Scapula and Clavicle pathology and anatomy
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
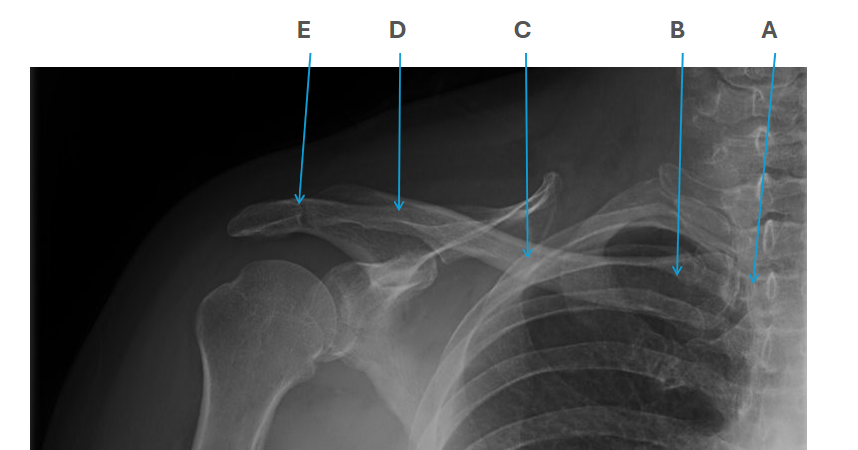
what is clavicle A
SC joint
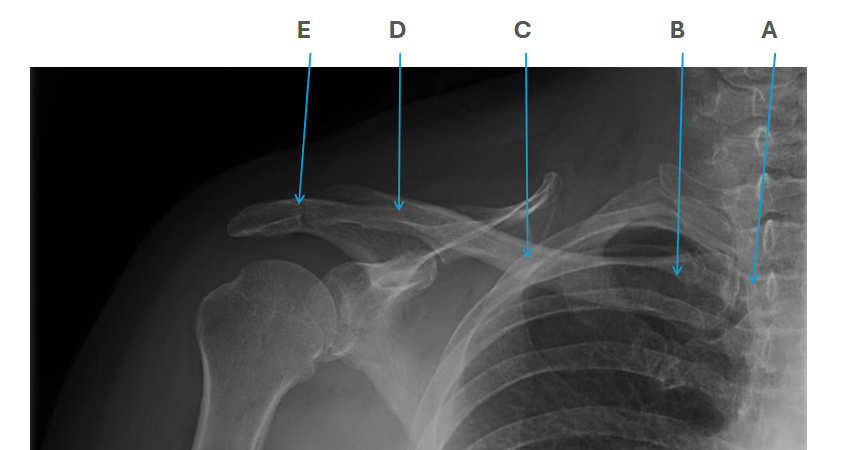
what is clavicle B
sternal end
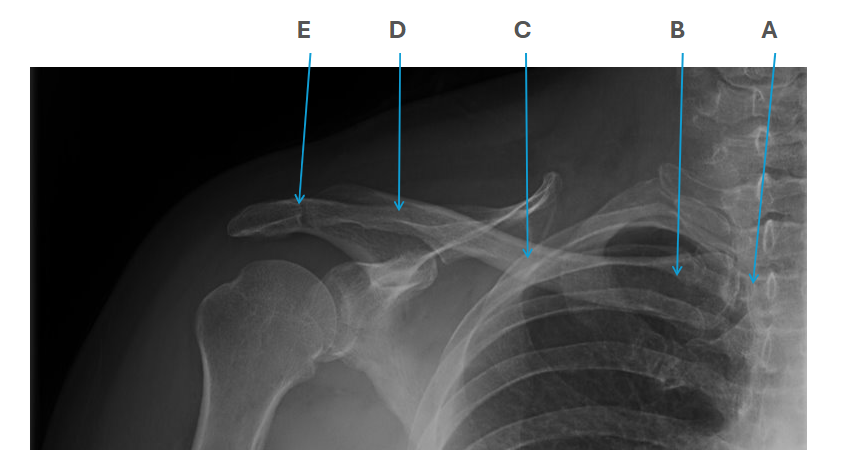
what is clavicle C
shaft/body
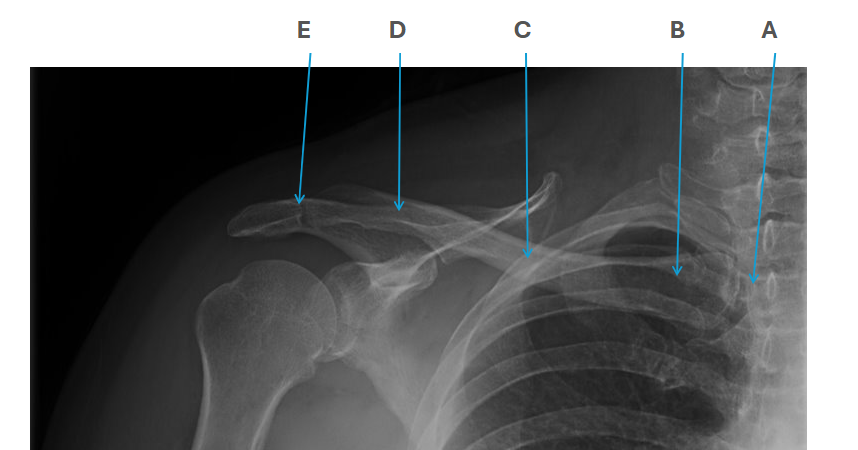
what is clavicle D
acromion
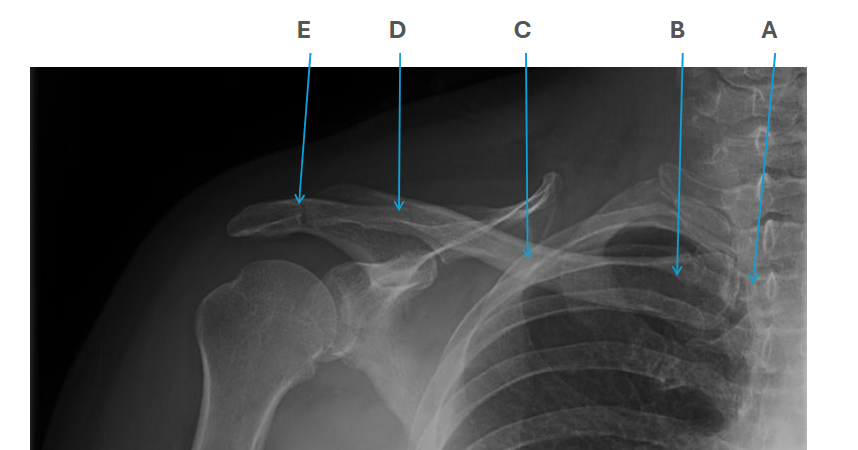
what is clavicle E
AC joint
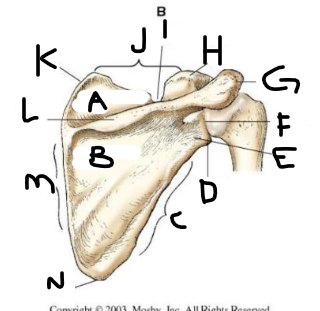
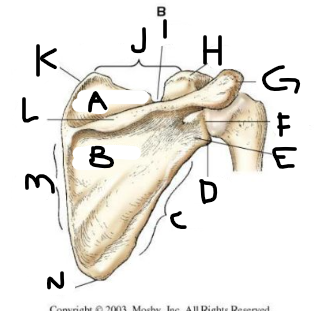
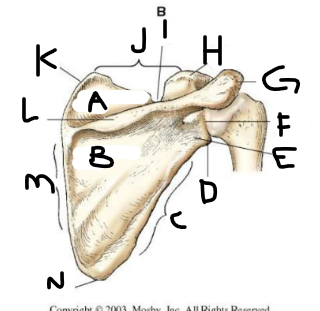
posterior scapula A
supraspinous fossa
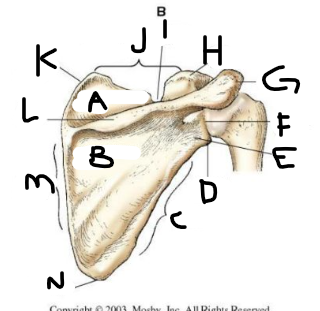
posterior scapula B
infraspinous fossa
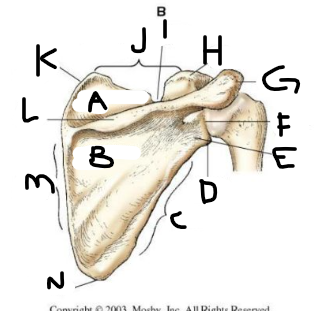
posterior scapula C
lateral border
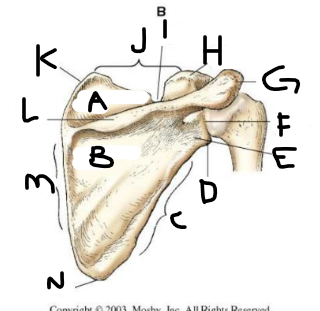
posterior scapula D
lateral angle
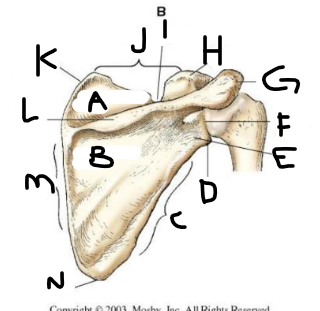
posterior scapula E
neck
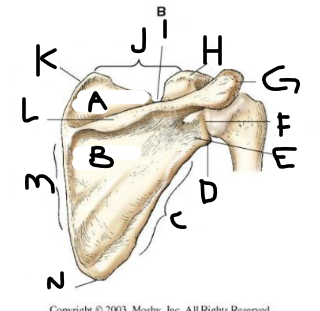
posterior scapula F
glenoid cavity
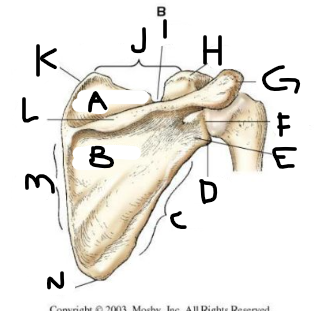
posterior scapula G
acromion
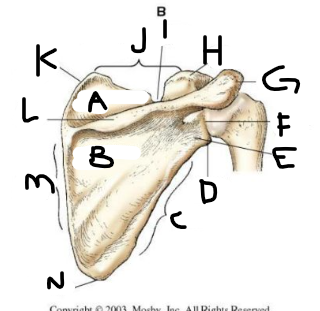
posterior scapula H
coracoid process
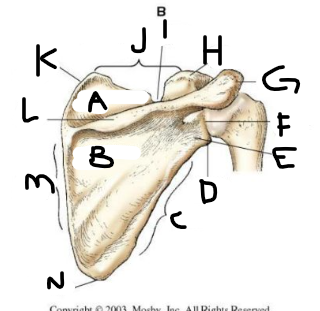
posterior scapula I
scapular notch
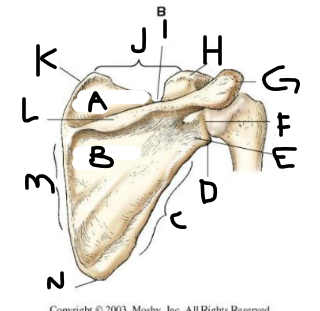
posterior scapula J
superior border
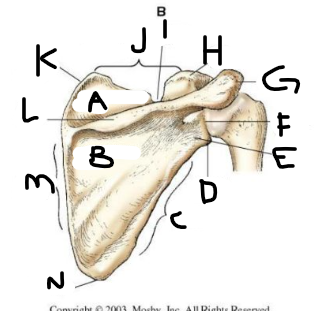
posterior scapula K
superior angle
posterior scapula L
crest of spine
posterior scapula M
medial border
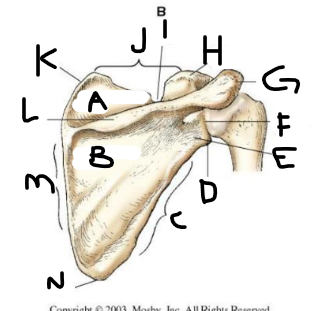
posterior scapula N
inferior angle
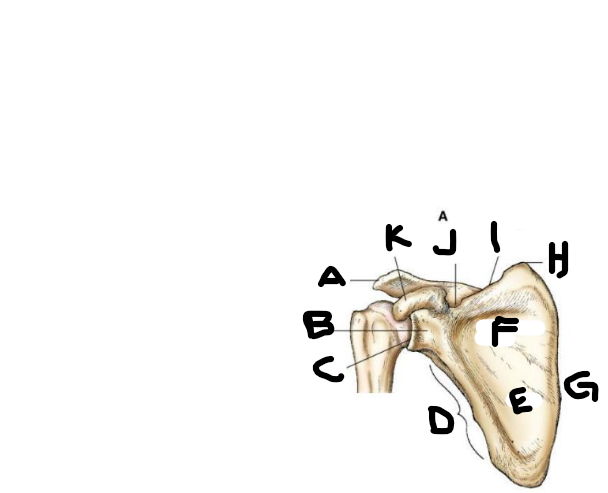
anterior scapula A
acromion
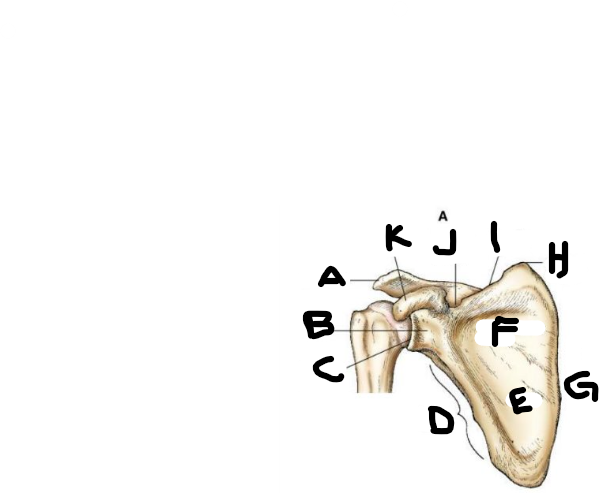
anterior scapula B
neck
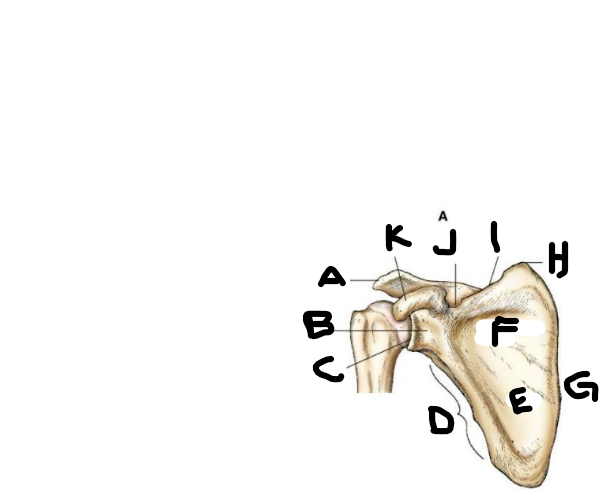
anterior scapula C
glenoid cavity
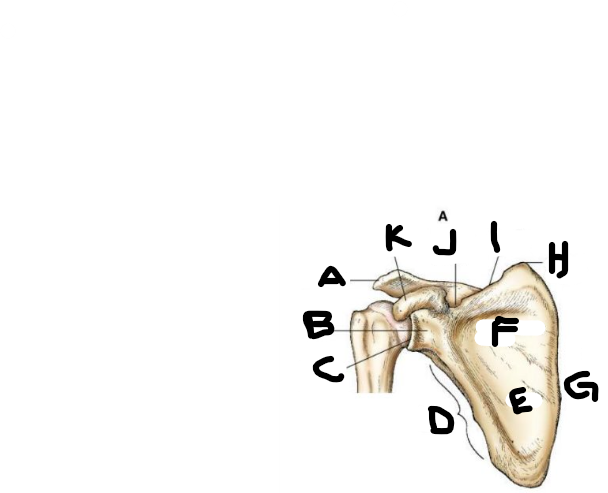
anterior scapula D
lateral border
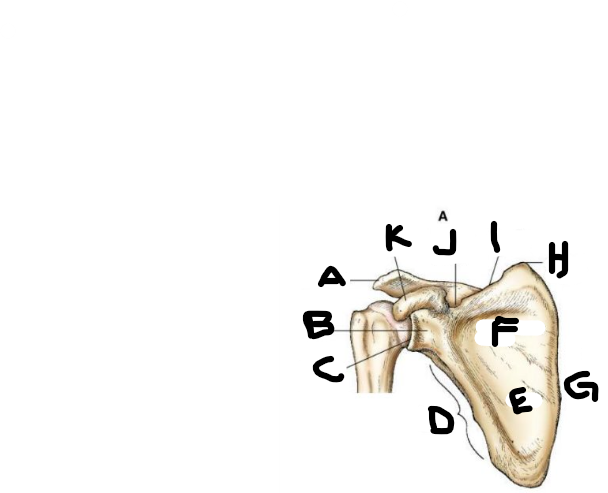
anterior scapula E
body
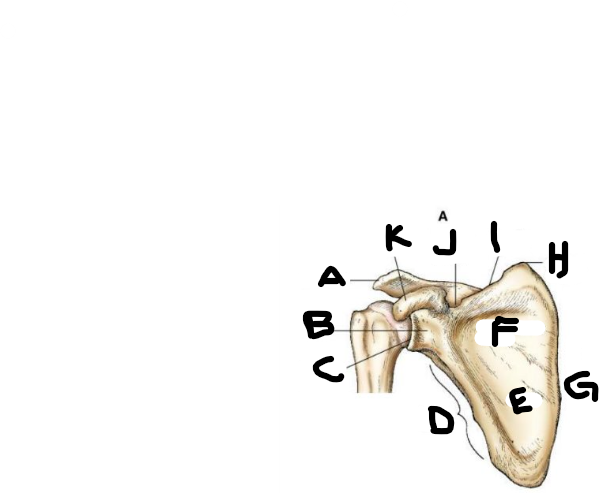
anterior scapula F
subscapular fossa
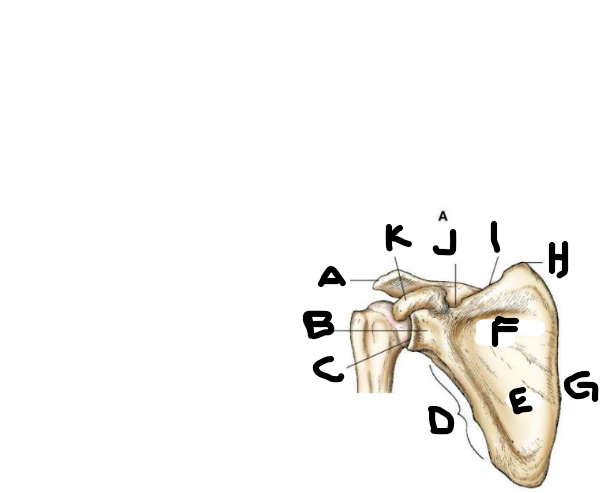
anterior scapula G
medial border
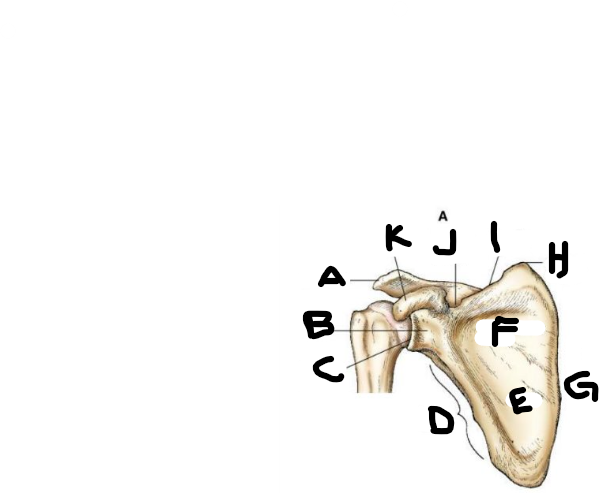
anterior scapula H
superior angle
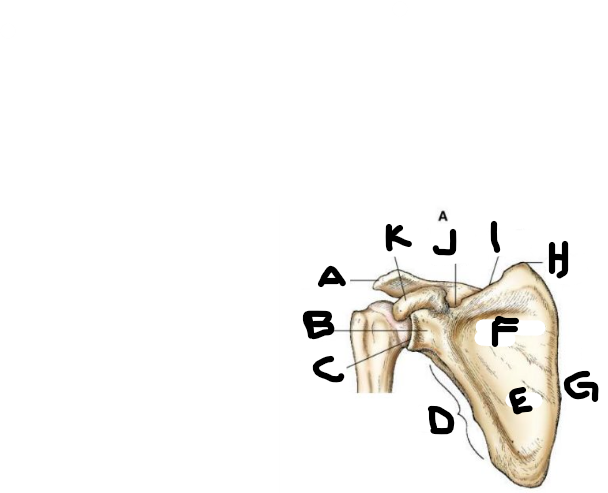
anterior scapula I
superior border
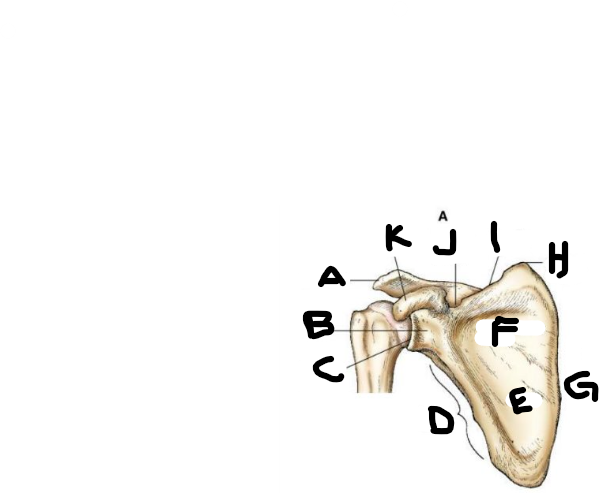
anterior scapula J
scapular notch
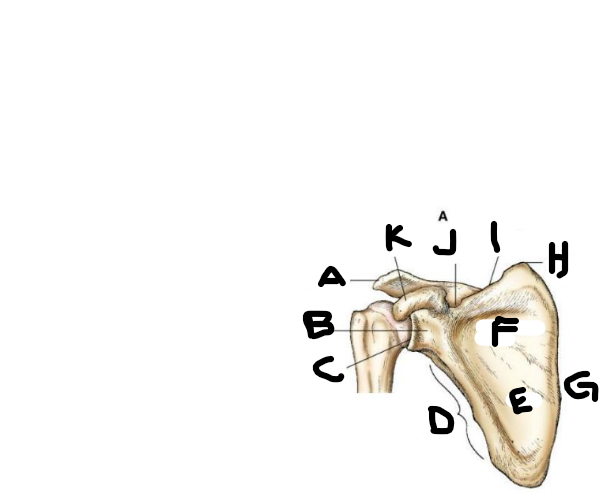
anterior scapula K
coracoid process
the clavicle on a female is
shorter, less curved
the clavicle on a male is
thicker, more curved
what type of bone is the clavicle
long bone (has two articular ends)
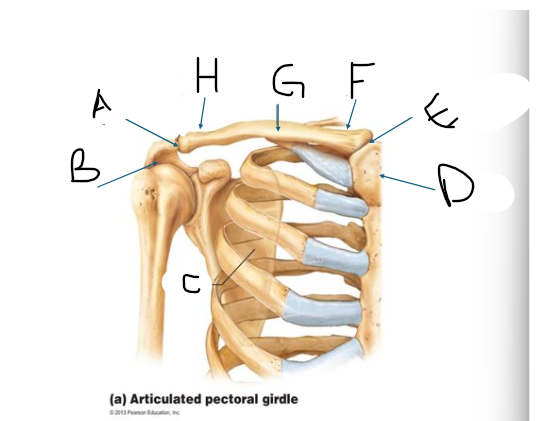
pectoral girdle A
AC joint
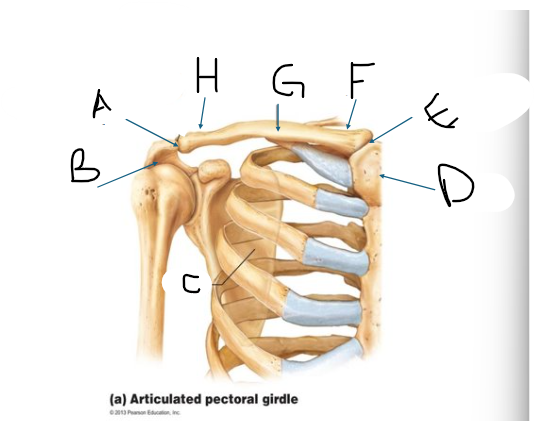
pectoral girdle B
acromion?
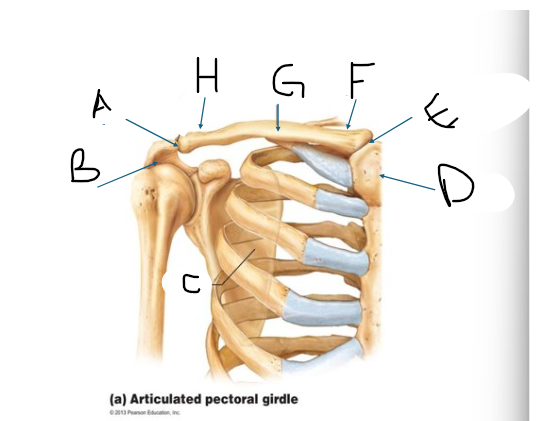
pectoral girdle C
scapula
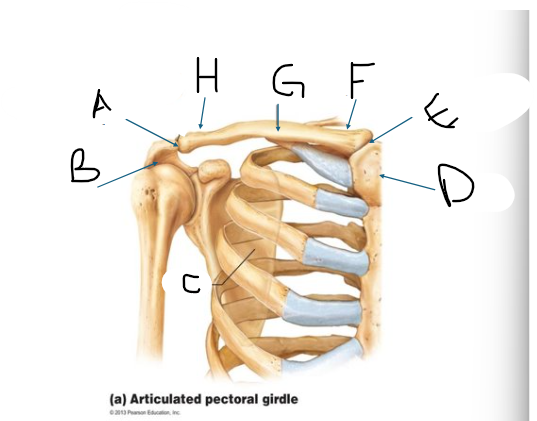
pectoral girdle D
manubrium/sternum
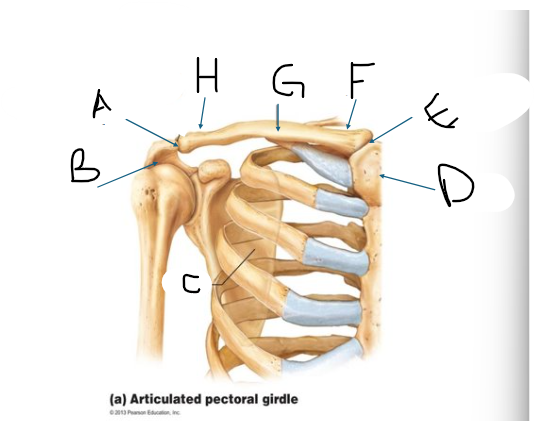
pectoral girdle E
SC joint
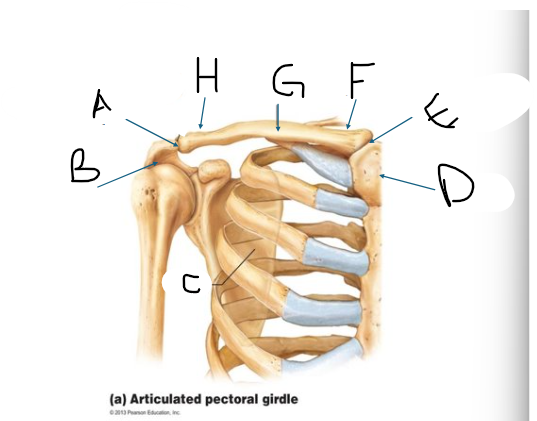
pectoral girdle F
sternal end
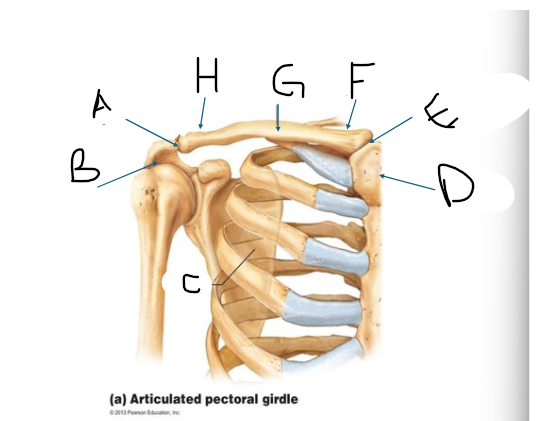
pectoral girdle G
clavicle body/shaft
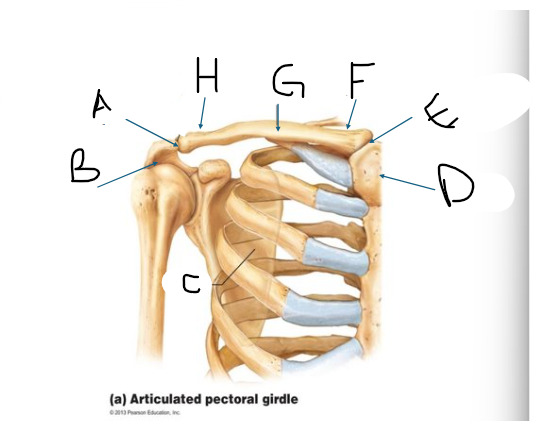
pectoral girdle H
acromial end
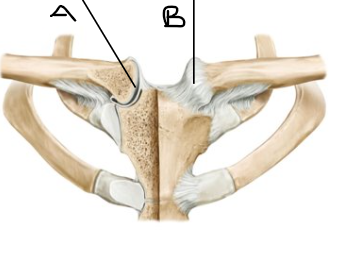
what is letter A? (joint)
sternoclavicular joint
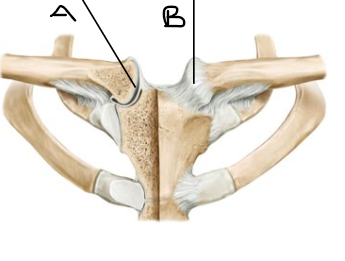
what is letter B? (joint)
sternoclavicular ligament
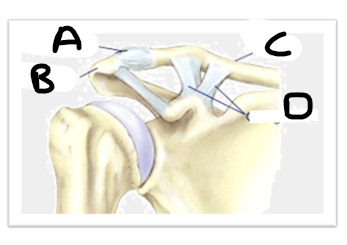
what is letter A (joint image)
AC ligament
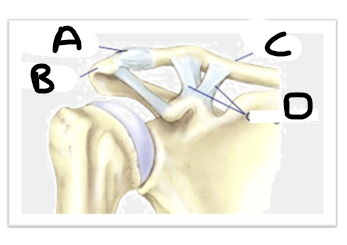
what is letter B (joint image)
acromion
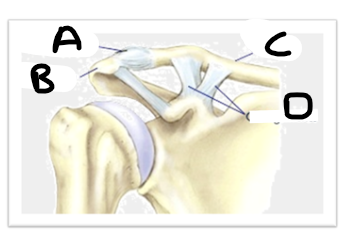
what is letter C (joint image)
clavicle
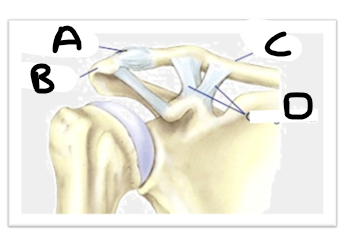
what is letter D? (joint image)
CC ligaments
acromioclavicular dislocation definition
clavicle separates from the scapula (acromion)
acromioclavicular dislocation cause
traumatic
radiographic appearance of acromioclavicular dislocation
widening of AC joint
technical change for acromioclavicular dislocation
no manual exposure factor change
impingement syndrome definition
impingement of the greater tuberosity and soft tissues on the coracoacromial ligamentous and osseous arch, generally during abduction (Bontrager)
impingement syndrome cause
trauma, idiopathic
radiographic appearance of impingement syndrome
the presence of bony excrescences arising from the anteroinferior aspect of the acromion and of flattening and sclerosis of the greater tuberosity of the humerus (RSNA) or os acromiale
technical change for impingement syndrome
no manual exposure factor change
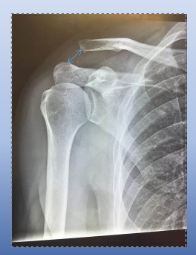
what is this an x-ray of?
acromioclavicular dislocation
Another cause of impingement syndrome
constant rubbing of the acromion and the rotator cuff (from class)
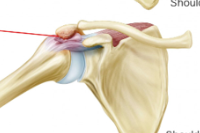
what is this an image of?
impingement syndrome
os acromiale
developmental aberration in which the distal acromion fails to fuse, can lead to impingement
AP Clavicle image critique
lateral half of clavicle above the scapula, with the medial half superimposing the thorax
entire clavicle centered on image
respiration for AP clavicle
suspended respiration
Merrill’s recommendations for AP clavicle
12 × 8 collimation
AP axial clavicle image critique
entire clavicle along with AC and SC joints
lateral 2/3rds of the clavicle projected above the ribs and scapula with the medial end superimposing the thorax
clavicle in horizontal orientation as compared with the AP projection
Merrill’s recommendations for AP axial Clavicle
0-15 degree for standing lordotic position
15-30 degrees for supine position
AP scapula image critique
lateral position of the scapular free of super imposition from the ribs
scapular horizontal and not slanted
scapular detail through the superimposed lung and ribs (shallow breathing should help obliterate lung detail)
acromion and inferior angle
lateral scapular (posterior oblique, AP projection)
lateral and medial scapular borders superimposed
no superimposition of the scapular body on the ribs
no superimposition of the humerus on the area of interest
inclusion of the acromion and inferior angle
Another way to do lateral scapula
can also be obtained as an Anterior Oblique (LAO or RAO) with affected side against the board
scapula is considered a
flat bone
anterior side of the scapula is called
costal side
posterior side of the scapula is called
dorsal side
the inferior border of the scapula is around the same location as the
7th rib
AC joints (AP Neutral/ AP neutral weightbearing image critique
AC joint visualized
L or R marker and weight bearing marker
AC joint separation, if present
Merrill’s note for AC joints
collimation 6×8
72” SID
recommends bilateral on one image
SC joints PA image critique
both SC joints and the medial ends of the clavicles
no rotation
SC joints PA oblique (RAO/ LAO) image critique
SC joint of interest in the center of the radiograph, with the manubrium and the medial end of the clavicles included
open SC joint space
SC joint of interest immediately adjacent to the vertebral column with minimal obliquity