Biology 1001 Chapter 4
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
organelles, cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Prokaryotic Cell
•Bacteria and Archaea
•No nucleus
•DNA in unbound region called the nucleoid region
•No membrane-bound organelles
What is inside the plasma membrane as a prokaryote?
•Cytoplasm: region of the cell that is contained within the plasma membrane
•Nucleoid region: location of DNA
•Ribosomes: protein synthesizers

Eukaryotic cells
•Compartmentalized by internal membranes
•Organelles
•Each organelle has a unique structure and function
•DNA housed inside membrane-bound nucleus
•Fungi, protists, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells
Proteome
When cells within the same organism (same genome) can have very different morphologies and functions
Cytosol
•Inside plasma membrane BUT region of eukaryotic cells that is outside organelles

Cytoplasm
•Everything inside the plasma membrane, including cytosol

Eukaryotic organelles

•Semiautonomous organelles
•Mitochondria and chloroplasts
•Nucleus
•Ribosome
•Endoplasmic reticulum
•Rough vs smooth
•Golgi apparatus
•Lysosomes
•Vacuoles
•Peroxisomes
The cell is a….
PROTEIN FACTORY!
Semiautonomous organelles

•Contain own DNA
•Grow and divide to reproduce themselves
•Depend on the cell for synthesis of internal components
(mitochondria and chloroplast)
Mitochondrial Function
•Cellular Respiration: In the presence of oxygen it can convert organic macromolecules (mostly sugars) into Energy for the cell (ATP).

Chloroplast Function
•Photosynthesis: Harness light energy
•Uses water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
Nucleus
•Enclosed by the nuclear envelope
•Nuclear pores regulate entry and exit of molecules
•Functions:
•Protection, organization, replication
•Expression of genetic material
•Assembly of ribosomal subunits
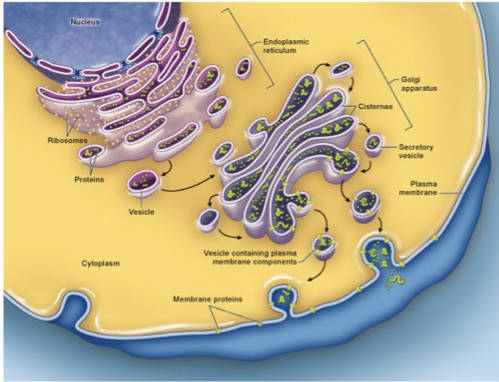
Ribosome
•Involved in protein production by assembling Amino Acids into polypeptides.
•Smallest organelles
•2 types
•Free: in the cytosol
•Bound: attached to E.R.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
•Structure
•Cisternae:
•Flattened, fluid-filled tubules made from a network of membranes
•2 types of ER (they are continuous):
•Rough ER
•Smooth ER

Rough ER
•Studded with ribosomes •Functions: •Sorting and fold proeins into tertiary structure •Synthesizing proteins •Glycosylating proteins and lipids •Attachment of carbohydrates to proteins and lipids |
Smooth Er
•Little to no ribosomes
•Functions in diverse metabolic processes:
•Carbohydrate metabolism
•Synthesis and modification of lipids
•Accumulation Ca2+
•Detoxifies drugs and poisons
Components of phospholipid bilayer
phospholipds
proteins
carboydrates
Leaflets
What is phospholipid bilayer is divided by
Leaflets
Half of a phospholipid bilayer
Asymmetrial —> extracellular, intracellular
What determines the fluidity of the membrane?
Lipid composition:
length of phospholipid tails
double bonds on phospholipid tails
cholesterol (animal cells)
Optimal bilayer fluidity is essential for a cell because…
function, growth, and division
Two types of integral proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Lipid-anchored proteins
Definition of an integral protein
Penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
Transmembrane proteins
span the membrane
hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Lipid anchored proteins
contain an amino acid that is covalently attached to a lipid
Peripheral proteins
loosely associated with membrane surface
Selective Permeability
allowing passage of some ions and molecules
allows cells to maintain favorable internal environment
Golgi Apparatus
•Stack of flattened, membrane bound compartments
•Cis
•Medial
•Trans
Functions:
Directs the processing of molecules from the ER
Protein “assemble, package and sort”
Quality control of protein-modification
Secretion of cellular molecules
Lysosomes
•Involved in intracellular digestion of macromolecules and pathogens
•Contain: acid hydrolases
•Break down polymeric molecules into monomers
•Requires water
•Function optimally at acidic pH
Vacuoles
•Function: storage, regulation of cell volume, and degradation
•Plants have one large central _____
Peroxisomes
•Single membrane, fluid-filled lumen
•Functions:
•Breakdown organic molecules
•Catalyze detoxifying reactions
What cell are lysosomes found in?
•Animal cells only
What cells are peroxisomes?
All eukaryotic cells
Endomembrane system is a network of membranes including
Nuclear envelope
•Endoplasmic reticulum
•Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
Nuclear Envelope
•Encloses nucleus
•Double membrane
•Outer membrane continuous with ER membrane
•Nuclear pores: regulates entry and exit of molecules
Endomembrane system/Major Function?
•Protein sorting/exportation
What are the two types of ribosome?
•Free: in the cytosol (creates cytosolic protein)
•Bound: attached to E.R. (creates protein that enters the endomembrane system)
What is a peroxisomes
•Use catalase to break down hydrogen peroxide H2O and O2

How does each protein reach its appropriate final destination

Protein Sorting
What are the three sorting signals?
•No signal
•Cotranslational sorting
•Post-translational sorting

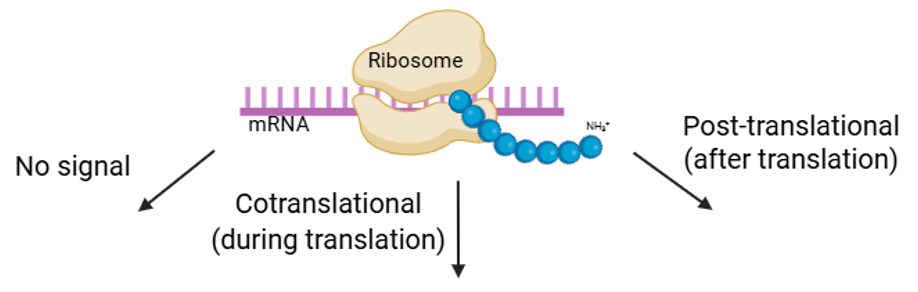
No signal
Cytoplasm
Cotranslational Sorting
ER
Golgi
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
Secretion
Post translational
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
Peroxisome
What 3 qualities do semiautonomous organelles have?
•Contain own DNA
•Depend on the cell for synthesis of internal components
•Grow and divide to reproduce themselves

Mitochondrion
•Plural: mitochondria
•Outer and inner membranes
•Inner membrane
•Highly folded
•Cristae
•Mitochondrial matrix
•Outer membrane

Chloroplast
•Carry out photosynthesis
•Structure
•Membranes:
•Inner membrane
•Outer membrane
•Thylakoid membrane

Functions of Smooth ER
-carbohydrate metabolism
-synthesis and modification of lipids
-accumulation of ca2+
-detoxifies drugs and posions
Functions of Rough ER
-sorting and folding proteins into tertiary structure
-synthesisizing proteins
-glycosating protiens and lipids (attachment of carbohydrates)
Functions of golgi apparatus
Directs the processing of molecules from the ER
Protein “assemble, package and sort”
Quality control of protein-modification
Secretion of cellular molecules
What are the four factors that affect ability of solute to pass through the membrane
size
polarity
charge
concentration
3 general ways to move across membranes
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
active transport
Passive transport includes
Simple and Facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion
higher concentration to lower concentration
passive transport —> no energy required
What is passive transport
does not require energy
molecules more down their concentration gradient: higher concentration not lower concentration
Osmosis
net diffusion of free water across a membrane
What type of transport is osmosis
PASSIVE
Define tonicity
ability of a surrounding of solution to cause a cell to gain or lose free water
3 types of tonicity
isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic
isotonic
solutie equal on both sides of the plasma membrane
hypertonic
higher solute concentration
hypotonic
lower solute concentration
Active transport
requires input of energy
moving lower concentration to higher