Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
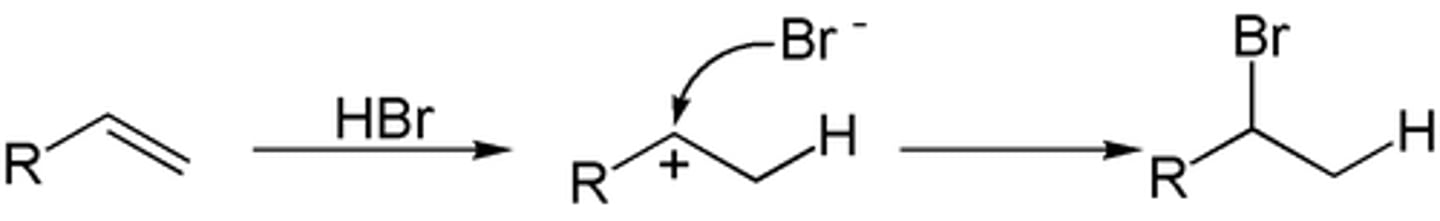
Hydrohalogenation of alkenes
- The addition of H and a halogen (Br)
- Markovnikov
- Forms a stable carbocation
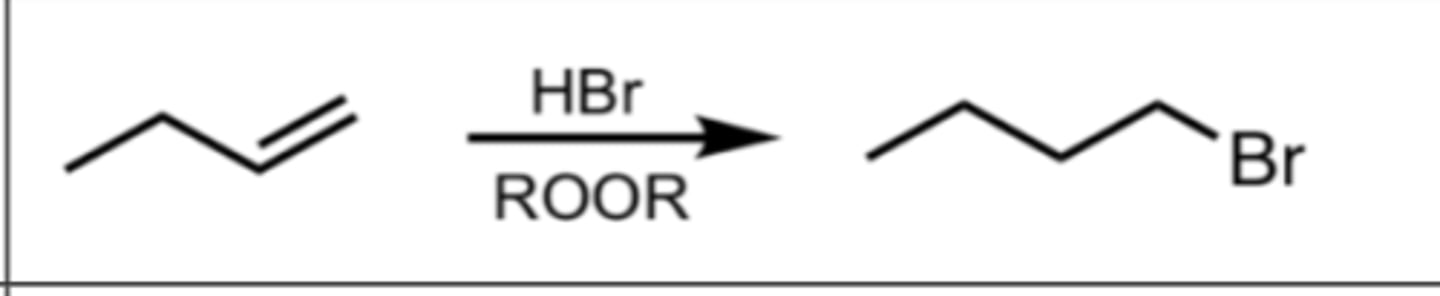
Hydrohalogenation with peroxide in alkenes
- The addition of a halogen (Br) and H with the use of a free-radical mechanism
- The use of free-radicals makes this anti-markovnikov
- No carbocation, but instead forms a stable free radical
Acid-catalysed hydration of alkenes
- Addition of H and OH
- Markovnikov, forms a stable carbocation
- Needs an acid catalyst to happen
- Acid catalysts include H+, H2SO4, or just H3O+
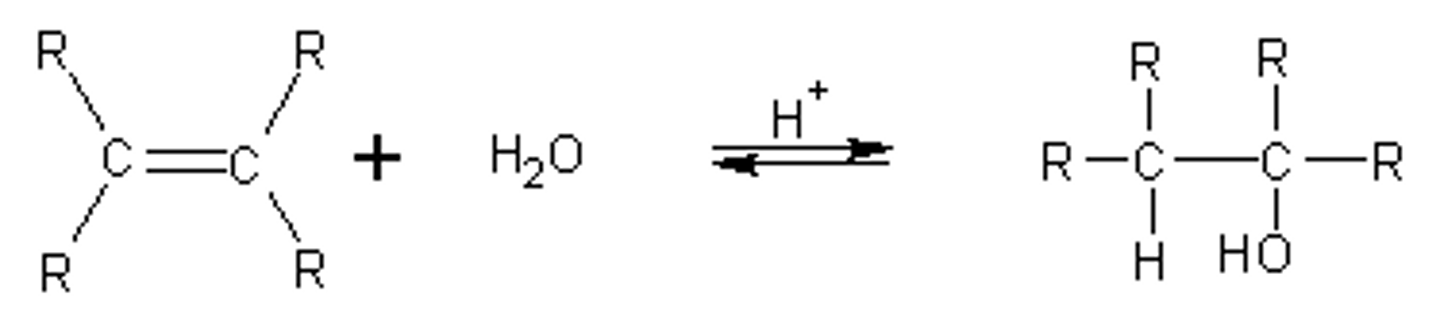
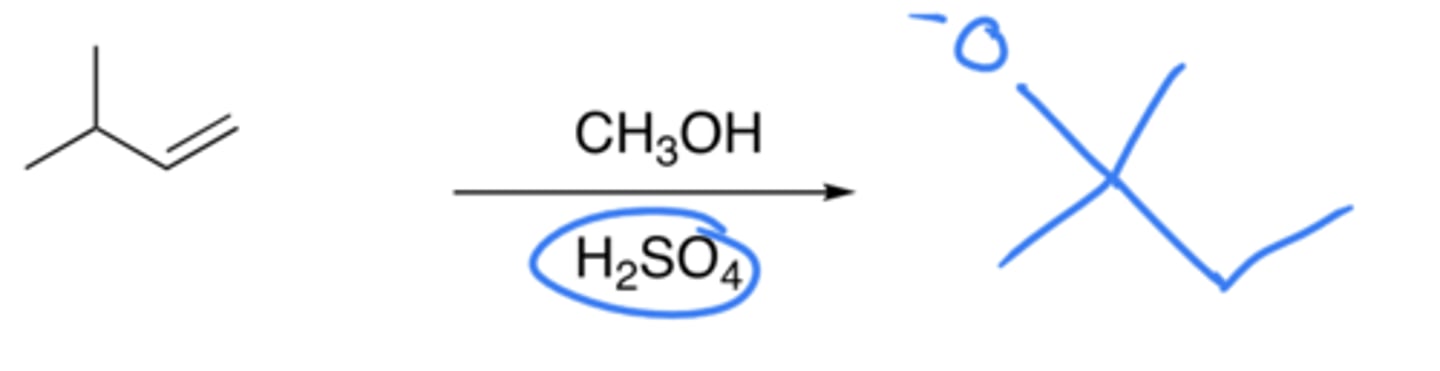
Acid-catalysed ether formation of alkenes
- Addition of H and OCH3
- This is a hydration reaction, but instead of H2O, we use CH3OH
- Markovnikov, forms a stable carbocation
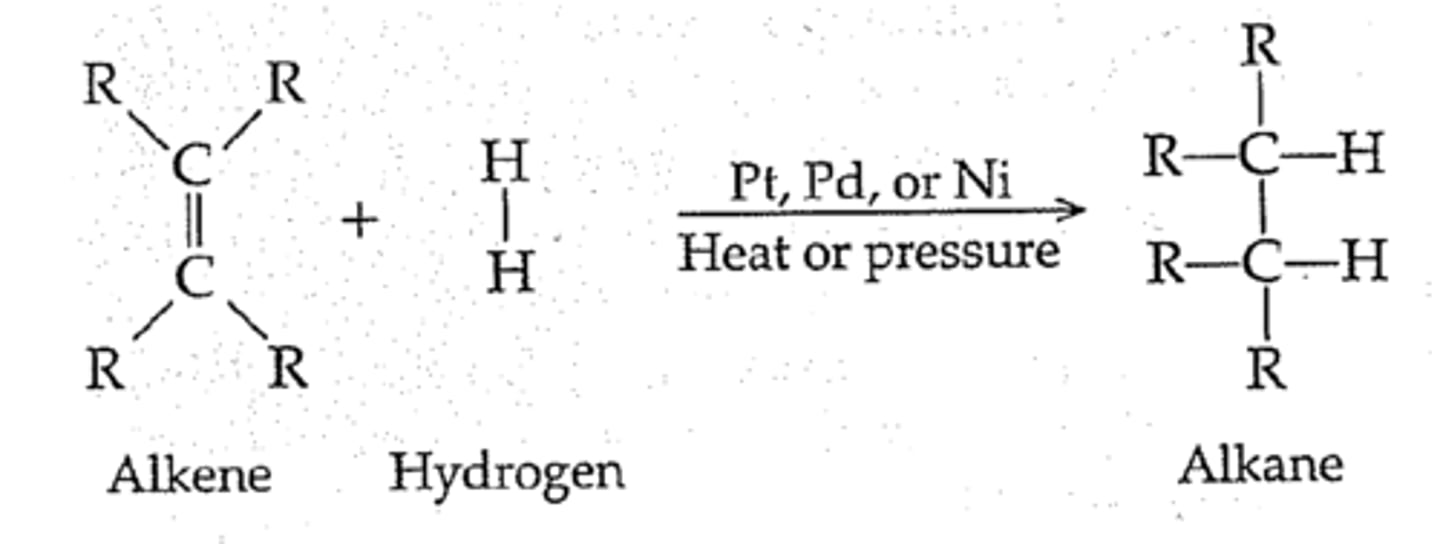
Hydrogenation of alkenes
- Addition of two H molecules
- Syn-addition
- Uses a metal catalyst (Pt)
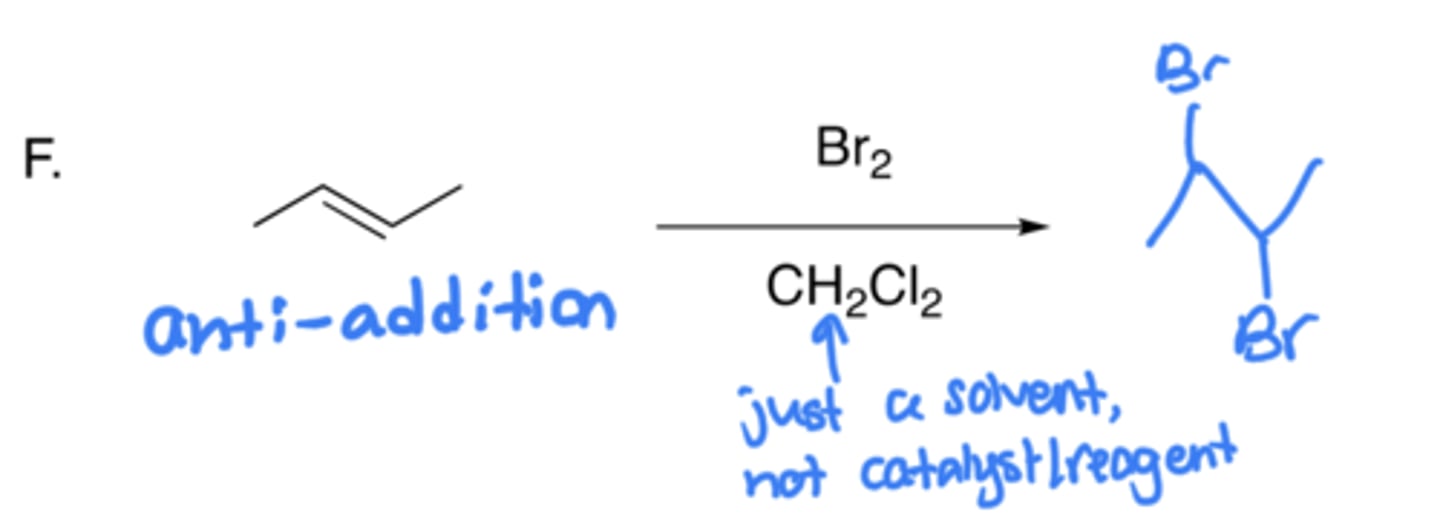
Halogenation of alkenes
- Addition of two halogens (Br)
- Anti-addition, no carbocation (due to cyclic bromonium formation)
- Uses a solvent like Ch2Cl2
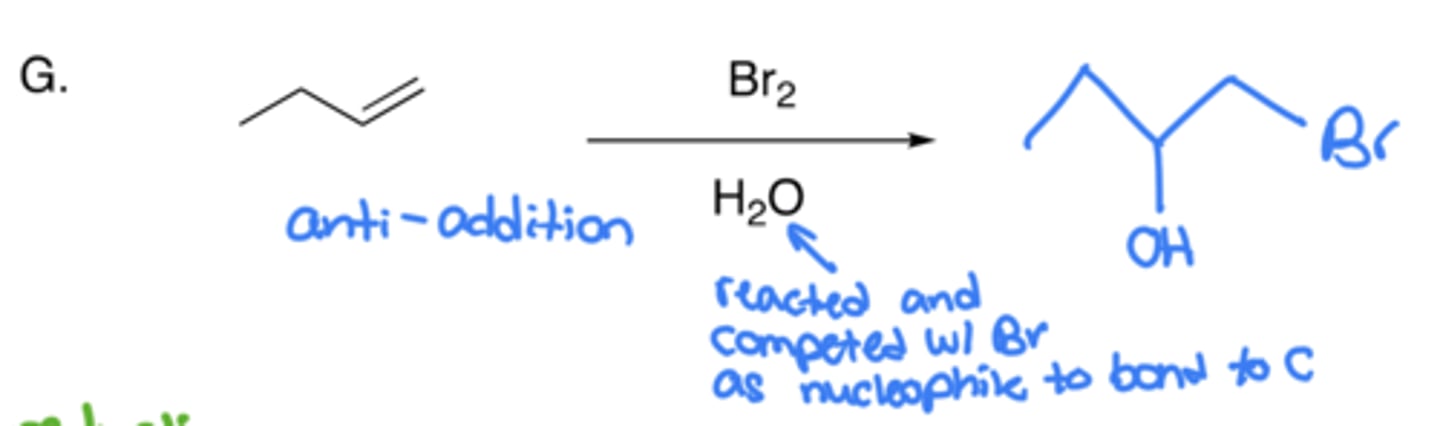
Halohydrin formation
- Addition of a halogen (Br) and OH
- Anti-addition, no carbocation (due to cyclic bromonium formation)
- The same thing as halogenation, but uses H2O as solvent instead of Ch2Cl2
- The H2O competes with Br to bind to C, and it wins because it is high in abundance
- The H2O attaches to the C with least H (Markovnikov)
- Can also be done with CH3OH or NaCl, where OH or Cl would add instead of Br
Oxymercuration-Reduction
- Addition of H and OH
- Markovnikov, no carbocation (no shift)
- Makes and alcohol like hydration and hydroboration-oxidation, but this may be done if no carbocations/shifts are wanted with markovnikov
- Step 1 Oxymercuration [ Hg(OAc)2 / H2O) ]: Hg-OAc bonds to C with least H and then H2O attacks the C with least H as a nucleophile; the left over OAc- takes an H off of the H2O, leaving it as OH- on the C
- Step 2 Reduction [ (NaBH4) / (NaOH) ]: The C-Hg bond is replaced with a C-H bond with the H coming from BH4
![<p>- Addition of H and OH</p><p>- Markovnikov, no carbocation (no shift)</p><p>- Makes and alcohol like hydration and hydroboration-oxidation, but this may be done if no carbocations/shifts are wanted with markovnikov</p><p>- Step 1 Oxymercuration [ Hg(OAc)2 / H2O) ]: Hg-OAc bonds to C with least H and then H2O attacks the C with least H as a nucleophile; the left over OAc- takes an H off of the H2O, leaving it as OH- on the C</p><p>- Step 2 Reduction [ (NaBH4) / (NaOH) ]: The C-Hg bond is replaced with a C-H bond with the H coming from BH4</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c15f53a1-b4dd-43af-9f1a-6f40a1ad9c13.png)
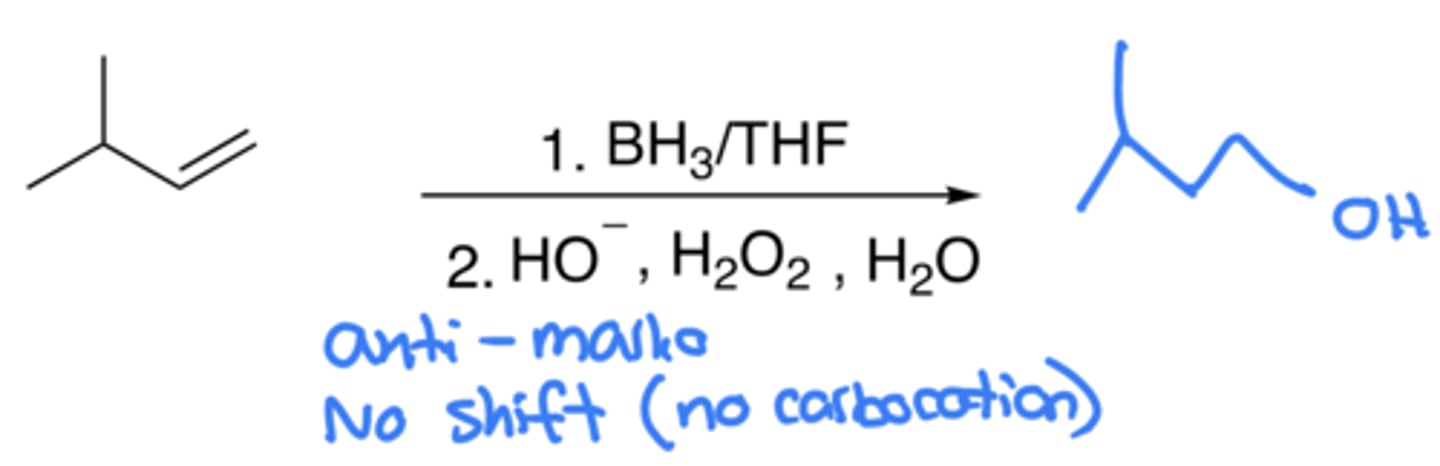
Hydroboration-Oxidation of alkenes
- Addition of OH and H
- Anti-Markovnikov, no carbocation (no shift)
- Same thing as hydration and oxymercuration-reduction, but this may be done if no carbocations wanted with anti-markovnikov
- Step 1 Hydroboration (BH4): An H in BH4 attacks the C with least H as a nucleophile, while BH3 attaches to the other C
- Step 2 Oxidation (OH-, H2O2, H2O): H2O2, OH-, and H2O are used in sequence to replace the BH3 on the C with OH
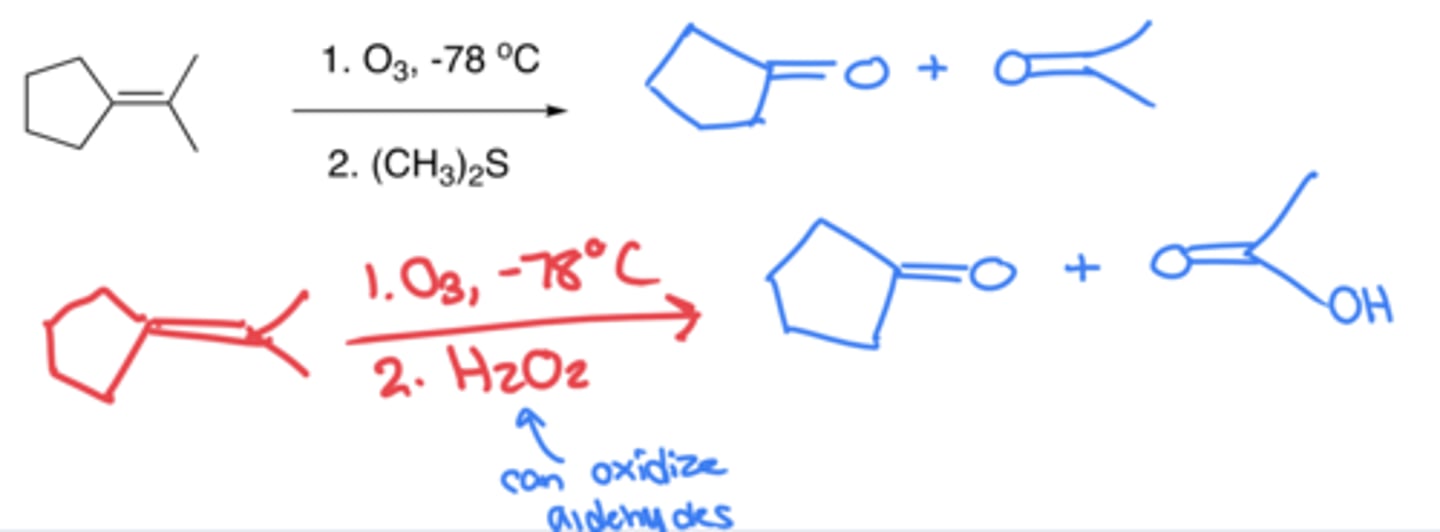
Ozonolysis
- Breaking of a double bond and forming ketones or aldehydes
- The usual solvent is (CH3)2S, but if done in H2O2, any resulting aldehydes would be oxidized with carboxylic acid groups
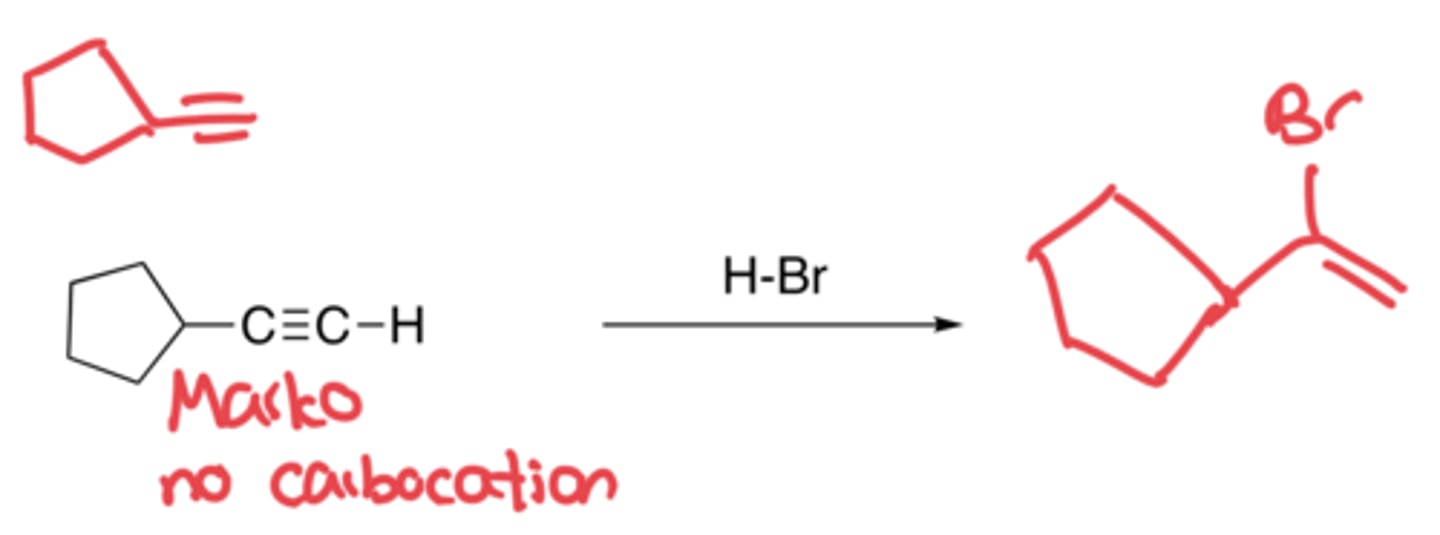
Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
- Addition of H and Br
- Markovnikov, no carbocation rearrangement
- If there is excess HBr, one more Br can be added to the C with least H
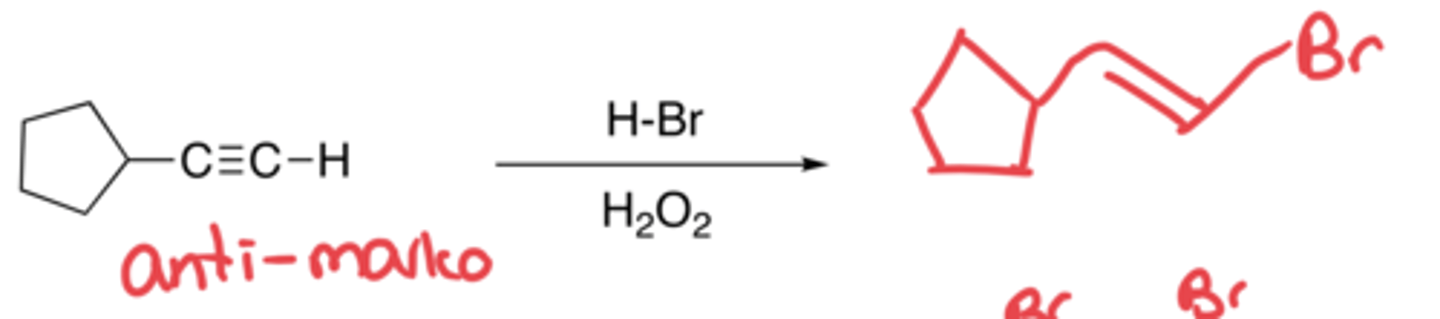
Hydrohalogenation with peroxide in alkynes
- Addition of Br and H with the use of free radicals
- Anti-markovnikov, no carbocation
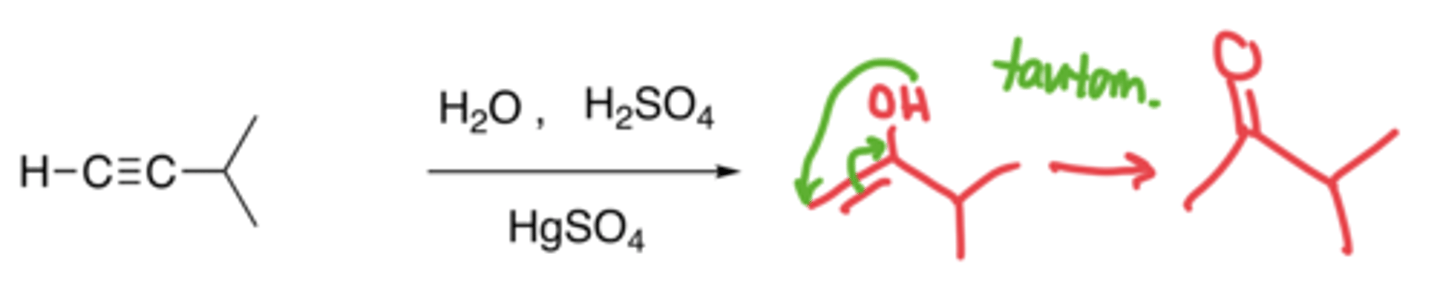
Hydration of alkynes
- Addition of an H and OH to make an alcohol, which then gets tautomerized into a ketone
- Markovnikov, no carbocation
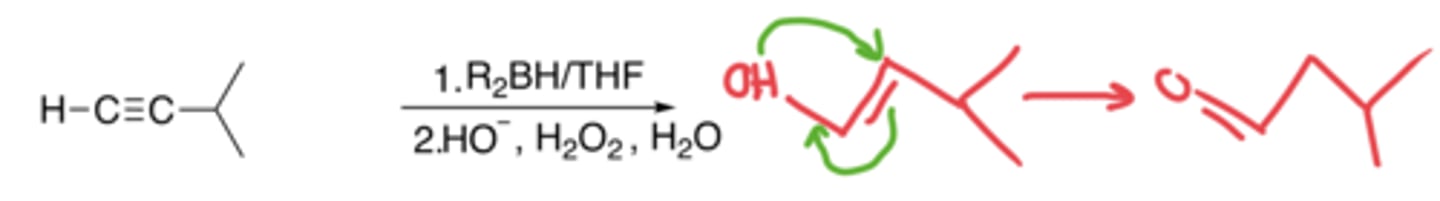
Hydroboration of alkynes
- The addition of an H and OH to make an alcohol, which gets tautomerized into a ketone
- Anti-markovnikov, no carbocation
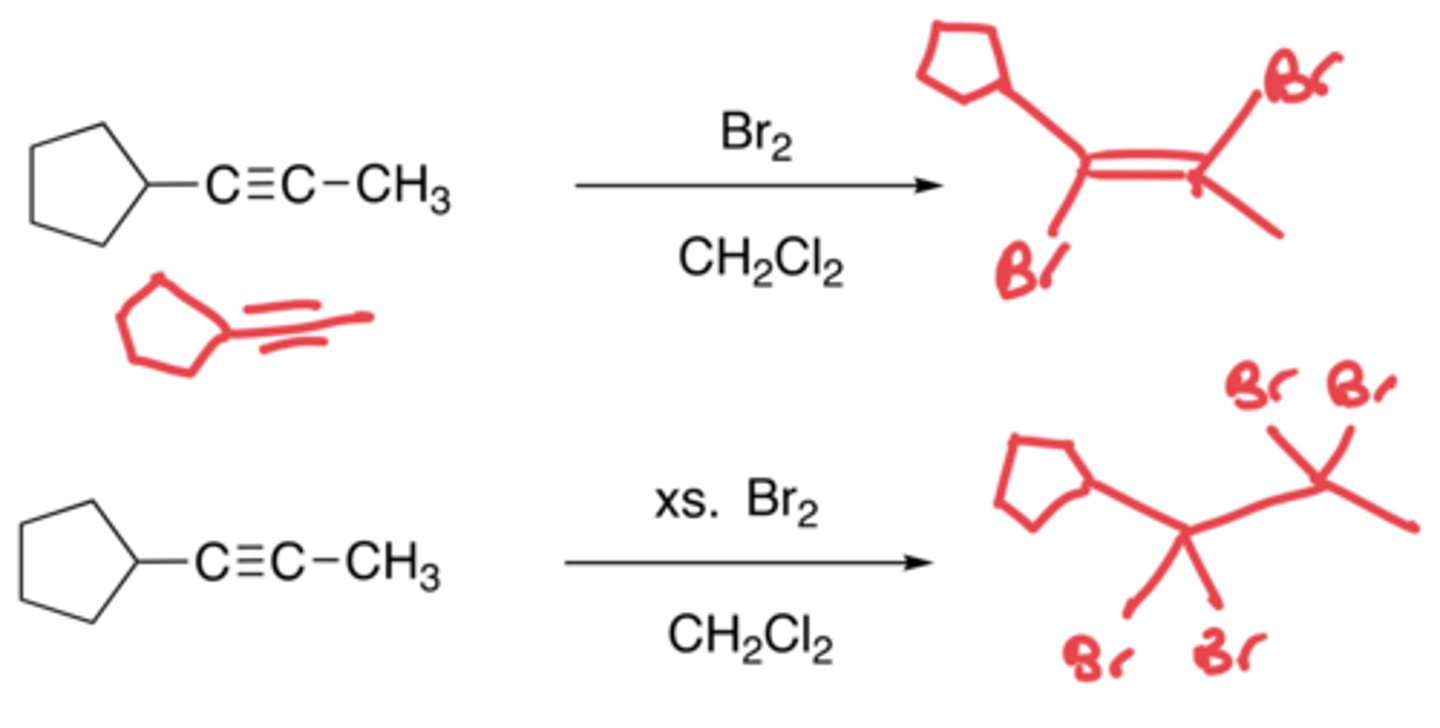
Halogenation of alkynes
- The addition of two halogens (Br) to an alkyne
- Anti-addition, no carbocation due to cyclic bromonium ion
- Uses a solvent like Ch2Cl2
- If excess Br2, two more will be added to the structure
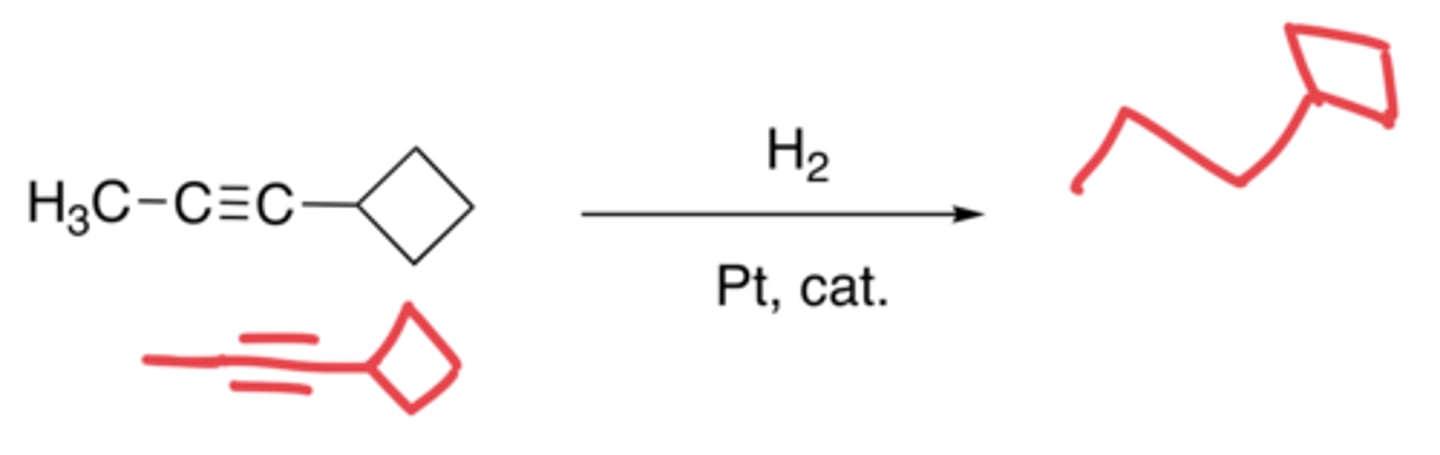
Hydrogenation of alkynes (Pt catalyst)
- The addition of H molecules
- Syn-addition
- Makes an alkane, no in between
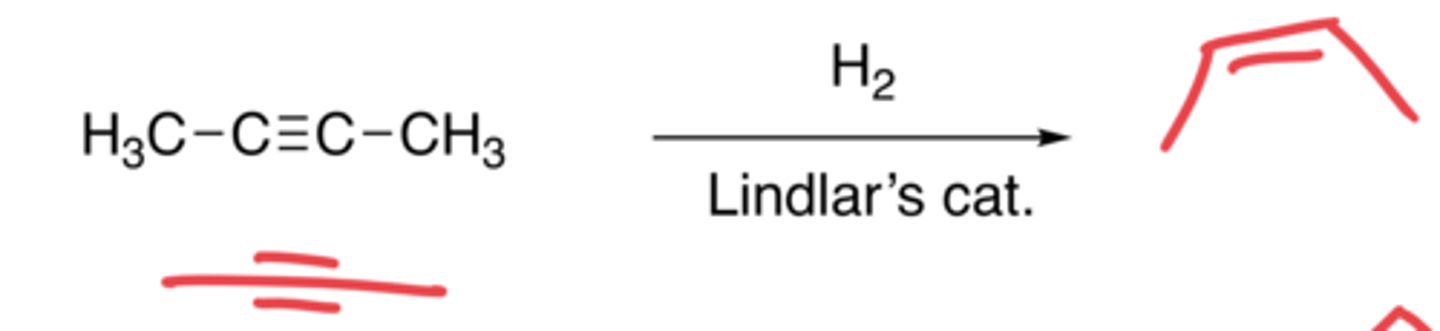
Hydrogenation of alkynes (Lindlar's catalyst)
- The addition of H molecules
- Syn-addition
- Makes a cis alkene
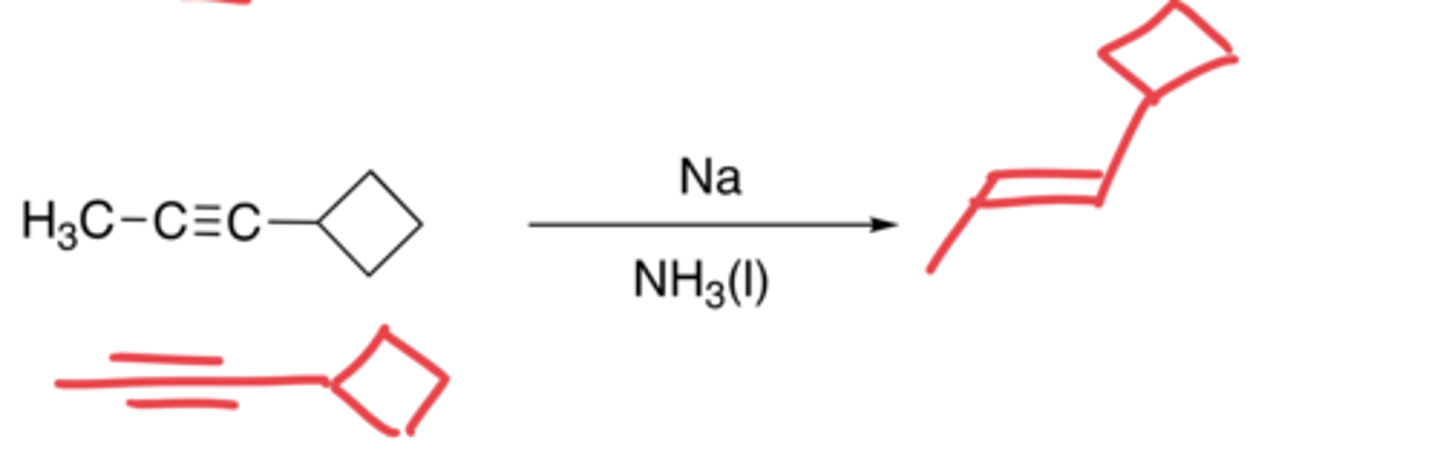
Hydrogenation of alkynes (Na/NH3 (l))
- The addition of H molecules
- Syn-addition
- Makes a trans alkene