BSCI 1510: Exam 3 Material
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
The Genome of the Bacterium E. coli is considered to be "streamlined," meaning that nearly all of the DNA is in the form of genes and there is little non-gene DNA. Name one possible advantage to human cells that might be associated with streamlining the genome.
Fewer genomes = faster replication
Less mutations possible
More streamlined
Name two disadvantages to human cells that might be associated with a more streamlined genome.
evolutionarily constrained, inability to adapt, more likely that a single mutation would hit an essential gene
Why is RNA less stable than DNA?
The added oxygen leads to the molecule wants to react more. Specifically a nucleophilic attack.
Do Eukaryotes mutate less or more than prokaryotes?
Less!
Do Viroids mutate more or less than Eukaryotes?
More!
What is the makeup of DNA?
Base, phosphate group, covalent bond, H-Bond, & a sugar (specifically deoxyribose)
When numbering the carbons on the nucleotides, which carbons are labeled with a "prime sign"?
the carbons on the sugars
On purines what is the linkage to the sugar?
9-1
on the pyrimidines what is the linkage to the sugar?
1-1
What does pyrimidine mean? what are the pyrimidines?
T&C, Single Ring
What does purine mean? What are the purines?
A&G, double rings.
What is a characteristic of a major groove?
No glycosidic bonds, Accessibility to make proteins.
What is the simplified DNA Repair Sequence?
1. Mutation is recognized
2. Repair Nuclease Nicks strand or excises base
3. DNA polymerase fills in
4. DNA Ligase Seals gap
What are the mechanisms of Repair that DNA utilizes?
DNA polymerase proofreads. Mutations that are not repaired by proofreading are repaired by mismatch (post-replication) Repair followed by Excision repair)
Mutations that occur spontaneously any time are repaired by excision repair
How many histones are present?
8. H2A H2B H3 H4 and there are two of each.
What does it mean to metalated?
Adding a methyl group (CH3) In order to silence a gene.
Where on the DNA strands does methylation occur?
Adenine Bases
How is DNA read?
3 prime to 5 prime
Does methylation occur after repair or before repair?
After repair the newly replicated strand is methylated.
What enzyme proof reads DNA?
DNA polymerase
What is a thymine dimer?
A thymine dimer is two adenine bases that are abnormally linked to together by covalent bonds. Inhibits DNA replication which can lead to the death of an organism
Draw adenine
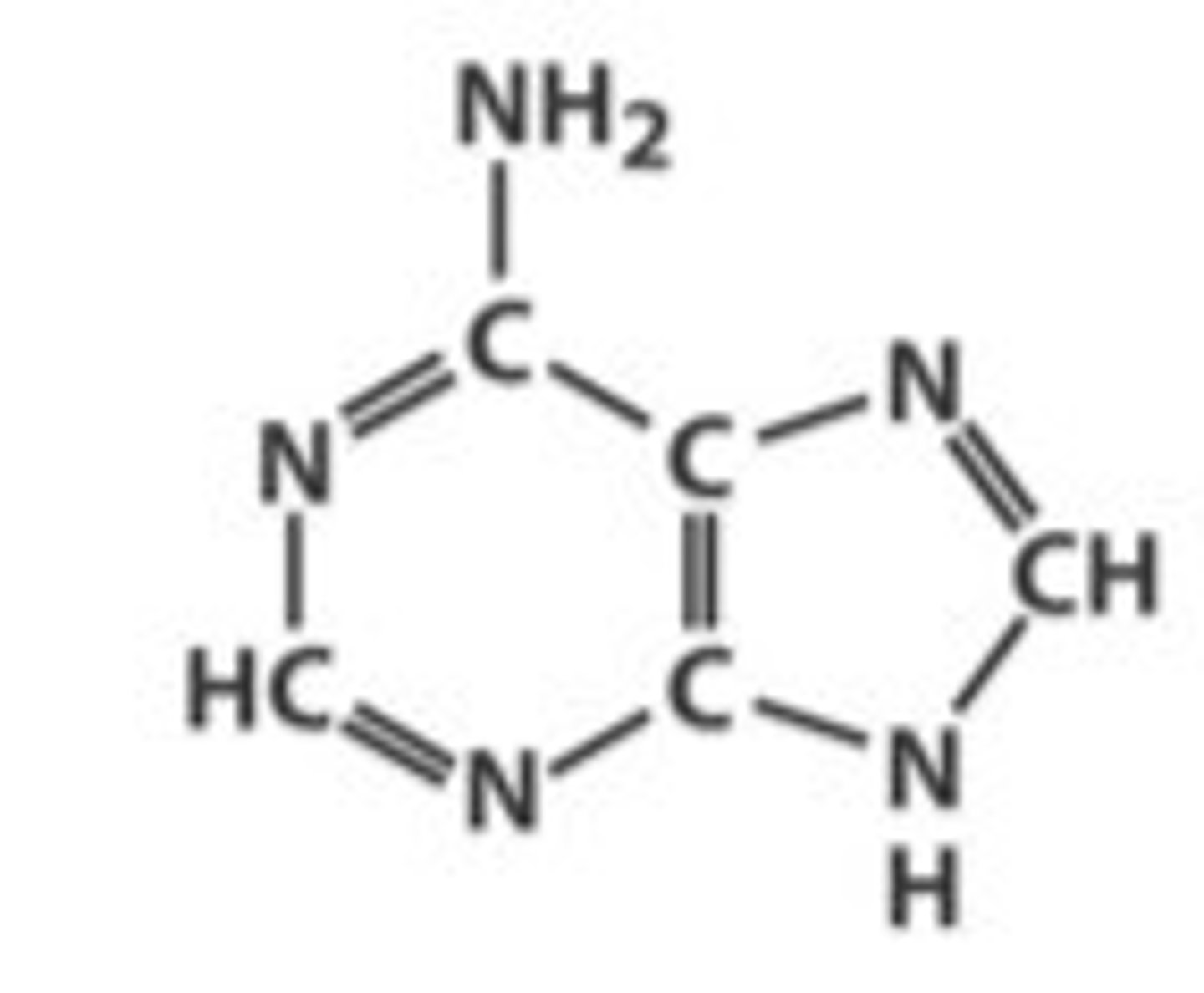
Draw Guanine
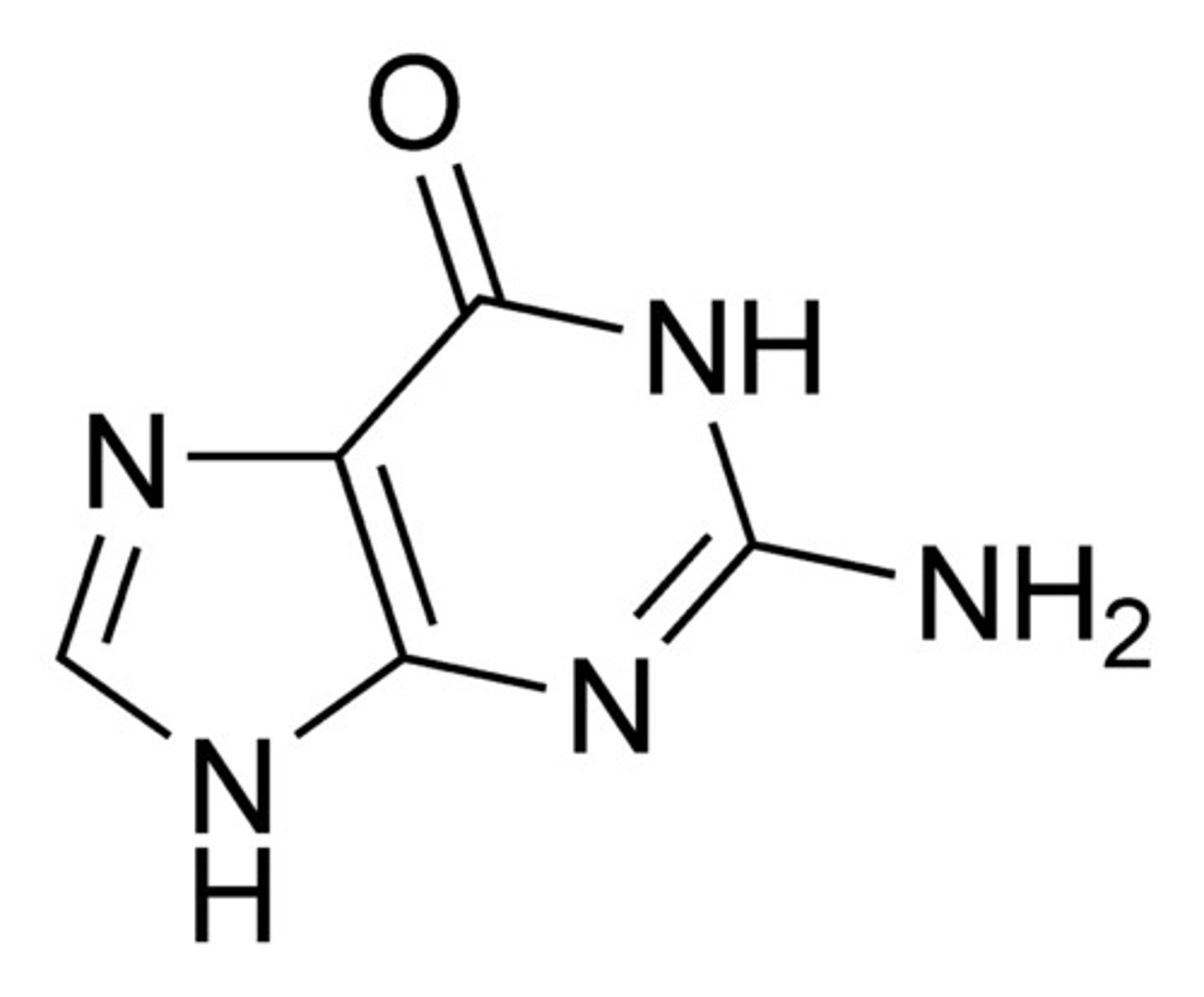
Draw Thymine
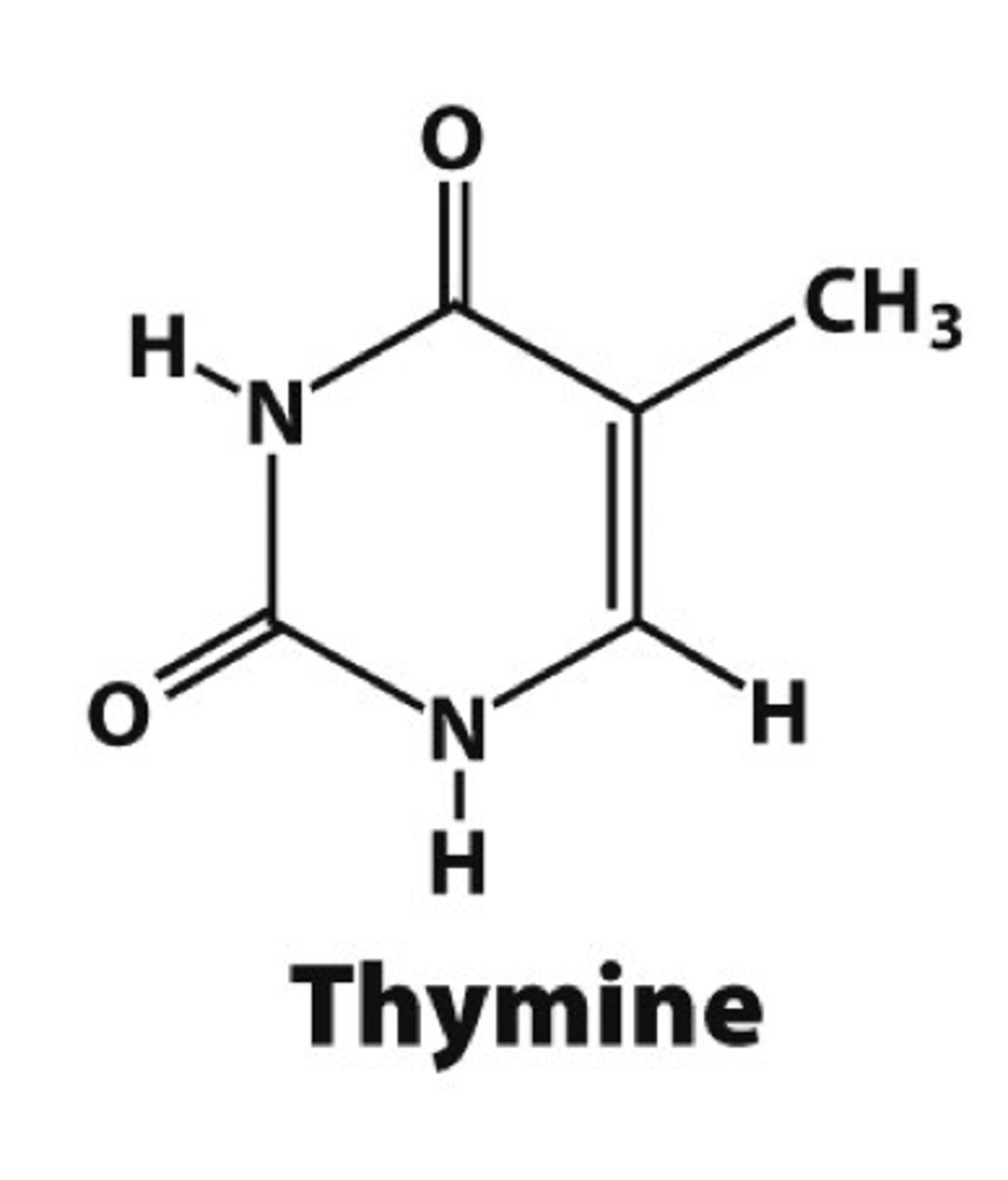
Draw cytosine
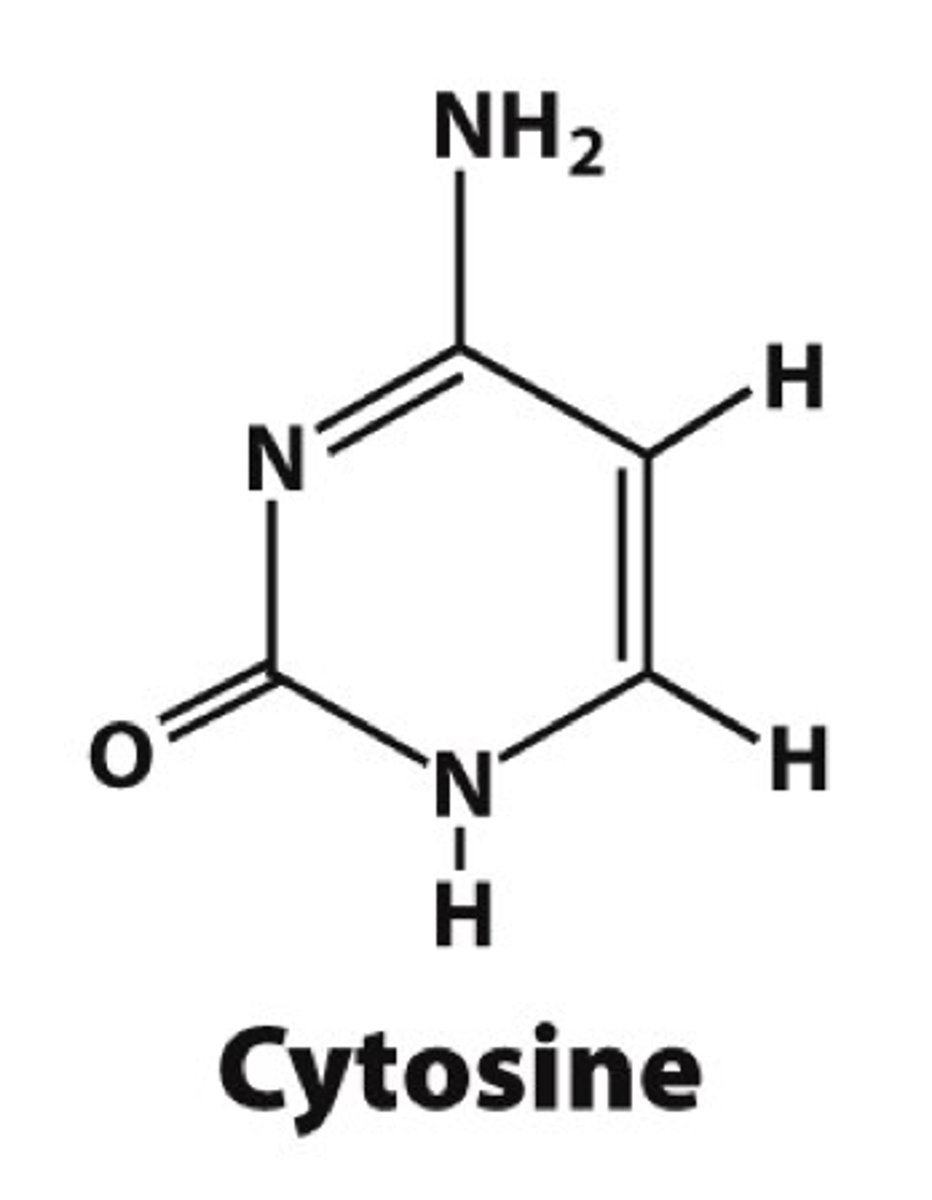
What is the directionality of DNA?
Anti Parallel
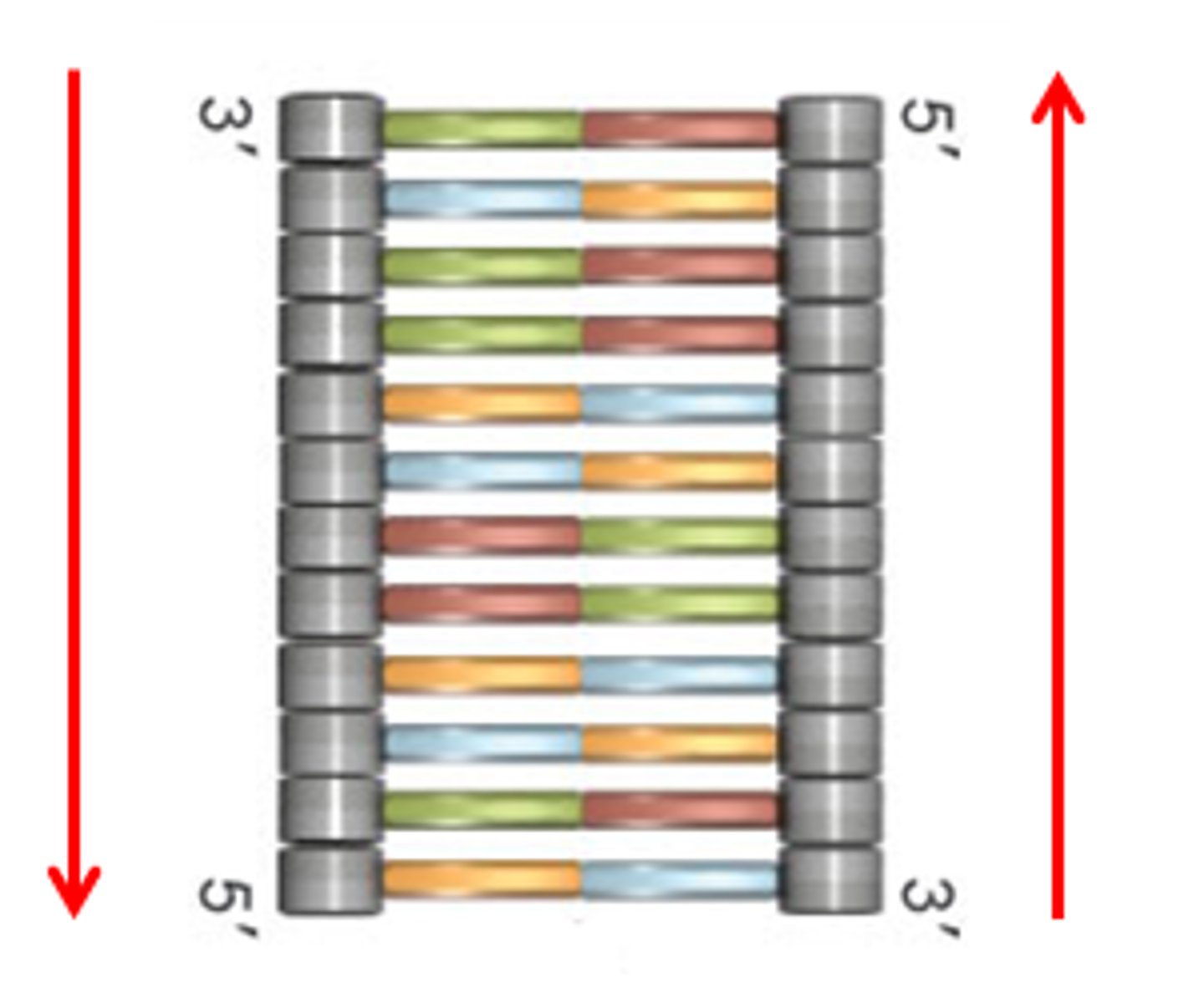
What are the three mechanisms utilized to stabilize DNA?
1. Hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides
2. Electrostatic interactions (base stacking so that the e- clouds are repelling each other equally)
3. Hydrophobic inner compartment of DNA (does not allow water within the molecule)
Tautomer Pairing: A:T
A(imino): C
Tautomer Pairing: T:A
T(enol): G
Tautomer Pairing: C:G
C(iminio): A
Tautomer Pairing: G:C
G(enol):T
What is the rare imino tautomeric form?
Cytosine mis-pairs with adenine resulting in a transition mutation
what is the purpose of the 5' cap on the finished mRNA strand?
Protection from exonuclease, but also promotes binding to ribosomes, as well as regulates nuclear export
A strand of mRNA is just finished splicing and has made its way to the cytosol. It is lacking a Poly A tail and a 5' Cap. What is going to happen to this mRNA?
The DNA will be attacked by the enzyme exonuclease and will not be converted into a protein.
Splicing occurs in the pre-mRNA. What would happen if the introns were not spliced out?
an mRNA with extra "junk" in it will be made, and a wrong protein will get produced during translation.
The reading Frame of an mRNA:
A. Begins with a start codon
B. Ends with a stop codon
C. Is read in groups of 3 nucleotides
D. Requires removal of introns
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
Which of the following is true:
A. Spliced mRNA is usually longer than the DNA from which it is transcribed
B. Splicing occurs in the cytoplasm
C. mRNA cannot be translated until it is fully spliced
D. Introns are short and exons are long
E. Introns contain coding sequences and exons do not
C. mRNA cannot be translated until it is fully spliced
Operons:
A. Are found in eukaryotes
B. Are groups of coordinately regulated genes
C. Produce monoisotopic transcripts
D. Contain introns
E. All of the above
B. Are groups of coordinately regulated genes
The International Human Genome Consortium published the finding that the human genome only contains approximately 20-25K genes. In contrast, it appears that human cells express a much more complex and diverse number of proteins. How can a small genome encode so many more proteins?
Alternative splicing- allows for a wider ranger of proteins and for the gene to even test out different proteins.
Base Pairing:
A. Is essential for intron recognition
B. Is essential for DNA replication
C. Is essential for DNA helix formation
E. All of the above
All of the above
What type of formation is DNA? What type of formation is RNA?
DNA is B form (right handed)
RNA is A form (left handed)
Polymerase III:
does most of the DNA replication in prokaryotes, synthesizes leading and lagging strand (primase needed to lay down RNA primers)
Polymerase I
can remove RNA primers and fill in gaps between Okazaki fragments in prokaryotes, also can fill in gaps made by exonuclease activity in proofreading
Polymerase Alpha
Initiates eukaryotic replication, can lay down primers
Polymerase Beta
Eukaryotic Repair
Polymerase Delta
Elongates Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes
Polymerase Epsilon
Elongates leading strand in eukaryotes
Which way is DNA proofread?
3' to 5'.
What is CMP referring to
A nucleotide with one phosphate
What is CDP referring to
a nucleotide with two phosphates
What is CTP referring to?
A nucleotide with three phosphates
Does Ligase have directionality?
No- it just joins adjacent 5'-P and 3-OH groups using ATP as an energy source.