Chapter 3: Sex Determination Mechanisms in Humans and Animals
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Non-chromosomal sex determination
Sex determined by environmental factors, not chromosomes.
Temperature-dependent sex determination
Sex determined by incubation temperature during development.
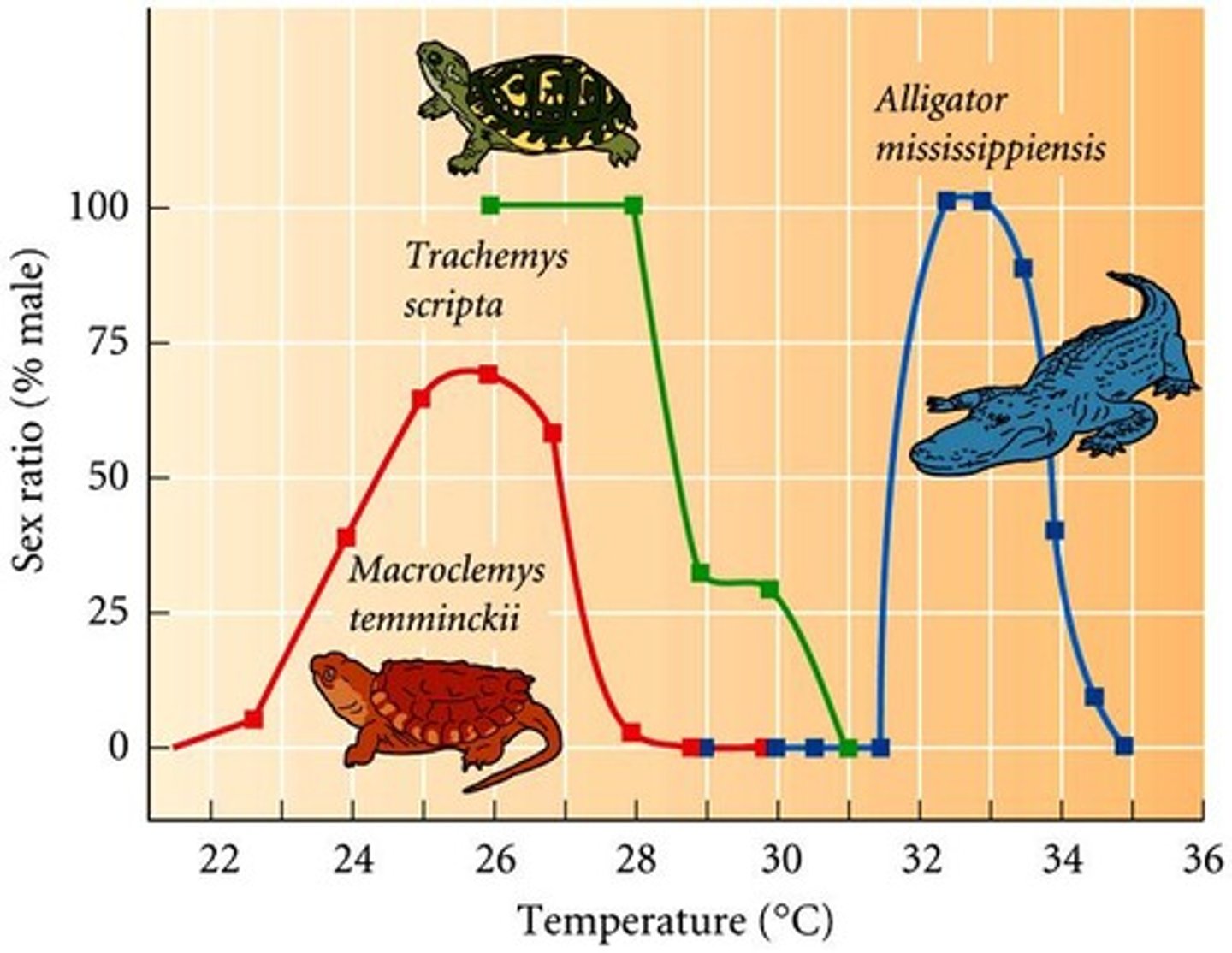
Population-dependent sex determination
Sex determined by social structure within a population.
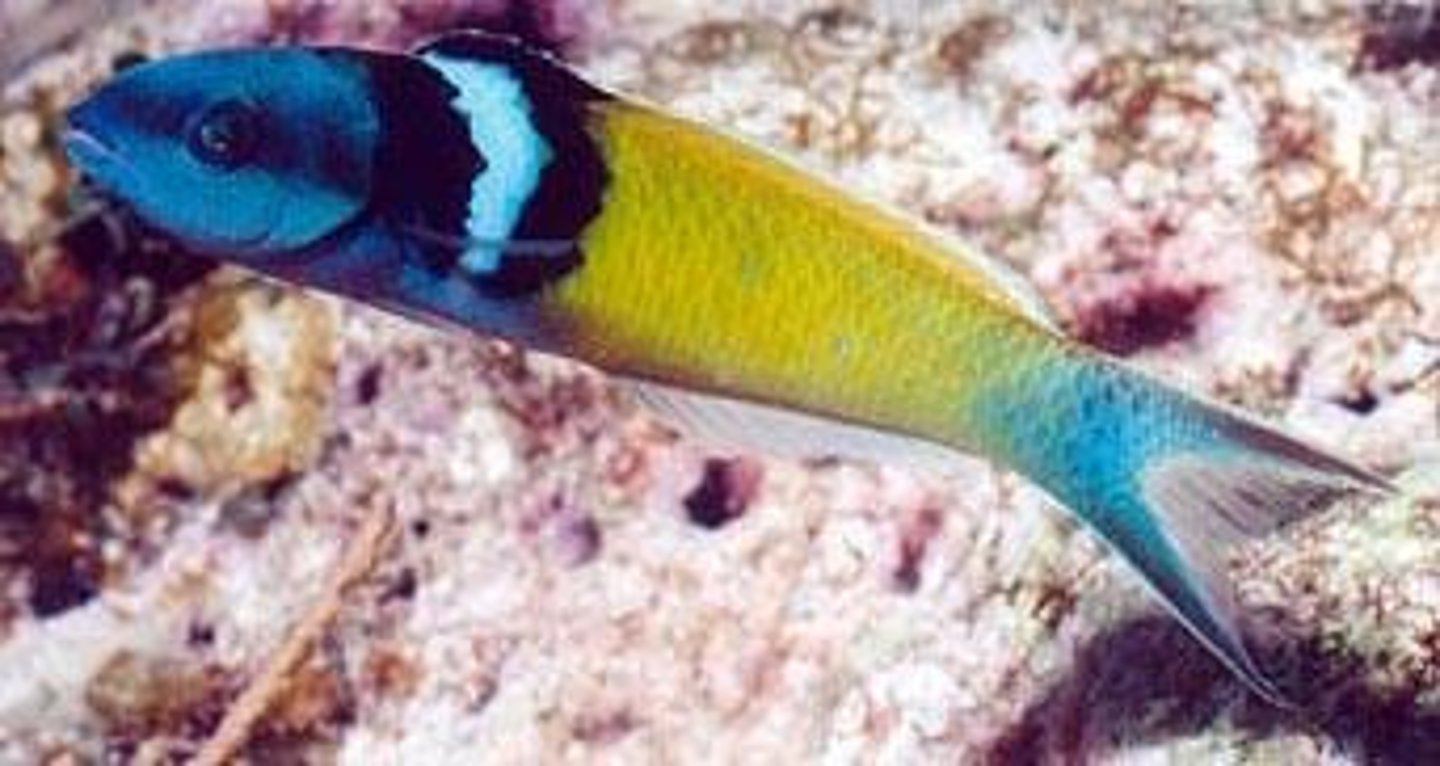
Blue-headed wrasse
Fish species with unique male-female transformation. When head male dies, largest female becomes male.

Chromosomal sex determination
Sex determined by specific chromosomes present.
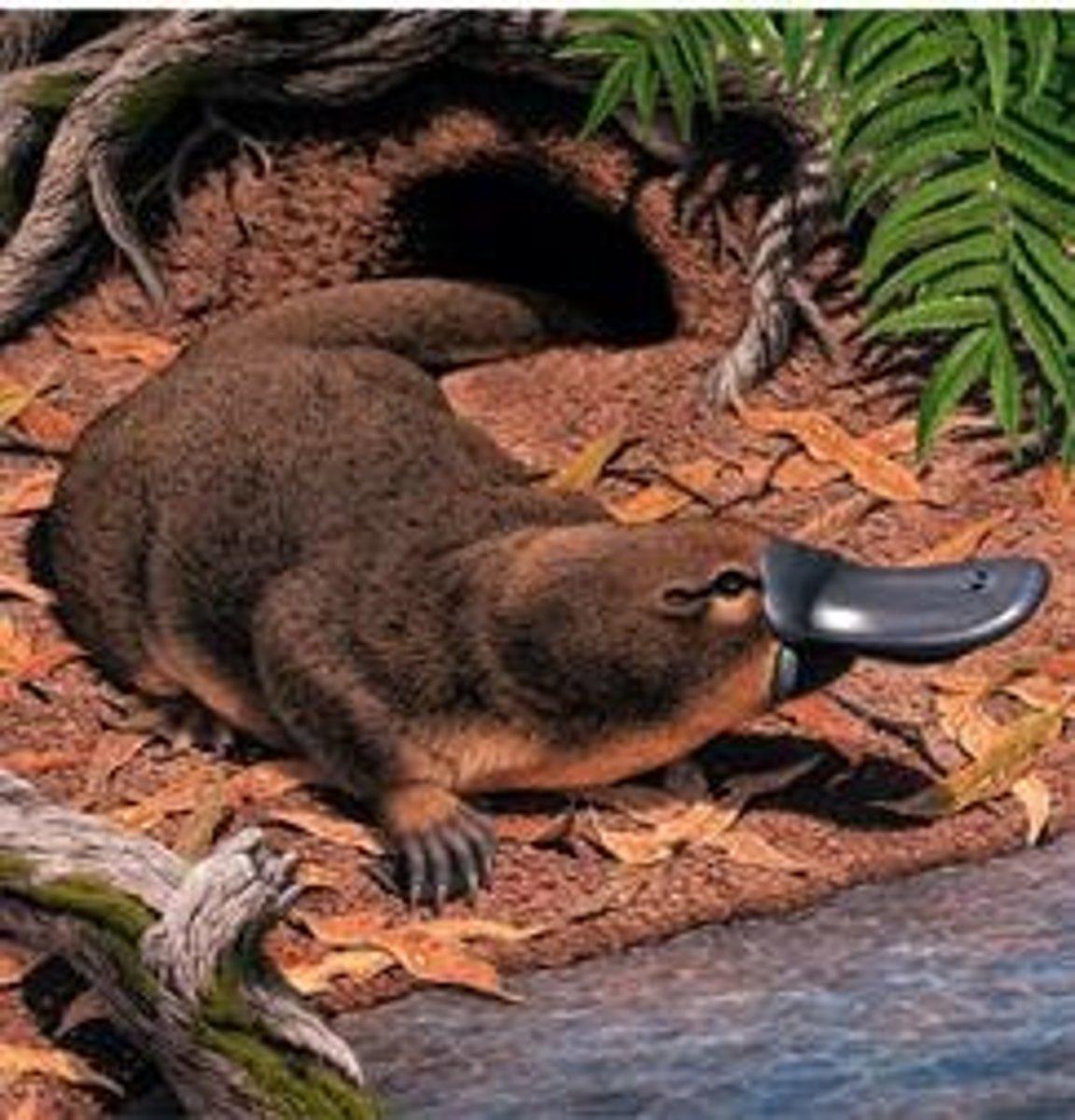
Platypus sex chromosomes
Females: 10 Xs; Males: 5 Xs, 5 Ys.

Lygaeus mode
Most common XX/XY heterogametic sex determination system.
Protenor mode
XX/XO system; no Y chromosome present.
Homogametic sex
Produces gametes with identical sex chromosomes. XX.
Heterogametic sex
Produces gametes with different sex chromosomes. XY.
Human chromosomal sex determination
Determined by presence of X and Y chromosomes.
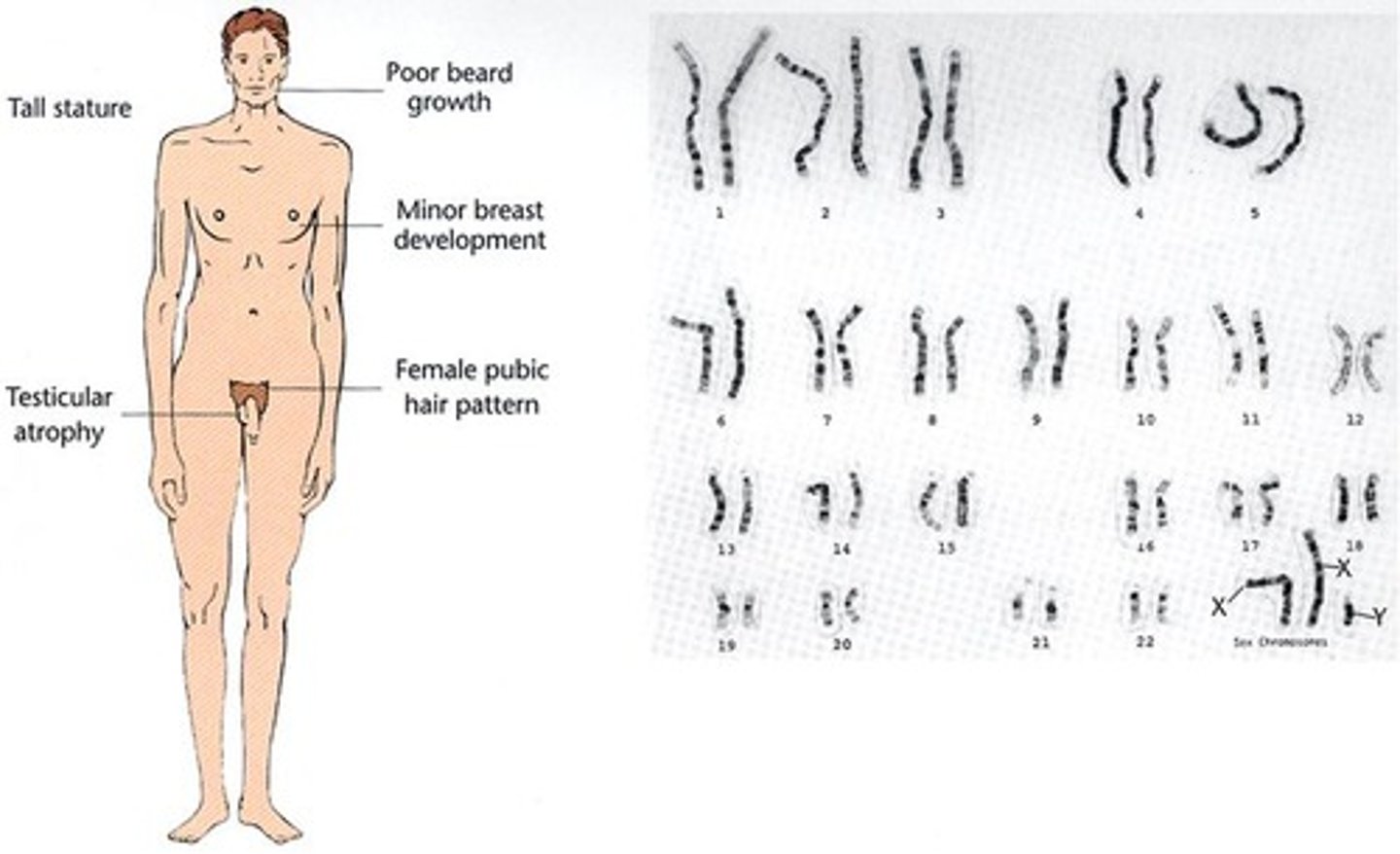
Klinefelter syndrome
47,XXY; male with extra X chromosome.
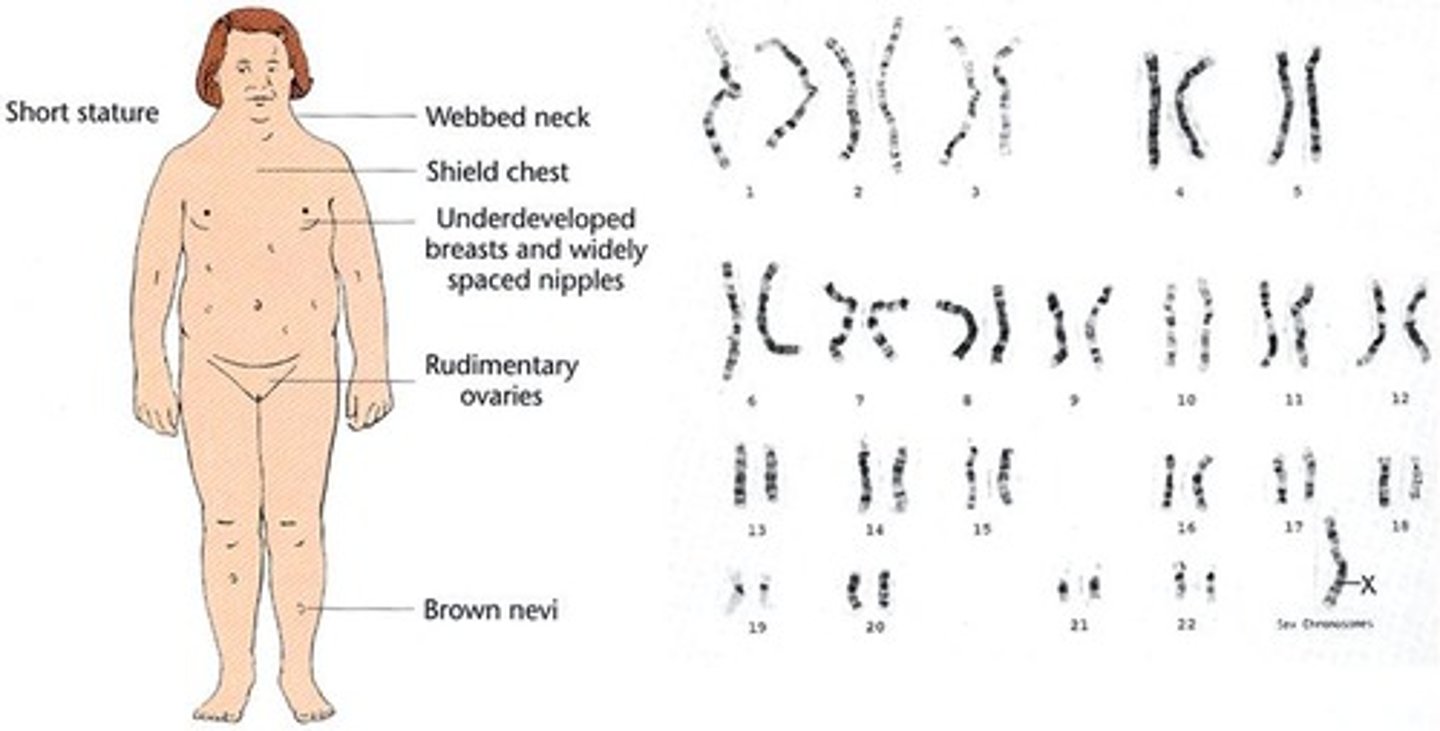
Turner syndrome
45,X; female with missing second X chromosome.
Jacob's syndrome
47,XYY; male with extra Y chromosome.
Y chromosome function
Presence determines maleness in humans.
Barr bodies
Visible in Interphase eon nucleus. Inactive X chromosomes (except one) in female cells. Creates Dosage compensation.
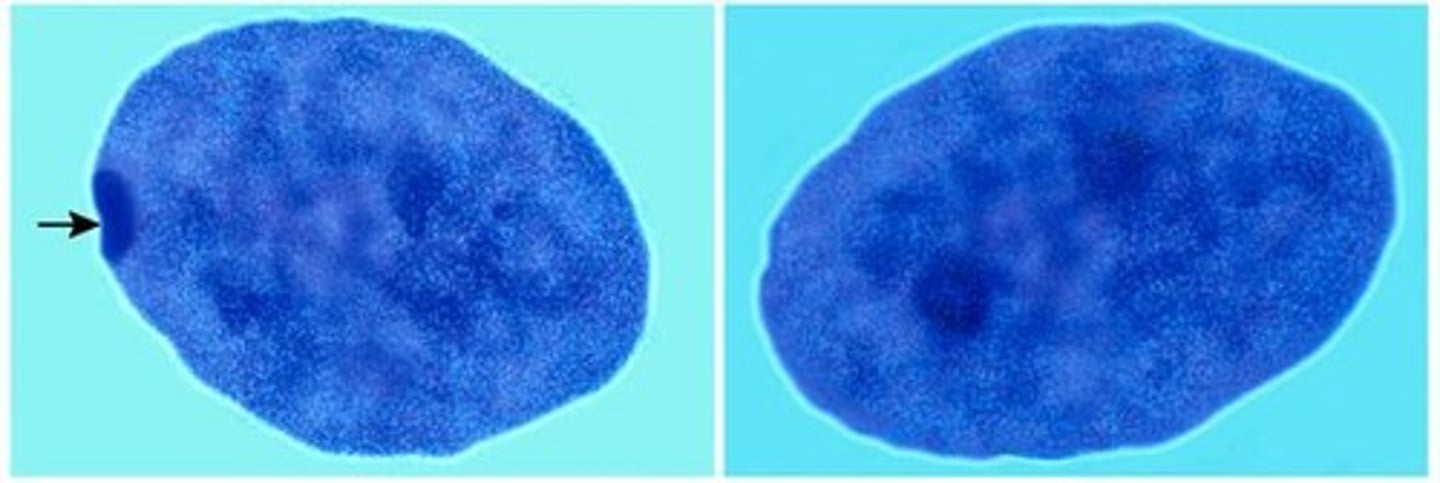
Dosage compensation
Equal expression of X-linked genes in females.
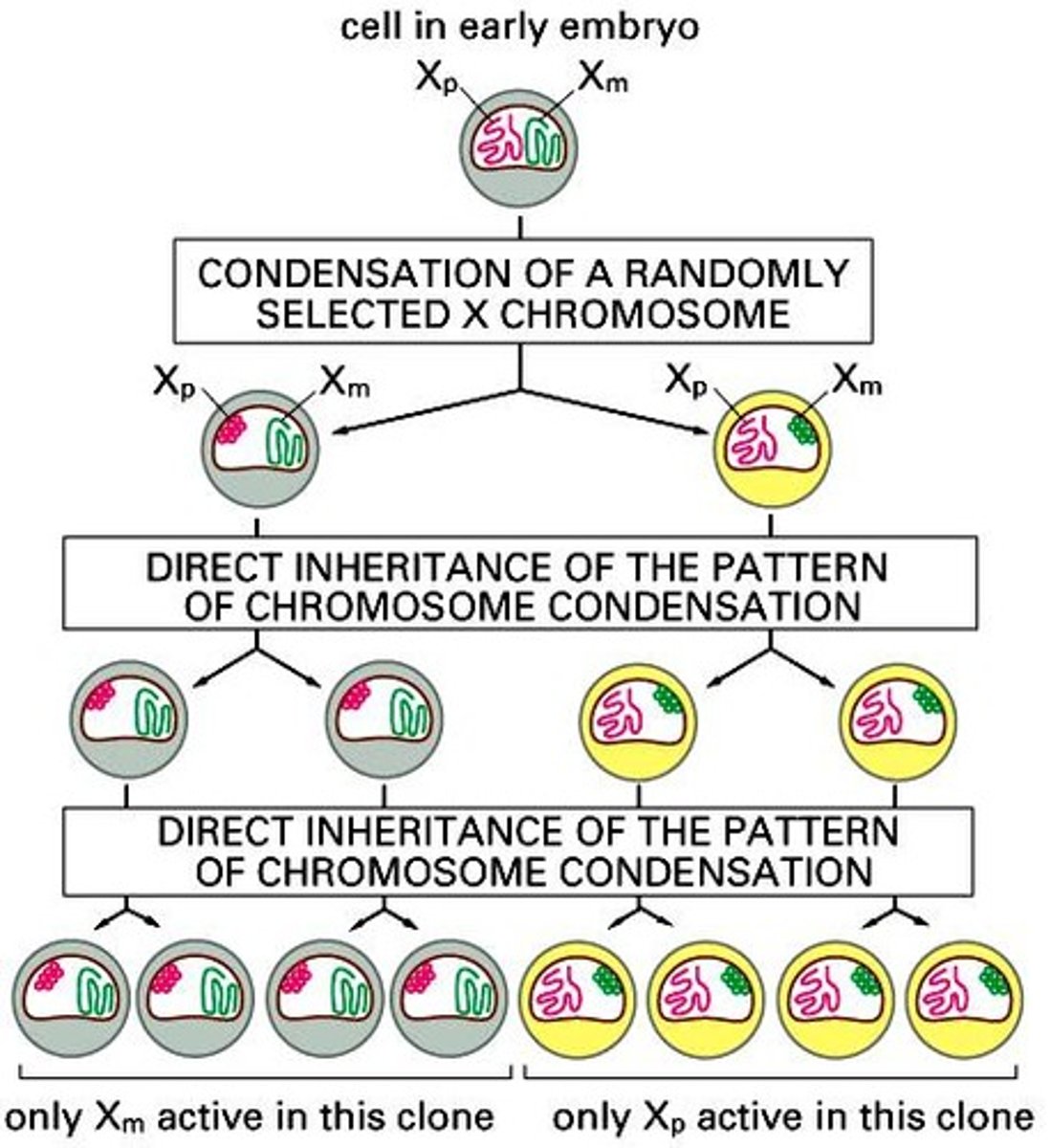
Mary Lyon hypothesis
Random X inactivation in early embryonic development. All descendants from each cell will have same X chromosome inactivated. Females become mosaics for all heterozygous X-linked loci.
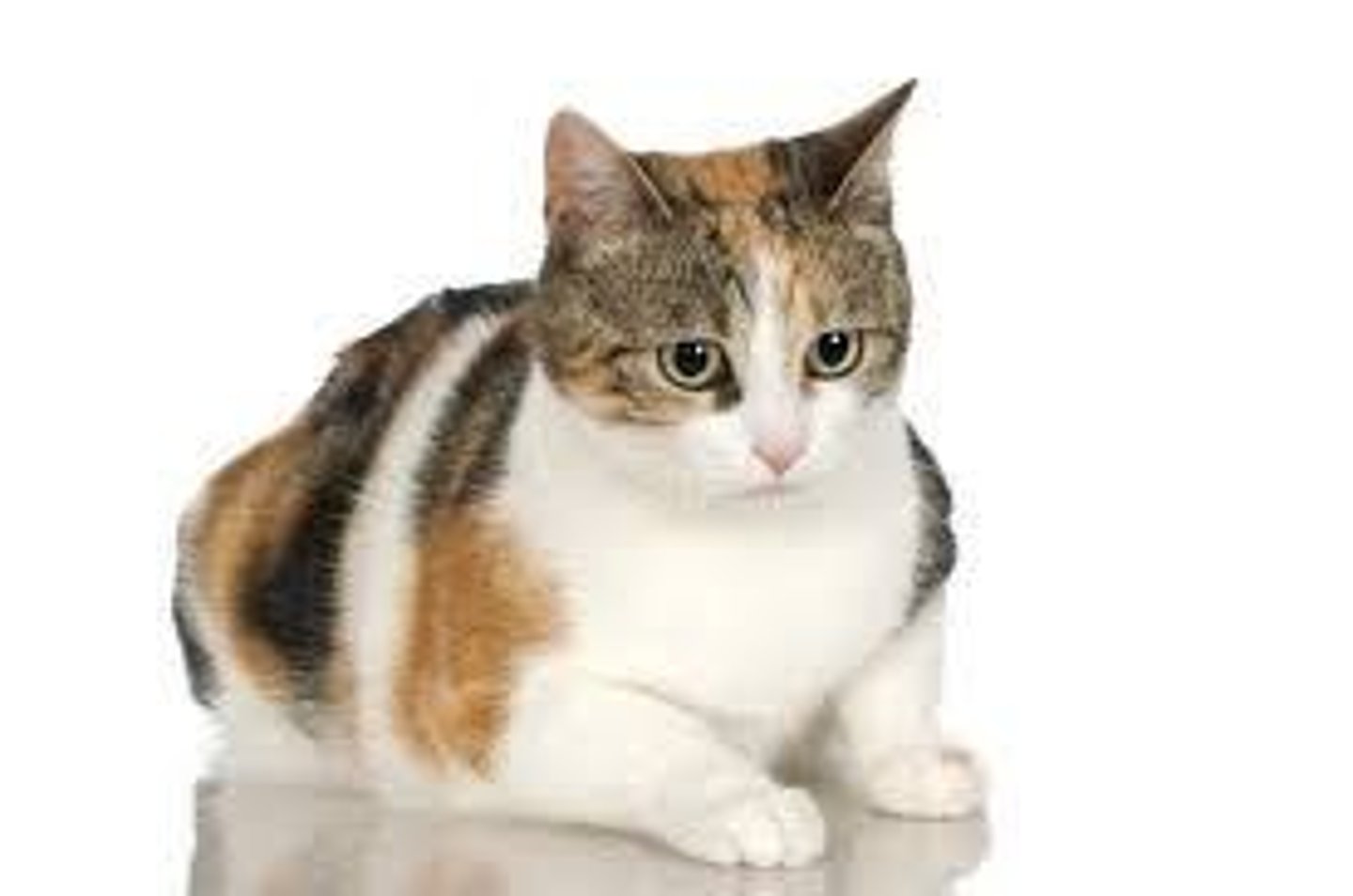
Tortoiseshell cat
Female with orange and black fur patches. X linked. XXY

Calico cat
Tortoiseshell with additional white spotting due to expression of separate white spotting gene.

Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
X-linked disorder causing lack of sweat glands in males and mosaic skin in females with. Affects hair and nails too.
X-linked inheritance
Traits determined by genes on X chromosome.
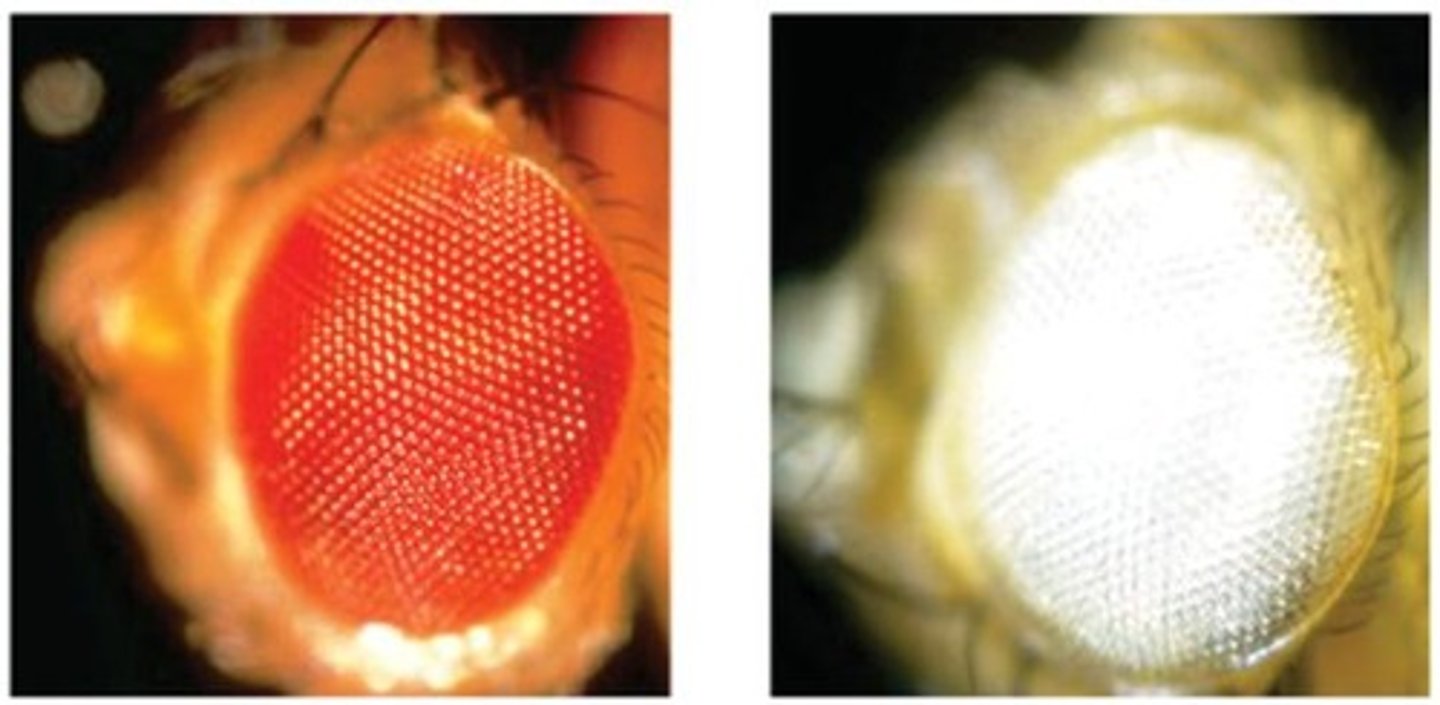
Drosophila white locus
Gene affecting eye color in fruit flies. Thomas H. Morgan
Punnett square
Tool for predicting genetic cross outcomes.
ZW system in birds
Females are ZW; males are ZZ.
Ca+ allele in peacocks
Z-linked allele causing blue feather color while ca allele causes cameo color.
Scalloped mutation in Drosophila
X-linked mutation causing irregular wing margins.
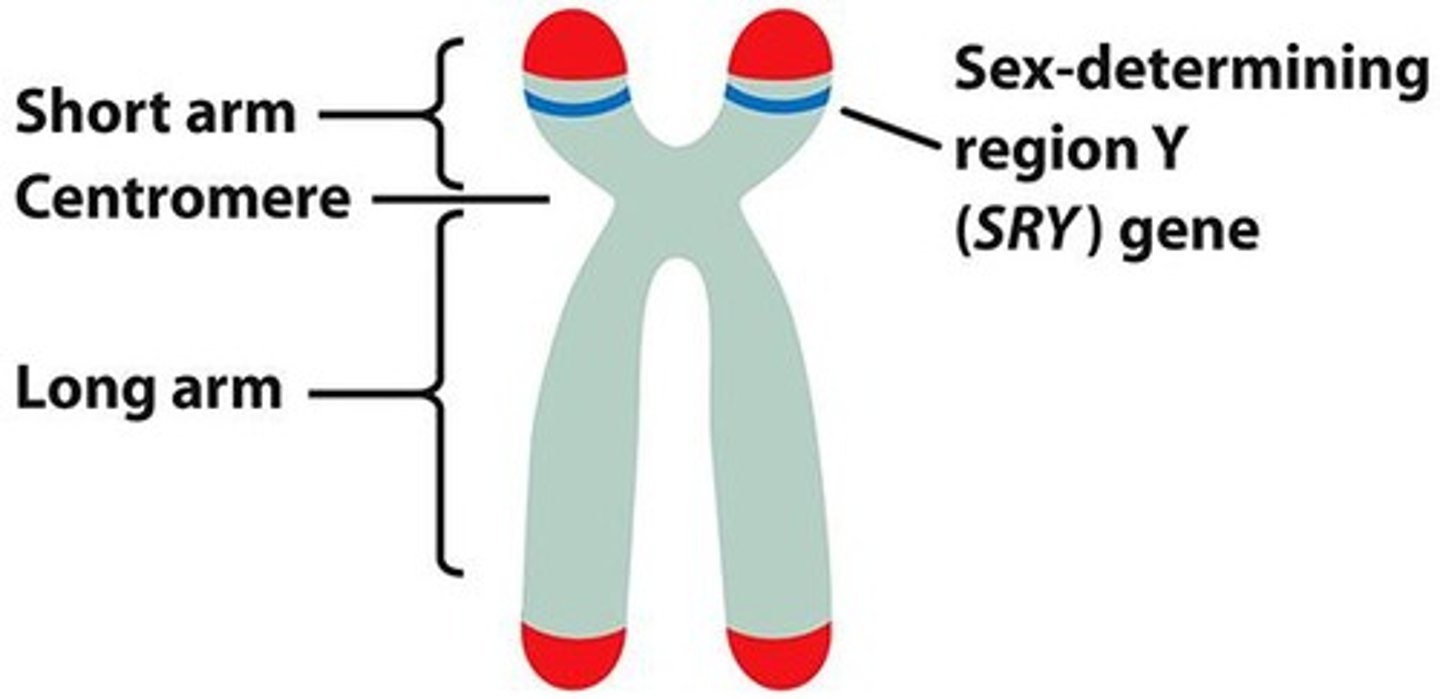
Sex-determining region of Y (SRY)
locus that controlsmale sexual development in humans
Primary and secondary pseudoautosomal region (PAR)
only area where X and Y chromosomes are homologous
holandric traits
Traits that are linked to genes in the nonpseudoautosomalregions (non-PAR) of the Y chromosome. Only in males.
Mosaics