Ecology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
Carbon Cycle
An example of a biogeochemical cycle. Carbon exchange in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide enters plants through photosynthesis and is converted to glucose. Carbon then moves
through food chains.
through food chains.
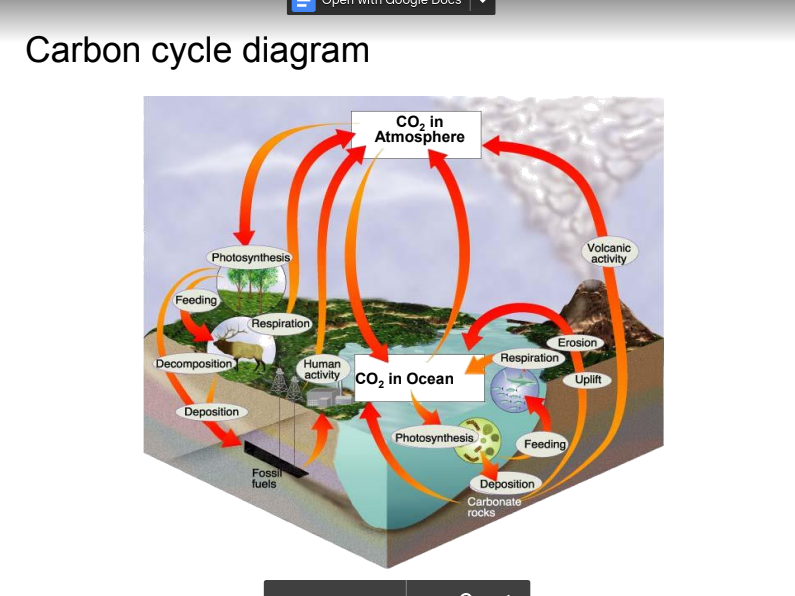
2
New cards
Water Cycle
An example of a biogeochemical cycle.
-Plants take in water through their roots. It can transpire (evaporation) and reenter the atmosphere.
-Animals drink water and eat plants. They then
respire and excrete water back into the biosphere.
-Decomposition of dead organisms also returns water
to the biosphere.
-Plants take in water through their roots. It can transpire (evaporation) and reenter the atmosphere.
-Animals drink water and eat plants. They then
respire and excrete water back into the biosphere.
-Decomposition of dead organisms also returns water
to the biosphere.
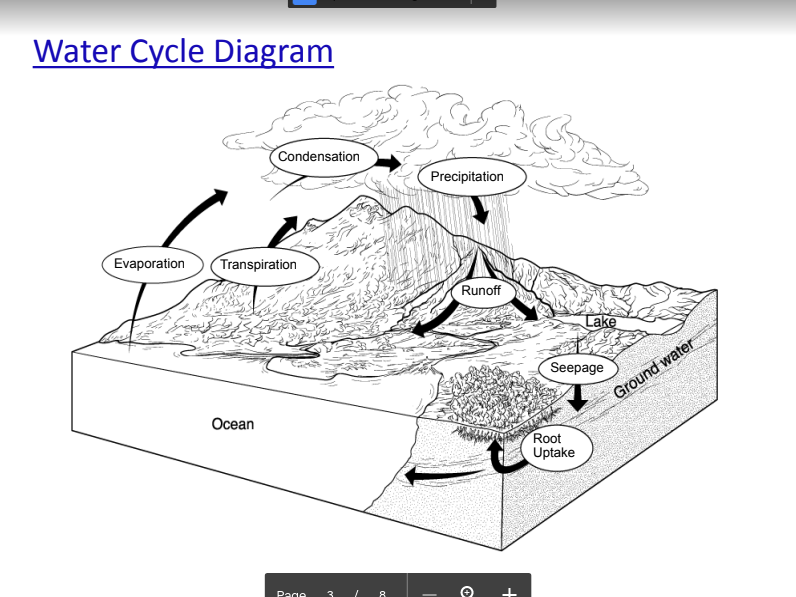
3
New cards
Nitrogen Cycle
An example of a biogeochemical cycle.
-Nitrogen is used to build proteins in all organisms.
-N2 (atmospheric nitrogen) cannot be used by organisms.
-Lightning and nitrogen-fixing bacteria can bond nitrogen to oxygen or hydrogen to make usable nitrogen
compounds. Synthetic fertilizers can also be added to the soil.
-Plants absorb these compounds from the soil. Usable nitrogen then moves through food chains.
-Decomposition and excretion return nitrogen to the soil.
-Nitrogen is used to build proteins in all organisms.
-N2 (atmospheric nitrogen) cannot be used by organisms.
-Lightning and nitrogen-fixing bacteria can bond nitrogen to oxygen or hydrogen to make usable nitrogen
compounds. Synthetic fertilizers can also be added to the soil.
-Plants absorb these compounds from the soil. Usable nitrogen then moves through food chains.
-Decomposition and excretion return nitrogen to the soil.
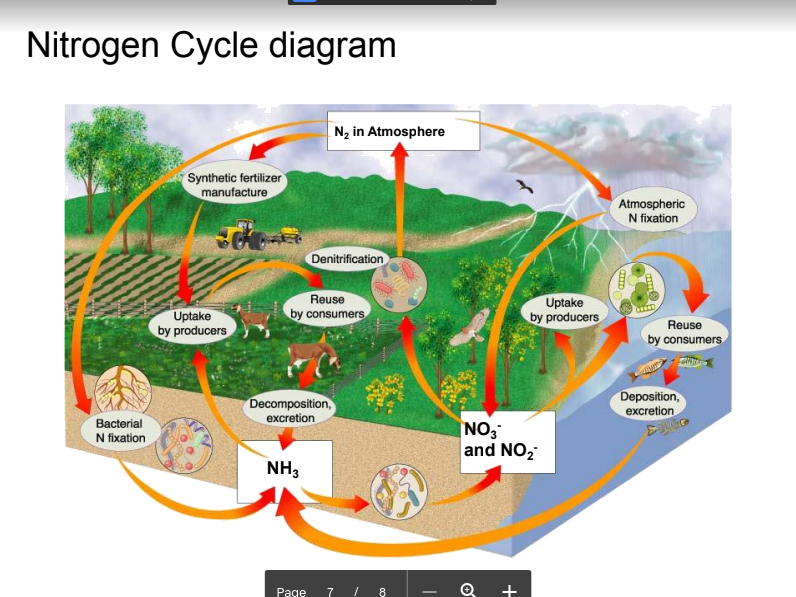
4
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle
An example of a biogeochemical cycle.
- Does not exist in a gaseous form.
- Phosphorus is tied up in rock, sediment,
and water. Plants take in phosphates that are dissolved in water. Phosphorus
then moves through food chains.
- Decomposition and excretion return phosphorus to the soil.
- Does not exist in a gaseous form.
- Phosphorus is tied up in rock, sediment,
and water. Plants take in phosphates that are dissolved in water. Phosphorus
then moves through food chains.
- Decomposition and excretion return phosphorus to the soil.
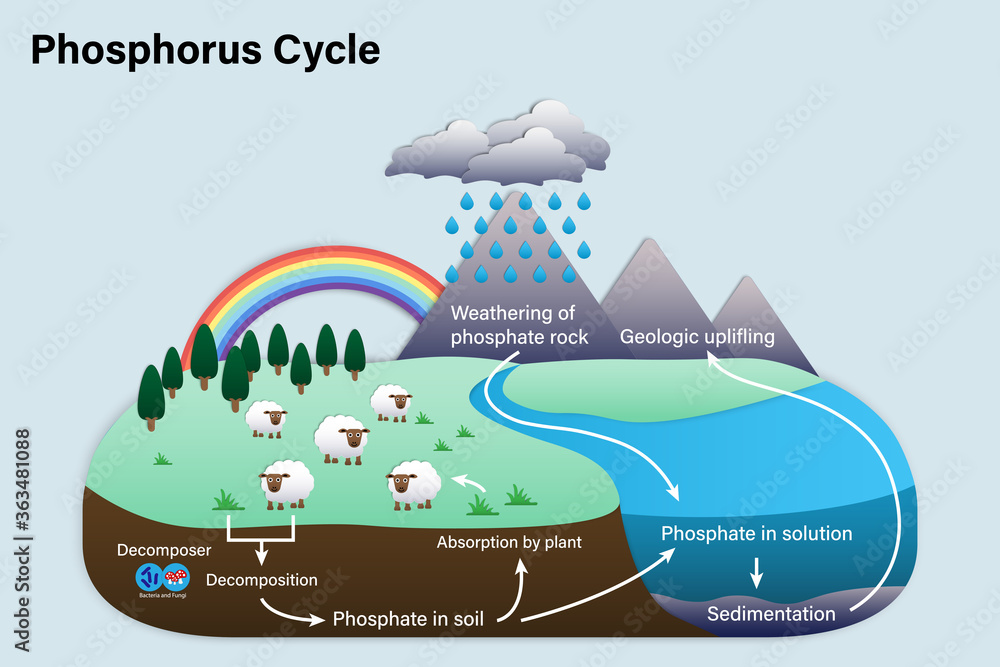
5
New cards
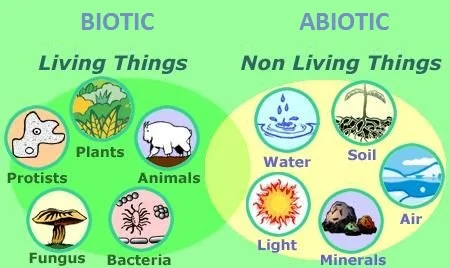
Abiotic Factors
A non-living part of an ecosystem that shapes its environment.
6
New cards
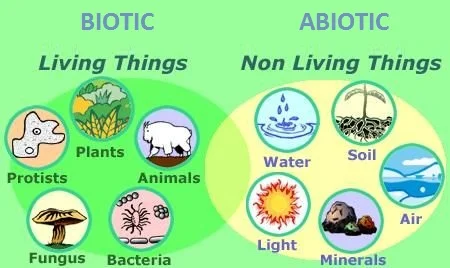
Biotic Factors
A living part of an ecosystem that shapes its environment.
7
New cards
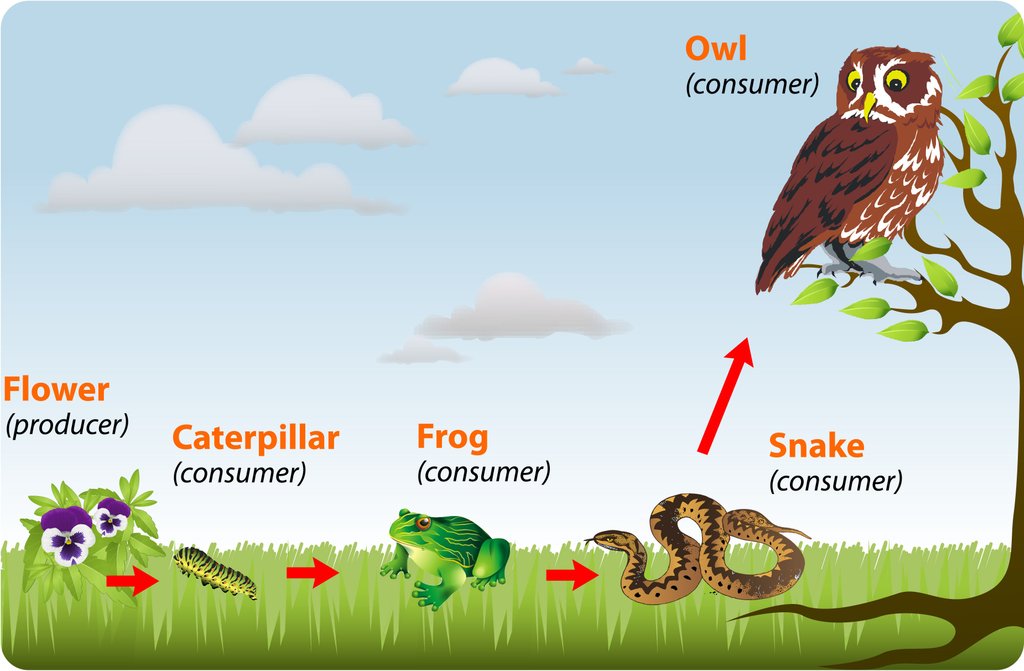
Food Chains
The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. Shows what organism eats what.
8
New cards
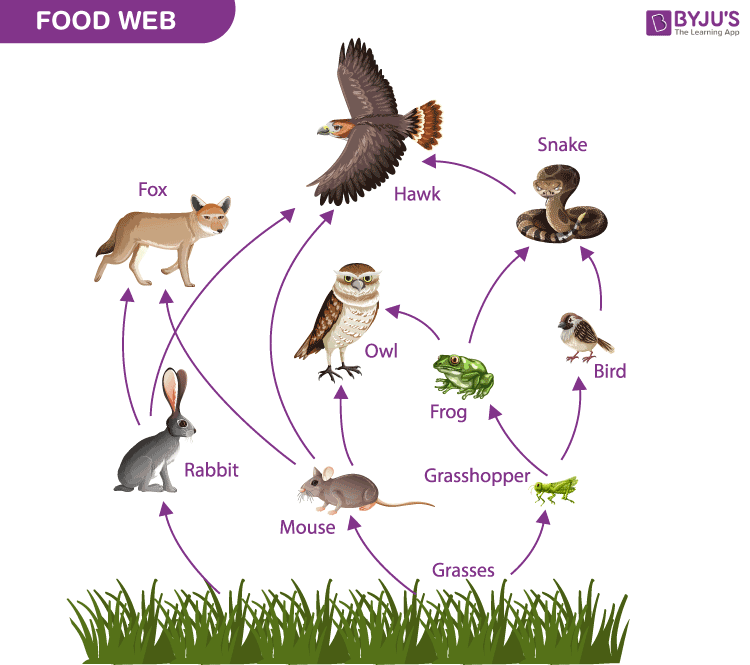
Food Webs
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community.
9
New cards
Ecology
The scientific study of how organisms interact with one another and their environment.
10
New cards
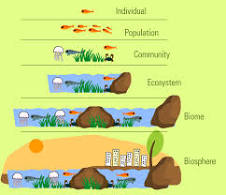
Levels of Organization
Organism, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biome, and Biosphere.
11
New cards
Producer
Photosynthesizing organisms (takes sunlight and makes it into sugars for consumers to eat)
12
New cards
Consumer
Organisms that can't make its own food (feeds on producers or other consumers)
13
New cards
Predator
An animal that hunts, kills, and eats other animals (prey)
14
New cards
Prey
What the predator hunts, kills, and eats.
15
New cards
Decomposer
Organisms that break down dead, organic material.
16
New cards
Scavenger
Something that consumes decaying biomass (like vultures)
17
New cards
Detritivore
An animal which feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus.
18
New cards
Saprotroph
An organism that feeds on or derives nourishment from decaying organic matter.
19
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.
20
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that eats other plants or animals for energy and nutrients.
21
New cards
Symbiosis
Any association or relatioship between two species populations that live together and interact closely.
22
New cards
Mutualism
A type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions.
23
New cards
Parasitism
Nonmutual relationship between two organisms in which one benefits at the expense of the other.
24
New cards
Commensalism
A relationship between individuals of two species in which one species obtains food or other benefits from the other without either harming or benefiting the latter.
25
New cards
Ecological Pyramids
There are 3:
Energy
Number
Biomass
Energy
Number
Biomass
26
New cards
Habitat
An environment where an organism lives throughout the year or for shorter periods of time to find a mate (such as freshwater, forest, cave, etc)
27
New cards
Niche
The role an organism plays in a community -- two different kinds of organisms can't have the same role
28
New cards
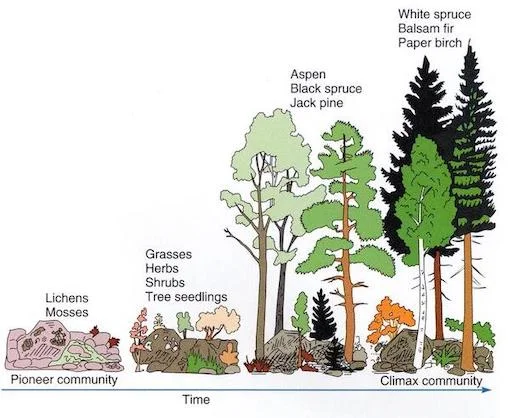
Pioneer Species
The species that first colonize new habitats (Primary Sucsession)
29
New cards
Climax Community
The final stage of sucsession where a community finally becomes stable
30
New cards
2 Kinds of Sucsession?
Primary - New soil introduced
Secondary - Already soil present
Secondary - Already soil present
31
New cards
Scientific Method (In Order)
Problem
Collecting Information
Hypothesis
Expirement
Collecting Data
Conclusion
Collecting Information
Hypothesis
Expirement
Collecting Data
Conclusion
32
New cards
Independent Variable
The change
33
New cards
Dependent Variable
The thing that is measured
34
New cards
Control Group
The normal
35
New cards
Constant
Used to compare.
36
New cards
Problem Form
The Effect of the_____IV_____on the_____DV_____

37
New cards
Hypothesis Form
If the _____(IV)_____ is _____(describe how it changes)_____
Then the _____(DV)_____ will _____(predict increase/decrease)_____
Then the _____(DV)_____ will _____(predict increase/decrease)_____
