Oesphagus, Finger Tip, Ureter and Uthera
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
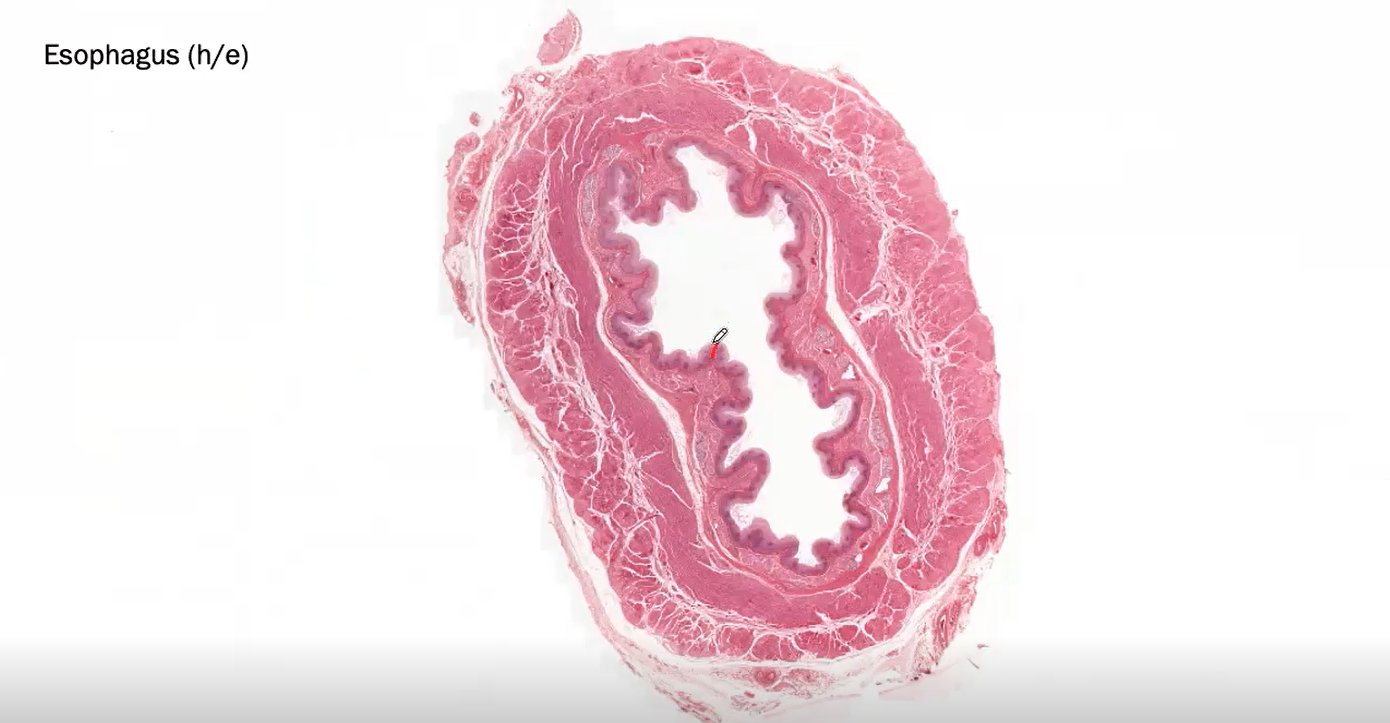
This is the Oesophagus
The LUMEN OF oesophagus has NON-KERATINISING Stratified Squamous Epithelium.
It is called Non-keratinising because the cells in the top-most part of the epithelium have NUCLEI so they are said to be living.
What layers does the epitheilum of the oesphagus have?
Stratum Superficiale/planocellulare
Stratum Spinosum/ Polygonale
Stratum Basale - bottom most layer that is closest to the basement membrane
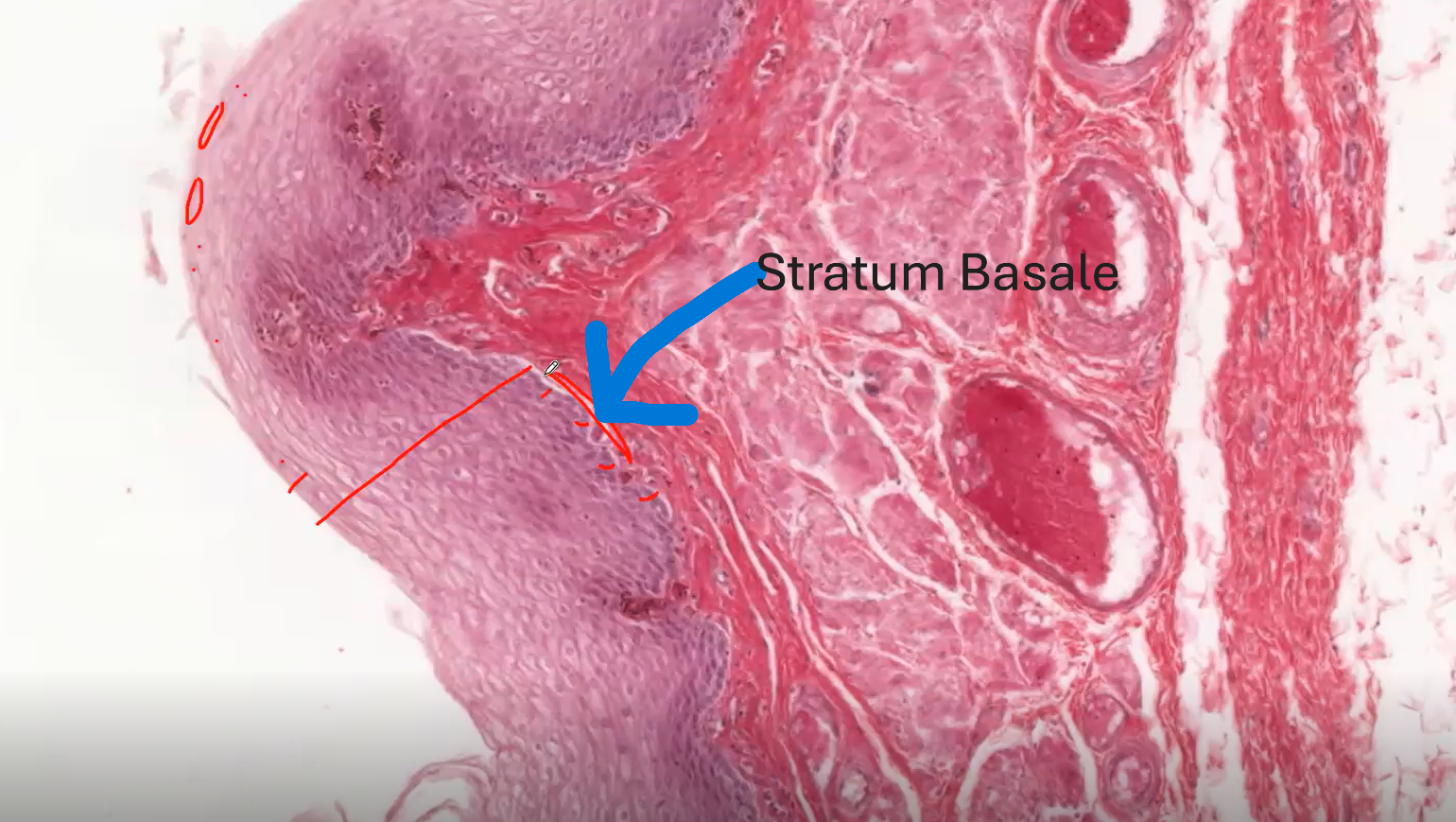
Stratum Basale
The bottom-most layer of this epithelium that is closest to the basements membrane is called the STRATUM BASALE.
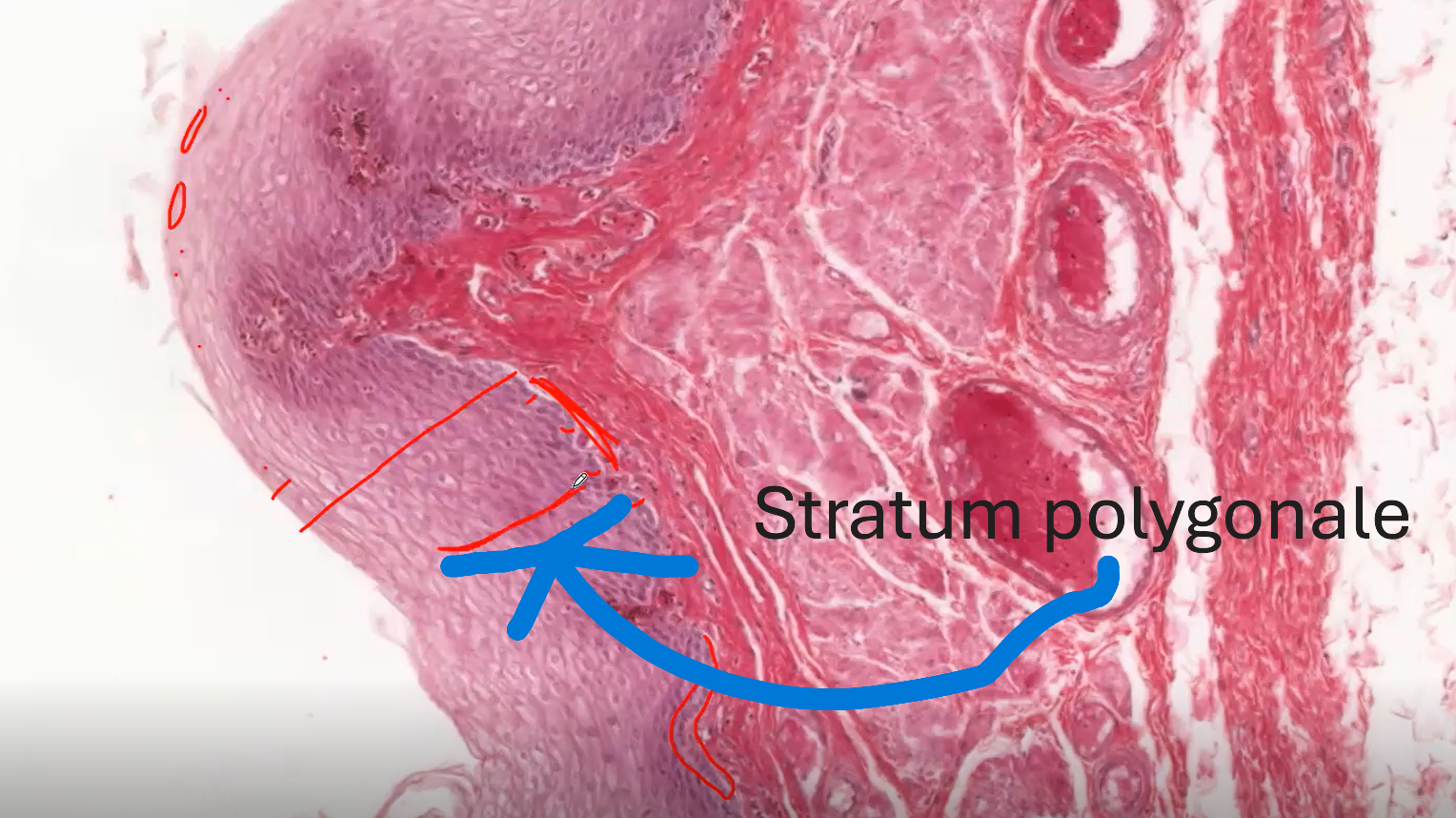
Stratum Polygonale
This is also called Stratum Spinosum. It is the next layer above the stratum basale.
The stratum Polygonale has polygonal cells. The cells in this layer appear to be spinous or prickly.
Why do the cells in the stratum polygonale look prickly or spinous?
This could be because of shrinkage of the cells during dehydration. OR This could be because of the presence of cell-to-cell juctions (desmosomes) which firmly connect these cells to each other.
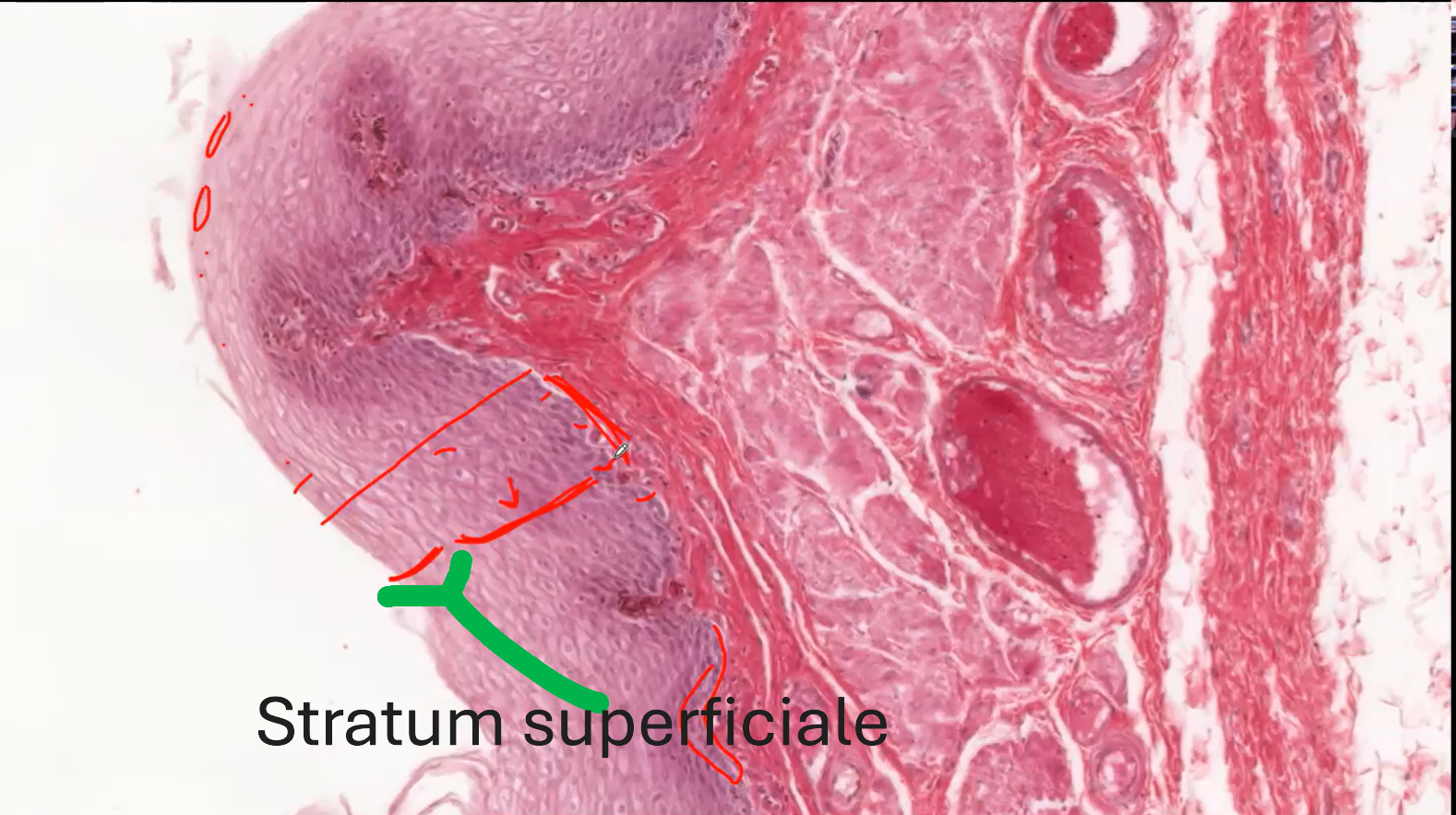
Stratum Superficiale
The top-most layer is called the Stratum Superficiale. It is also called the Stratum planocellulare.
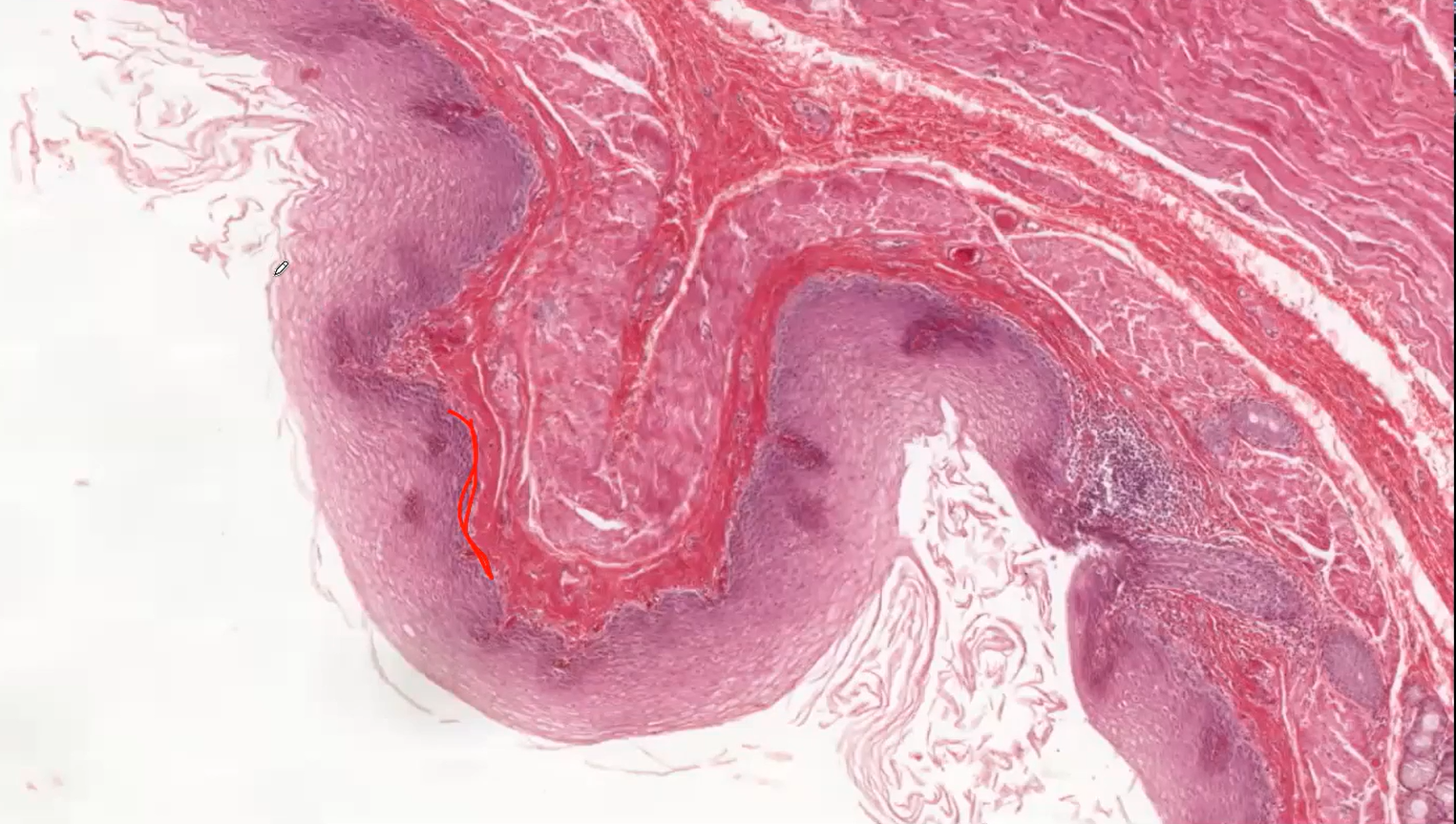
What is the function of the Connective tissue Papillae?
The connective tissue papillae are highly vascularised (providing nutrients and oxygen to diffuse towards the epithelium); the lumen of the blood vessels frequently contain red blood cells, giving even more prominent red colour to the papillae.
Why is the cytoplasm of the cells in this stratified squamous non-keratinising lightly stained?
This is because the glyogen stored which has been lost during formalin fixation (artefact)
Finger Tip
What are the two types of skins and there differences
Thin Skin
Thick Skin
SIMILARITIES:
Both of them have stratified squamous keratinsing epithelium.
DIFFERENCES:
Thin Skin
Thin skin contains HAIR
It has 4 layers
Thick skin
DOES NOT CONTAIN HAIR.
Has 5 layers
What is skin called thin or thick
A thick skin has a thicker stratum corneum while the thin skin has a thinner Stratum Corneum.
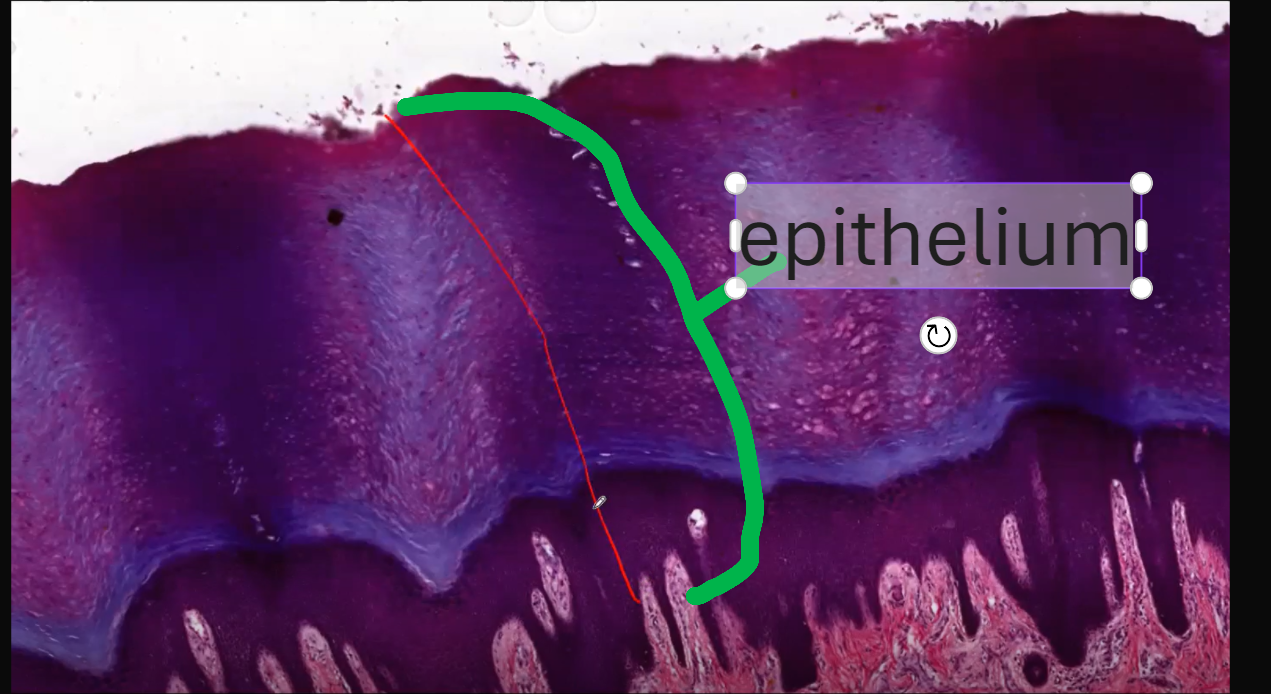
This epitheilum is a stratified squamous keratinsing epithelium. The top layer is really dark (blue) which shows it has Keratin. Also the cells do NOT have NUCLEI. This is shown as small white dots in the top layer.
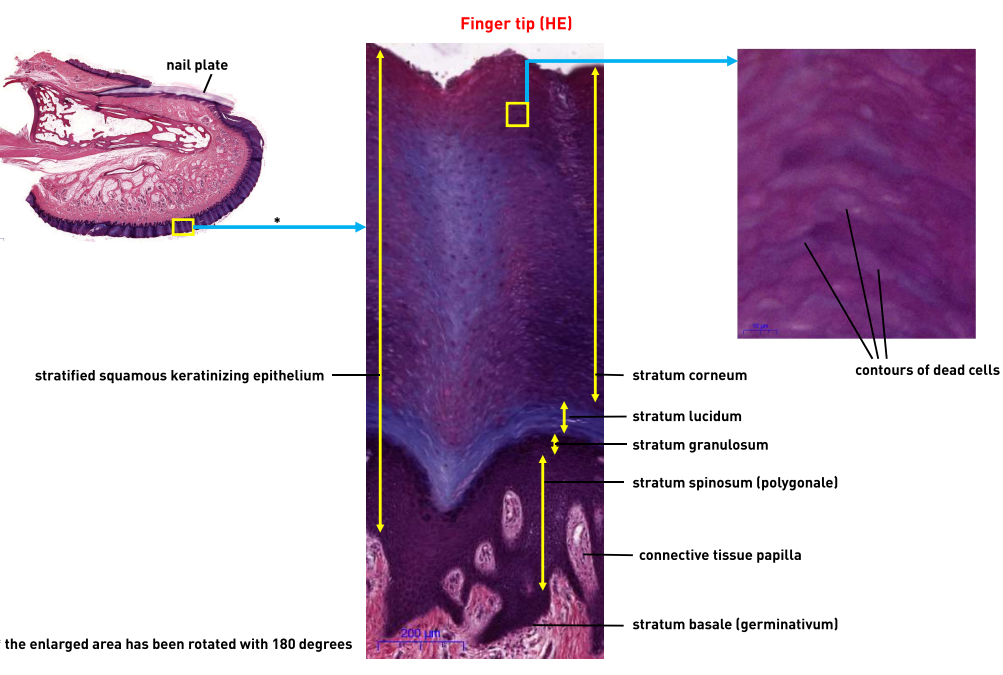
What are the layers of this epithelium?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidium
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Polygonale/ spinosum
Stratum Basale
Stratum Corneum
Why are small white dots at the stratum Corneum?
This shows the absence of nucleus. The lack of nuclei is due to APOTOTIC CELL DEATH which occured during CORNIFICATION.
Why is the free surface of the stratum corneum irregular over the palmar surface?
This is responsible for the fingerprint.
Stratum Lucidum
This is the homogenous layer found beneath the stratum Corneum.
This layer light blue.
Stratum Granulosum
This layer is found beneath the stratum Lucidum. It is the most basophilic layer of the epithelium
Why is the stratum granulosum heavily stained?
The intense staining of these cells is caused by the basophilic granules, which contain keratohyaline.
so KERATOHYALINE IS THE CAUSE OF THE STARTUM GRANULOSUM HEAVILY STAINED.
Stratum Polygonale/ Spinosum
REMEMBER: The polygonal cells in the stratum polygonale are connected to each other by desmosomes.
Stratum Basale
This layer is located directly on the basement membrane.
REMEMBER: The cells in the stratum basale are stem cells that contribute to the continous renewal of the epithelium.
What type of skin is on the finger tip?
This is a THICK SKIN.
This is because this skin doesn’t have hair follicles.
WHAT Layer does the THICK Skin have that the Thin skin doesn’t
The Thin skin has all the layers that the thick skin has EXCEPT for the Stratum Lucidium
Ureter
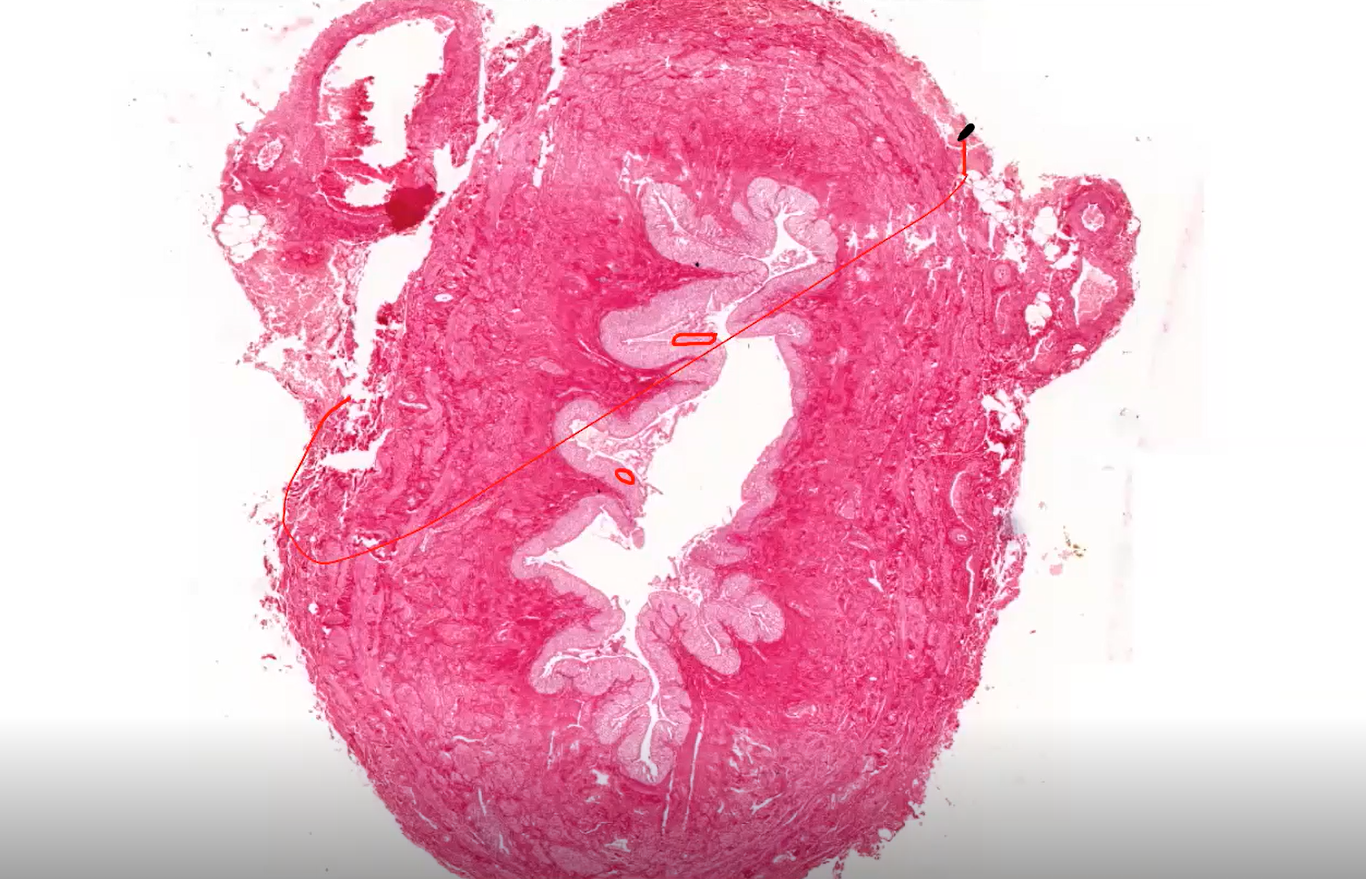
What type of Epithelium lining the ureter internally?
Transitional Epithelium
What are the cell at the most apical cell row called?
The umbrella-shaped cells in the most apical cell row overlie more than one cells in the subsequent row, and they slightly protrude into the lumen.
What are some features of the umbrella cells found at the topmost part of this epithelium
They are Unusually thick and aree strongly EOSINOPHILIC. This shouws the presence of lots of proteins.
What happens when the
Male Urethra
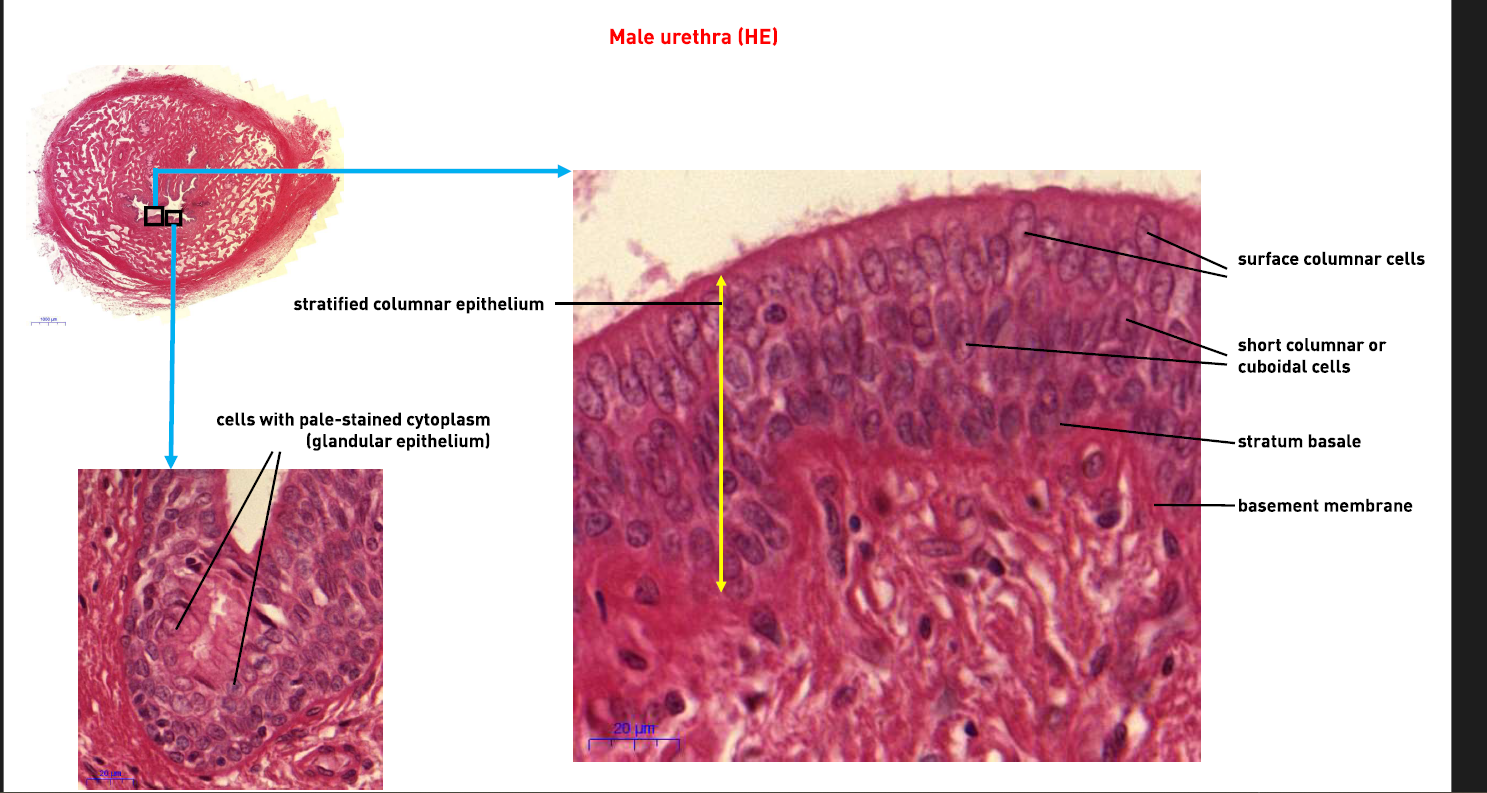
What type of epitheilum does the male Urethra have?
Stratifies columnar Epithelium
