World War 1 Review
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
Treaty of Versailles
Peace conference did not include all major powers.
No Central Powers were present or active in decision making.
Allied Big 3 were decision makers, and their approach varied widely.
1. US
2. Great Britain
3. FranceAdd Italy to make Big 4—but in reality decisions rested with the Big 3.
Major Provision of the Treat of Versailles
Established 9 new nations.
Countries “supposedly” along historically nationalistic lines.
Yugoslavia, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Austria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Finland, Poland.
Demilitarization of Germany.
Stripped Air Force.
Army left at 100,000 for national protection.
Navy almost completely gone.
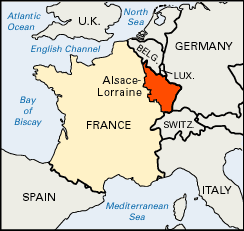
Alsace-Lorraine went to France.
$33 billion in war reparations to be paid by Germany.
War-guilt cause.
Germany acknowledges it was responsible for WW1.
Germany is named but not actually held solely responsible.
Establishment of the League of Nations.
League of Nations
Introduced by US President Woodrow Wilson.
Wilson also supported the idea of self-determination (rejected by Europe).
The right of people to choose their own form of government.
The League was based on the idea of collective security:
A system in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all.
More than 40 nations joined the League.
They agreed to negotiate disputes rather than resort to war and to take common action against any aggressor state.
The US Senate worried that joining the League would drag the nation in to future wars and therefore never ratified the treaty.
The US never joined the League of Nations.
This will weaken the League’s power.

Major Issues/Implications
Humiliation of Germany.
Russia lost more land than Germany.
Germany was stripped of colonial possessions.
Did not grant Italy and Japan the holdings they requested.
League of Nations lacked any power to enforce decisions.
