Systems Path Section 6 - Pulmonary infections
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
alveolar inflammation from infection causing fever and lung consolidation
pneumonia
what type of acute bacterial pneumonia affects multiple lobes?
bronchopneumonia
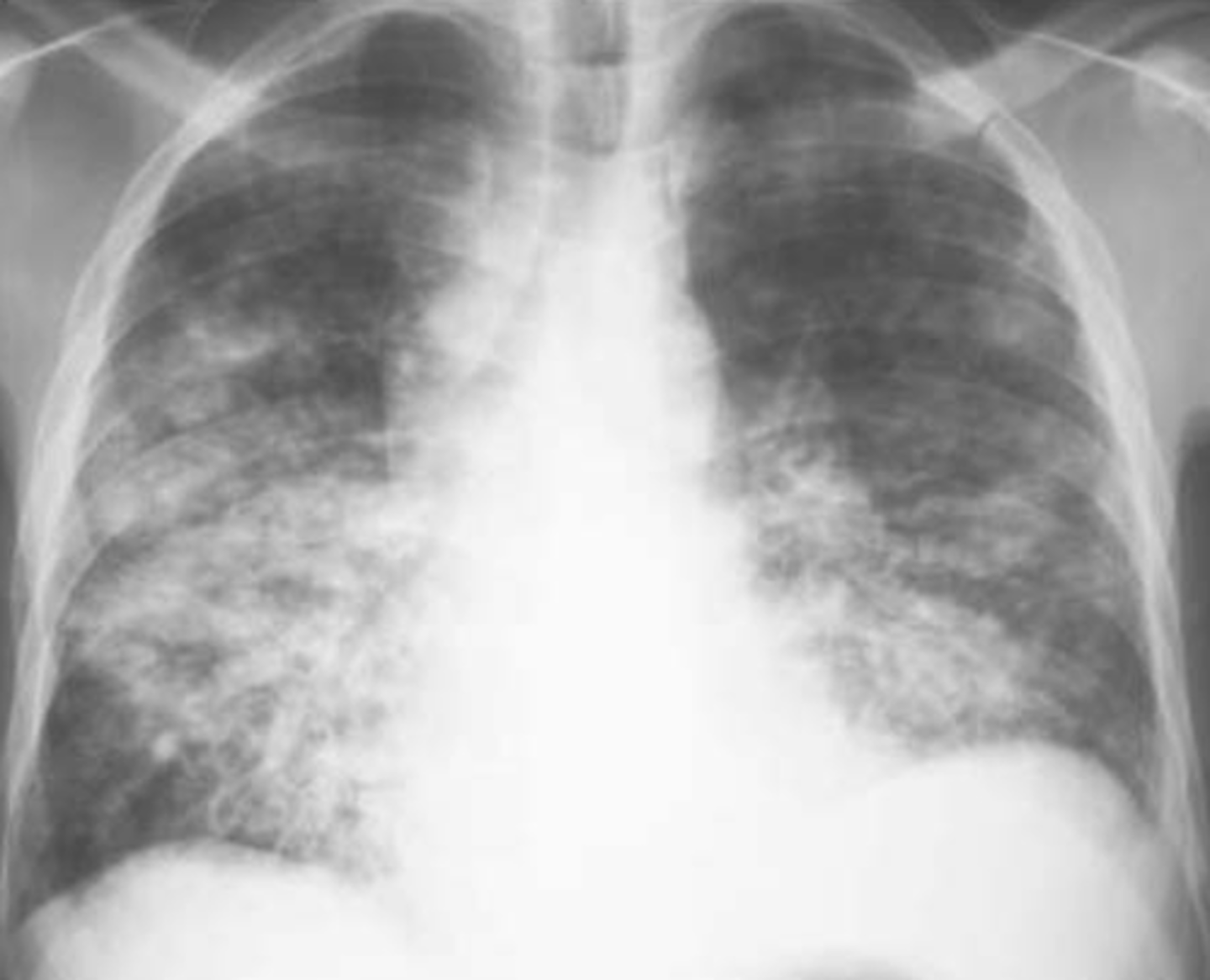
90% of lobar pneumonia is from what?
strep. pneumoniae
what type of pneumonia affects a single lobe, has homogenous consolidation and an abrupt line of radiopacity?
lobar pneumonia
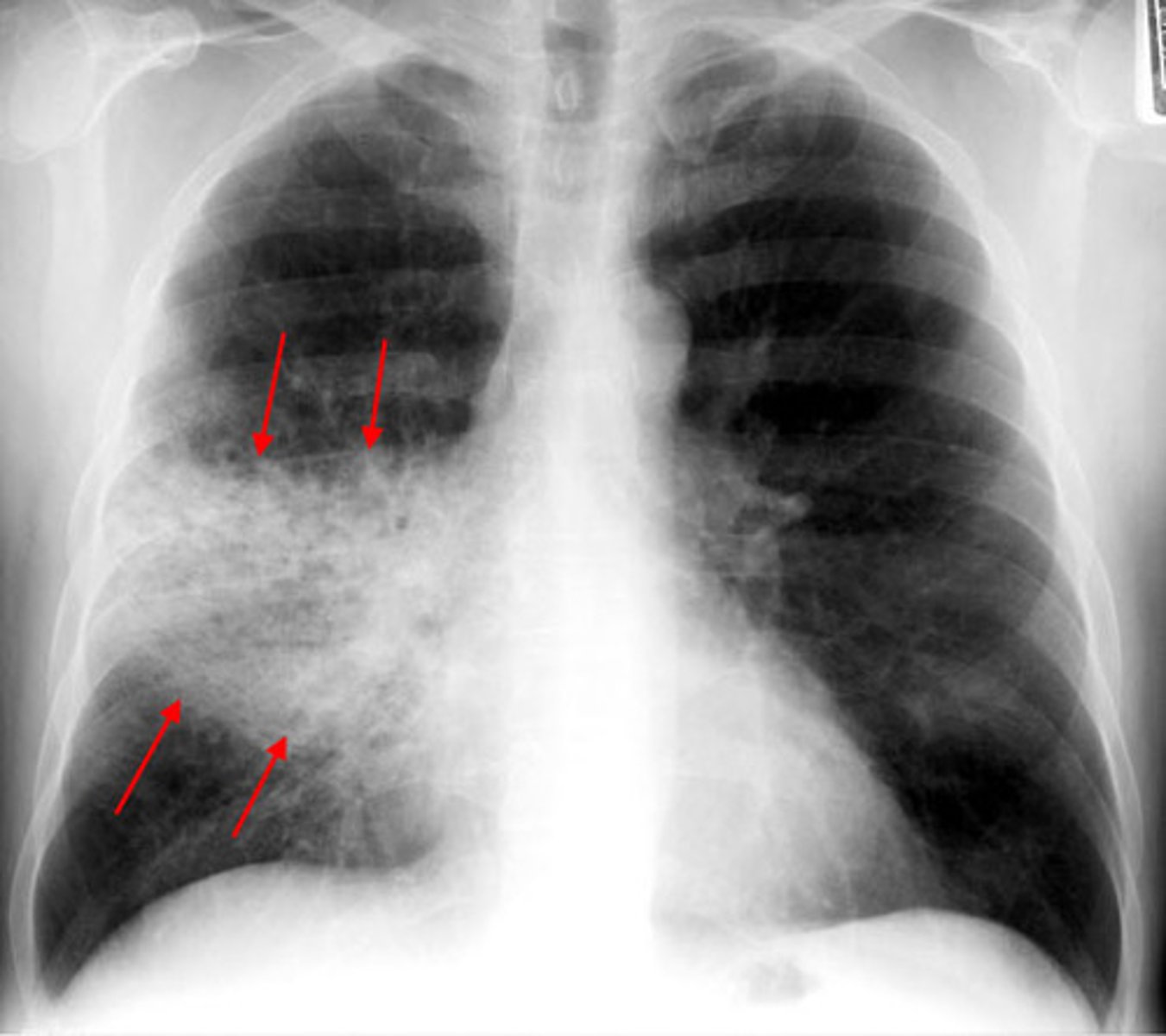
acute lung infection from strep pneumonia, commonly follows a viral URTI, causing productive cough, fever and dyspnea
community-acquired acute pneumonia (able to be seen on X-ray)
how does community-acquired acute pneumonia develop?
local inflammation -> consolidation
risks factors associated with developing community-acquired acute pneumonia
diabetes, CHF, COPD, immunosuppression, reduced splenic function
a lobar pneumonia caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila which causes dyspnea, fever and aches
legionnaire disease
pathology caused by legionella pneumophila causing a mild URTI
pontiac fever
"self limited" acute lung infection from common cold virus/mycoplasma pneumonia ; causes non-productive cough and mild dyspnea
community-acquired atypical pneumonia
how does community-acquired atypical pneumonia develop?
local inflammation of alveolar septa ( no consolidation on X-ray)
what is different about community-acquired atypical pneumonia?
edema is confined to alveolar septa
community-acquired atypical pneumonia causative agent
mycoplasma pneumoniae
what type of pneumonia is caused by staph aureus (MC) or E.coli and acquired after being in a hospital setting for 48+ hours?
hospital-acquired (nosocomial)
Symptoms of hospital acquired pneumonia
productive cough, dyspnea, fever
how does hospital acquired pneumonia develop?
local inflammation = consolidation (able to be seen on xray)
pneumonia caused by inhalation of foreign material such as gastric contents
aspiration pneumonia
aspiration pneumonie causative agents
strep pneumoniae, staph aureus, H. influenze
areas of suppurative necrosis due to bacterial infection causing foul/purulent septum, cavitation (right-side), fever, cough, etc.
lung abscess
causes of a lung abscess
aspiration, bronchial obstruction, hematogenous spread
chronic infection of mycobacterium tuberculosis which is the MC cause of infectious disease worldwide
tuberculosis
What type of tuberculosis simply means infected, not symptomatic or contagious?
primary
what type of tuberculosis is symptomatic with hemoptysis, productive cough, fever and malaise and the infection is no longer dormant
secondary
what is TB diagnosed by?
tuberculin test
how does primary TB develop?
sensitization and walling off in granulomas
how does secondary TB develop?
re-emergence of T-cell hypersensitivity resulting in destructive cavitations
How is TB transmitted?
respiratory droplets
who is most likely to get TB?
80% in endemic areas of Africa and Asia
subpleural caseous granulomas
ghon focus
sub pleural and lymph node regions have granulomas (tuberculoma)
ghon complex
calcification and fibrosis of hisar nodes
ranke complex
systemic tuberculosis infection caused by pulmonary lymphatic and hematogenous spread
military tuberculosis
who can develop military TB?
anyone with secondary TB
MC form of extrapulmonary TB
lymphadenitis
TB in the spine
Pott's disease
what poses as a risk for developing pneumonia?
immunosuppression (AIDS, transplant recipients, elderly, radiation)
opportunistic viral pathogen causing fever and respiratory infection
cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)
hallmark of CMV
owl's eye appearance
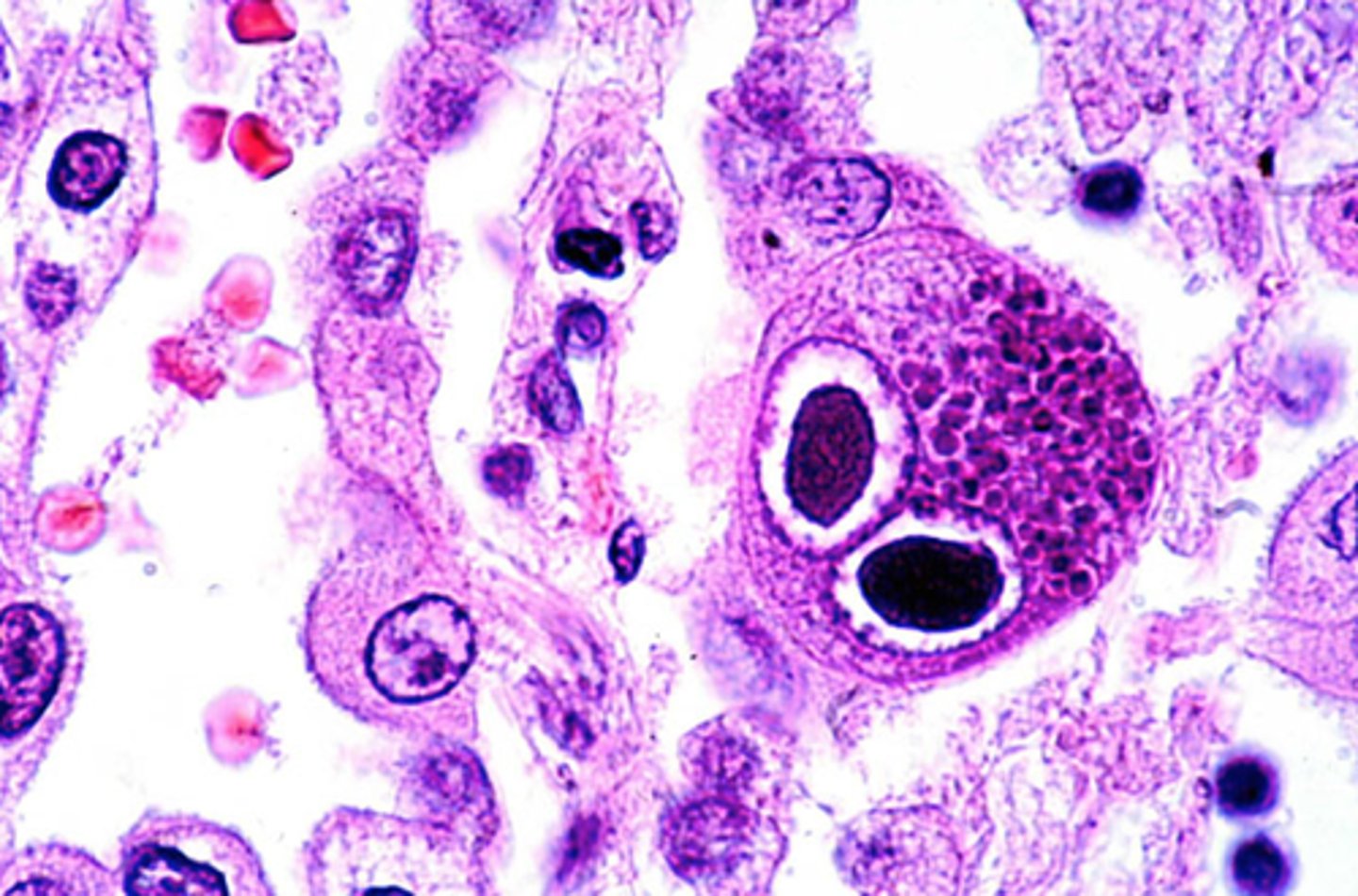
opportunistic fungal affection associated with AIDS, transplant patients, malnourished infants
pneumocystis pneumonia
pneumocystis pneumonia causative agent
Pneumocystis jiroveci
hallmark of pneumocystis pneumonia
cup-shaped cyst
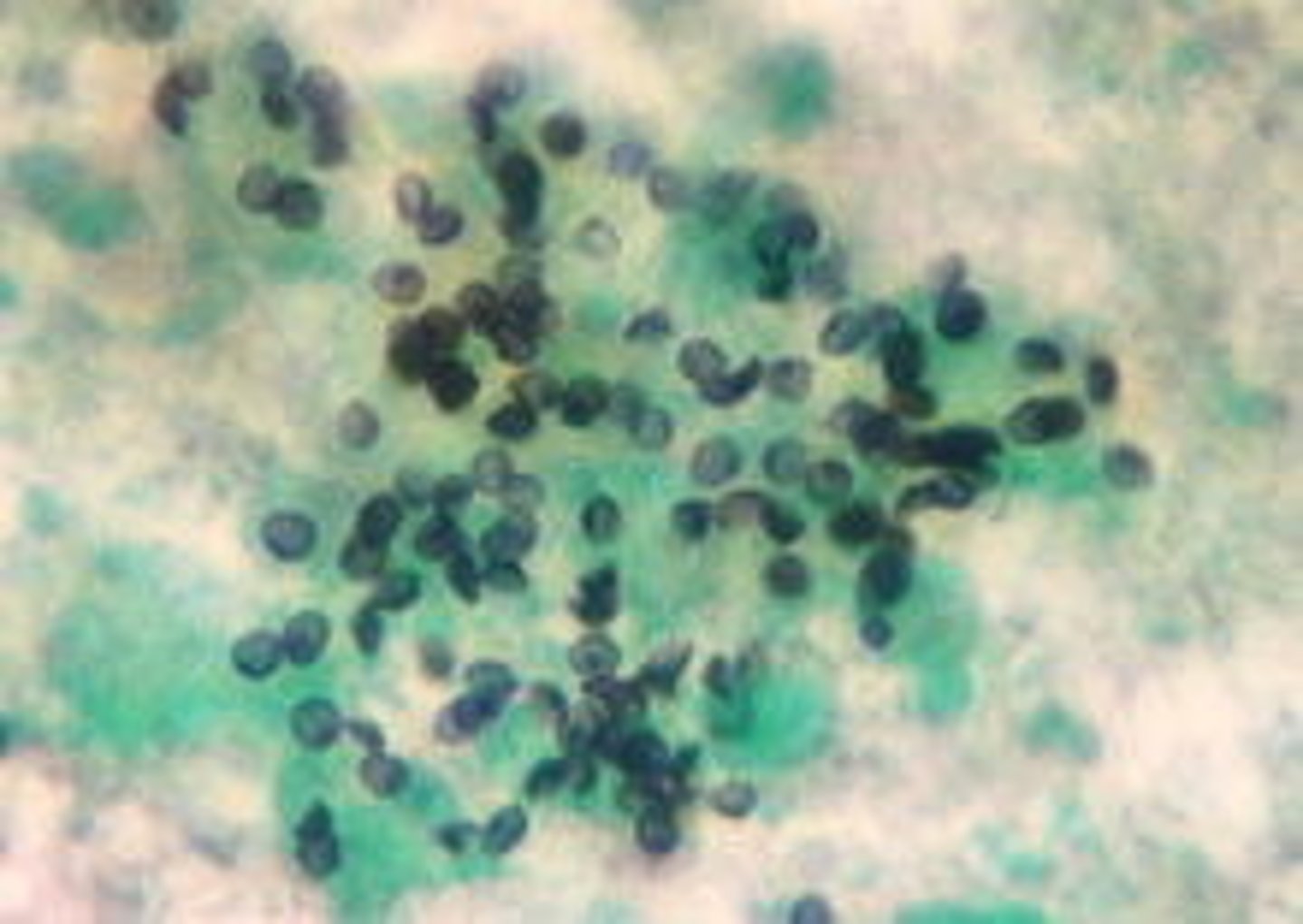
opportunistic fungal infection of normal flora - oral, GI, GU
candidiasis
hallmark of candidiasis
pseudohyphae (budding yeasts)