SOCPSY W11: Prejudice, Stereotyping, & Discrimination
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Prejudice
Generalised attitude toward members of a social category
Stereotypes
Beliefs about members of a social category
Discrimination
Behaviours directed toward others because of their group membership
Link between the three (PSD):
*Note: each of these can be positive, negative or neutral

The nature of discriminatory behaviours
Doesn’t have to be morally wrong, just needs to be exclusive/treat certain people differently
Real life example of discrimination in new car salesrooms
Different concessions were made based on race (& gender): white women > black women > black men (though they used the same bargaining strategies)
Sexual harassment
Unwanted sexual behaviour acted on an individual
Sexual harassment perception based on status differences
Harassment is considered more harassing when performed by person in power (perceived as an abuse of power)
But social status is also viewed more favourably by:
Women
Ev: Women found it to be more upsetting if asked repeatedly on a date by construction workers, garbage collectors, janitors, and gas station attendants than premed students, grad students or rock stars
Sexual harassment perception based on attractiveness differences
Considered less harassing when performed by an attractive single individual
Sexual harassment perception based on gender difference
Women more likely to define staring and flirting as sexually harassing than men
Explicit vs Implicit prejudice
Explicit: positive or negative feelings of which you are aware (and consciously display)
Implicit: feelings of which you are unaware (unconscious, natural attitudes)
Example of what would tap into both explicit & implicit prejudice
Asking someone’s feelings towards CMIO
Stereotype threat
When a salient negative stereotype of your group impairs your performance
Eg. white men did worse in math when they thought they were being compared to an Asian
(study x2)
4 Goals of PSD: (SMSG)
Seeking mental efficiency
Managing self-image
Supporting and protecting one’s group
Gaining social approval
Seeking mental efficiency
Using cognitive heuristics based on stereotypes
Advantage and limitations of stereotypes
(+)
Contain at least a kernel of truth (elements of accuracy)
(-)
Don’t account for individual differences
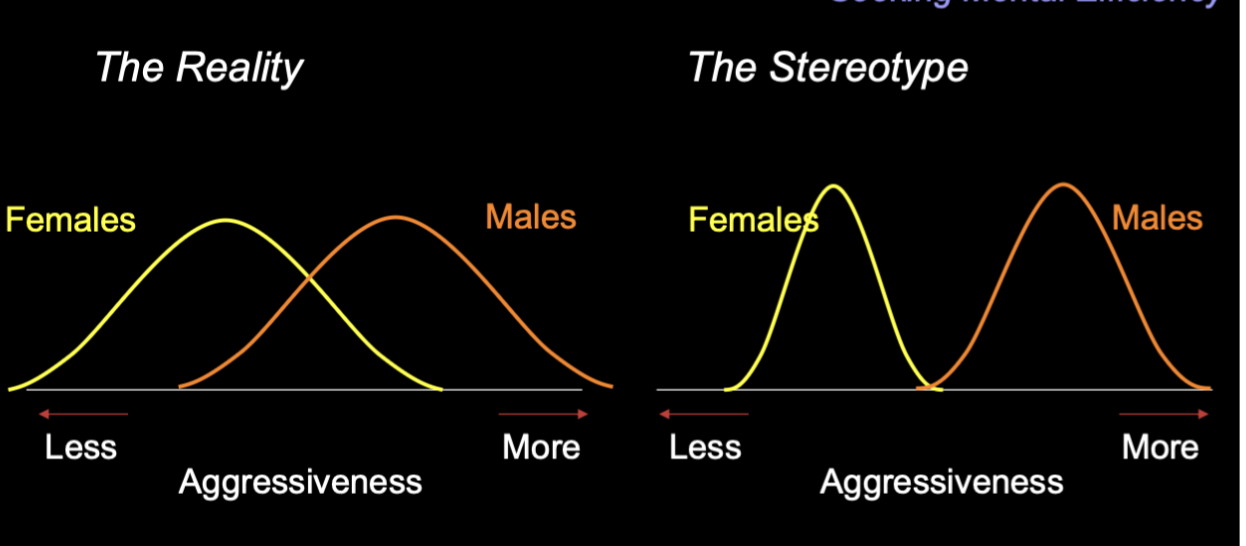
Eg. Overestimating sex differences in aggression —> there’s a wider variation of aggressiveness in both genders in reality
Why do we often increase distinctions between groups and decrease differences within groups
To save time and cognitive effort
Outgroup homogeneity
We are likely to perceive members of outgroups to be more similar to each other than members of our in-group to be (“they are alike; we are diverse”)
How does mood affect one’s use in stereotypes and cognitive shortcuts?
A happy person, or one who has arousing emotions (eg. anger, anxiety, fear, euphoria) is more likely to use cognitive shortcuts and rely on stereotypes
Managing self-image (no definition)
Social identity
Beliefs and feelings we have toward the group we consider we belong to
Social identity theory
Part of our identity is derived from our membership in groups
What do we do to feel good about our groups?
Compare our in-group with less well-off outgroups (like how individual social comparison can boost self-esteem)
R/S between self-esteem and derogation of outgroups
People with low SE generally derogate outgroups more commonly
Exception to that
People with high SE may exhibit more prejudice when their self-image is threatened with failure
(study)
Supporting and protecting one’s group (no definition)
Realistic conflict theory
Intergroup conflict, negative prejudices and stereotypes emerge from actual competition between groups over desired resources
Eg. Israel-Palestine war
Minimal intergroup paradigm
Research method that demonstrates how individuals show favouritism toward their in-group, even when group distinctions are trivial or arbitrary; meaningless
(study)
Social dominance orientation (SDO)
Measures one's preference for group-based hierarchies (their group to dominate others) and social inequality (be socially and materially superior to them)
Examples of weaker groups in 4 countries whom high SDO people prejudiced against:
Arabs, blacks & homosexual individuals in the US
Natives & asian immigrants in Canada
Native Taiwanese in Taiwan
Sephardic Jews & Palestinians in Israel
Differences in SDO based on gender
Men are higher in SDO across cultures and are more likely to:
Seek jobs involving dominance eg. police, military
Band together to conquer other groups
Why? (evolutionary explanation)
Dominance is linked to male mating success; SDO can be linked to sexual selection
Real life examples of intergroup competition
Economic downturn increased lynchings of Blacks in the South, and increased violence against Blacks and immigrants in the North
Eagles vs Rattlers summer camp: boys in competing teams raided e/o’s cabins, stole & burnt their flags, and viewed them negatively
Gaining social approval (no definition)
Which group of people are especially likely to express bias/hostility toward outgroups?
Newcomers, as they are uncertain of their acceptance and social standing in their group
(study)
4 types of religiosity (& their r/s with prejudice):
Extrinsic religiosity
Intrinsic religiosity
Fundamentalism religiosity
Quest religiosity
Extrinsic religiosity
An orientation that sees religion as a means of gaining friendship status, comfort or other valuable ends
How do these people express prejudice?
They express more prejudice than non-religious people
Intrinsic religiosity
An orientation that sees religion as an end in itself, and people attempt to internalise religious teachings
How do these people express prejudice?
They present themselves as unprejudiced, but may exhibit discriminating behaviour if they think others are not watching
Fundamentalism religiosity
An orientation that sees religion as providing absolute truth
How do these people express prejudice?
(Same as extrinsic) They express more prejudice than non-religious people
Quest religiosity
An orientation that sees religion as a personal journey taken to understand complex spiritual and moral issues (vs. quick, simple answers)
How do these people express prejudice?
They are unprejudiced in word and in deed
What is the original hypothesis of negative stereotypes and prejudice?
That they are due to ignorance
How could they be reduced then?
Expose people to members of different groups
Limitation of this method
Such contact has not generally worked except when the 6 principles of effective group contact is applied
6 principles of effective group contact:
Contact is only effective when:
Outgroup members have traits & abilities challenging negative stereotypes
Contact is supported by local authorities and norms
Contact is at individual level
Contact is rewarding for all
Groups are of equal status
Groups work toward common goals
The effect of working toward a common goal
Eg. jigsaw classroom: students in a mixed race group who are given different task for a class project are more likely to form cross-ethnicity f/s inside and outside classroom
+ (study)