OB ectopic pregnancy
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
most common location for ectopic pregnancy?
typically happens in the Fallopian tube
connection between uterine & peritoneal cavities.
symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
classic triad (less than 45% of patients)
vaginal bleeding
pelvic pain
adnexal mass
most common presentation of ectopic pregnancy?
History of amenorrhea (suggesting pregnancy)
Pelvic pain
Irregular vaginal bleeding (spotting to hemorrhage)
how many ectopic pregnancy patients may be completely asymptomatic?
Up to 50% of patients
when are most ectopic pregnancies diagnosed?
between 6 & 10 weeks’ gestational age/pregnancy
when is an ectopic pregnancy large enough to rupture the tube?
Around 8 weeks
causes symptoms
when should βhCG roughly double?
should roughly double every 48 hours until it peaks at about 8 weeks
should rise at least 53%
Ectopic pregnancies tend to have ________ βhCG levels
lower
rise more slowly than normal IUP
discriminatory cutoff for βhCG (definition and number)?
the βhCG level at which a pregnancy should be visible by ultrasound.
1000 mIU/ml (transvaginal discriminatory zone!)
if beta level is high but you don’t see a sac in the endometrial cavity, what should you do?
go look for an ectopic
on what side should you more closely look for ectopic pregnancies?
the side with the CL (where egg came from)
what percent of ectopic pregnancies are in the fallopian tube?
95%
most common location in the fallopian tube for ectopic pregnancies?
Ampulla (70%)
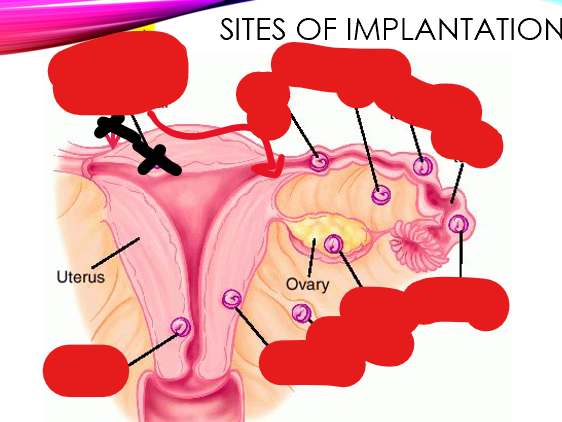
sites of implantation for ectopic pregnancies
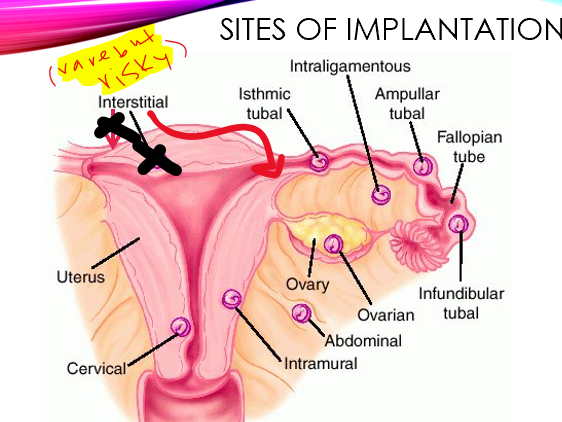
what implantation site is extremely dangerous for ectopic pregnancies? why?
interstitial
dual arterial supply (high blood supply)
extreme hemorrhage upon rupture
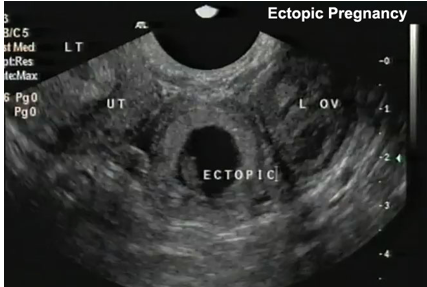
what is shown?
tubal pregnancy
note left ovary has corpus luteum
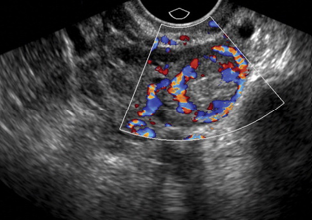
what is shown?
typical presentation of an ectopic pregnancy
Not easy to see, just presents as an adnexal mass
This is with color flow to help diagnose with ring of fire!!!
a cervical pregnancy can be confused with…
how can you differentiate?
inevitable spontaneous abortion
Sliding sac sign
what is a sliding sac sign?
if sac moves with pressure of transvaginal probe, it is NOT a cervical pregnancy
pressure will cause an aborting sac to “slide” in the cervical cavity while a cervical pregnancy will not.
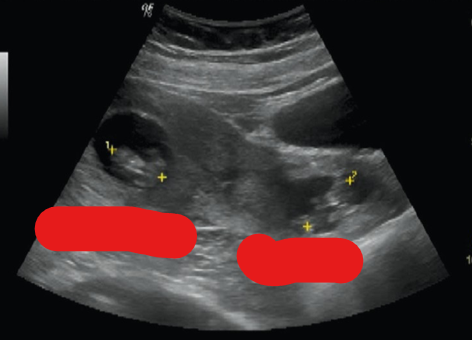
what is shown?
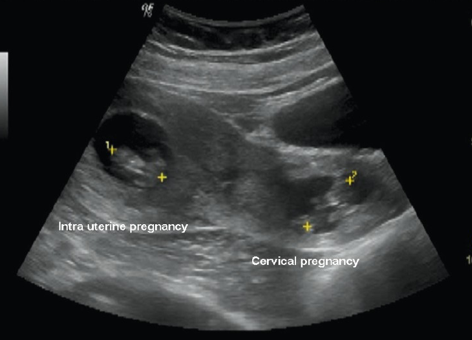
what is a heterotopic pregnancy?
coexisting intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies
most common symptom of heterotopic pregnancy?
abdominal pain
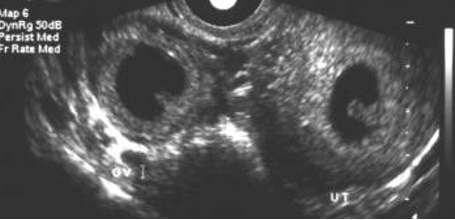
what is shown?
heterotopic pregnancy
what is the primary goal of ultrasound in ectopic pregnancy patients?
determine presence of an IUP
first thing the sonographer looks for when evaluating for ectopic is a pregnancy inside the uterus.
Transvaginal detection rate for ectopics?
90.9% detection rate with very few false positives
TV can see IUP earlier (1500 mIU/ml βhCG)
what should you use to determine an ectopic pregnancy if a patient is going into shock?
transvaginal
usually just use TV anyways
sonographic signs for ectopic?
No IUP
Potential Pseudosac (not going to have a decidual rection)
Free fluid in the pelvis
Also look at Morison’s pouch & Paracolic gutters
Adnexal mass
Most common sign of cervical pregnancy?
hourglass shaped uterus
Gestational sac distends cervical canal between internal & external ossae
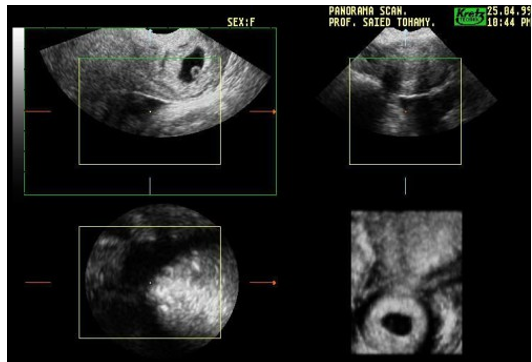
what is shown?
cervical pregnancy
color flow for ectopic pregnancy?
“Ring of Fire”
peripheral vascularity associated with trophoblastic flow
Surgical intervention for ectopics?
Salpingectomy with or without oophorectomy (MOST COMMON)
Tubal resection—remove section of tube
Salpingotomy—cut open tube and remove pregnancy without removing tube
Use when trying to preserve fertility