Week one Intro to Environmental Economics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
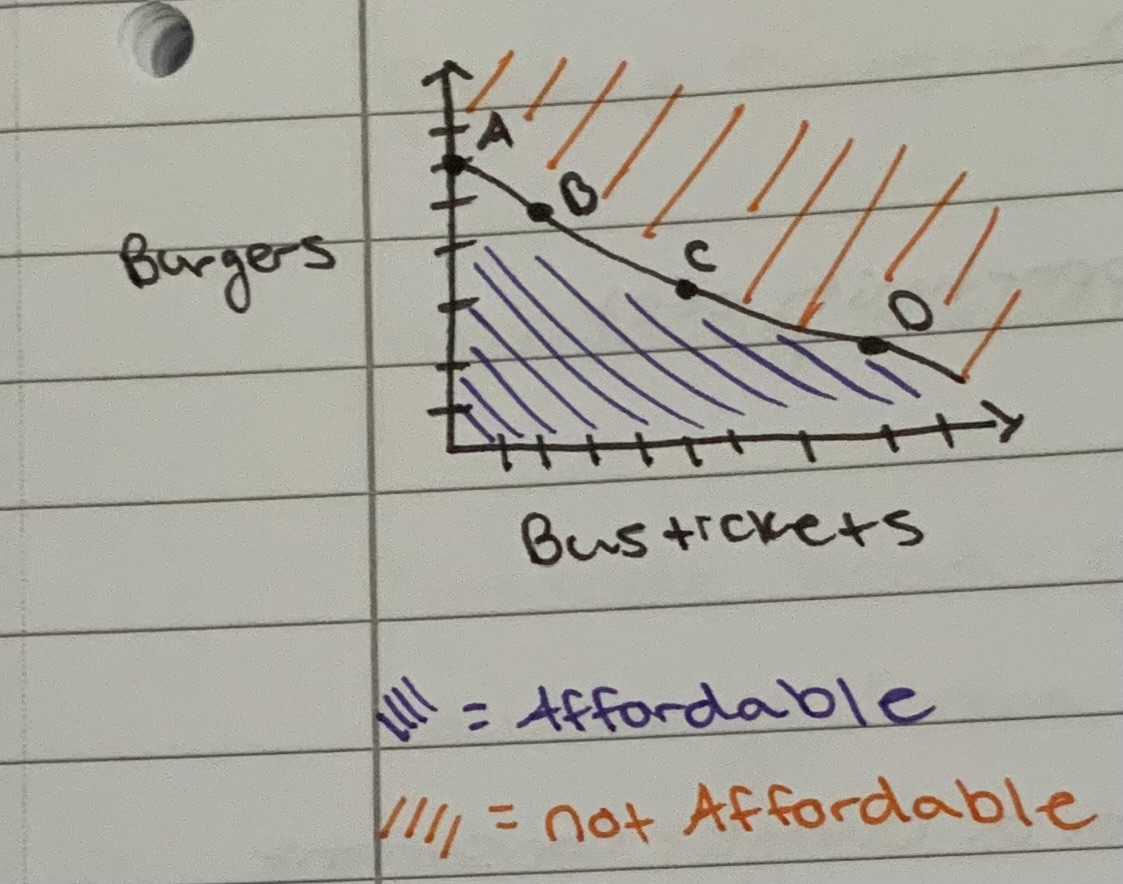
Budget constraint
All possible consumption combinations of goods that someone can afford, given the price of goods, when all income is spent, the boundary of the opportunity set.
equation: P1(Q1)+ P2(Q2) = budget for 2 items
Opportunity cost
Measures cost by what we give up/forfeit in exchange; opportunity cost measures the value of the forgone alternative.
Example: if you sleep through a lecture, the opportunity cost is what you could have learned and understood if you went to the lecture.
Marginal analysis
Is the examining the benefits and costs of choosing a little more or a little less of a good
Utility
Positive outcome from choosing a good or service
Law of diminishing marginal utility
A person receives more of a good, the additional (or marginal) utility from each additional unit if good declines.
For example: first slice of pizza brings more satisfaction than the sixth
Sunk costs
Are costs that were incurred in the past and cannot be recovered, should not affect the current decision
Production possibilities frontier (PPF)
A diagram that shows the productively efficient combinations of two products that an economy can produce given the resources it has available.

Law of increasing opportunity cost
As production of a good or service increases, the marginal opportunity cost of producing it increases as well.
Productive efficiency
It’s impossible to produce more if one good (or service) with out decreasing the quantity produced of another good or service
Allocative efficiency
The mix of good produced represents the mix that society most desires
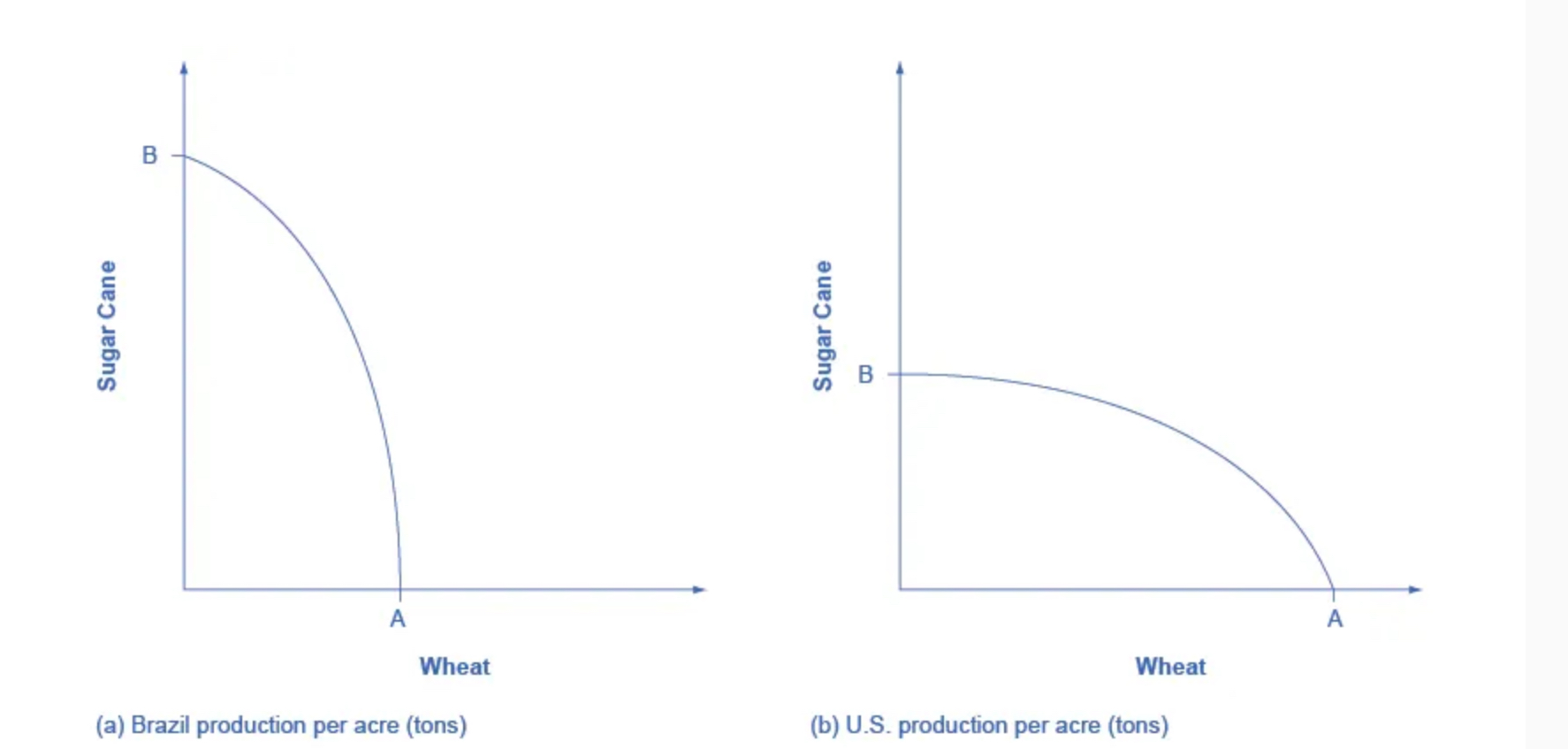
Comparative advantage
When a country can produce a good at a lower cost in terms of other goods or when a country has a lower opportunity cost of production
Positive statements
Describe the world as it is
Normative statements
How the world should be
Invisible hand
Possibility that broader social good can emerge from selfish individual actions
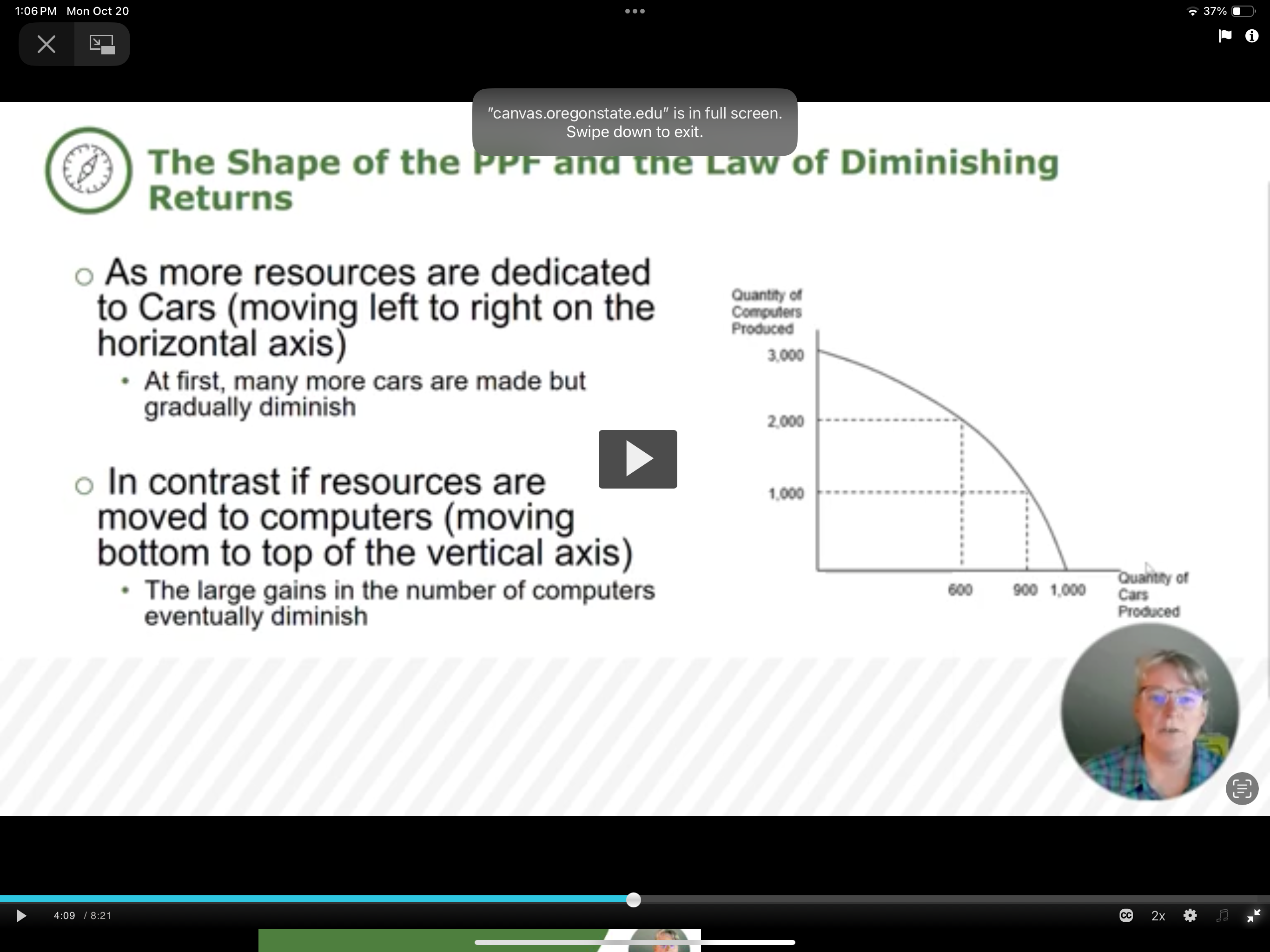
Law of diminishing returns
As additional increments of resources to producing a good or service are added, the marginal benefit from those additional increments will decline
Exchange/Trade
When a comparative advantage is recognized, entities may trade/exchange goods
Specialization
When an entity trades and focuses on producing a good they have comparative advantage in.