Intro to Medical Terminology
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2025 ATI Nurse Readiness
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Medical terminology
A standardized language that all health care professionals use to communicate with each other.
The structure and function of the body, manifestations of disease processes, medical equipment, and therapeutic and diagnostic procedures are all written using medical terminology
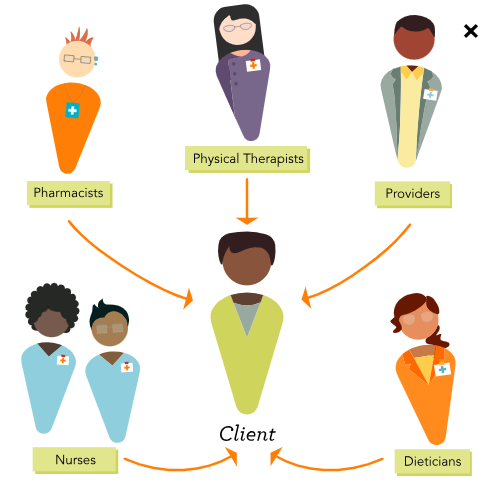
Interprofessional team
A group of diverse health care professionals, such as nurses, providers, pharmacists, dietitians, respiratory therapists, unlicensed assistive personnel, and physical therapists, who collaborate to care for clients.
Case Study:
Scenario Introduction: Nurses encounter medical terminology throughout the day while they work with members of the interprofessional team to care for clients.
Nurse and Respiratory Therapist -
Respiratory therapist: The client who has pneumonia reported dyspnea, and their oxygen saturation was 89%. I administered a respiratory treatment and placed the client on 2 liters of O2 via nasal cannula.
Nurse: I will continue to monitor the client for hypoxia.
Nurse and Provider -
Nurse: The client in room 102 has an elevated BP of 168/90 and a headache.
Provider: I will prescribe an anti-hypertensive medication.
Nurse and Dietitian
Dietitian: The laboratory results for the client who has partial to full thickness burns show hypoalbuminemia.
Nurse: How should we increase protein in the client’s diet?
Scenario Conclusion:
As can be seen from the examples of collaborating with the interprofessional team, medical terminology and abbreviations are used frequently throughout the day.
Understanding medical terminology allows nurses to communicate with the interprofessional team to provide high-quality, safe, and effective care to clients and ensure continuity of care.
Client Education
An understanding of medical terminology requires training and experience working within the health care field. Many clients do not have a background in health care.
Therefore, an important aspect of nursing is client education.
Nurses need to translate medical terminology into terms that the client can understand.
For EX, if a client has a cerebral hematoma, the nurse can translate the terminology by explaining to the client that they have a collection of blood within the skull.
The nurse can also provide written educational material or videos to the client.
Client educational materials should be written at or below a sixth-grade reading level to ensure clients with varying degrees of health literacy can understand.
It is important for clients to understand their medical condition and prescribed treatments and medications.
If clients do not, they may not be able to manage their health effectively at home or advocate for the health care they receive.

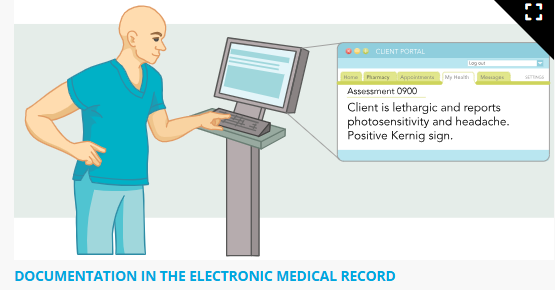
Client Documentation
It is important for nurses to document in the client’s medical record accurately. Using consistent, standardized medical terminology in the client’s medical record ensures continuity of care and communication with other members of the health care team.
Using standardized medication terminology decreases the risk of subjectivity when documenting client care and the misinterpretation of client data in the client’s medical record.
For EX, nurses document the client’s physical assessment, response to treatments, administration of prescribed medications, and client teaching.
Accurate documentation using medical terminology allows other members of the health care team to identify any changes or improvements in the client’s condition as well as any additional needs the client may have.
Medical terminology is the cornerstone of clear and effective communication within the interprofessional team both verbally and within the client’s medical record.
Clear communication with clients and the interprofessional team contributes to better client outcomes. When all members of the interprofessional team understand the client’s medical condition and treatment plan, the care is more consistent and effective.
Translating medical terminology to clients and avoiding medical jargon keeps clients informed and empowers them to be active in their care.
A nurse is teaching a student nurse about medical terminology. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Medical terminology increases efficiency when communicating about a client’s needs.
Explanation: Medical terminology facilitates efficient collaboration with clear and concise exchanges of information which is imperative for timely decision making and coordinated care.
Abbreviations
shortened words that can save health care professionals time writing and reading medical documents or prescriptions
Acronyms
An abbreviation formed from the first letter of each word in a phrase.
EX: ASAP (as soon as possible)
BP (blood pressure)
BMI (body mass index)
NICU (neonatal intensive care unit)
Prescription
A medication order written by the provider that includes the name of medication, amount to be given, the route, and frequency of administration.
The Joint Commission Official “Do Not Use” List
Some abbreviations and symbols are subject to error and should never be used within the health care setting in neither handwritten nor electronic form.
These appear in "Do Not Use" lists published by organizations that promote client safety, such as The Joint Commission and the Institute for Safe Medical Practices (ISMP).
The Joint Commission Official “Do Not Use” List
Do not use | Potential problem | Best practice |
|---|---|---|
U, u (unit) | Mistaken for "0" (zero), the number "4" (four) or "cc" | Write "unit." |
IU (International Unit) | Mistaken for IV (intravenous) or the number 10 (ten) | Write "International Unit." |
Q.D., QD, q.d., qd (daily) Q.O.D., QOD, q.o.d, qod (every other day) | Mistaken for each other Period after the Q mistaken for "I" and the "O" mistaken for "I" | Write "daily." Write "every other day." |
Trailing zero (X.0 mg)* Lack of leading zero (.X mg) | Decimal point is missed | Write X mg. Write 0.X mg. |
MS MSO4 and MgSO4 | Can mean morphine sulfate or magnesium sulfate | Write "morphine sulfate." Write "magnesium sulfate." |
*Exception: A “trailing zero” may be used only where required to demonstrate the level of precision of the value being reported, such as for laboratory results, imaging studies that report size of lesions, or catheter/tube sizes. It may not be used in medication orders or other medication-related documentation.
Examples From the ISMP List of Error-Prone Abbreviations and Symbols
Examples From the ISMP List of Error-Prone Abbreviations and Symbols
Do not use | Potential problem | Best practice |
|---|---|---|
AD, AS, AU | Mistaken as OD, OS, OU (right eye, left eye, each eye) | Use “right ear,” “left ear,” or “each ear.” |
OD, OS, OU | Mistaken as AD, AS, AU (right ear, left ear, each ear) | Use “right eye,” “left eye,” or “each eye.” |
D/C | Premature discontinuation of medications if D/C (intended to mean “discharge”) has been misinterpreted as “discontinued” when followed by a list of discharge medications | Use “discharge” and “discontinue.” |
Qhs | Mistaken as qhr (every hour) | Use QHS or qhs |
SC, SQ, sq, sub q | SC mistaken as SL (sublingual); SQ mistaken as “5 every” The “q” in “sub q” has been mistaken as “every” (for example, a heparin dose ordered “sub q 2 hours before surgery” misunderstood as every 2 hours before surgery) | Use “subcut,” “SUBQ,” or “subcutaneously.” |
> and < | Mistaken as opposite of intended Mistakenly use incorrect symbol “< 10” mistaken as “40” | Use “more than” or “less than.” |
½ tablet | Mistaken as 1 or 2 tablets | Use “half tablet.” Avoid using fractions or decimals. |
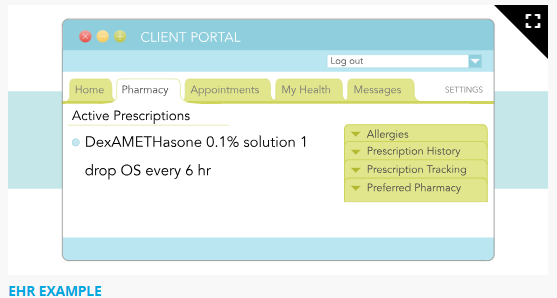
The nurse is reviewing the above prescription for a client. What action should the nurse take?
My answer: The nurse should not use the term "os" as it may be mistaken for ad, as, or au and referring to the ear.
Expert Response: The nurse should clarify the prescription. The abbreviation “OS” is on The Joint Commission's “Do Not Use” list. “Left eye” should be used in the prescription instead of OS. OS could be misinterpreted as AS, which is left ear.
Tall Man Lettering
A strategy in which parts of the medication names are written in uppercase letters to draw attention to differences between look-alike or sound-alike medications.
Examples of Medications Using Tall Man Lettering
Medication name | Recommended name |
|---|---|
Bupropion Buspirone | buPROPion busPIRone |
Chlorpromazine Chlorpropamide | chlorproMAZINE chlorproPAMIDE |
Dimenhydrinate Diphenhydramine | dimenhyDRINATE diphenhydrAMINE |
Dobutamine Dopamine | DOBUTamine DOPamine |
Glipizide Glyburide | glipiZIDE glyBURIDE |
Hydralazine Hydroxyzine | hydrALAZINE hydrOXYzine |
Nicardipine Nifedipine | niCARdipine NIFEdipine |
Drug Safety Alerts
Long-term use of medications can lead to the identification of side effects that were not discovered during the medication trials.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) monitors the safety of medications even after they have been approved. If a new safety concern about a medication is identified, the FDA releases a Drug Safety Communication to health care providers and clients.
The picture is an example of a Drug Safety Communication from the FDA.
Knowing medical terminology is important when reviewing and understanding professional health care-related publications. This drug safety alert contains medical terminology such as osteoporosis, hypocalcemia, and dialysis and the abbreviation CKD (chronic kidney disease). Therefore, the nurse must be knowledgeable about medical terminology to understand the safety alert and communicate the findings to clients.

Summary
In conclusion:
Understanding medical terminology is crucial for working in an interprofessional health care team.
An interprofessional team includes various health care professionals who collaborate to provide client care.
Medical terminology is a standardized language used for clear communication among health care professionals.
Knowledge of medical terminology is necessary to stay updated with evidence-based practices through professional publications.
Nurses play a key role in educating clients by translating medical terms into understandable language.
Clients' understanding of their conditions and treatments is vital for effective health management and self-advocacy.
Nurses must document client care accurately using standardized medical terminology to ensure continuity of care.
Consistent use of medical terminology reduces the risk of misinterpretation in medical records.
Abbreviations and acronyms can save time in documentation.
Some abbreviations are prone to error and are listed in "Do Not Use" lists by safety organizations like The Joint Commission and ISMP.
Nurses must adhere to facility policies on abbreviations and clarify any ambiguous orders to ensure client safety.
Prescribing, dispensing, and administering medications are critical tasks that require attention to avoid errors with look-alike or sound-alike medications. The FDA recommends using tall man lettering to highlight differences in similar medication names to prevent errors.
The FDA continues to monitor medication safety post-approval and issues Drug Safety Communications for new concerns. Nurses must be able to understand the medical terminology used in the Drug Safety Communications and relay the information to clients without using medical jargon.
A nurse is preparing educational materials for a client who is learning to manage their new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following abbreviations should the nurse avoid? (Select all that apply.)
HS
U
SQ
A nurse is preparing educational materials for a client who is learning to manage their new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Which of the following abbreviations should the nurse avoid? (Select all that apply.)
Contact the prescribing provider for clarification.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions for a medication prescribed with a frequency of "Q.O.D". After clarifying with the provider, which of the following frequencies should the use to ensure client safety?
Every other day
A nurse is preparing to administer a medication SQ. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to ensure the correct route is used?
Clarify the route with the prescribing provider.
Clarifying the route with the provider as "SUBQ" or "subcutaneously" prevents confusion and ensures the correct route is used.
A nurse is preparing to discharge a client who has a new prescription. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to promote the safe use of the medication at home?
Provide written material about the medication written at a 6th grade level.
A nurse is transcribing a telephone medication prescription from a provider that includes the abbreviation "MSO4". Which of the following actions should the nurse take to ensure client safety?
Clarify the prescription with the prescribing provider.
A nurse is reviewing a medication label and sees "niCARdipine" written on it. Which of the following does the capitalization in the medication name indicate?
The medication name is differentiated from a similar medication name.
Explanation: "Tall man" lettering is used to differentiate "niCARdipine" from "NIFEdipine," which are similar medication names.
A nurse is reviewing a client's medication administration record. Which of the following abbreviations should the nurse identify as an error-prone abbreviation?
U
Explanation: "U" can be mistaken for "0" or "4" and should be corrected to "unit" to prevent errors.
A nurse is reviewing a prescription for a medication that contains the abbreviation “AU” for the route the medication is to be administered. What is the intended meaning of this error-prone abbreviation?
Each Ear
Explanation: "AU" is an error-prone abbreviation that means each ear. "Each ear" should be used instead.
A nurse is reviewing documentation in a client's medical record. Which of the following statements describes the use of medical terminology in the medical record?
It ensures continuity of care and communication with the health care team.