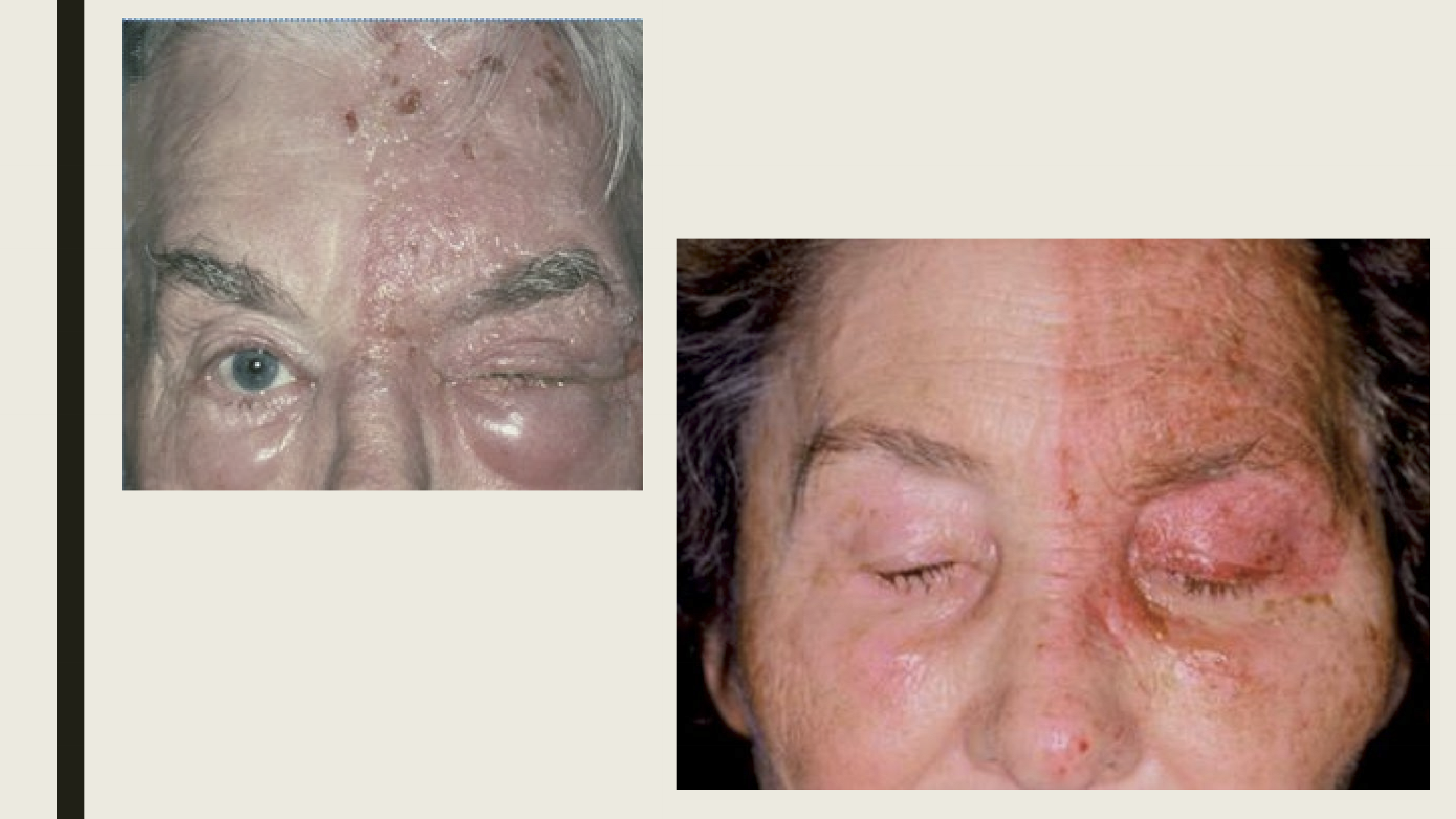
What percentage of Herpes zoster infections occur in the trigeminal nerve (V1)?
20%
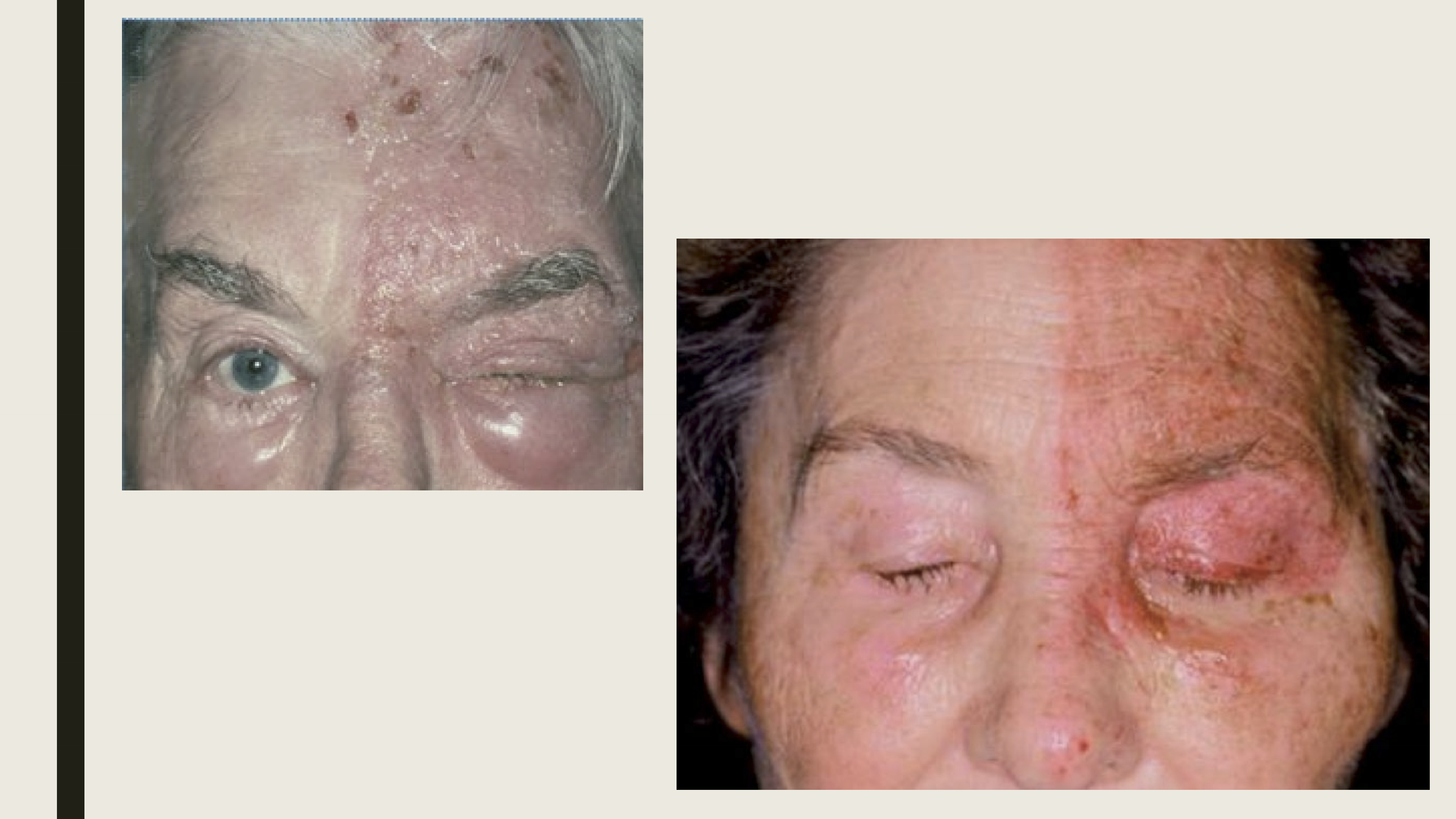
What are the presentations of HZI?
Pain along the first division of the trigeminal nerve
Maculopapular rash on forehead
Vesicles and pustules
Eyelid edema
Tends to be unilateral
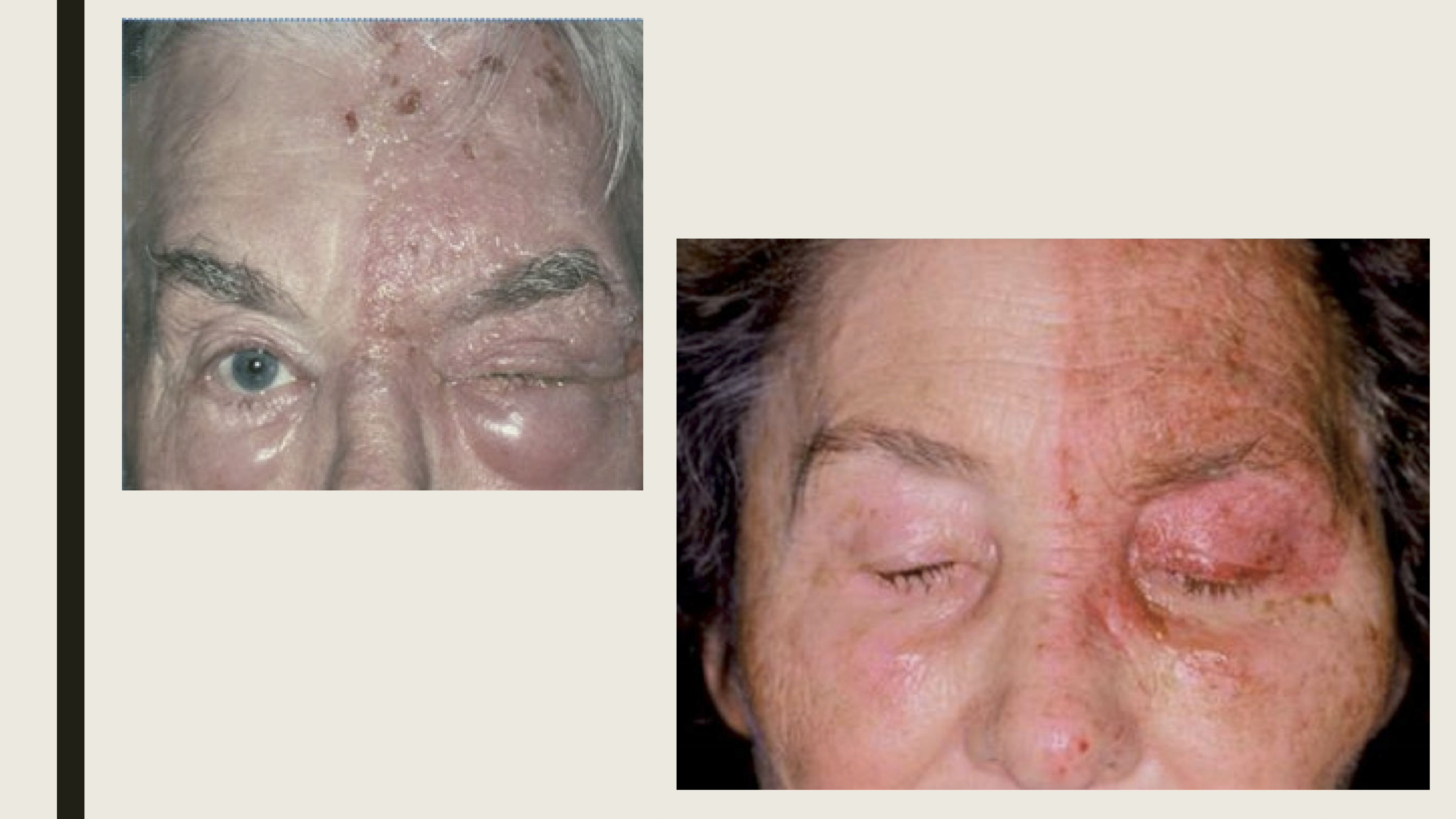
What are the treatments for HZO?
Oral antivirals or topical antiviral cream
Topical antibiotic-steriod cream to prevent skin infections
What is Shingrix?
2 shot vaccine separated by 2-6 months. It is recommended for immunocompetent adults over 50 yrs old and reduces the risk for developing HZ by 97% for 50-69 yrs old. 91% for adults older than 70 yrs old.
What is Zostavax?
A single dose shot vaccine recommended for adults over 60 yrs old.
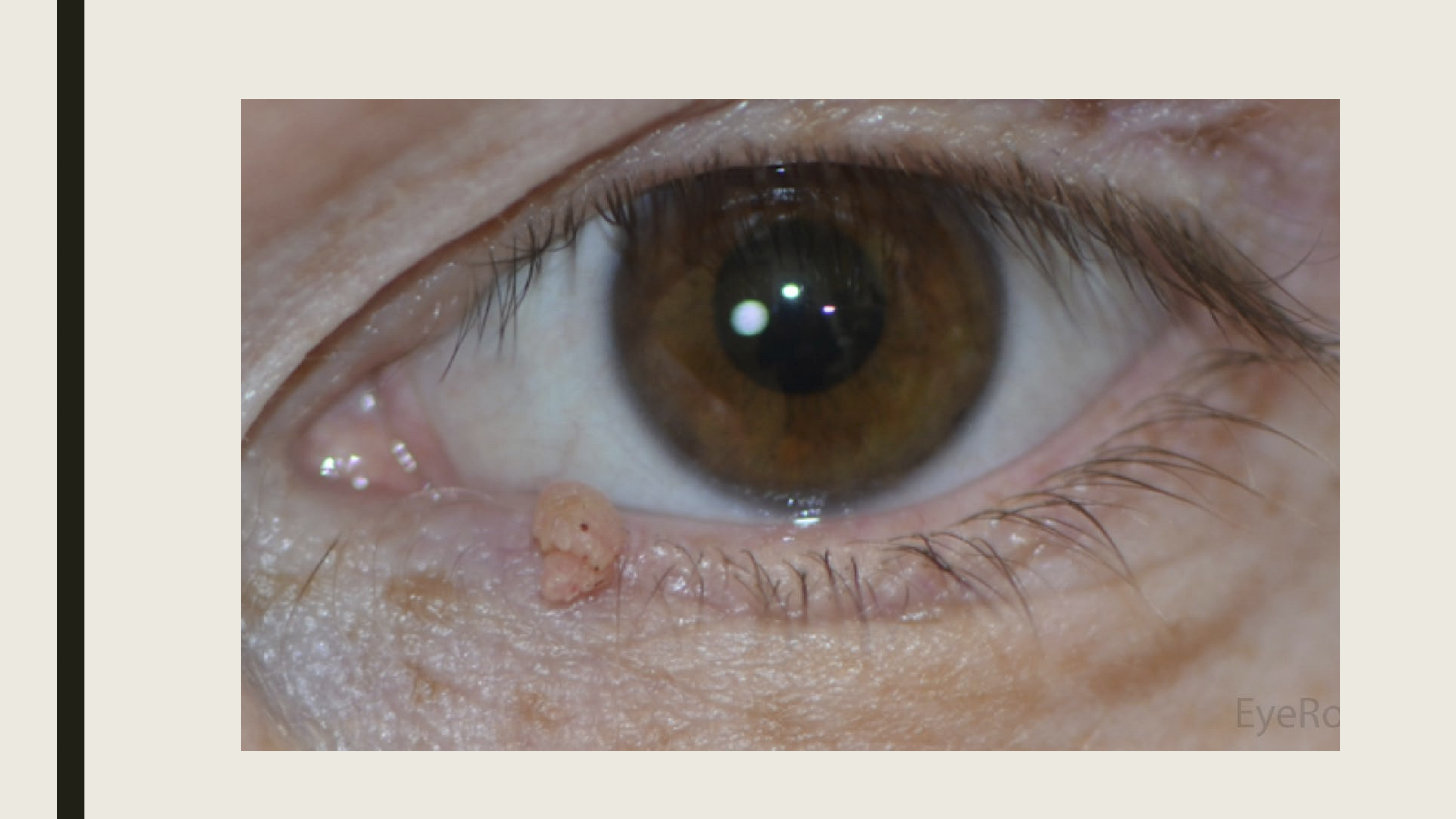
What are the presentations of Verruca Vulgaris (viral wart)?
Small non-pigmented papule
Finger like projections from papule
Located near lid margin
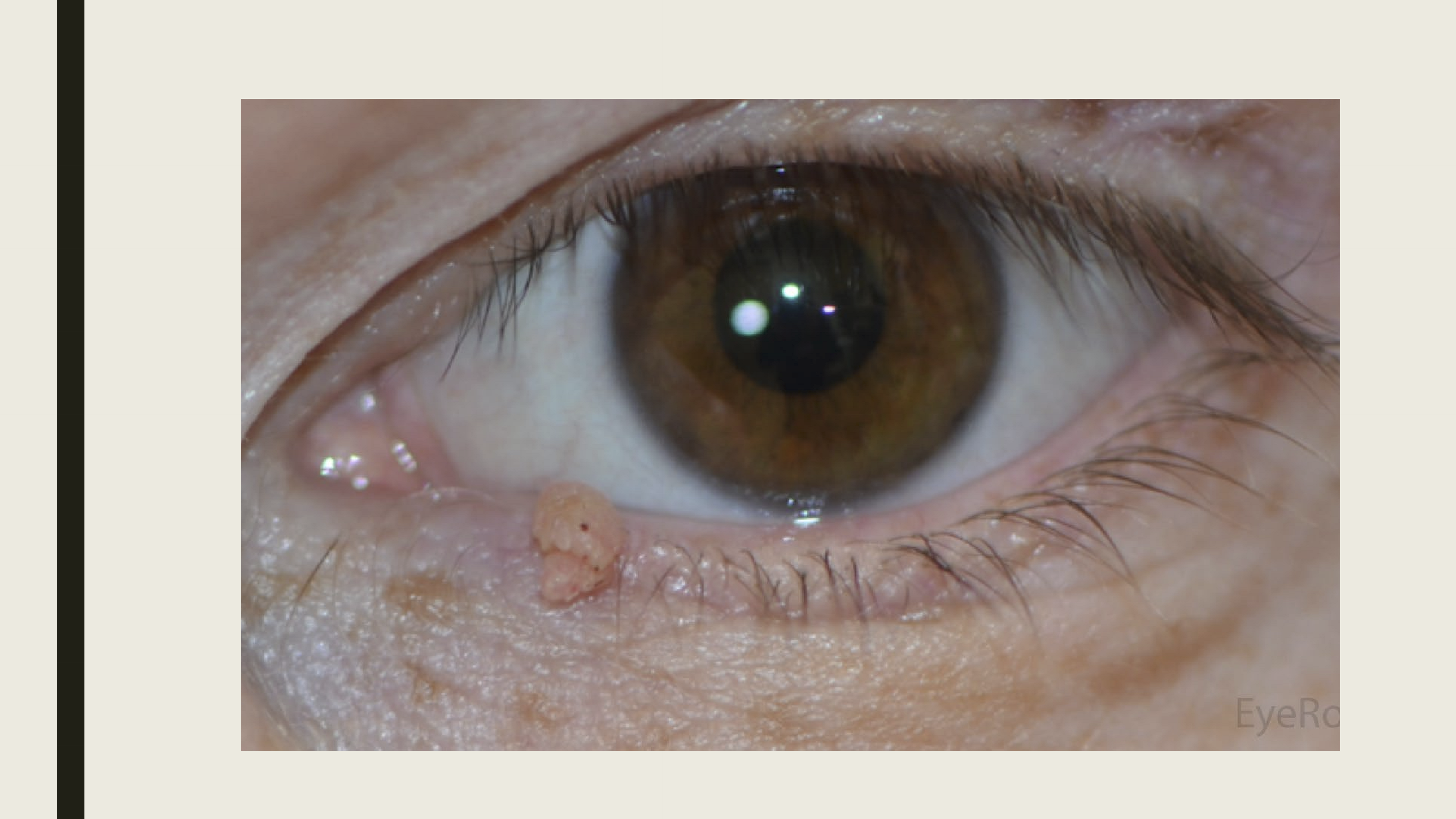
What is the treatment for Verruca Vulgaris?
Excision, oral antivirals will not work.
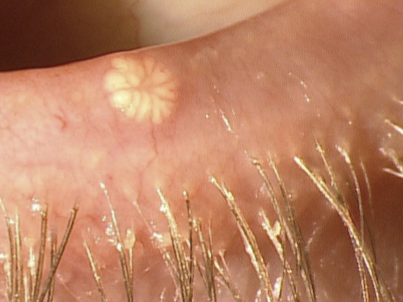
What are the presentations of Molluscum contagiosum?
Pale, waxy, umbilicated nodules
May be single or multiple lesions
Located on the lid margin
White discharge may be expressed from the lesion (contains infected degenerate cells)
Chronic Red Eye
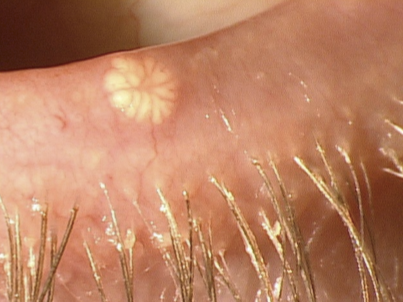
What are the treatments for Molluscum contagiosum?
May spontaneously resolve in 6-12 months
Excision, cryotherapy, laser if spontaneous resolution does not occur
Only give antiviral if corneal involvement
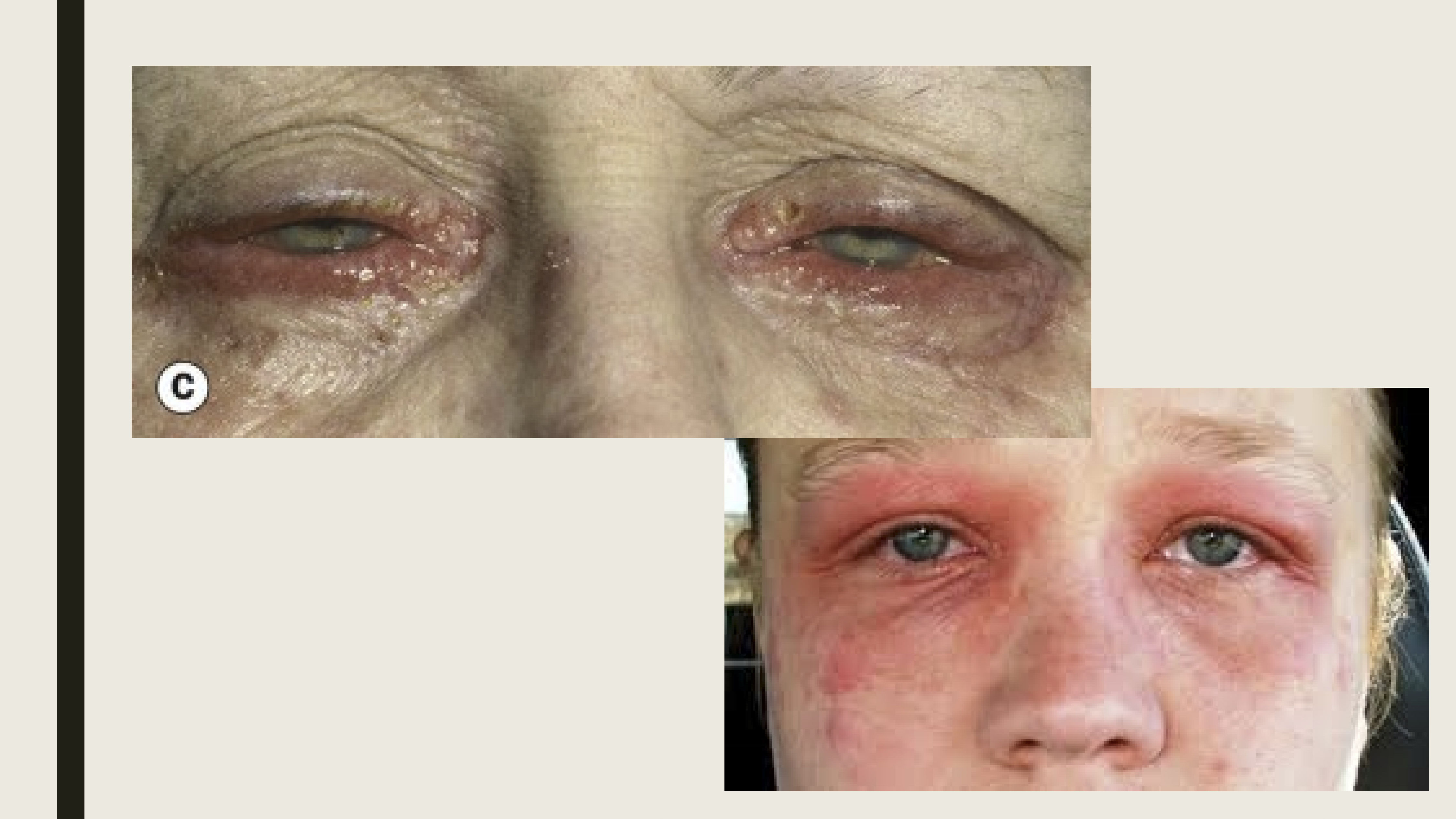
What is anterior blepharitis?
Inflammation of the eyelid margins, specifically meibomain glands.
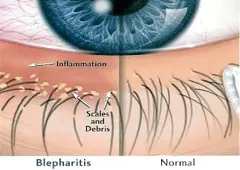
What types of anterior blepharitis are there?
Staphylococcus aureus (infectious)
Seborrheic (non-infectious)
What are the symptoms and presentation of Ant Bleph by staphylococcus aureus?
Chronic irritation worse in the morning
Burning, grittiness, photophobia and crusting
Scales around the base of the eyelashes (collarettes)
Hyperemic eyelid margin (takes years)
If chronic, scarring and hypertrophy of the eyelid margin
madarosis, trichiasis, poliosis
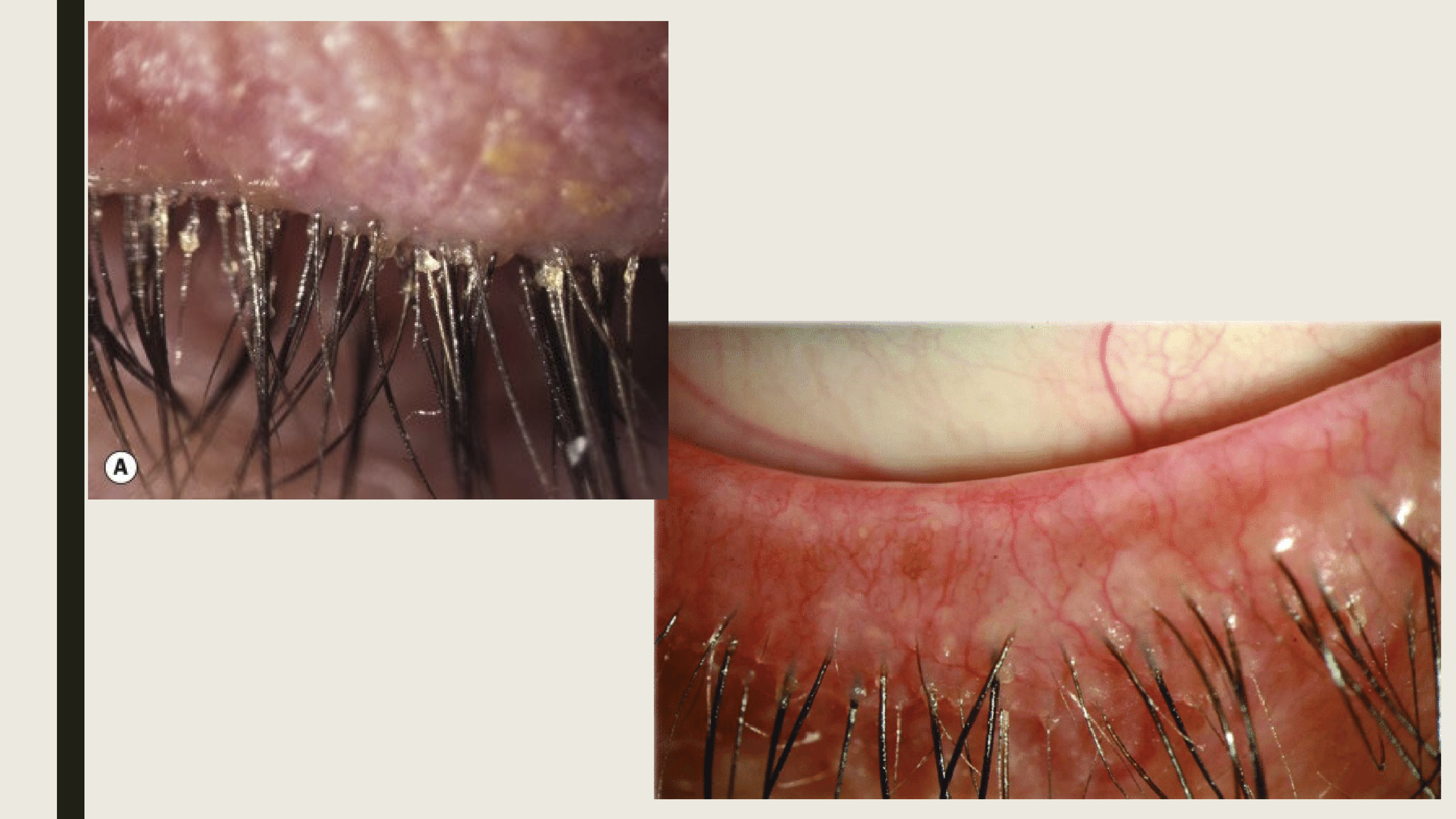
What are the complications of Ant Bleph by staphylococcus aureus?
Tear film instability
External hordeolum formation
PEE, vascularization, and infiltrate
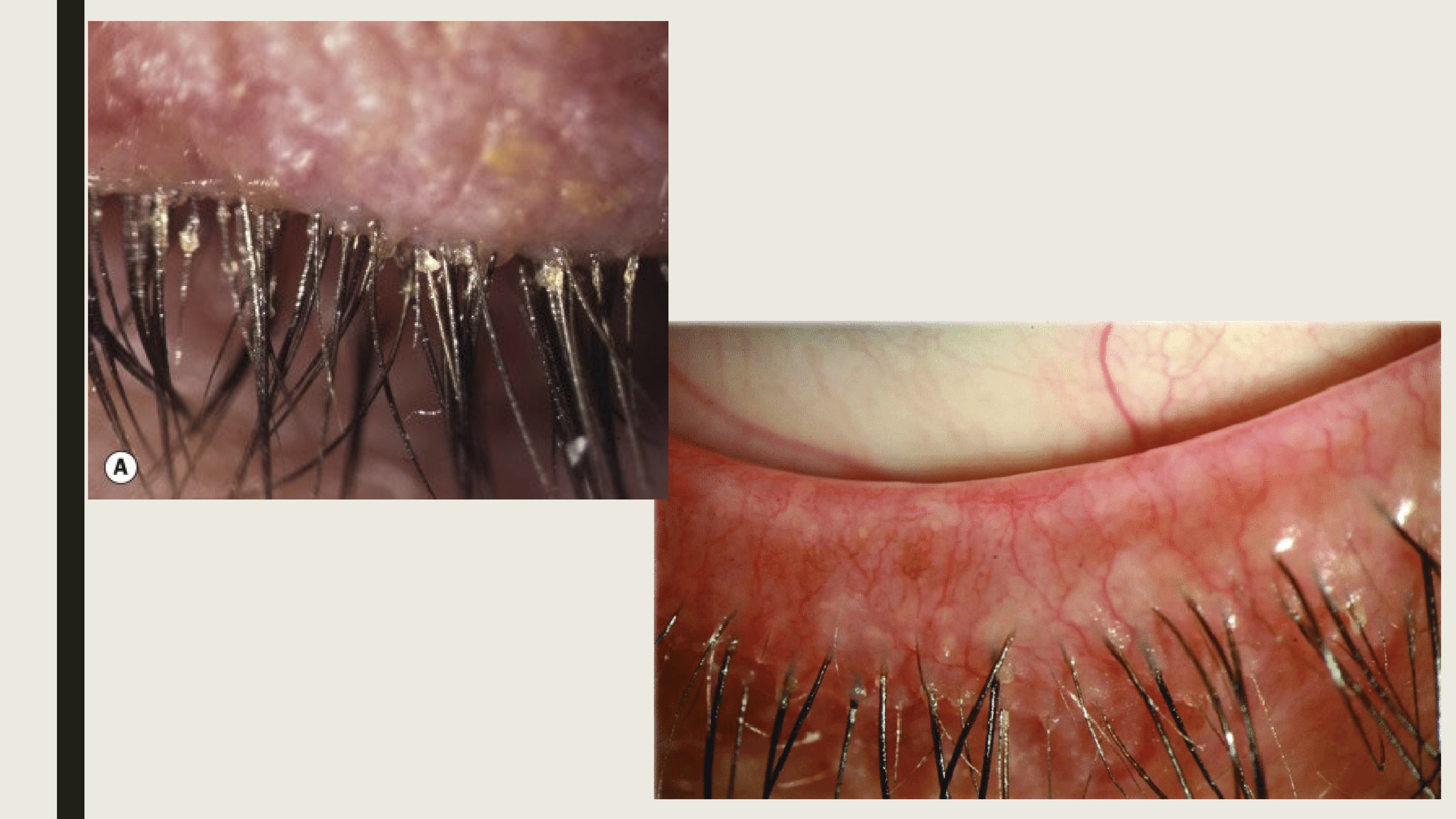
What are the treatments for Ant Bleph by staphylococcus aureus?
Lid hygiene
Topical antibiotic ointment
Topical antibiotic/steroid ointment
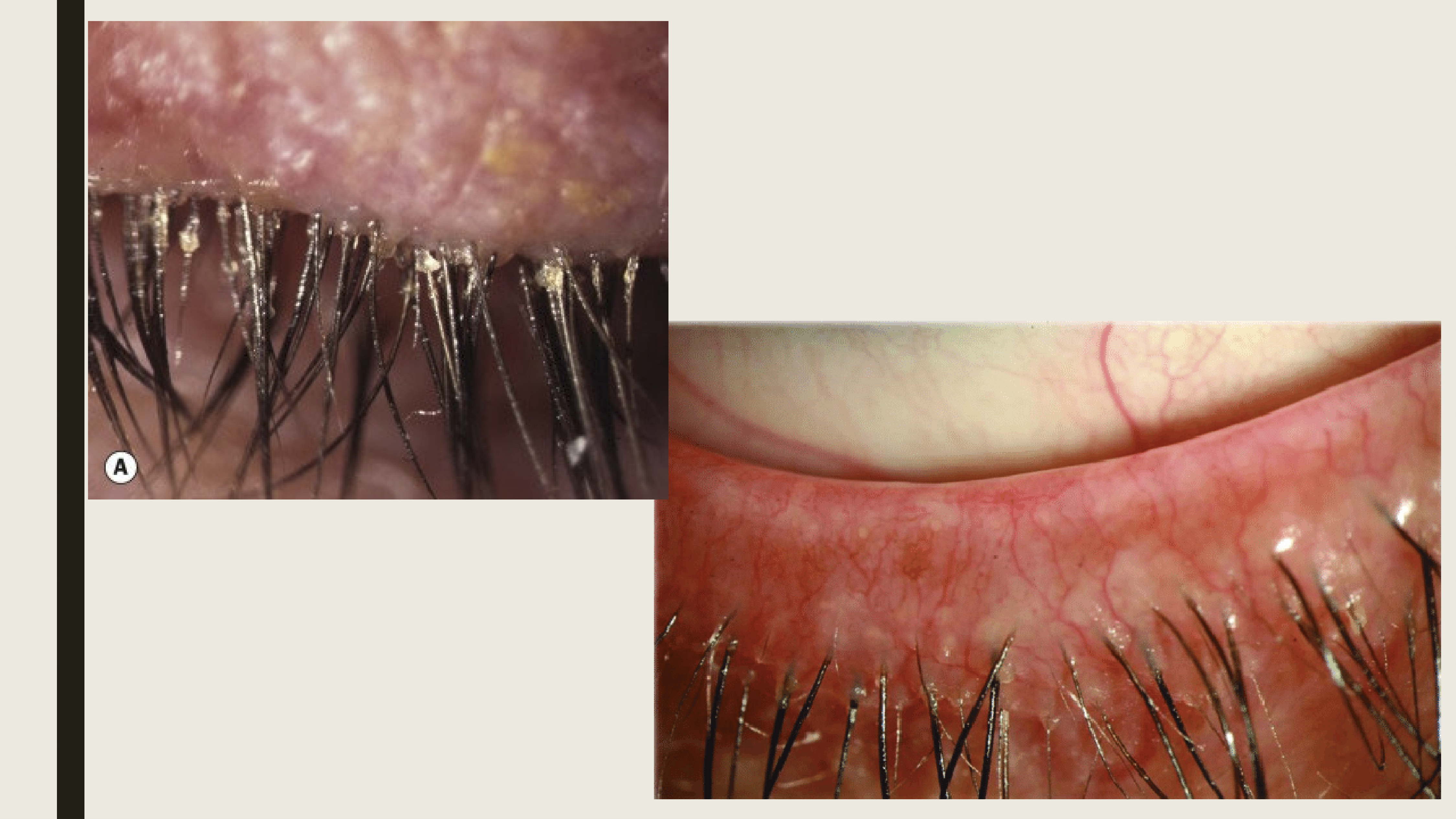
What are the symptoms and presentations of seborrheic blepharitis?
Hyperemic, greasy eyelid margin
scaling of the lid margin and lashes
Eyelashes are stuck together
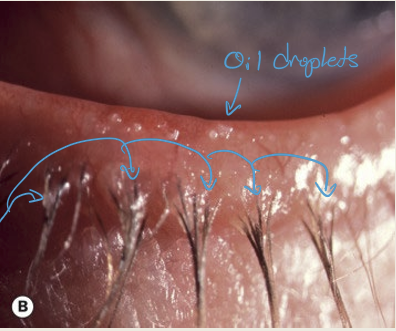
What are the complications of seborrheic blepharitis?
Dry Eye & PEE, vascularization, infiltrates
What causes seborrheic blepharitis?
Malfunctioning glands of Zeis causing an overproduction of oil
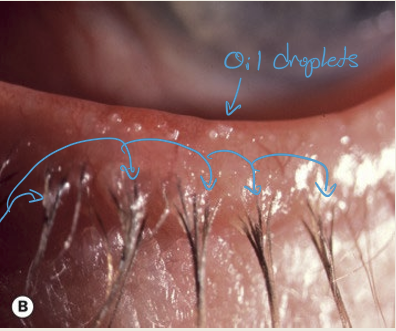
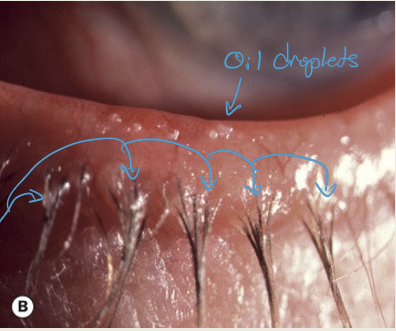
What are the treatments for seborrheic blepharitis?
Lid hygiene
What is angular blepharitis?
An infection of the canthus by Staphylococcus aureus or Moraxella lacunata
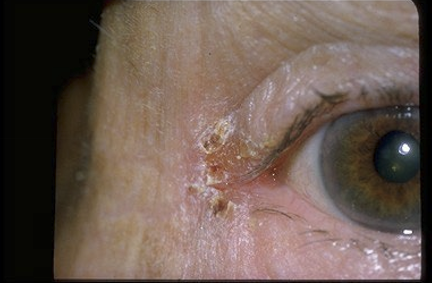
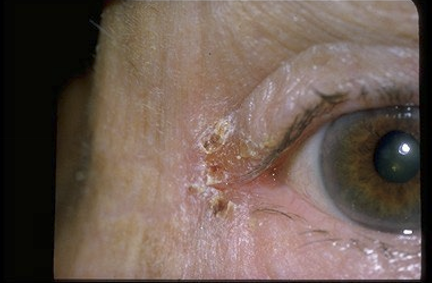
What are the presentations of angular blepharitis?
Scaling and hyperemia of the lateral or medial canthus
Unilateral
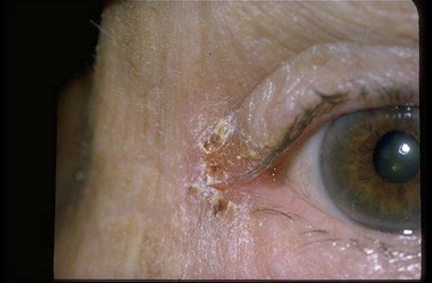
What are the treatments of angular blepharitis?
Lid hygiene
Topical antibiotic ointment for 7 days
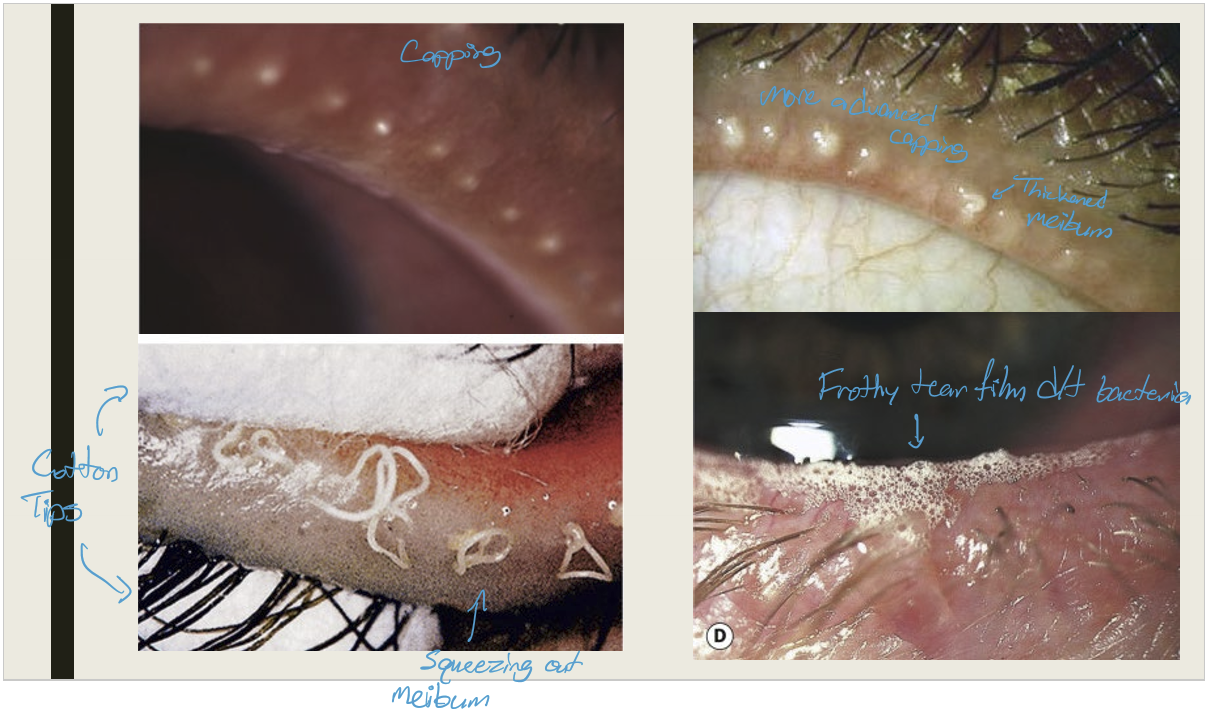
What is posterior blepharitis/ meibomianitis?
Inflammation of the meibomian glands and the lid margin posterior to the meibomian glands
What causes posterior blepharitis?
Altered meibomain gland secretions
increased melting point of meibum
expression from meibomian glands is reduced
increased Staphylococcus aureus growth
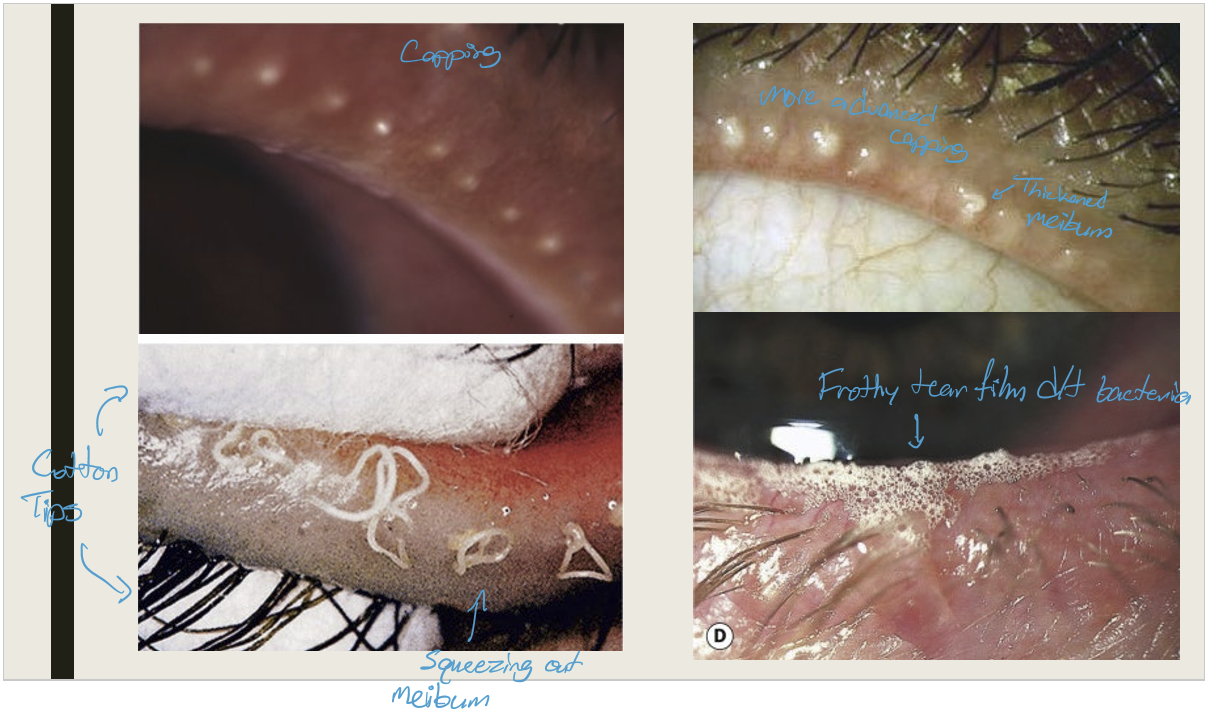
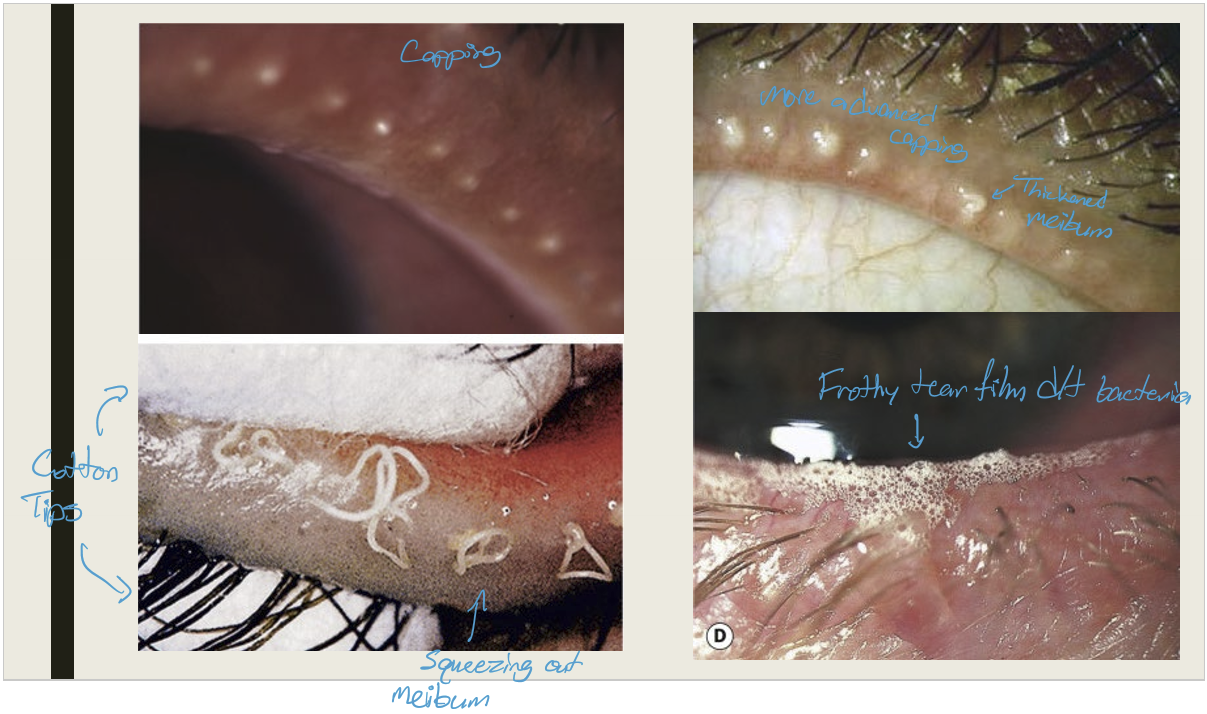
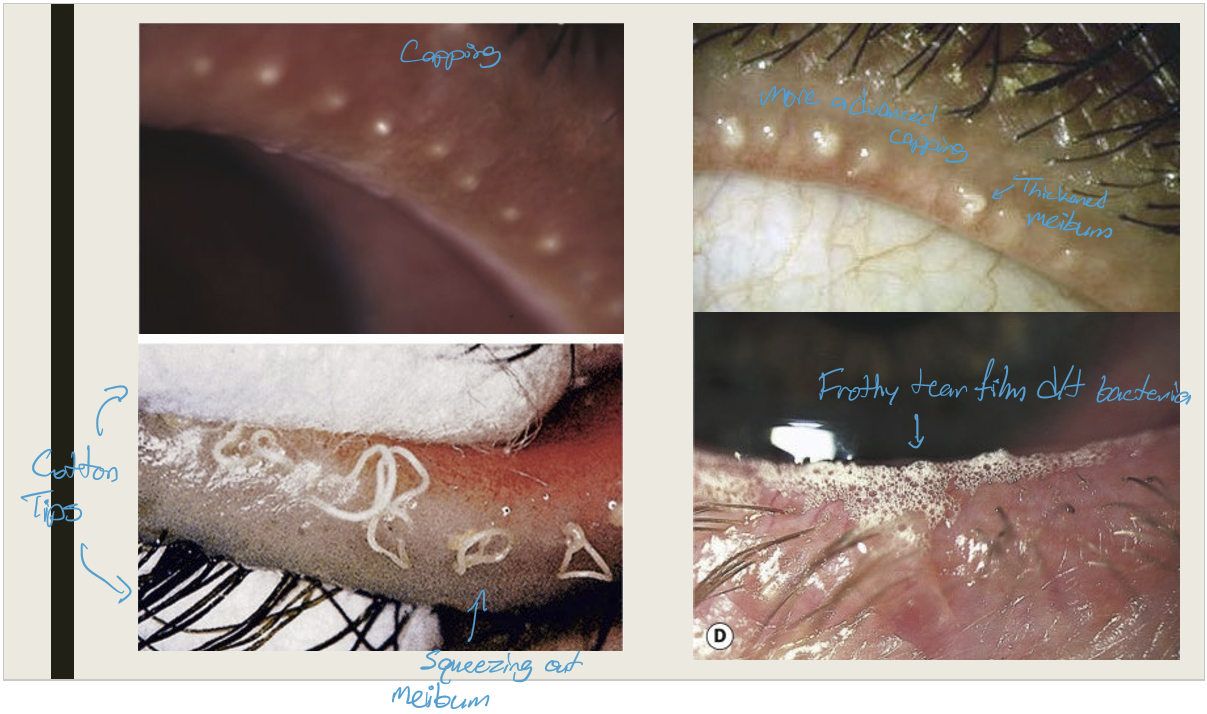
What are the symptoms and presentations of posterior blepharitis?
Symptoms:
Chronic irritation worse in AM;
Burning, grittiness, photophobia, & crusting
Presentation:
Capping of meibomian glands;
thickened meibum w/ meibomian gland expression;
lid hyperemia and telangiectasia;
Permanent gland loss
frothy or oily tear film
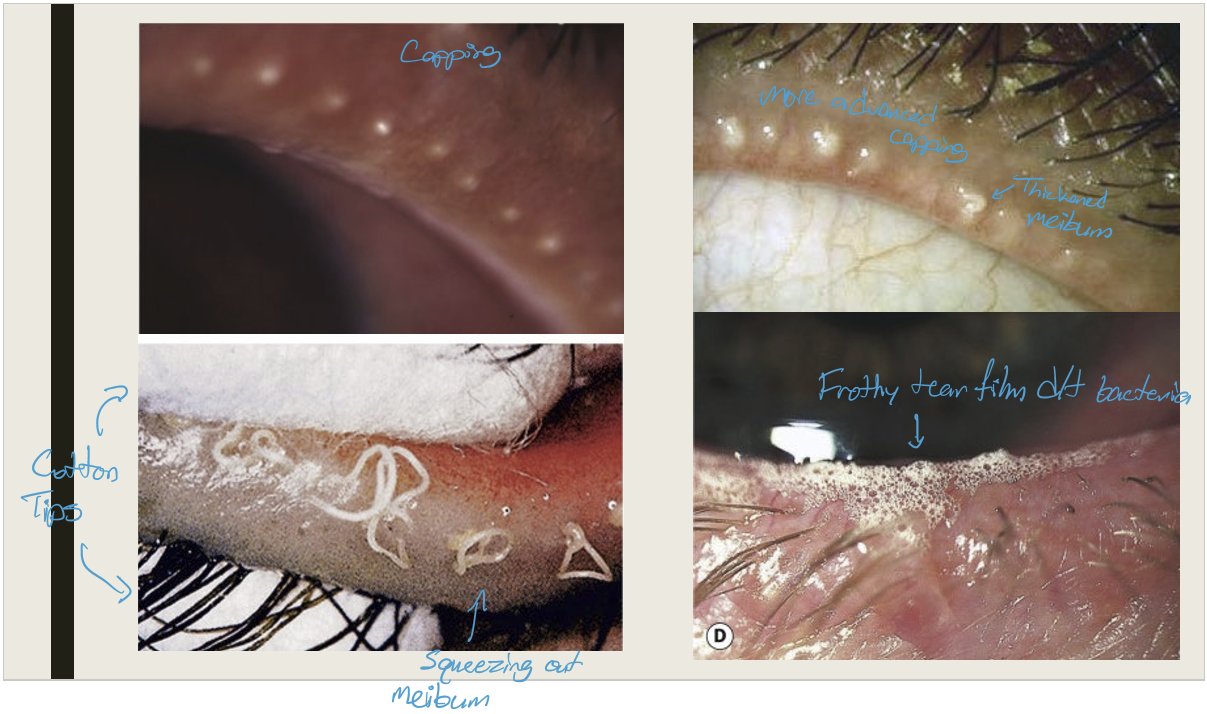
What are the complications of posterior blepharitis?
Dry eye
Notching of the lid margin
Foaming of the tears
PEE, neovascularization and infiltrates
What are the treatments for posterior blepharitis?
Lid hygiene
wam compresses with digital massage
Oral tetracyclines
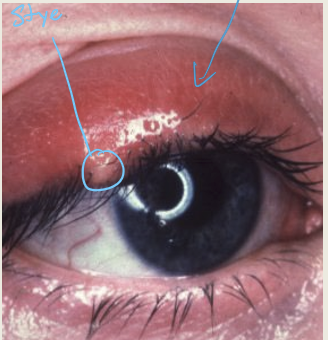
What is an external hordeolum/style?
An acute staphylococcal infection of the eyelash and gland of Zeis
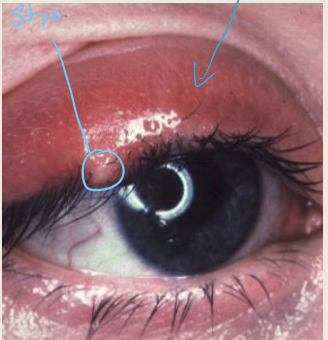
What are the presentations of external hordeolum?
Pustule at the eyelash or gland of Zeis. Can have localized or general lid edema.
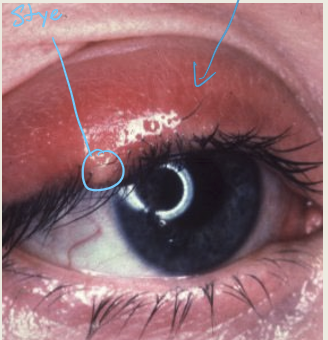
What are the treatments for an external hordeolum?
Topical antibiotics
Hot compresses to allow area to open and drain
Eyelash epilation
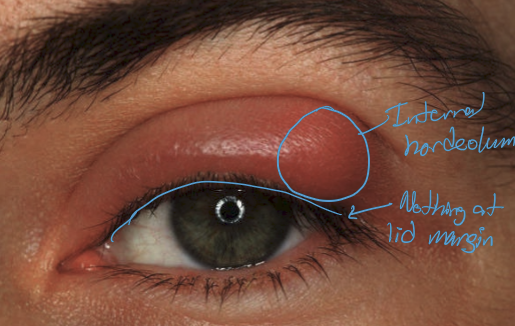
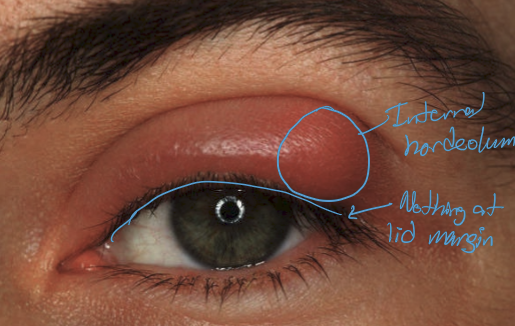
What is an internal hordeolum?
Infection of the meibomian gland, typically caused by staphylococcal infection
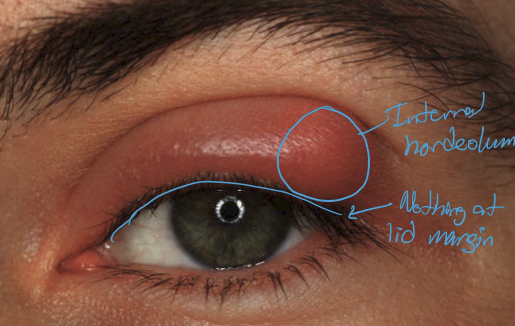
What are the presentations of an internal hordeolum?
Inflamed meibomain gland
Tenderness over inflamed meibomian gland
calor
overlying hyperemia
What is commonly assocaited with internal hordeolum?
Blepharitis and acne rosacea
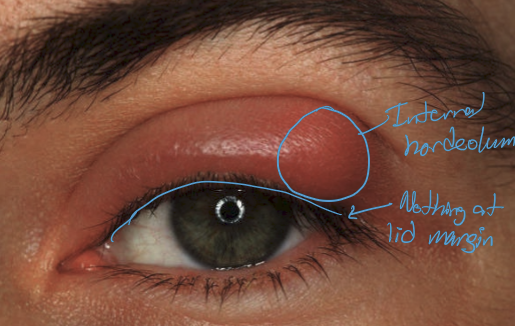
What are the treatments for internal hordeolum?
May spontaneous resolve
Lid hygiene: warm compress and lid scrubs
Oral antibiotics
What is preseptal cellulitis?
Infection of the subcutaneous tissue anterior to the orbital septum
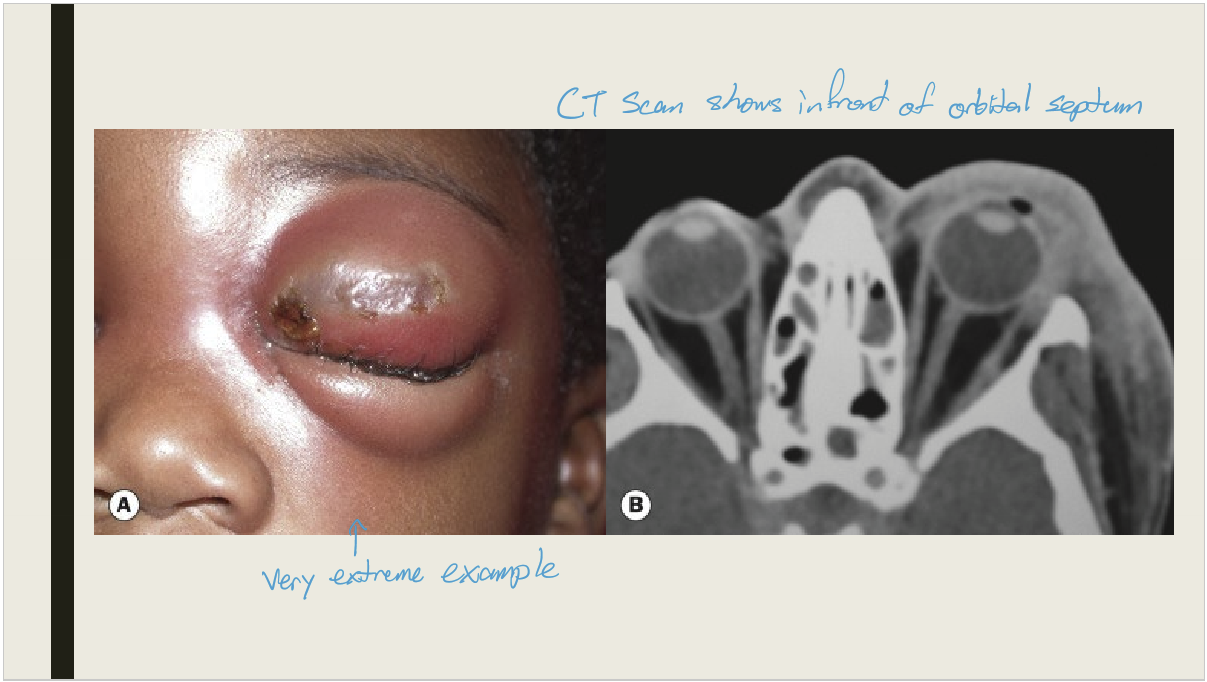
What are complications from internal hordeolum?
Preseptal cellulitis, an infection of the subcutaneous tissue anterior to the orbial septum
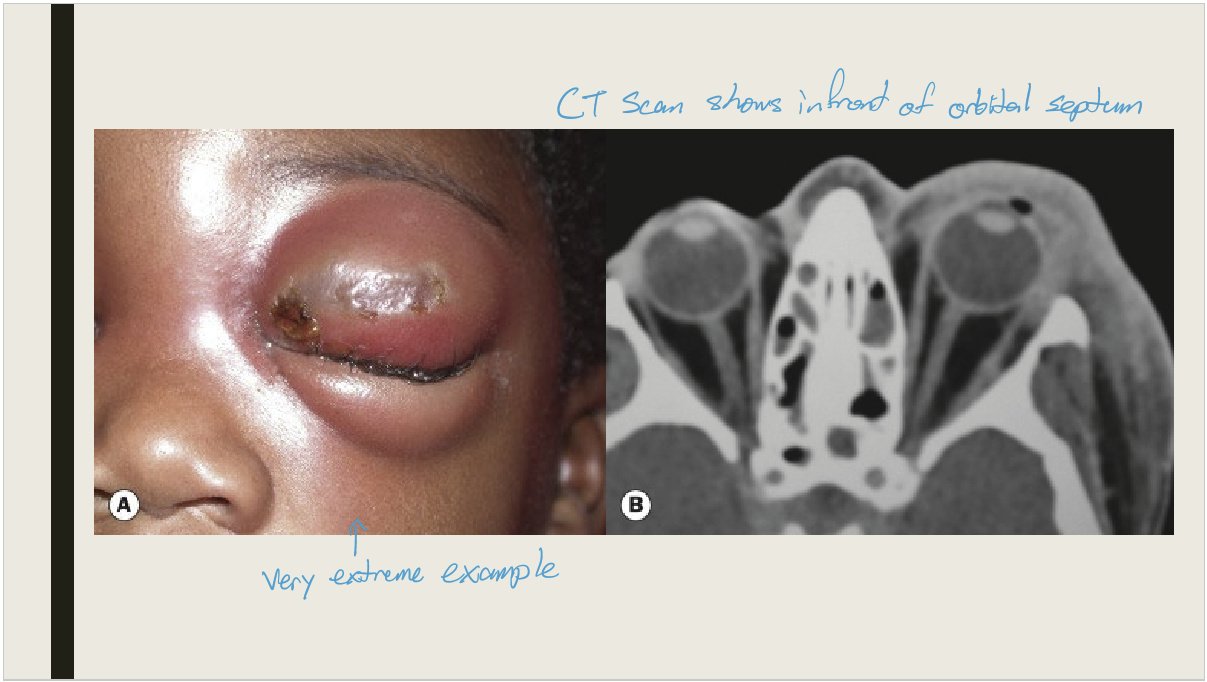
What causes preseptal cellulitis?
Spread of local infection
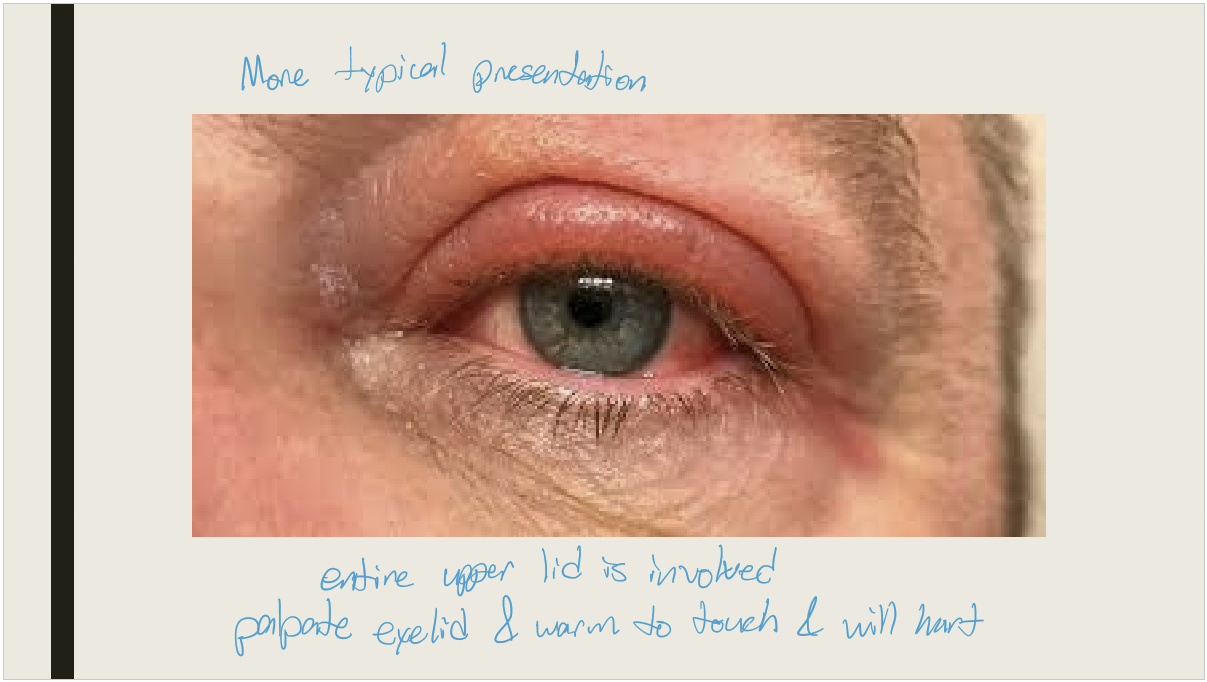
What are the presentations preseptal cellulitis?
Hyperemic lid with periorbital edema that is tender and warm to the touch (calor)
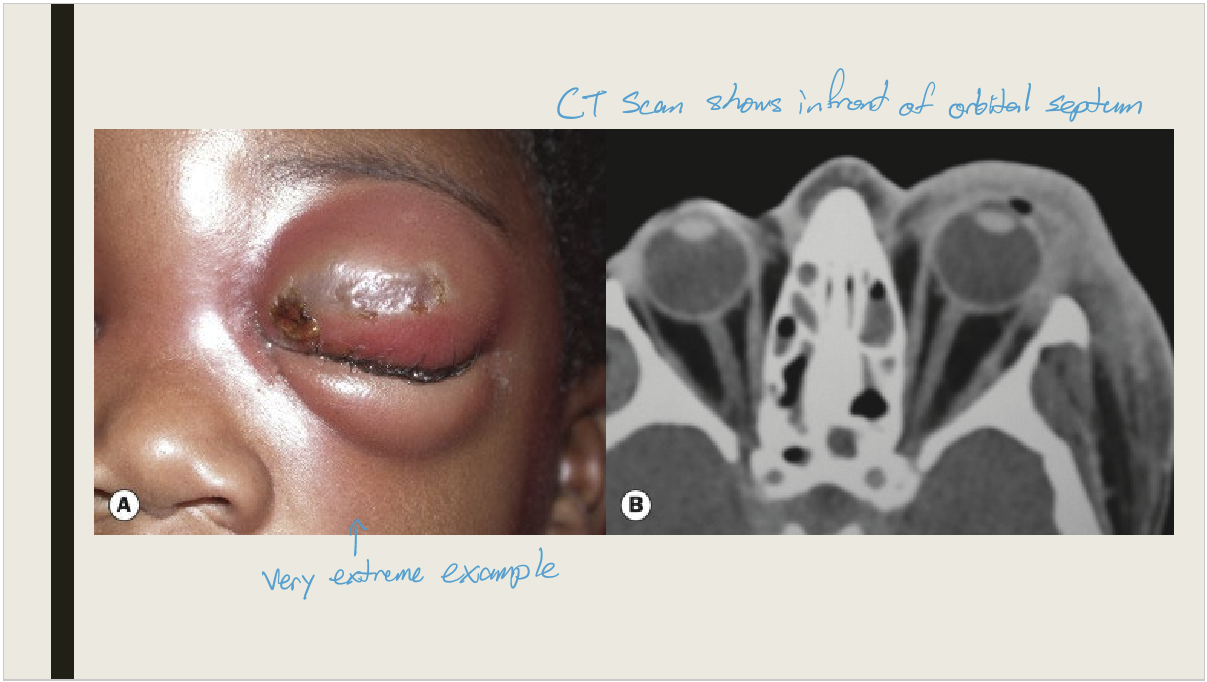
What is orbital cellulitis?
Infection of soft tissue behind the orbital septum
What causes orbital cellulitis?
Extension of preseptal cellulitis
Sinus related (commonly ethmoidal)
Local spread (Dacryocystitis, mid-facial, or dental infection)
Post-trauma (onset 72 hours after injury)
Post-surgical complication
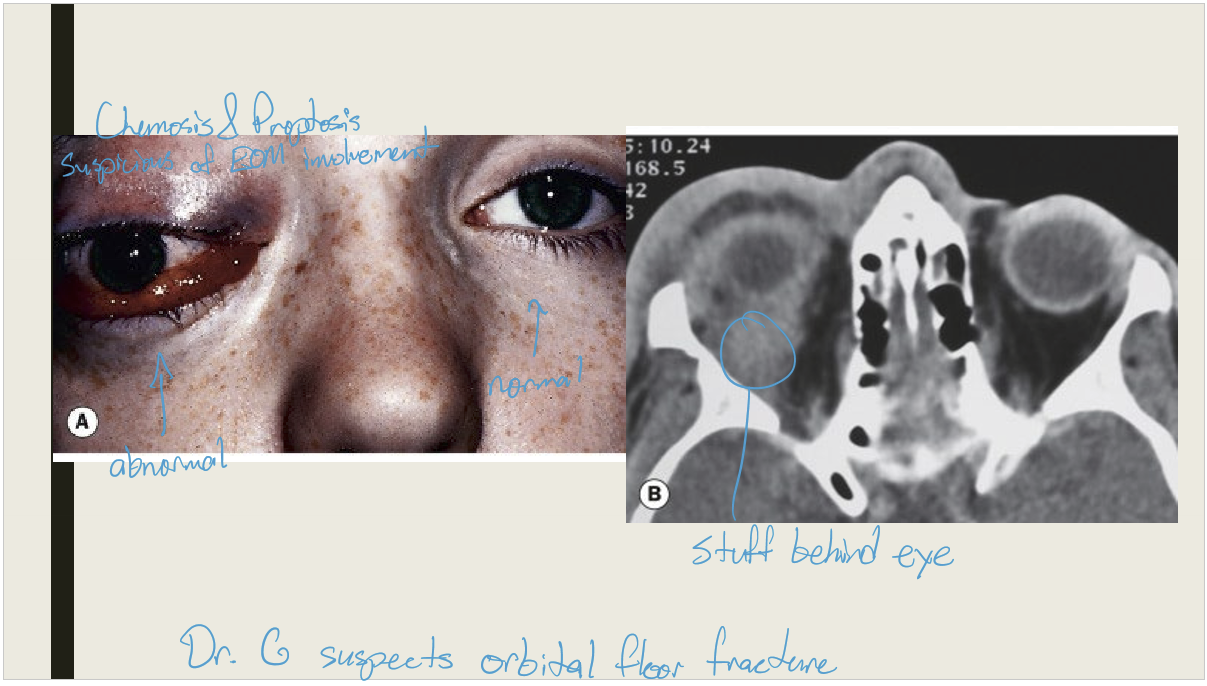
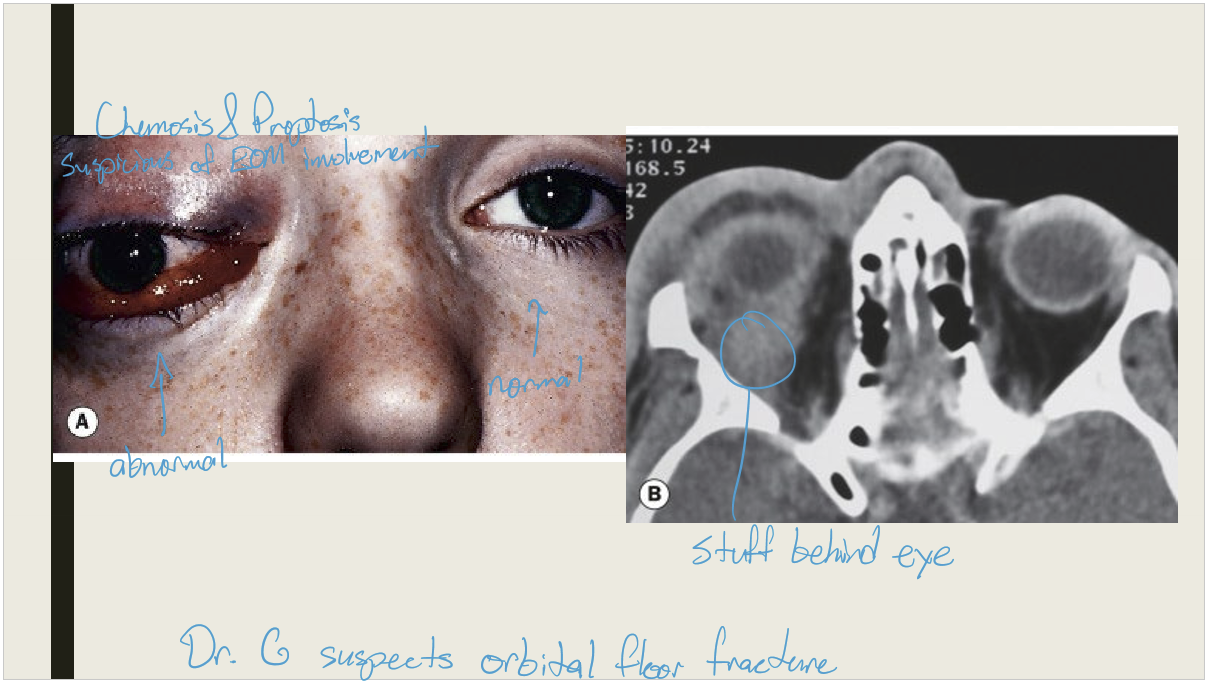
What are the presentations of orbital cellulitis?
Unilateral periorbital edema that is tender and calor
Proptosis
Pain on eyemovement
Restriction on eye movement
Optic nerve abnormalities (pupil abnormalities, dyschromatopsia)
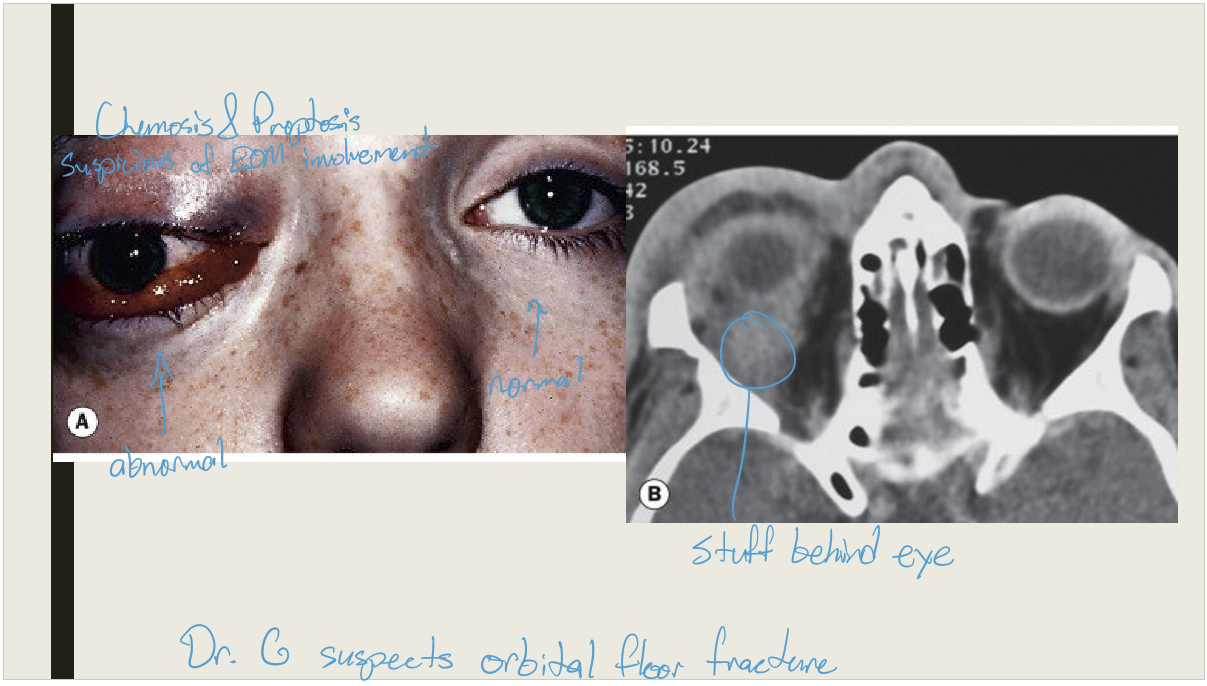
What are the treatments for orbital cellulitis?
Hospital admission with consult of infectious disease specialist. Broad spectrum IV antibiots for several days. Once improvement is seen, switched to oral antibiotics for weeks
What is Phthiriasis palpebrarum?
An infestation of the eyelashes by crab lous Phthirus ubis (lice)
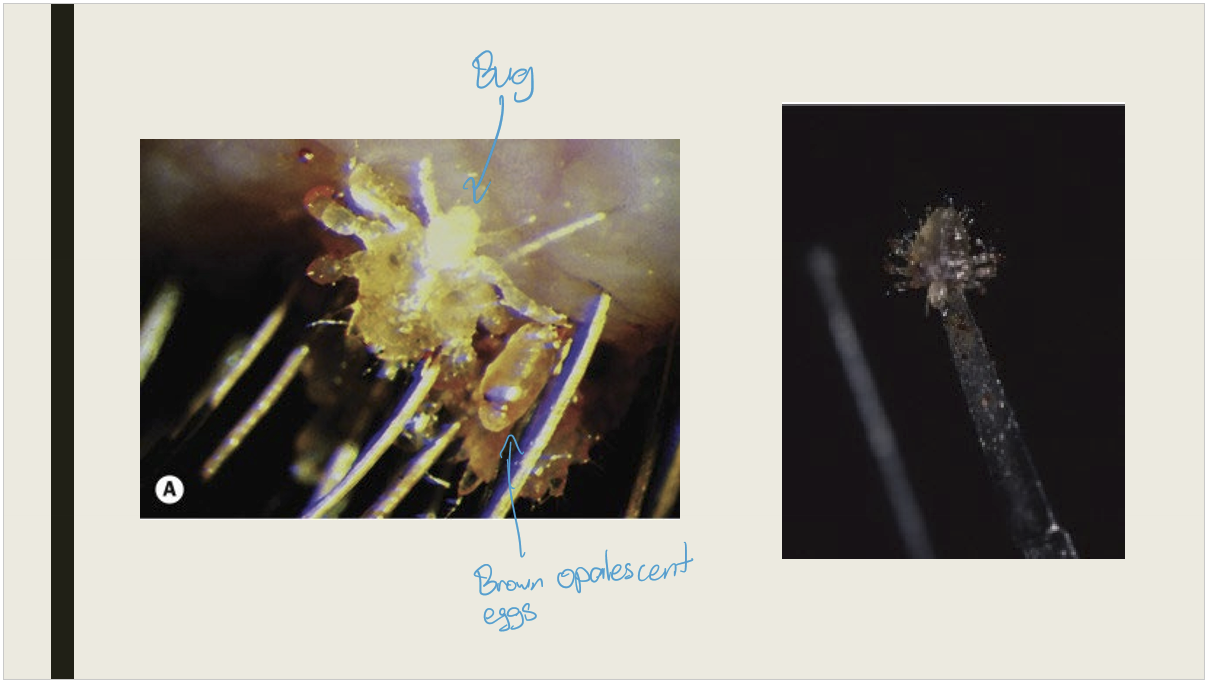

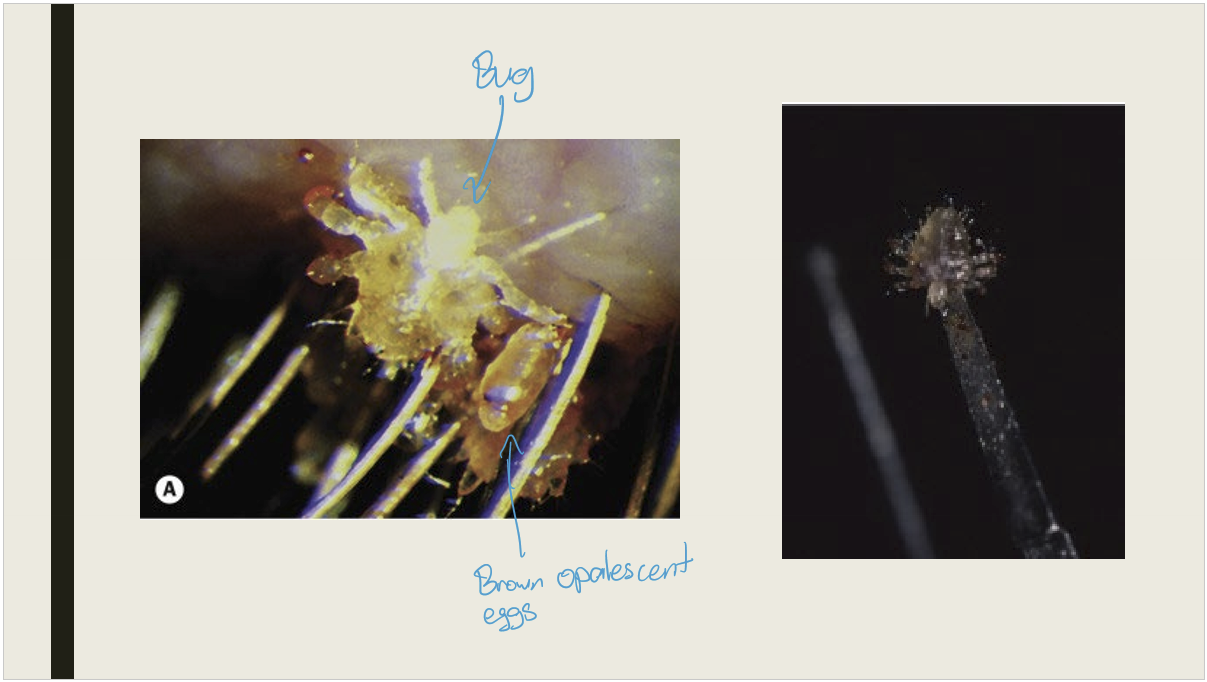
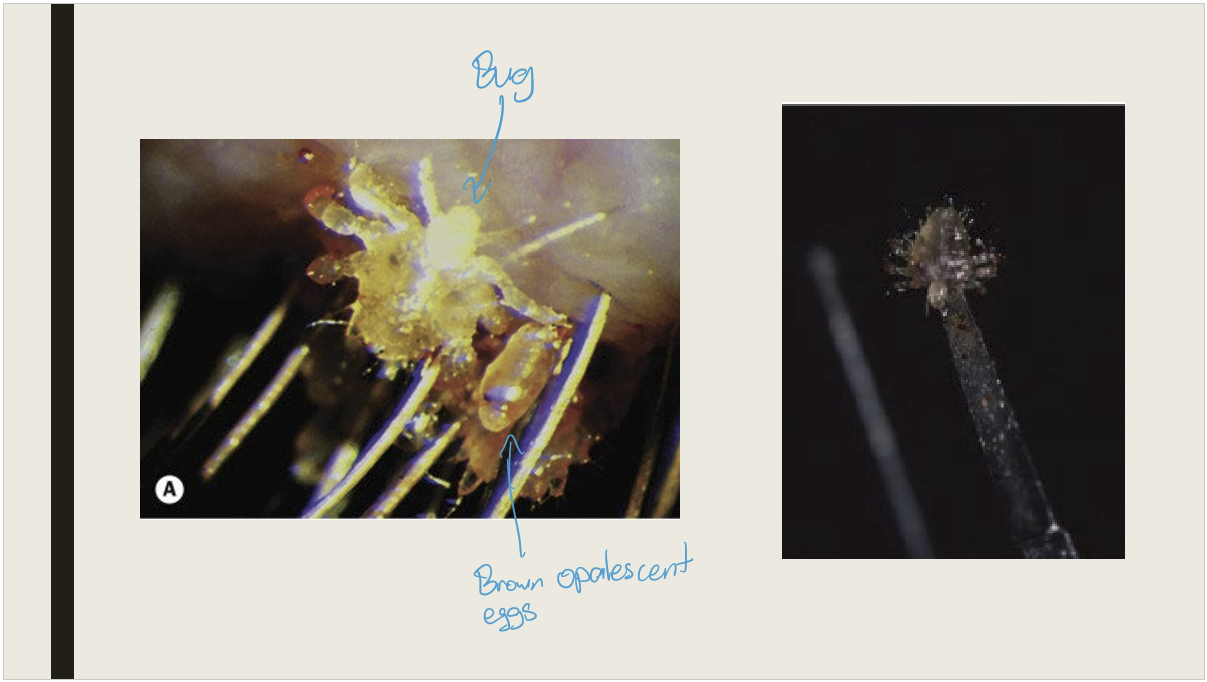
What are the signs/presentations of phthiriasis palpebrarum?
Chronic irritation and itching
Lice anchored to lashes
Small brownish opalescent pearls adhered to the base of lashes
Typically affects children living in poor hygienic conditions

What are the treatments for phthiriasis palpebrarum?
Mechanical removal of lice with jeweler’s forceps
Petroleum jelly/ antibiotic ointment to suffocate remaining bugs and eggs

What is Demodex?
A common parasite that lives on the skin. Tends to be more prevalent in individuals with poor hygiene and rosacea.
What types of Demodex are there?
Demodex folliculorum
Demodex brevis
Where is demodex folliculorum found?
Eyelashes and small hair follicles. Base of lashes serve as food source.
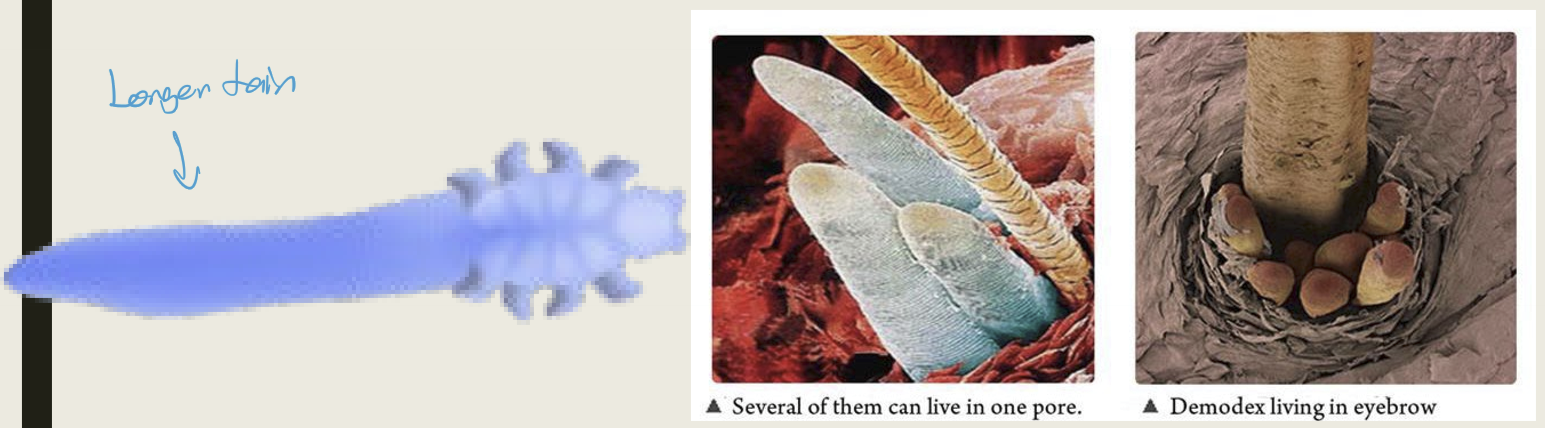
Where is demodex brevis found?
In sebaceous glands including meibomian glands, feeding on the sebum found within the gland.
How is demodex treated?
Tea Tree Oil lid scrubs
Essential oil from the Melaleuca alterniforlia plant
Performed in office and at home with high conc at office to kill mites and lower conc at home to disrupt mating cycle
TP-03/XDEMVY
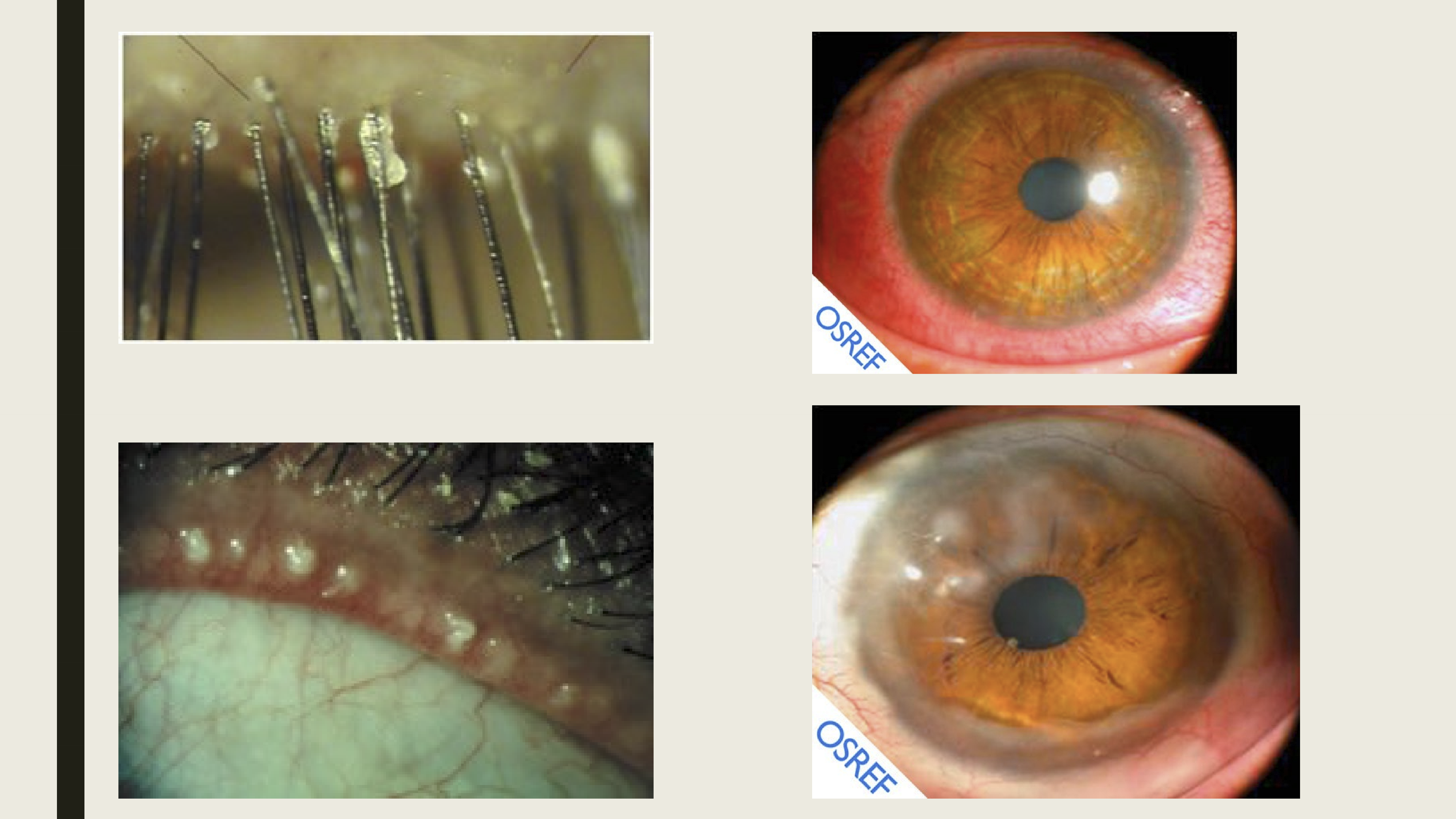
What are the clinical presentations of rosacea?
Red patches in the center of the face, nose and cheek area
Small blood vessels become dilated and visible
On the face, eyuelid, or eye
Swollen red bumps-resemble acne
Enlarged nose
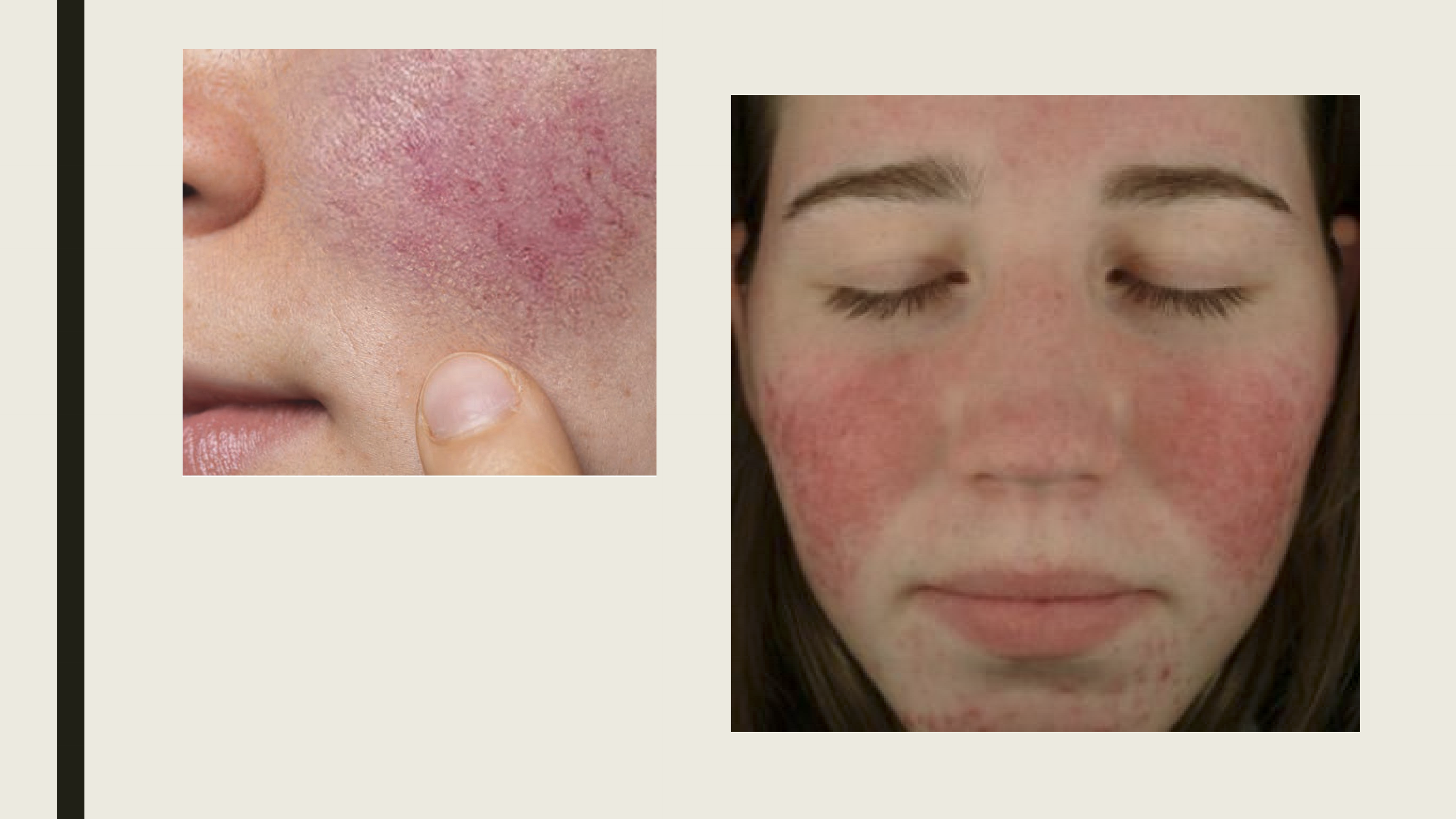
What can cause rosacea?
Sun, spicy food, stress, alcohol, exercise
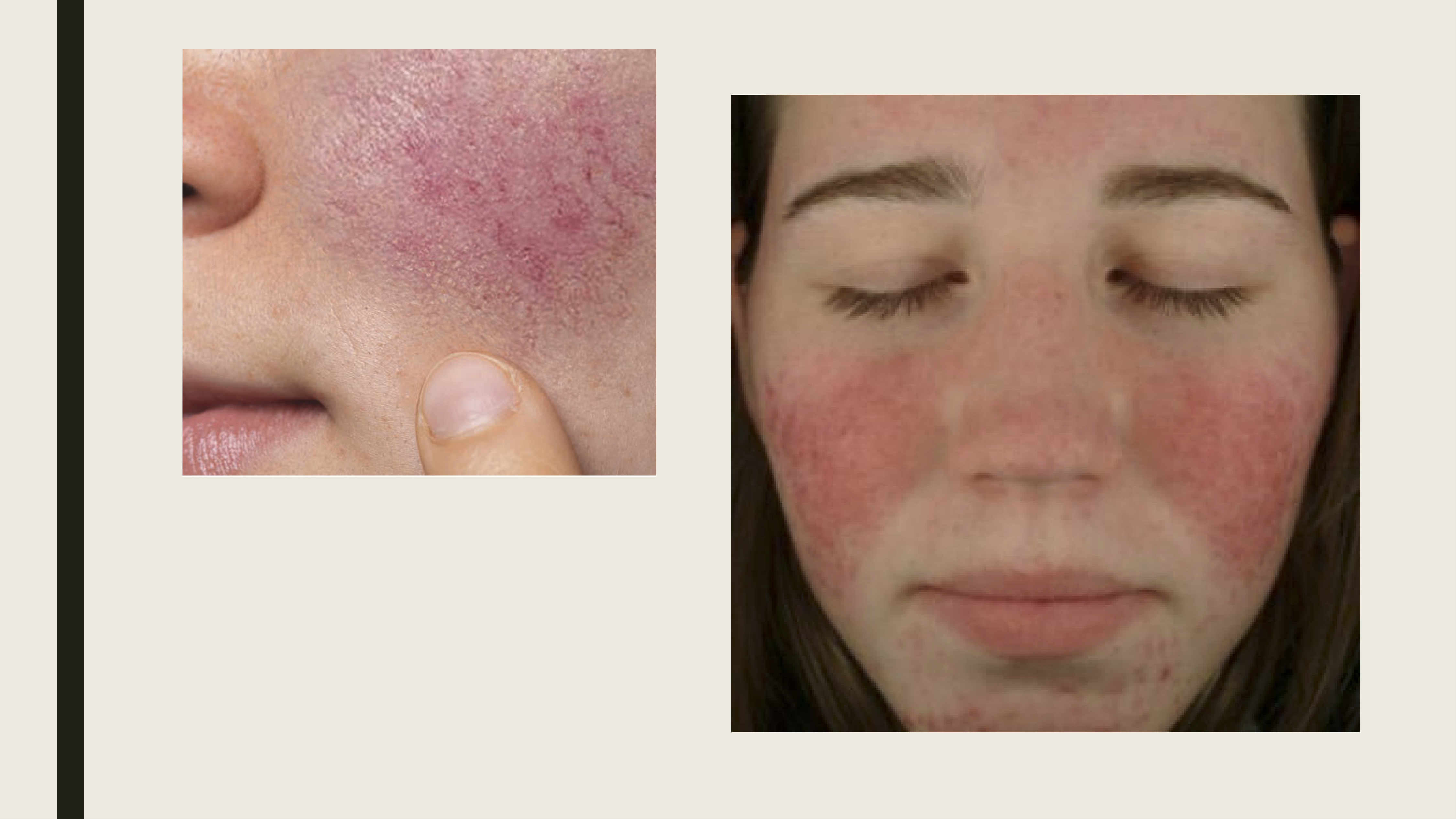
What are the clinical presentations of ocular rosacea?
Symptoms: Foreign body sensation, pain/irritation, burning, photophobia, redness, epiphora, decrease vision
Signs: Blepharitis, meibomianitis, tear film disruption, hordeola, chalazia, conj hyperemia, punctate keratitis, epithelial erosion, corneal vascularization, corneal thinning/ulceration/perforation, uveitis
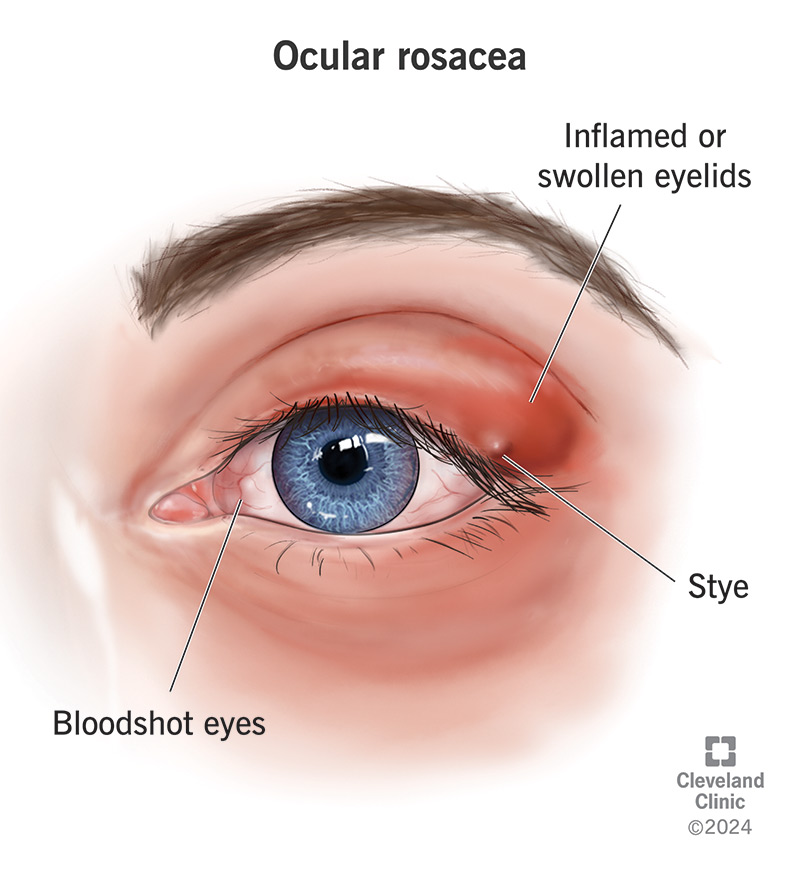
What are the treatments for ocular rosacea?
Lid hygiene, oral antibiotics (tetracycline for meibomianitis)
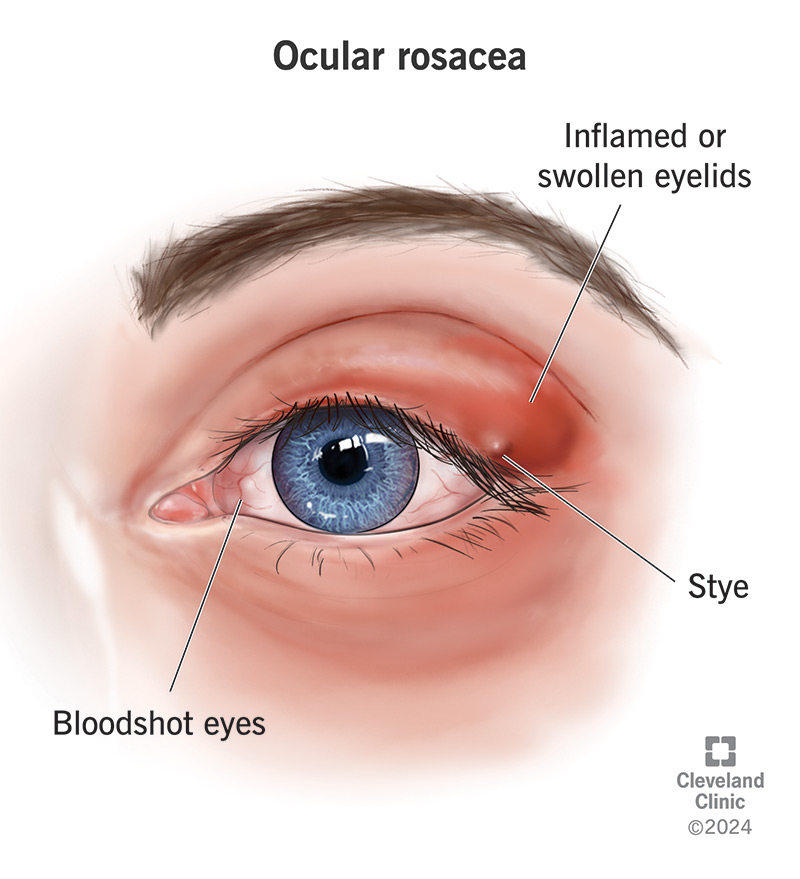
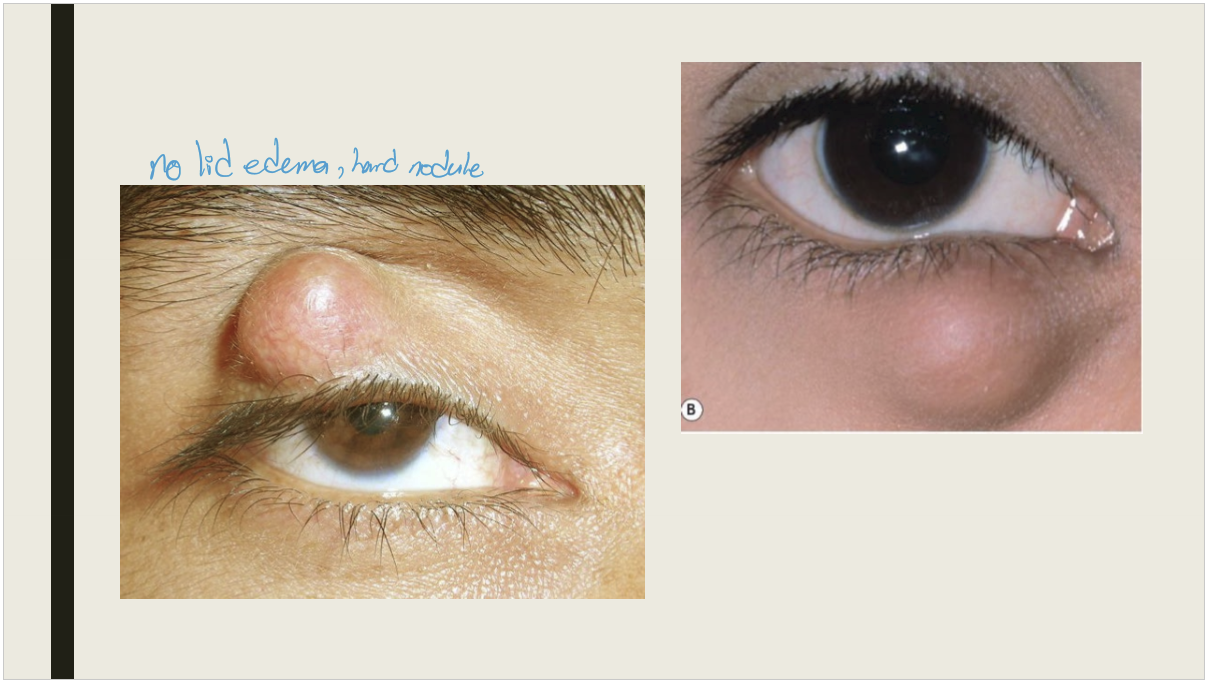
What is a chalazion?
A granulomatous inflammatory lesion of the meibomian gland
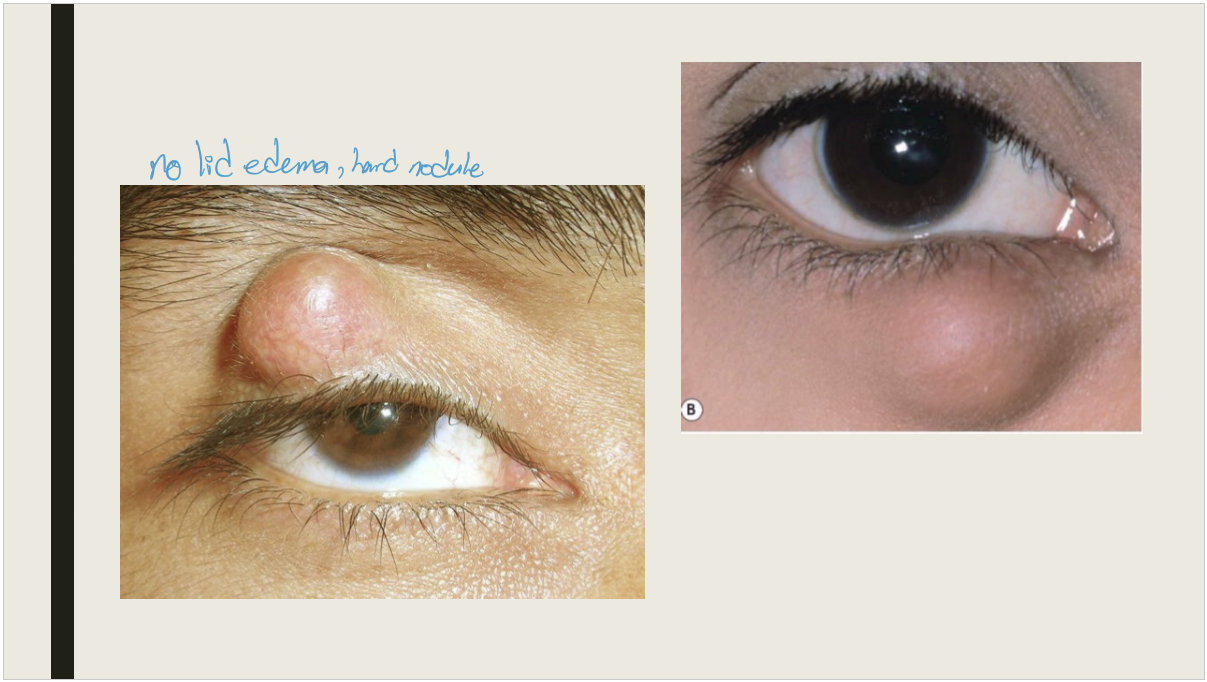
What causes chalazions?
Sebaceous secretion leaking from meibomian gland or adjacent sebaceous glands
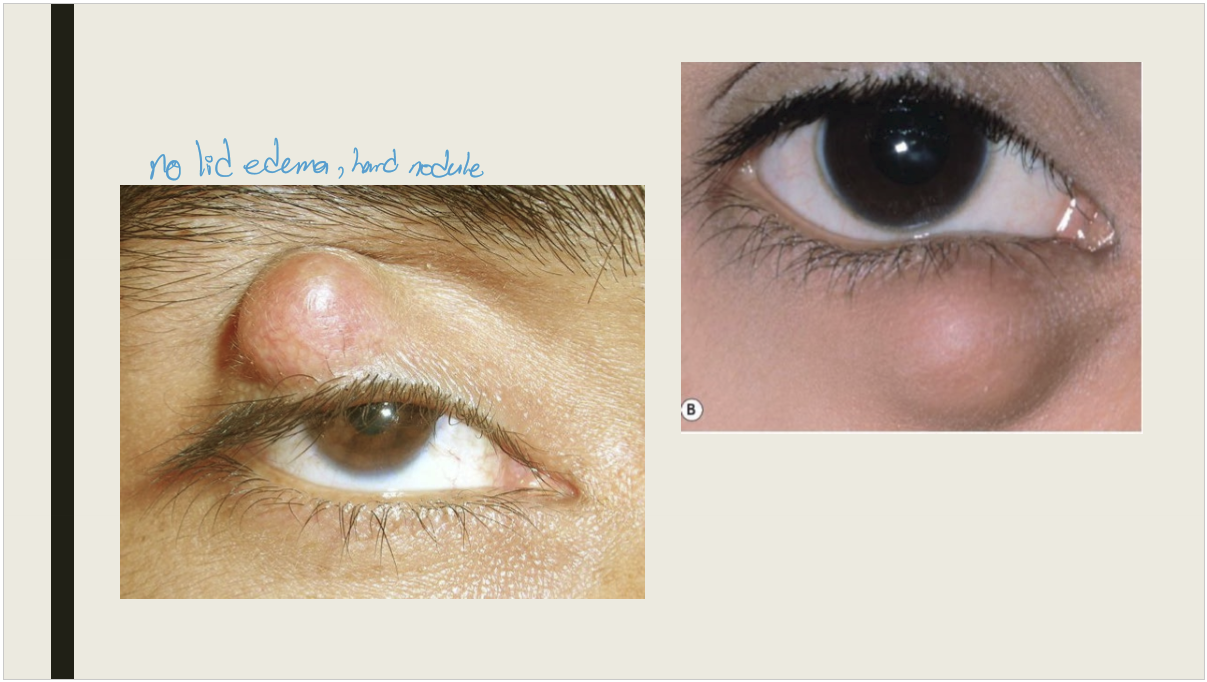
What are the signs and presentation of a chalazion?
Presentation: Painless nodule, usually on the upper lid
Signs: Nodule within the tarsal plate
What are the treatments for chalazion?
Monitor: 33% spontaneous resolve
Surgery: lesion is incised and drained
Injection: steroid injected into lesion (can thin skin and change color)
Oral antibiotics may be used for prophylaxis
What is Xanthelasma?
A benign condition characterized by the development of soft, semisolid, yellow papules or plaques containing cholesterol
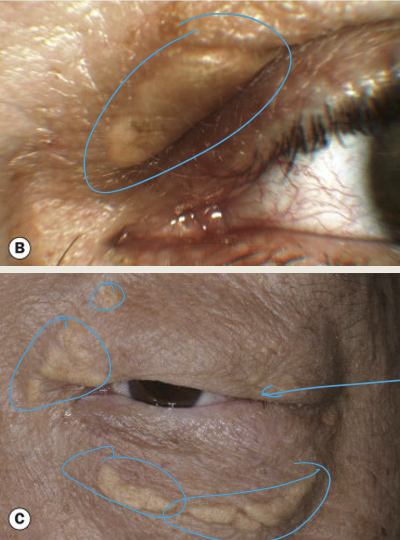
What are the presentations of Xanthelasma?
Yellow plaques located medial
Bilateral condition
Typically found in older individuals
Can be associated with elevated cholesterol levels
What are the treatments for Xanthelasma?
Observation or Excision or laser removal
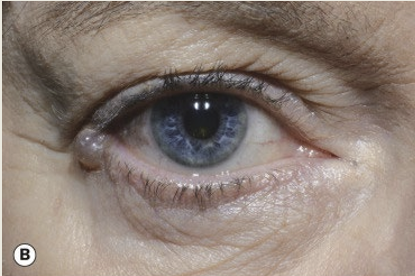
Describe a cyst of moll.
As a round translucent cyst on the anterior lid margin. It is not painful and the treatment is observation.
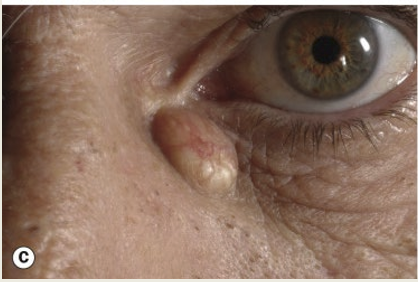
Describe a sebaceous cyst.
A blocked pilosebaceous follicle that conatins sebaceous secretions. It occurs at the inner canthus. The treatment is observation.
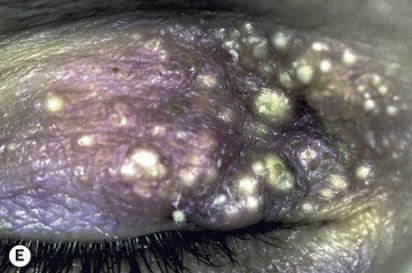
Describe a milia.
A tiny epidermal cyst that are caused by occlusions of pilosebaceous units. They appear as white round papules that occur in groups. The treatment is observation.
Describe a cyst of zeis
A small translucent cyst on the anterior lid marign. It is caused by obstructed sebaceous gland associated with the eyelash follicle. The treatment is observation.
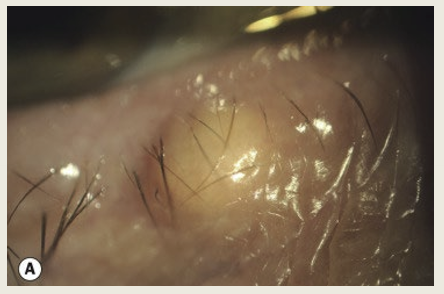
Describe a eccrine hidrocystoma.
A sweat gland cyst. It appears at the medial or lateral aspect of the lid. It does not directly involve lid margin. The treatment is observation.
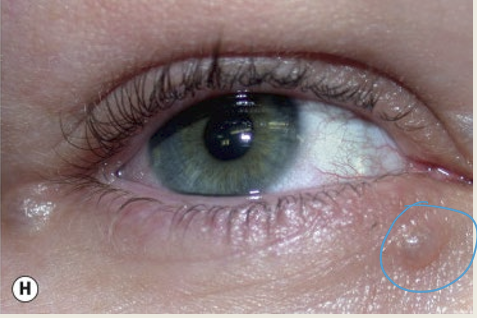
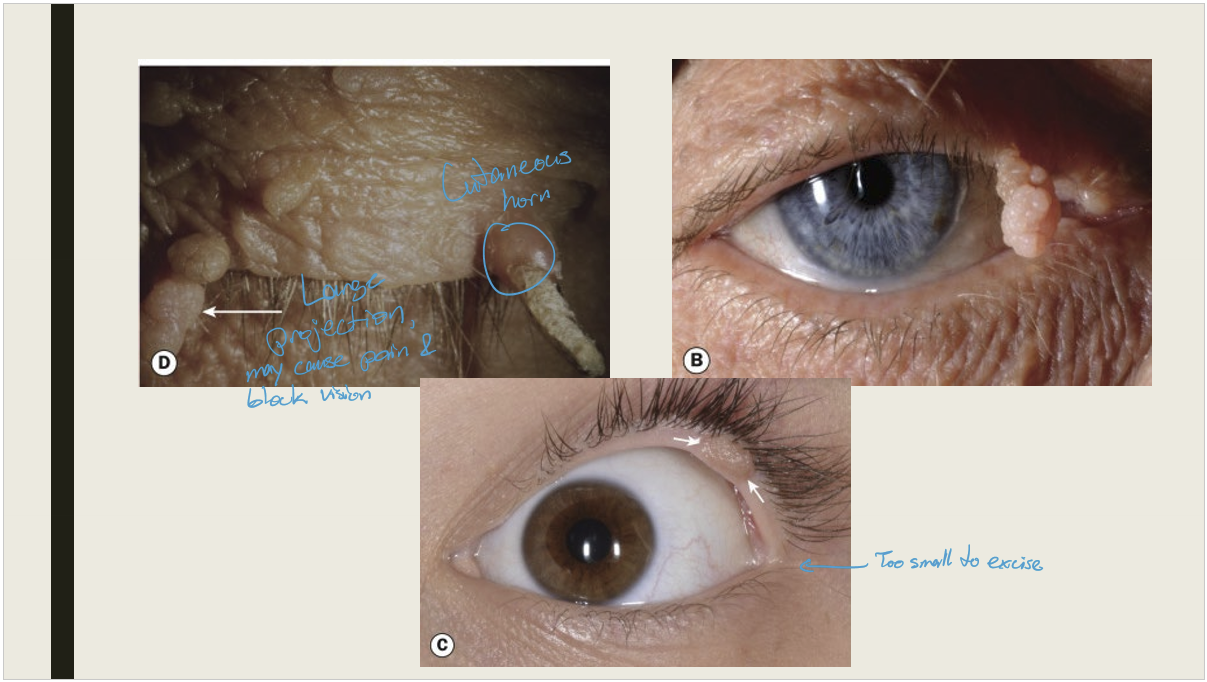
What is the appearance of squamous cell papiloma?
A pedunculated (stalk like) flesh colored lesion OR a sessile lesion that has raspberry appearance.
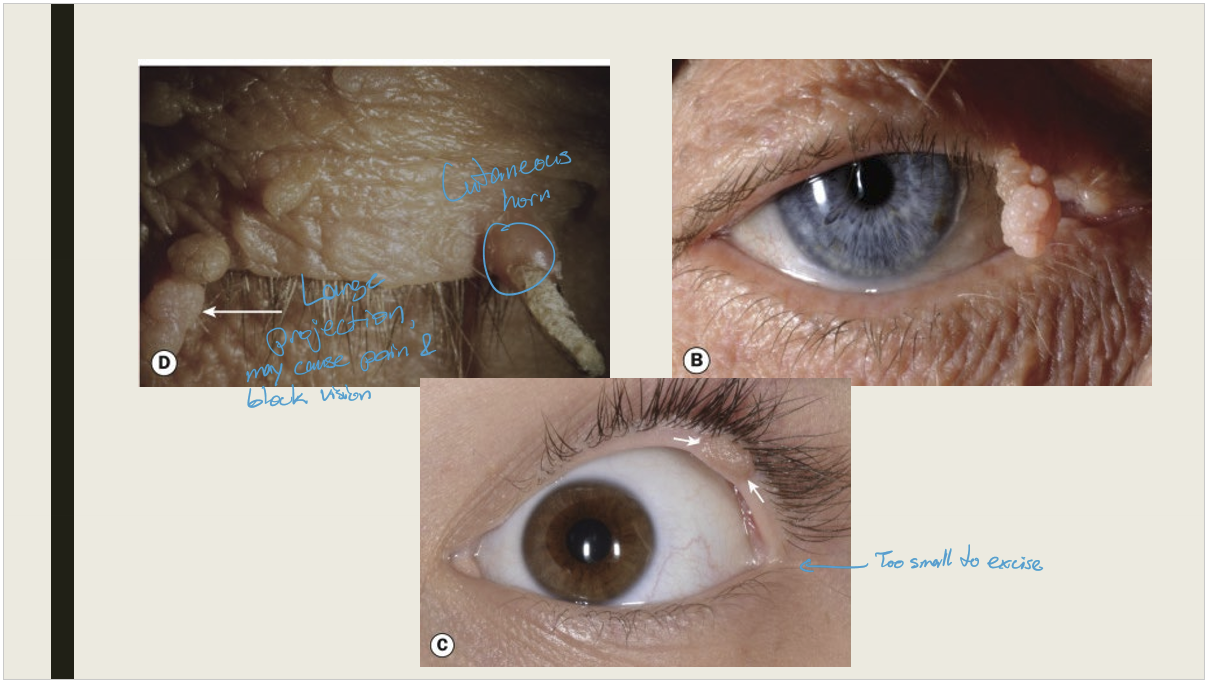
What is the treatment for squamous cell papiloma?
Excision
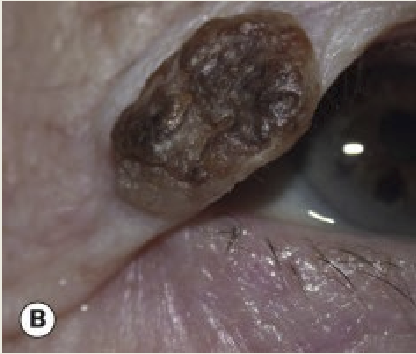
What are the presentations for seborrhoeic keratosis/basal cell papiloma?
Discrete, brown, greasy plaques that tend to be slow growing. It is more commonly seen in elderly
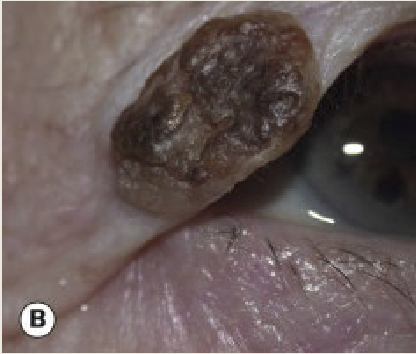
What is the treatment for seborrhoeic keratosis?
Excision
What are the presentations for actinic keratosis/solar keratosis?
Hyperkeratotic plaque with scaly surface
Typically affects elderly
Seen with large amount of UV exposure
More common on forehead and back of hands
Potential to develop into cutaneous horn or squamous cell carcinoma (low risk)
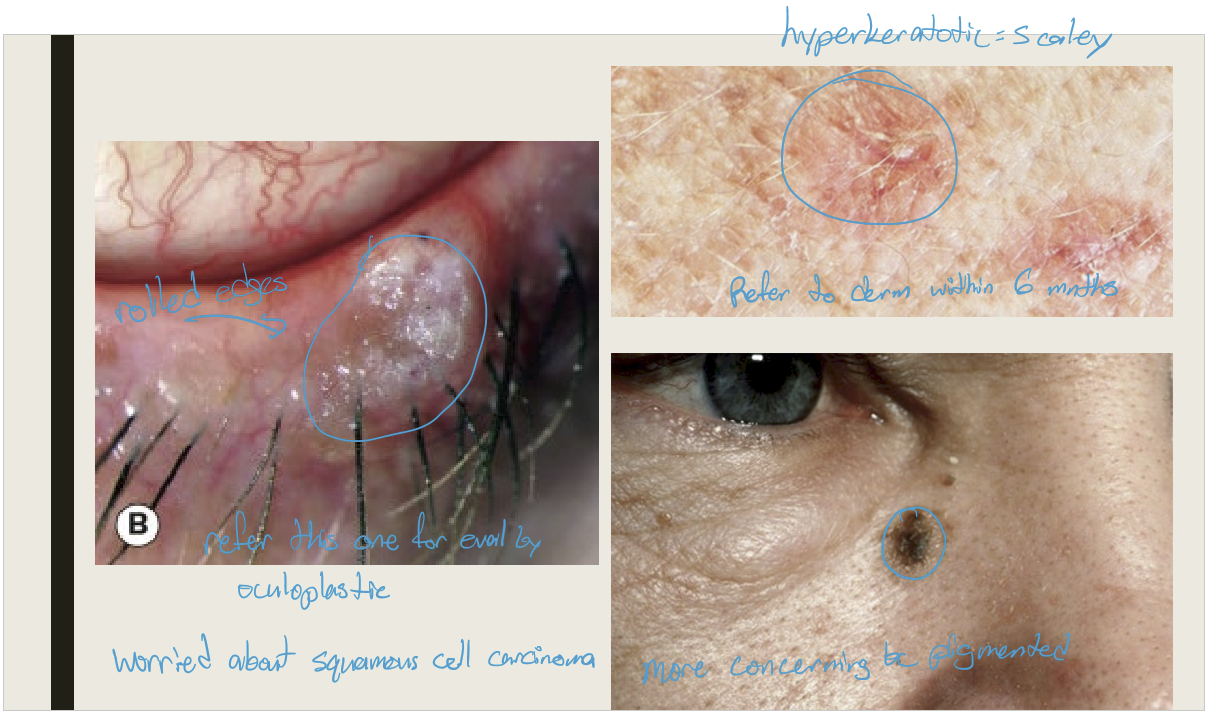
What are the treatments for actinic keratosis?
Excision or cryotherapy with biopsy
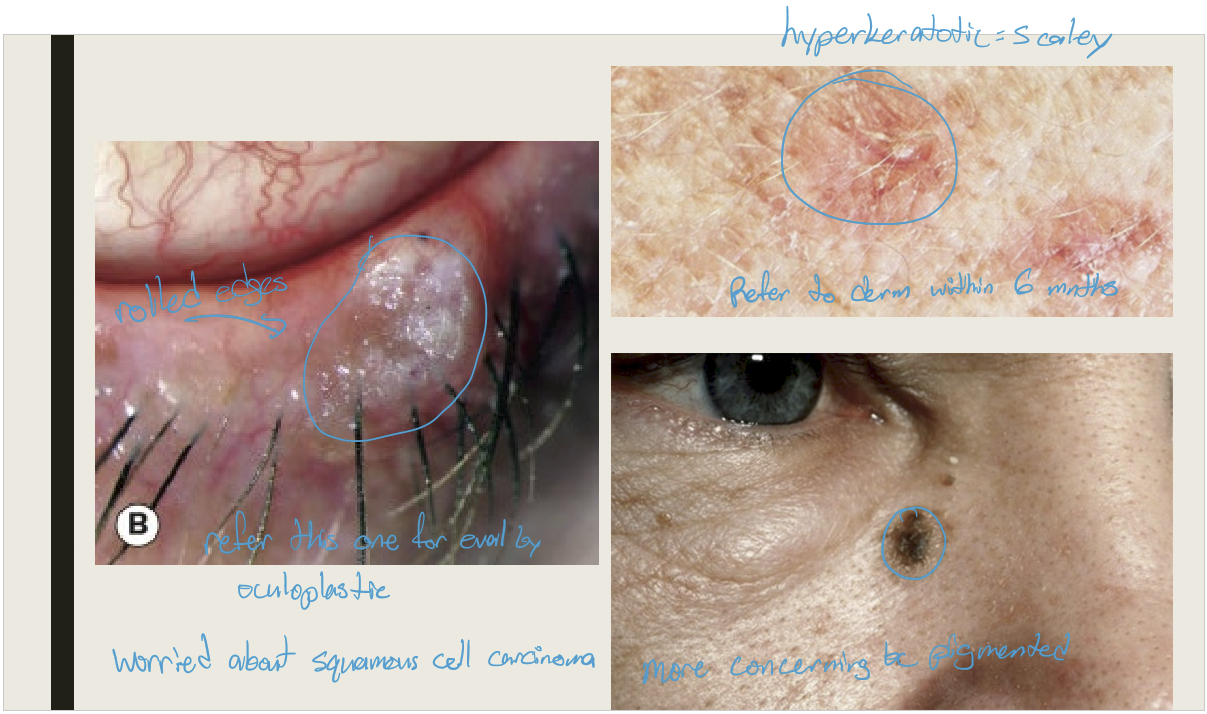
What are the presentations of a cutaneous horn?
A conical or coned like keratinized mass protruding from the skin. It is more common in fair skinned elderly individuals. Found on sun exposed areas.
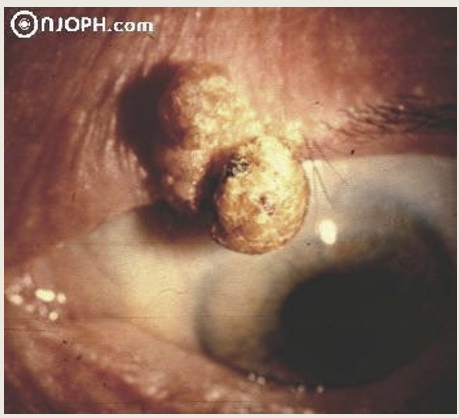
Cutanous horns found on the face are more likely to be what?
2x more likely to be Premalignant or malignant
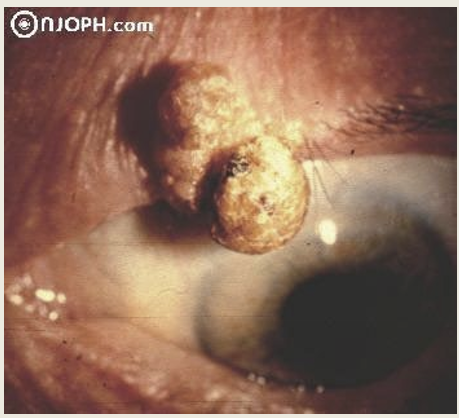
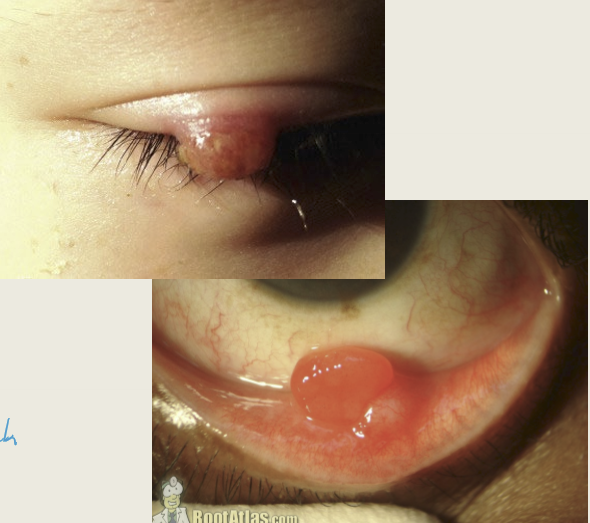
What are the presentations for pyogenic granuloma?
Red polypodial lesion that are painful and bleeds easily with minor trauma. It can be a complication of surgery.
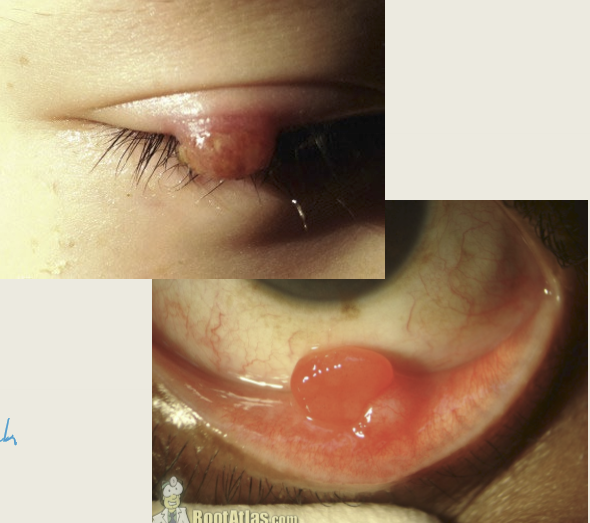
What are the treatments for pyogenic granuloma?
Excision, but can come back.