entm final
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what’s beetles diet: Ground and Tiger beetle (Family Carabidae)
predator
what’s beetles diet: Diving beetles (Family Dystiscidae)
predator
what’s beetles diet: Whirligig beetles (Family Gyrinidae)
predator
what’s beetles diet: Lady bird beetles (Family Coccinellidae)
predator
what’s beetles diet: Dung Beetle (Family Scarabaeidae)
scavenger
what’s beetles diet: Rhinoceros beetles Family Scarabaeidae)
scavenger/herbivores
what’s beetles diet: Japanese beetles (Family Scarabaeidae)
Scavenger and Herbivorous
what’s beetles diet: Carrion beetles (Family Silphidae)
Scavenger (decomposers)
what’s beetles diet: Jewel Beetles (Family Buprestidae)
Wood Borer (eats wood)
what’s beetles diet: Leaf Beetles (Family Chrysomelidae) (Colorado potato Beetle)
Herbivore
what’s beetles diet: Darkling Beetle (Family Tenebrionidae)
Herbivore
what’s beetles diet: Weevils (Family Curculionidae) (Boll weevil)
Herbivores
what’s beetles diet: Desert Stink beetle (Family Tenebrionidae)
Herbivore
name of the disease the fly spreads and if possible agent:
Biting Midges
disease: Bluetongue disease in sheep
name of the disease the fly spreads and if possible agent:
Sand Flies
Disease: Leishmaniasis. Cutaneous, Mucocutaneous and Visceral infections. Affects the macrophages (white blood cells)
Agent: parasite (protozoan parasite)
name of the disease the fly spreads and if possible agent:
Tsetse Fly:
Disease: Sleeping sickness invades the nervous system
Agent: Parasite (Protozoan parasite) Trypanosome
name of the disease the fly spreads and if possible agent:
Black Fly
Disease: River Blindness (Onchocerciasis). Affects the skin (nodules), and can cause blindness.
Agent: Microfilariae of a parasitic nematode
name of the disease for each mosquito species:
Culex mosquito
Disease: Various encephalitis including (WNV)
name of the disease for each mosquito species:
Aedes mosquito
Disease: Dengue, Yellow Fever, WNV, Zika, canine heartworm
name of the disease for each mosquito species:
Anopheles mosquito
Mammalian malaria, Various viruses, Canine heartworm
how much percentage of beetles make of ALL species
~25%
What is the main morphological characteristic of beetles
mouth parts have been modififed for chewing in adult and larva
What are the function of the elytra
armor
retention of water
stabilzation during flights
protection of Hindwing
Most beetles elytra cover entire mesothorax, metathorax, and abdomen. What beetle is elytra fused together to make them flightless
Darkling beetles
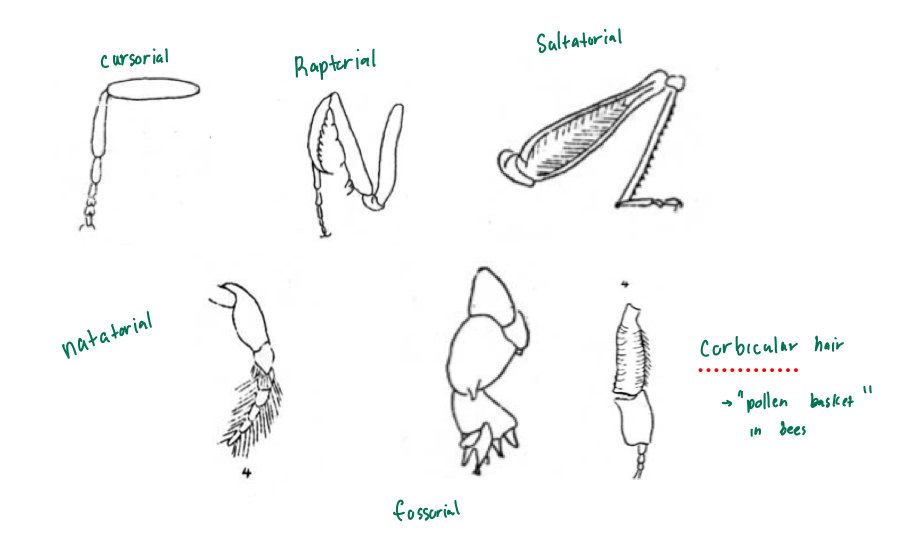
brief description of each modified leg
cursorial leg
fossorial leg
natatorial leg
saltatorial leg
T/F: although beetles have holometabolous development, the larva and adults have similar habitats and eat similar foods
True
what disease does the bark beetle spread? What agent does it spread?
disease:
chestnut blight on American chestnut
Dutch elm disease on American elm
agent: fungus
Characteristic of Robber flies
predacious
aggressive mimicry
stylate mouthparts surround by a “beard”
concave (depression inwards)
what are the defensive characteristic of swallowtail butterfly caterpillar?
mimicry
osmeterium: defensive organ of caterpillars that emits odorous chemicals
75% of this family of butterfly have ant-associations
family lycaenidae (glossamer-winged butterflies)
Main way to distinguish moth from butterflies
antennae
moth feather like (bipectinate) or thin antennae
butterflies have thicker antennae, with bulb or hooks on end
what are several method to distinguish a sawfly larvae and caterpillar?
number of prolegs
caterpillars have 5 or fewer
sawfly have 6 or more
metamorphosis
caterpillars becomes butterflies or moth
sawflies look like wasp
caterpillars have little hooks (crochet) on prolegs, sawflies don’t
haplodiploidy
in hymenoptera
females are diploids (two complete set of chromosomes)
females are able to reproduce for haploid male without mating
males are haploid (one set of chromosomes)
type of modified antennae ant have?
geniculate (elbow shape)
two innovation in ant subfamily myrmicinae
seed harvesting
fungus growing (our farmer the leaf cutter ants”
describe eusociality
live in groups as adults
cooperative brood care
reproductive division of labor (caste system)
overlapping generation of adults
types of pupa
puparium - flies
chysalis - butterflies
cocoons - moths
tumblers - mosquitos (can move by swimming)
Specialized ovipoitor (tubular organ, female deposits eggs) in ants and bees
worker female cannot reproduce, ovipositor becomes stinger
forensic entomology
insect are poikilothermic (varies of internal temperature)
growth and aging depends on surrounding temperature
hotter = faster growth and age
forencis entom, data pulled from weather station to calculate insect age (degree hour)
T/F: ¾ of world’s flowering plants depend on animal pollinators
true
How do honey bees make a queen
feed the larval royal jelly throughout their development
two ways bumble bees forage
by buzz pollinaions (move their flight muscle rapidly, releasing pollen)
nectar robbing (make hole near base of flower, access nectar while avoiding pollen transfer)
T/F: solitary bees make up on 40% of bee species
False, about 85% (majority of bee species)
comparison of bees and wasp
bee:
feed on nectar
larvae feed on pollen
Chunky with round bodies
hairy body and legs
wasp:
ADULTS feed on nectar
larvae feed on prey
hairless bodies and legs
What insect goes through Adenotrophic viviparity (development of larvae within female’s body)
Tsetse fly
Monarch butterflies host plant is Milkweed. What compound does milkweed produce as a defence?
Cardenolides are toxic, cardiac glycosides found in milkweed family (asclepiadaceae)
flight behavior between tiger swallowtail vs giant swallowtail
giant swallowtail:
“hopping” flight patterns
females beat wing slowly but move quickly due to large wings
eastern tiger swallowtail
gracful and leiserely flight
fly high above woods and forests