C1.3 Photosynthesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
It is when plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, through chlorophyll
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
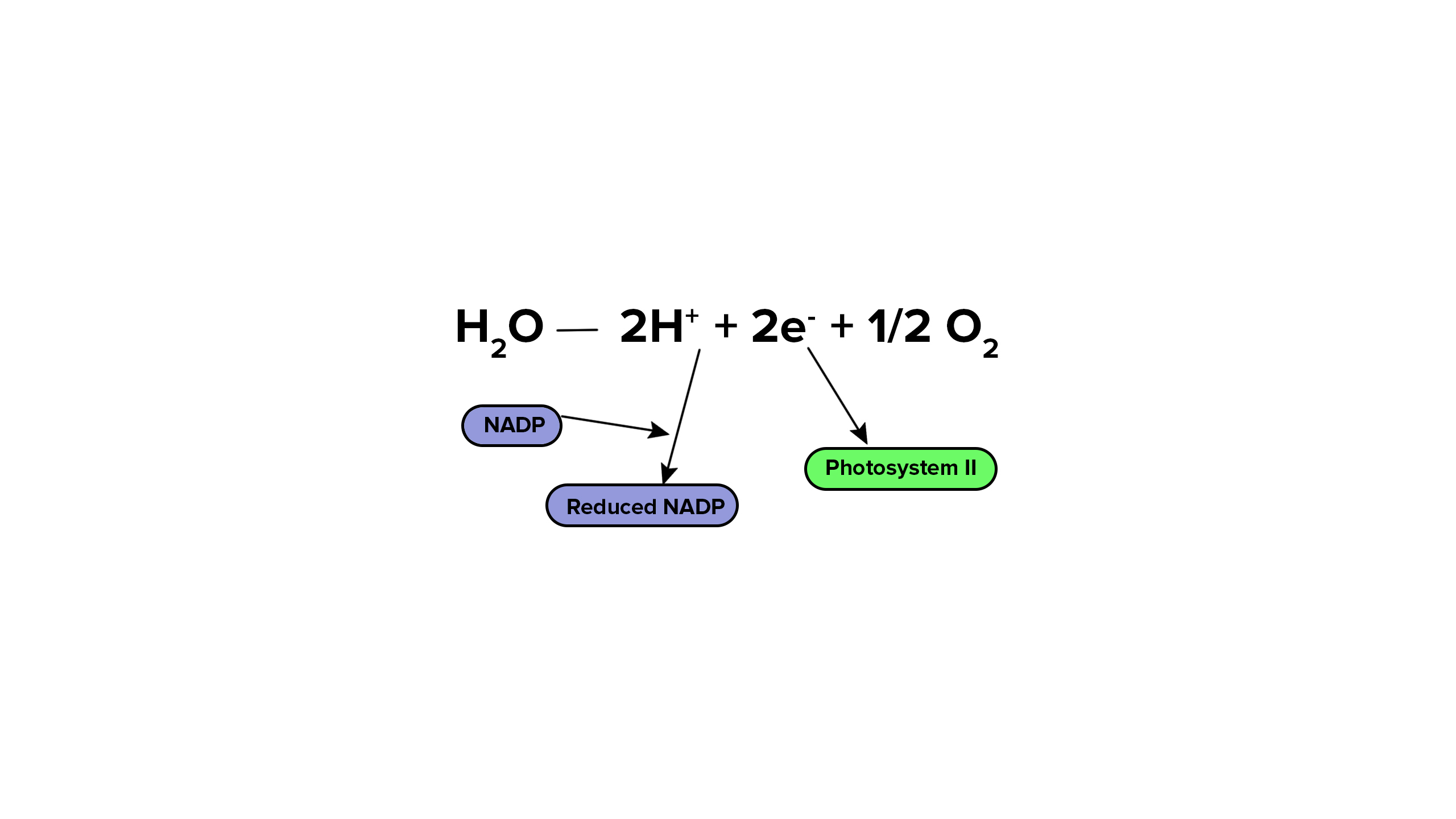
What is photolysis?
Water isn’t useful on it’s own, so it is split with the energy from light, in order to release oxygen, electrons and hydrogen protons. The oxygen isn’t useful, so it is released as a byproduct into the atmosphere. The proton hydrogen is used to form NADPH which is used in the next step, and the electron is formed into ATP which is also used for the next step.
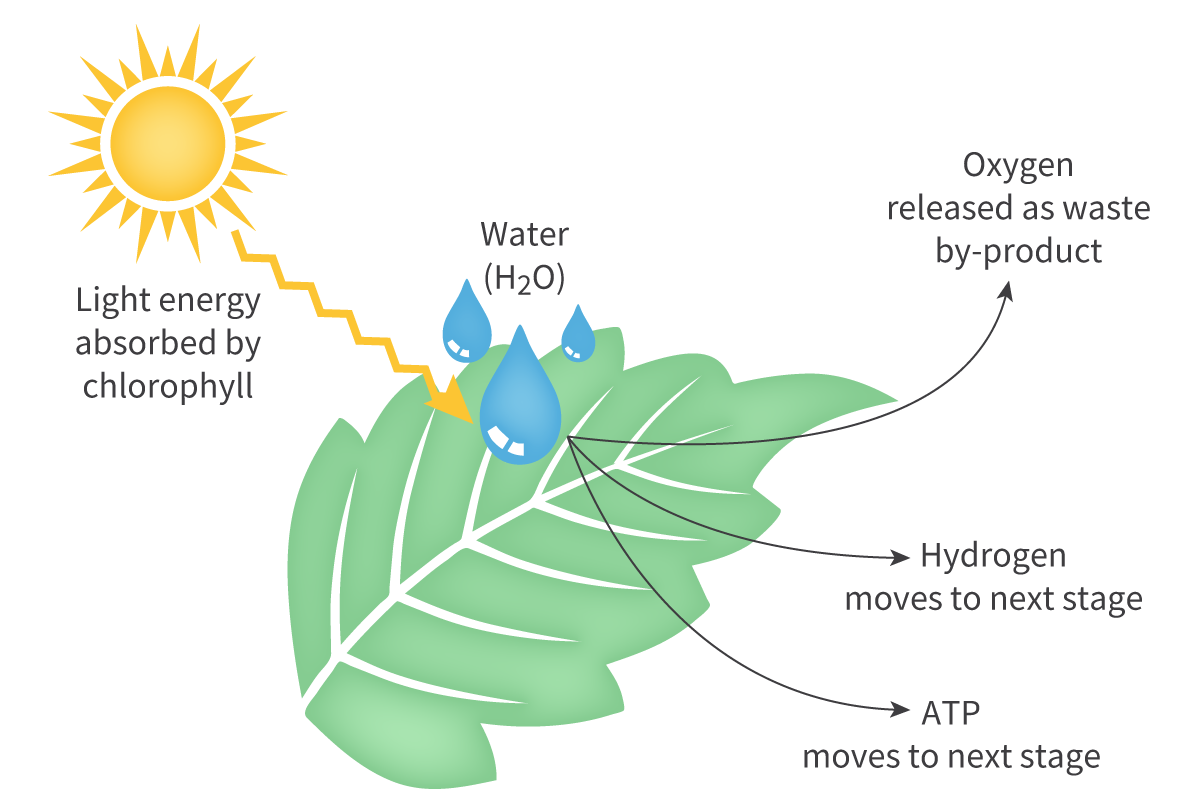
What is the equation for photolysis?
The oxygen is released as a byproduct, and the hydrogen proton is used to form NADPH for the next step, and the electron is made into ATP which is also used for the next step
What are the two main sets of reactions in photosynthesis?
Light-dependent and light-independent
Is photolysis a light-dependent or light-independent reaction?
It is a light dependent reaction, as it requires light to occur
What is the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle takes place in the Stroma of chloroplasts. In this cycle, the electrons and hydrogen protons that are derived from photolysis are used to reduce carbon dioxide to produce glucose
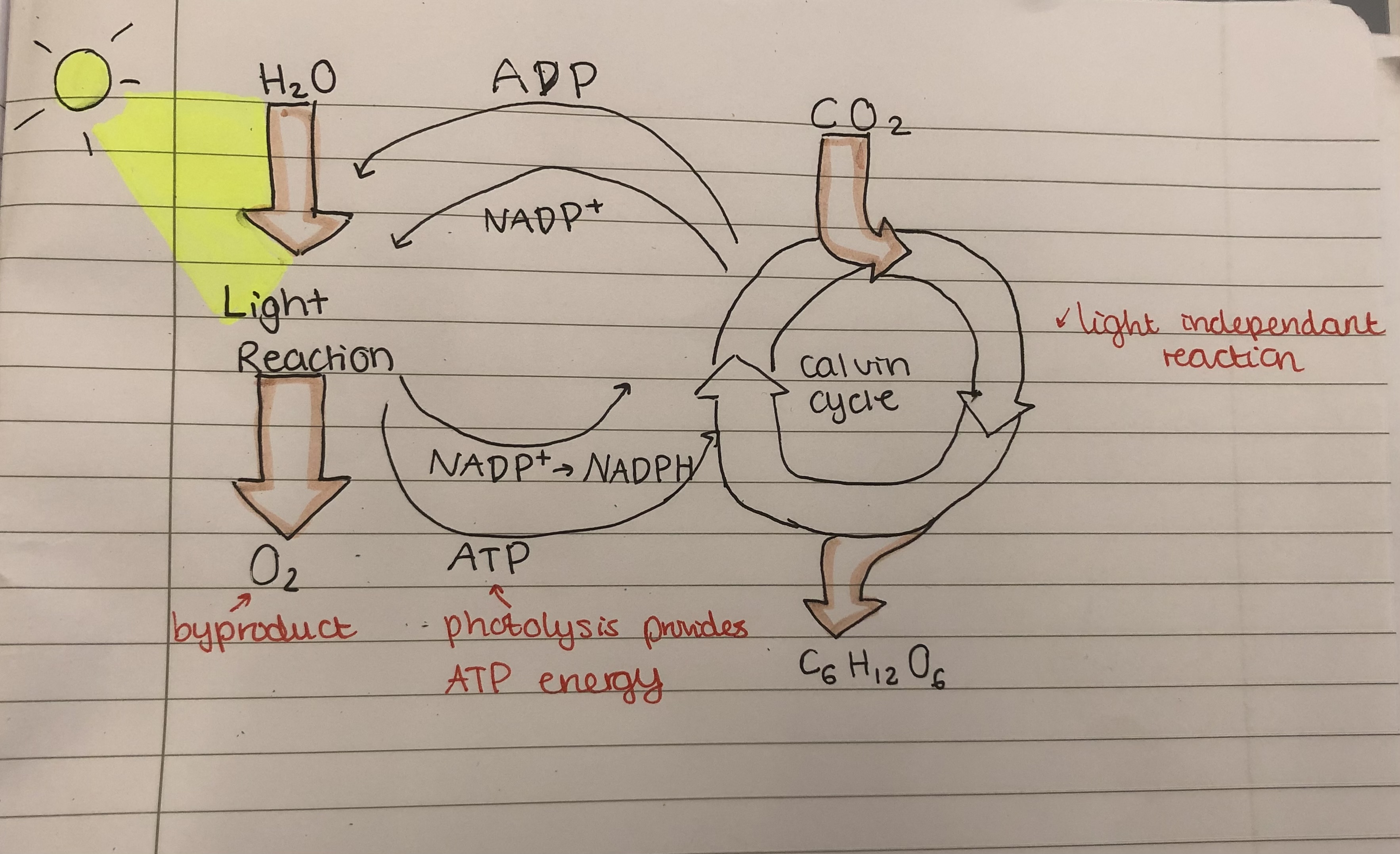
Overall, what occurs in photosynthesis?
In photosynthesis, hydrogen, which is obtained from the splitting of water with light energy, provides the necessary protons and electrons which are needed for the conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose
Photosynthesis not only occurs in plants but also in…
algae and cyanobacteria
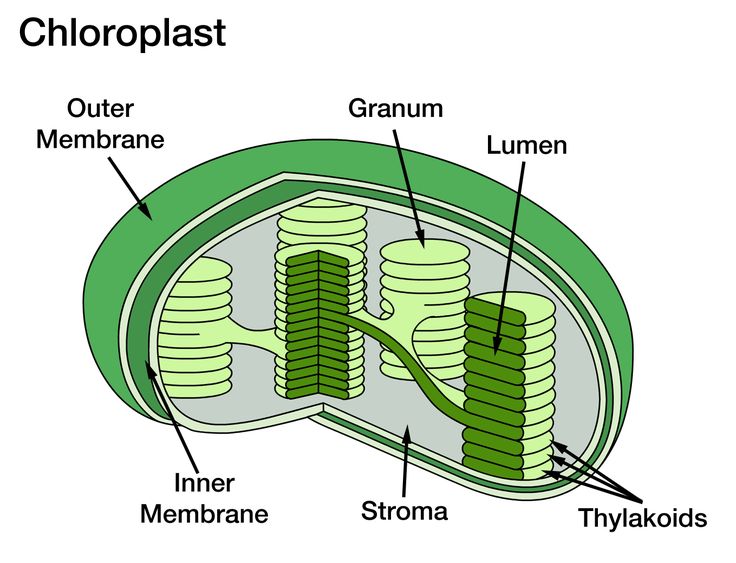
Where does photolysis occur?
In the thykaloid membranes of chloroplasts (this is also where chlorophyll is located, which traps sunlight for the light-dependent reaction)
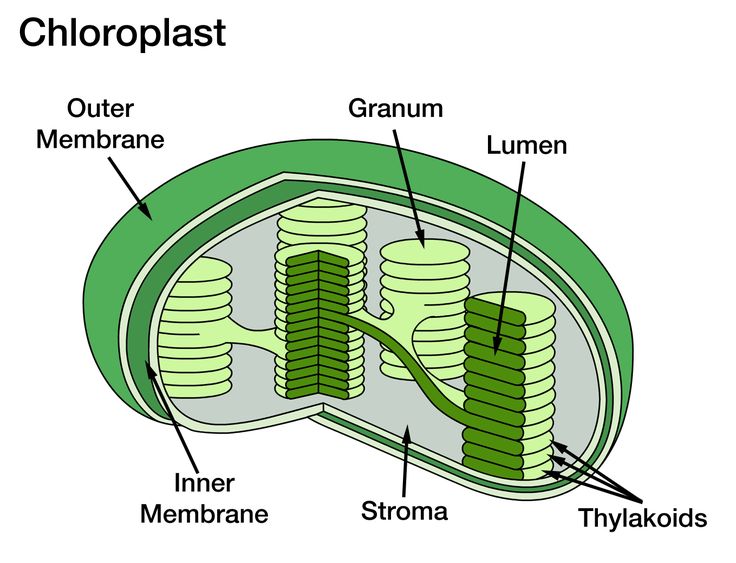
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
In the stroma of chloroplasts
Why is the release of oxygen into the atmosphere good?
It helps maintain atmospheric oxygen levels, which allows for a breathable environment for organisms that carry out aerobic respiration
How are the photosynthetic pigments in plants separated and identified?
Through Chromotography, as the different pigments absorb specific wavelengths of light, while transmitting others. The more soluble the pigment, the further the movement of it
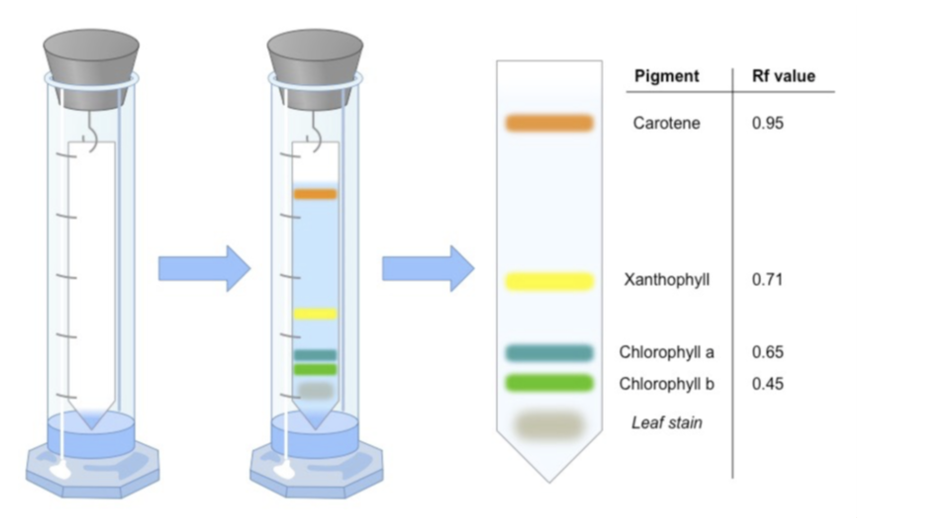
How do you calculate Rf?
Distance travelled by pigment/distance travelled by solvent
What are the roles of the pigments?
They trap light energy. They have different absorption peaks, and they absorb different types of wavelengths of light more effectively. This allows them to adapt to diverse environments
What is the absorption spectrum?
The ability of photosynthetic pigments to absorb specific wavelengths of light, often with peaks corresponding to the wavelengths it absorbs most efficiently
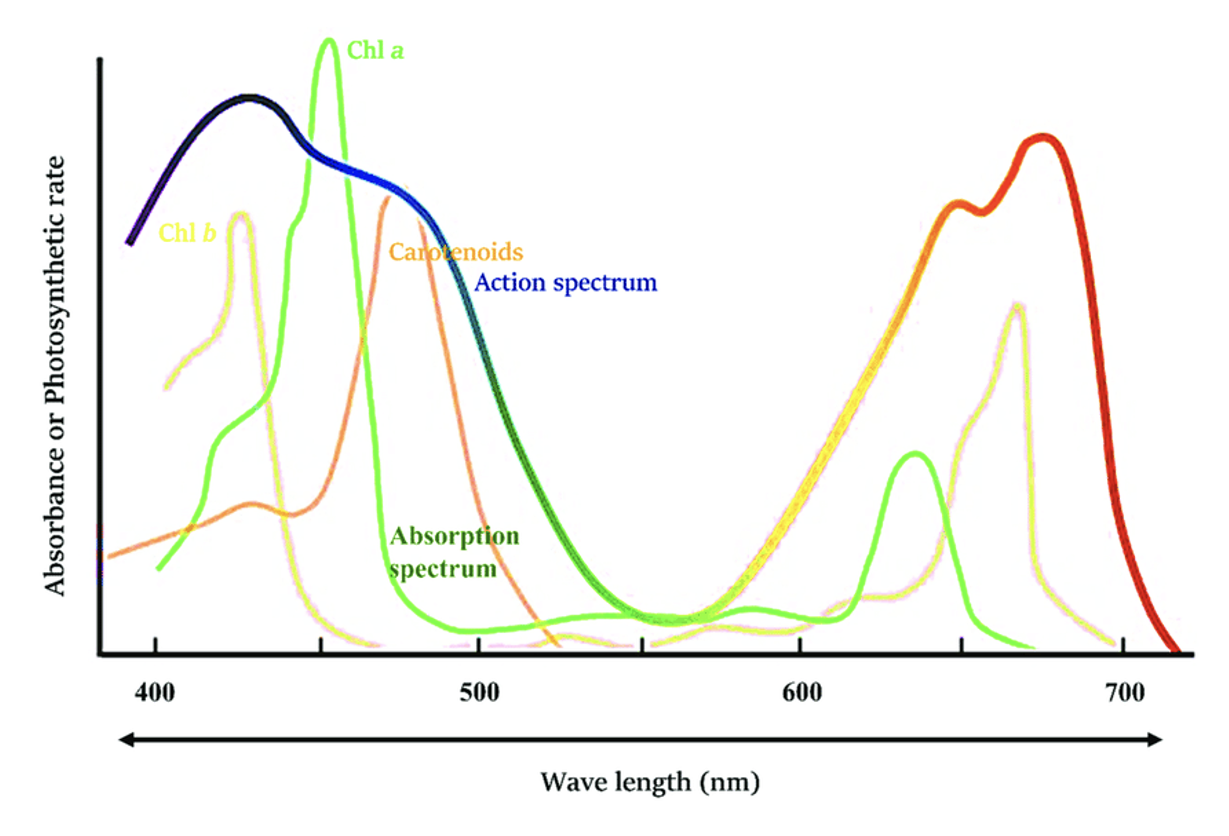
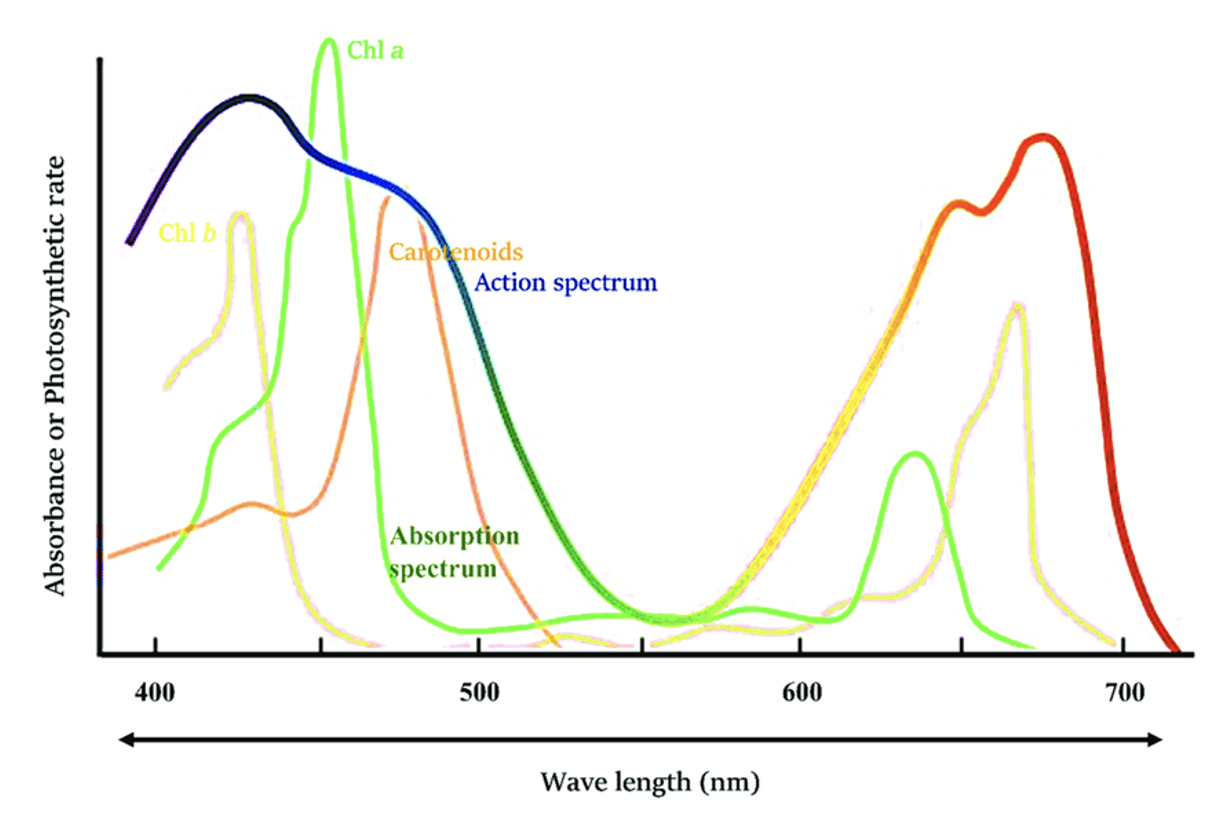
What is the action spectrum?
It shows the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths → the effectiveness of the pigments
What are factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Light intensity
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The higher the light intensity, the higher the rate of photosynthesis, until a limiting factor such as temperature occurs
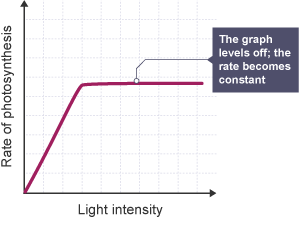
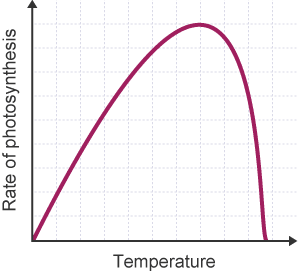
How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of photosynthesis
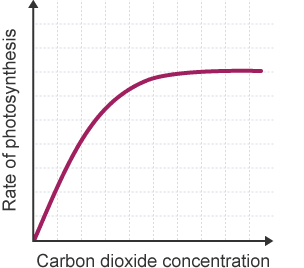
How does carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The higher the carbon dioxide concentration, the higher the rate of photosynthesis, up to a certain point, until it plateaus as another factor is limiting it
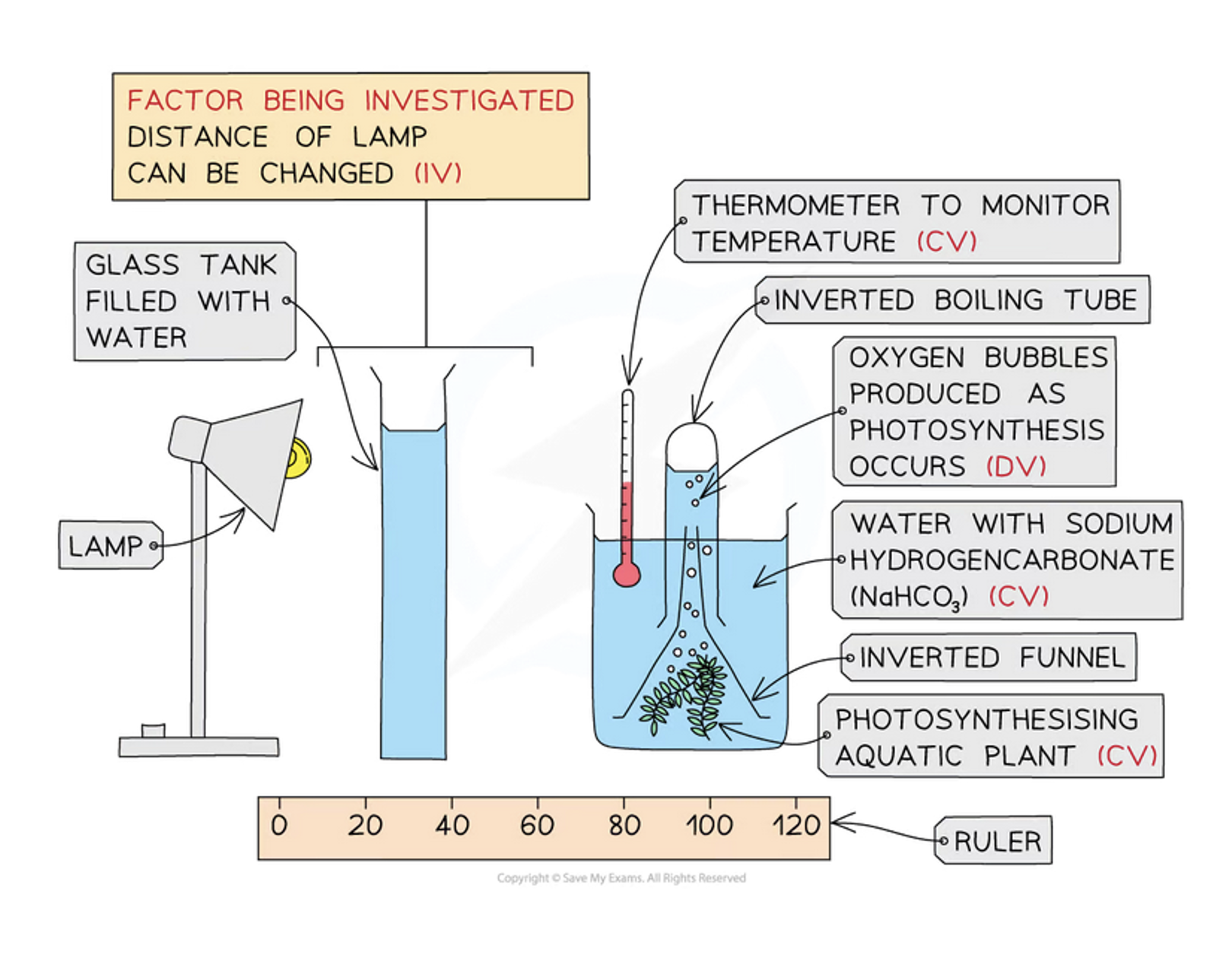
How are factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis investigated?
What are carbon dioxide enrichment experiments?
They help to predict how different plant species will respond to increased CO2 levels. This is important for predicting shifts in ecosystems and biodiversity. It also provides insights into plant adaptability. For example, monitoring and controlling CO2 levels in enclosed greenhouses, and observing how fruit, vegetables and plants grow