Chapter 4- Eukaryotes
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
endosymbiosis
organism lives inside the cells of another
bacteria stays in our cells and becomes mitochondria
what do mitochondria do
generate atp*
cilia
shorter and more numerous
only found on eukaryotes
cell walls of fungi
rigid and provide support and shape
cell walls of protozoa and helminths
do not have them
cytoplasmic membrane
selectively permeable barrier
nucleous
protects dna
nucleolus
where you make rna
chromatin
made of dna and histone proteins
genetic material of cell
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes on surface make proteins
transports materials from nucleus to cytoplasm
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
nutrient processing
closed tubular network without ribosomes
storage of lipids
golgi apparatus
site of protein modification and shipping
contains cisternae
cisternae
flattened sacs on golgi apparatus
do not form continuous network
lysosomes
carrying digestive enzymes
transitional vesicles
picked up at the face of the Golgi apparatus
condensing vesicles
pinch off of the Golgi apparatus and
are then conveyed to lysosomes or transported outside
the cell
vacuoles
membrane bound sacs containing fluids or solid particles
to be digested, excreted, or stored
mitochondria
generate atp
cristae
on the mitochondrias inner membrane of inner folds
extracts chemical energy contained in nutrient molecules and stores it as ATP
chloroplasts
found in algae and plant cells
capable of converting energy from sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis
Ribosomes
on rough ER
Staging areas for protein synthesis
Cytoskeleton
anchoring organelles
moving RNA and vesicles
permitting shape changes
movement
Actin filaments
from cytoskeleton
helps cell move
microtubules
maintain shape of eukaryotic cells without cell walls
holds shape
intermediate filaments
structural support to cell and organelles
road network
forms of fungi
unicellular
colonial
complex/multicellular-mushrooms, puffballs
septae in molds
Cross walls found in fungi that allow flow of organelles and nutrients between adjacent compartments
Non-septate hyphae
one continuous cell
Vegetative hyphae
responsible for the visible
mass of growth
Reproductive or fertile hyphae
what appendages do prokaryotes have
flagella
fimbraie
pillus
what appendages do eukaryotes have
flagella
cillia
need to know about fungi
nutrition: heterotrophs-eat other organisms
reproduction: spores
can cause primary and secondary infection
mycoses
fungal infection
functions of fungi
used for antibiotics, alcohol and decomposing
fungal nutrition-Heterotrophic
acquire nutrients from a wide variety of organic substrates
fungal nutrition-saprobic
nutrition from dead plants
fungal nutrition-parasitic
grow on bodies of living animals or plants
fungi reproduction
spores
how do fungi eat
secrete enzymes outside their body and absorb the food
sporangiospores
formed on inside for protection
conidiospores
formed on outside for dispersion
protozoa
single celled, aquatic, heterotrophic
heterotrophic
eat other organisms
what do amoeba have instead of appendages
pseudopod
cyst
protozoa in bad environment
balled up protozoa
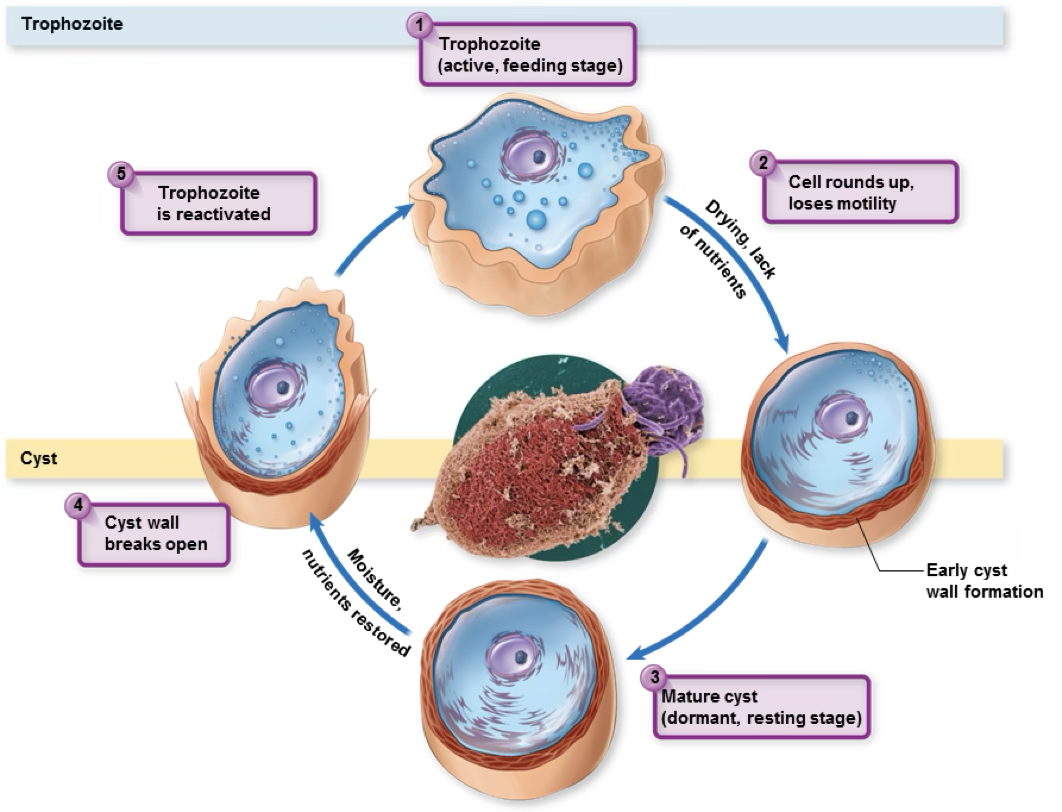
trophozoite
protozoa in good enviroment
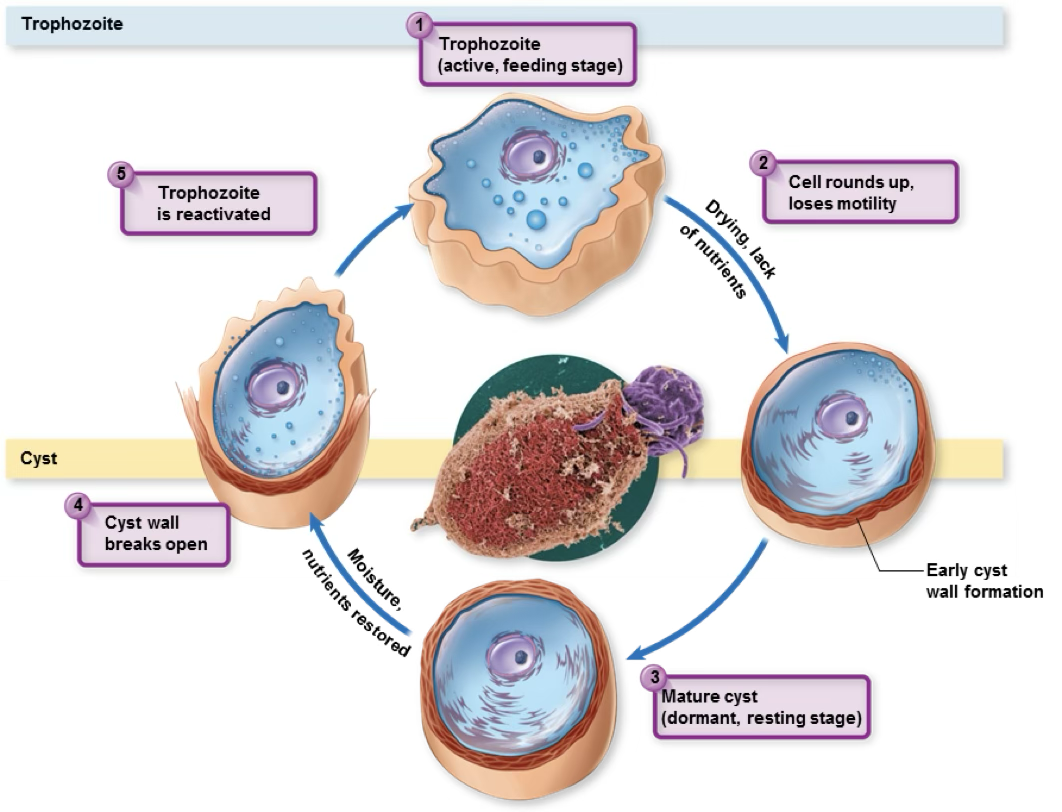
helminths
parasitic worms
tapeworms, flukes, roundworms
flat worms
called cestodes(tapeworms) and trematodes (flukes)
roundworms
also called nematodes
have organs
Enterobius vermicularis
pinworm disease
infestation of large intestine