LC CHEMISTRY- GASES
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
REBECCA'S LC CHEMISTRY GASES KNOWT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Mole definition
amount of pure substance that contains (6.02×10^23) of particles
Avogadro's number (number of particles in 1 mole)
6 x 10²³
Molar mass DEFINITION
the mass of one mole of a substance in grams
Diffusion
the spontaneous spreading out of a substance due to the natural movement of its particles
Temperature
a measure of the degree of hotness of an object
Convert from Celsius to Kelvin
add 273 to the Celsius value
SI unit of temperature
Kelvin
0 K
the temperature at which a gas would occupy zero volume, if it could be cooled indefinitely without becoming a liquid or a solid
SI unit of pressure
N/m² or Pascal
Normal atmospheric pressure in Pa
100,000 Pa
SI unit of volume
m³
Number of litres in 1 m³
1000 L
Standard temperature in kelvins
273 K
Standard pressure (Pa)
100,000 Pa
Boyle's Law
at constant temperature, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
Charles' Law
at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its temperature measured on the Kelvin scale.
Gay-Lussac's Law of Combining Volumes
when gases react together, they do so in volumes which bear a simple whole number ratio to one another and to the volumes of any gaseous products, provided the volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure
Equation for Combined Gas Law
P₁ x V₁/T₁ = P₂ x V₂/T₂
Avogadro's Law
equal volumes of gases under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, contain equal numbers of molecules.
Molar volume in words def
The volume occupied by one mole of any gas
Molar Volume at s.t.p.
22.4 L
The 5 Assumptions of the Kinetic theory of Gases
gases are made up of particles that are in continuous motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container.
there are no attractive or repulsive forces between the molecules of a gas.
the volume of the gas molecules is negligible compared with the spaces between them.
when molecules collide, the collisions are perfectly elastic.
the average kinetic energy of the molecules is proportional to the temperature in Kelvin scale.
2 Limitations to the Kinetic theory of Gases
there are attractive and repulsive forces between the molecules of a gas
volume of gas particles not negligible compared to the distances between them.
Ideal gas
a gas which obeys all the gas laws and under all conditions of temperature and pressure
Conditions at which real gases behave most like/become closest an ideal gas
low pressure
high temperature
Equation of State for an Ideal Gas
pV=nRT
why does ammonia gas deviate from ideal gas behaviour
strong H bonding (intermolecular forces) between molecules
why is charles law consistent with pV=nRT (state for ideal gas equation)
n and R are constant for fixed mass or gas and p also constant
Suggest a way that further deterioration of the painting1 by this chemical reaction could be prevented or delayed (chemical: malachite)
keeping it dry
give 2 reaosns why real gases (steam etc) deviate from ideal behaviour at high pressure and low temperatures
collisions are not elastic
intermolecular (van der waals) forces
which of the real gasses are most likely to act like an ideal gas and why?
hellium, lowest boiling point
m3 from cm3
cm3 × 10-6
litres to m3
Litres/1000
R
8.3 JK-1 mol-1
n
number of moles
T
temperature in Kelvin
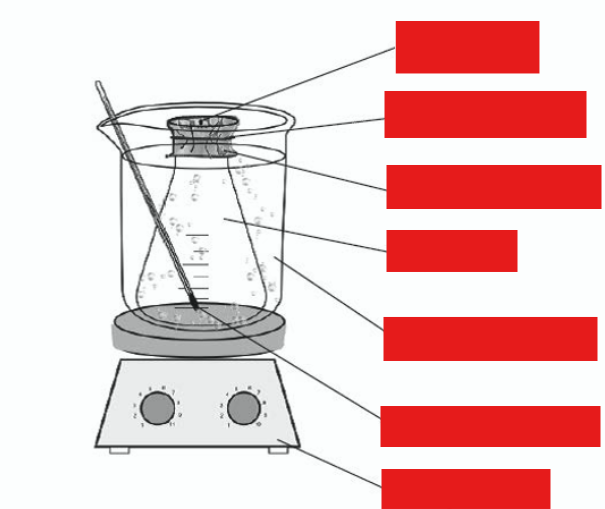
label this diagram
pinhole
aluminium foil
boiling water
vapour
hotplate
rubber band
thermometer
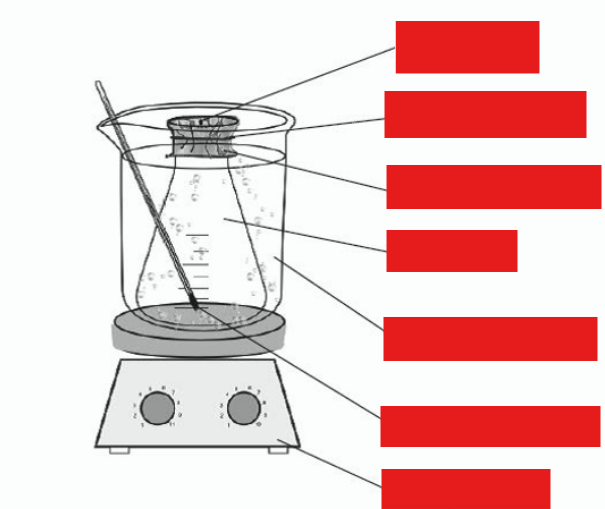
describe this diagram using words
flask sealed (covered with foil) with small hole (pinhole) immersed so that at least half is underwater
Volatile liquid
a liquid with low boiling point
Relative molecular mass
average mass of a molecule compared to 1/12 of the carbon 12 isotope