Biology Gcse Paper 1
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
extremely simple and simplfied version
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Types of eukaryotic cells
plant and animal
type of prokarytoic cell
bacteria
whats the tail in a bacteria cell called
flagella
what do ribosomes do
protein symphasis
what goes in and out of the cell
cell membrane
are prokaryotic cells unicelluar or multicelluar
unicellular
do prokarytoci cells have a cell wall
yes
where is DNA stored in a prokarytoic cell (give 2 exps)
circular single strand of DNA and plasmids
in a circular single strand of DNA they contain info they need to…(2)
survive and reproduce
what contains aerobic respiration
mitochondria
which is cheaper light microscopes or electron microscopes
light microscopes
which have a higher resolution microscopes or electron microscopes
electron microscopes
what do chloroplasts contain
chlorophyll
is binary fission the same as mitosis or meiosis
no
eukaryotic or prokaryotic binary fission
prokaryotic
eukaryotic or prokaryotic mitosis and meiosis
eukaryotic
when one bacteria cell divides into two
binary fission
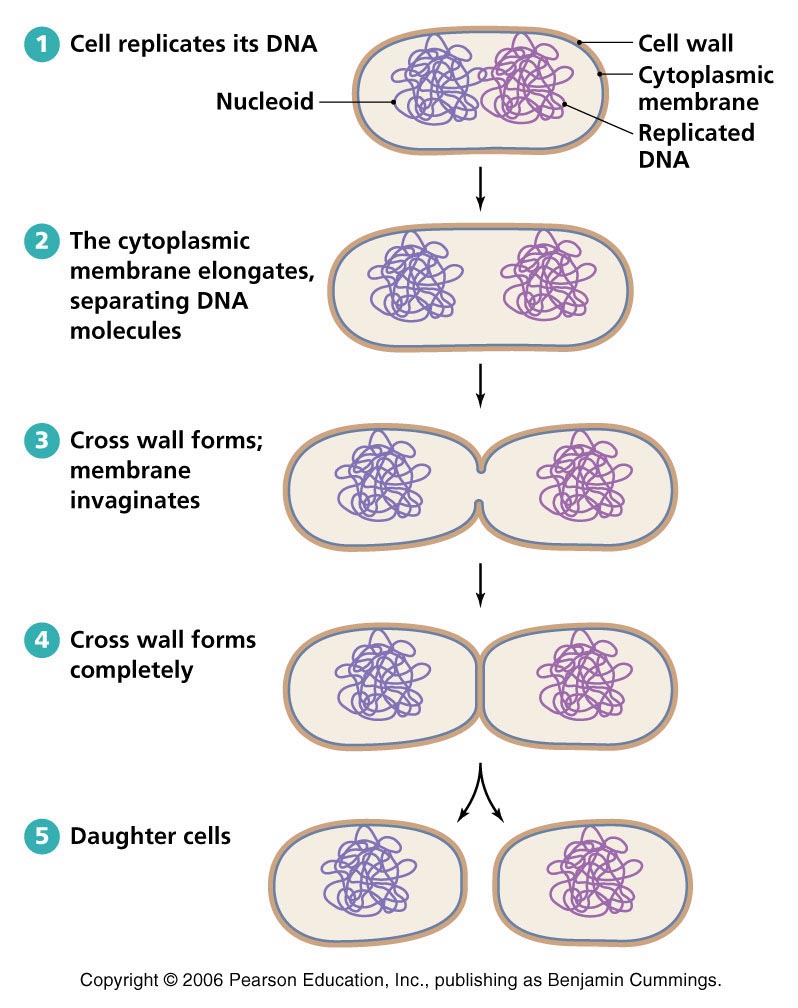
where a bacteria cell can undergo binary fission it has to do 2 main things which are..
grown and replicate genetic material
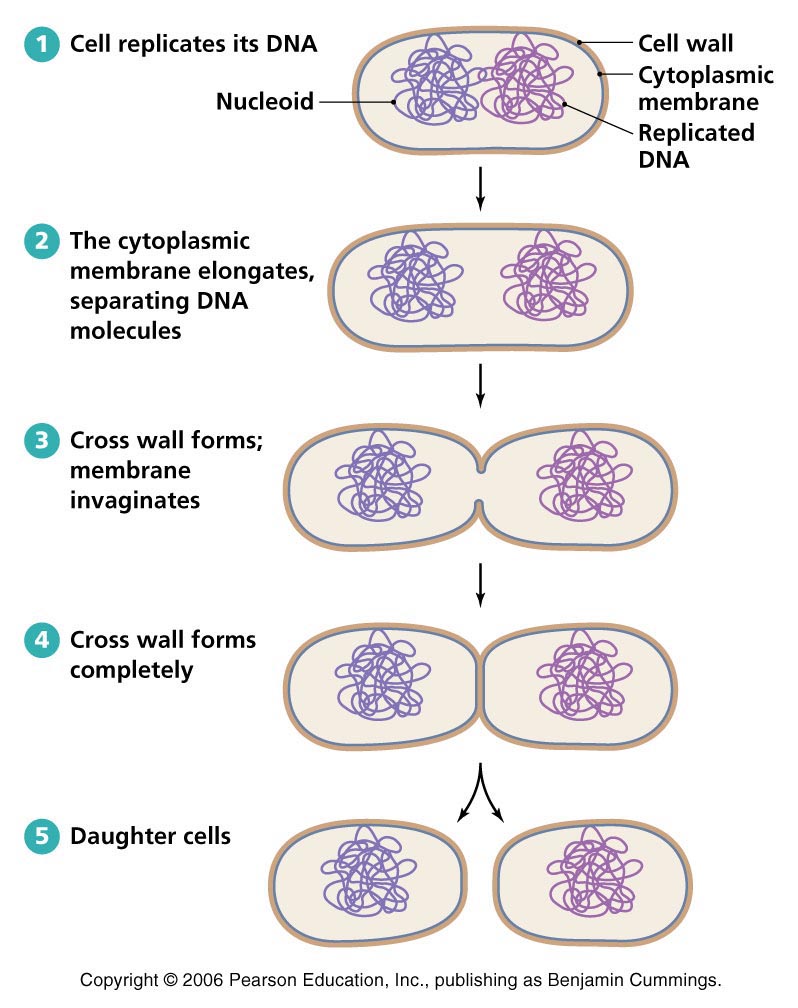
when genetic material replicated (prokaryotic durning binary fission) the material will…
seperate
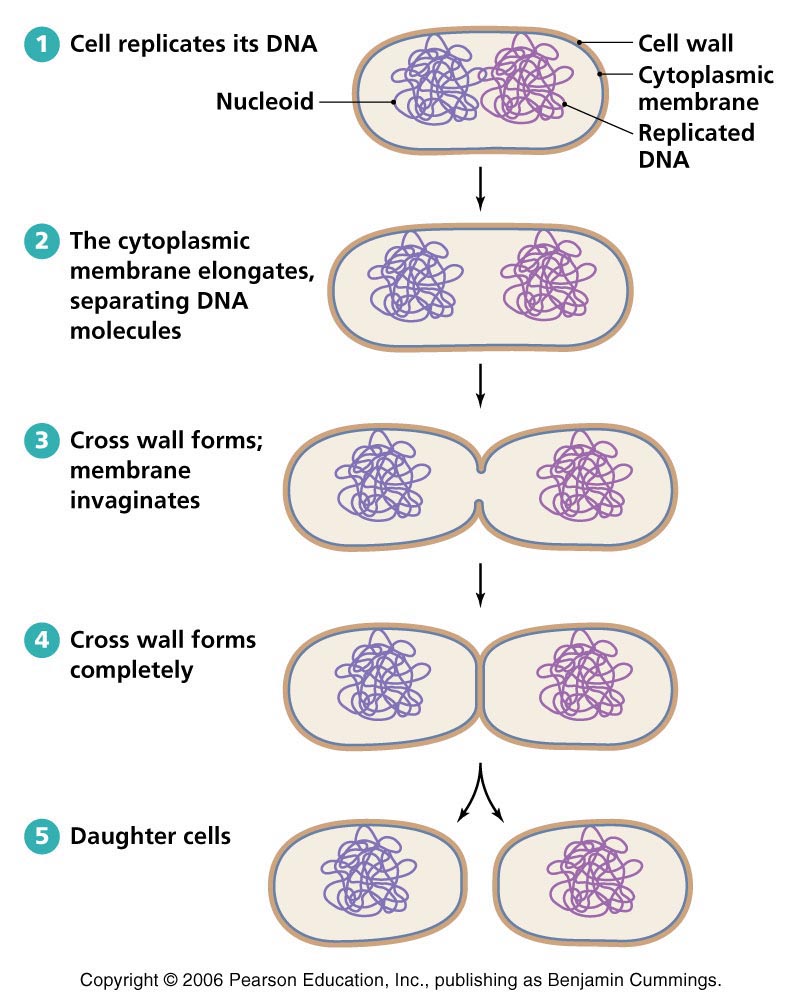
(binary fission) when ready to divide it produces a new…in the middle where they pull apart
cell wall
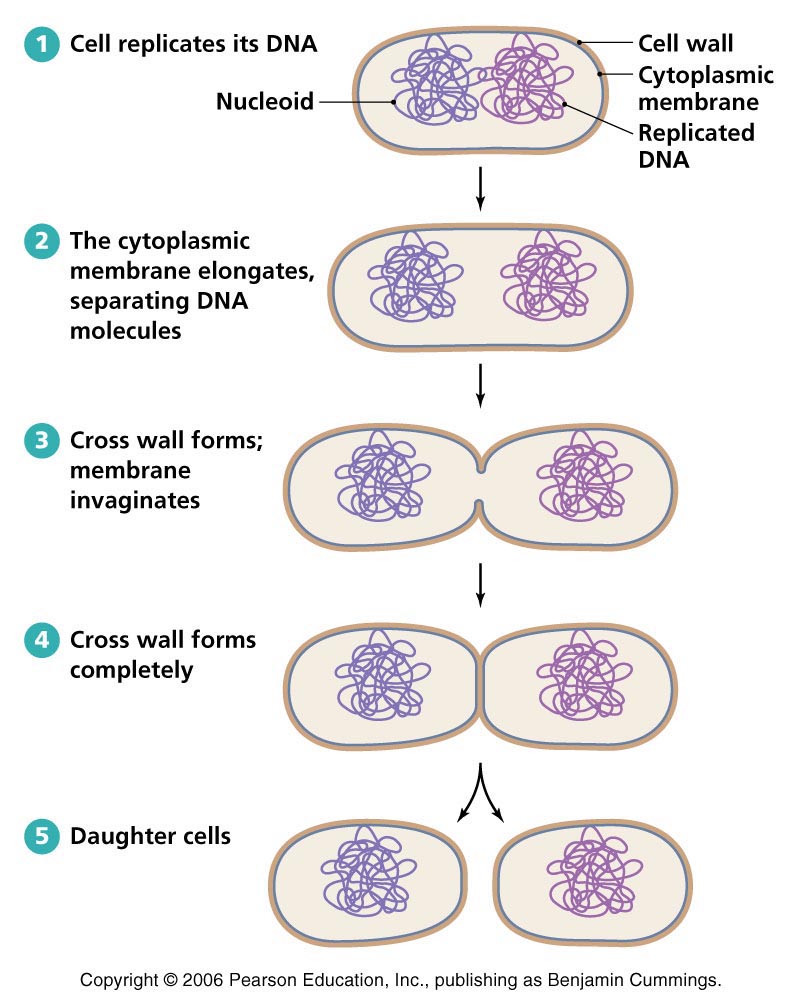
does binary fission take long?
no
a bacterial cell has a mean division time of 30 minutes.How many cells would it produce after 3hrs? and how many rounds of division
6 rounds and 64cells (1×2^6)

what does the mean division time depends on (2)
species and conditions
best conditions for bacteria growth (3)
moist,warm,plenty of nutrients
a new supply of cells is needed for (3)
growth,repair,development
how many pairs of chromosones do humans have
23
eukaryotic cells have a very large number or cells. have to be able to divide
cell cycle
DNA replicates to form copes of each chromosome,grows and copies its internal structure (mitochondria and ribosomes) what stage of the cell cycle is this
first stage
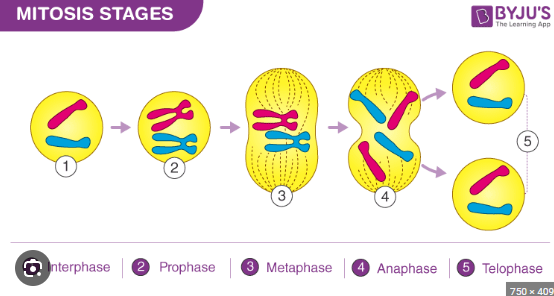
in the secound stage of the cell cycle what takes place
mitosis
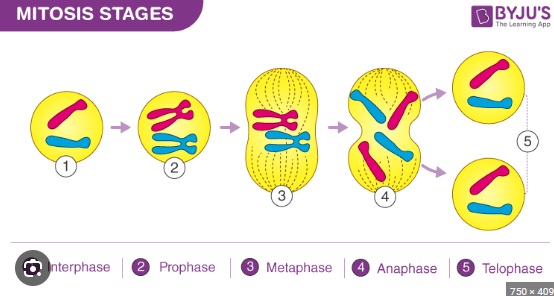
one set of chromosones is being pulled to each end of the cell,nucleus divides what stage of cell cycle
2 stage
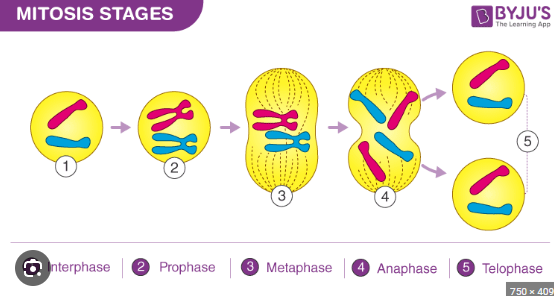
cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to make identical cells what stage of the cell cycle is this
final stage
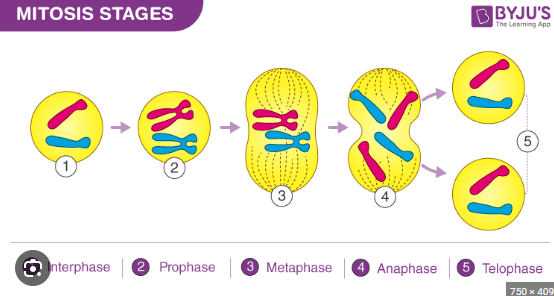
mitosis is essential for _____ and ________of multicelluar organisms (plant/animal)
growth and development
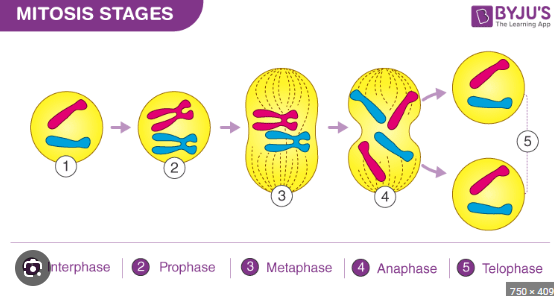
when does mitosis take place
when an organism repairs itself (broken bone heals)
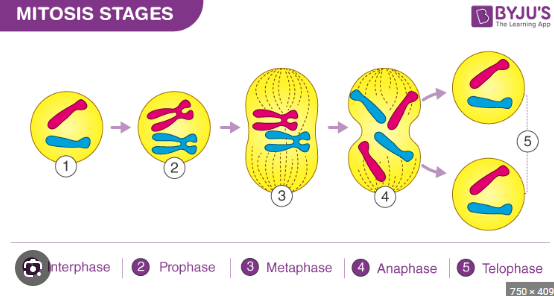
what does PMAT stand for
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase

the beginning stage of mitosis the nucelus is still there chromsones are condesing (thick and visible)
prophase
middle, chromosones line up in the middle of the cell nucleus dissambled so longer there
metaphase
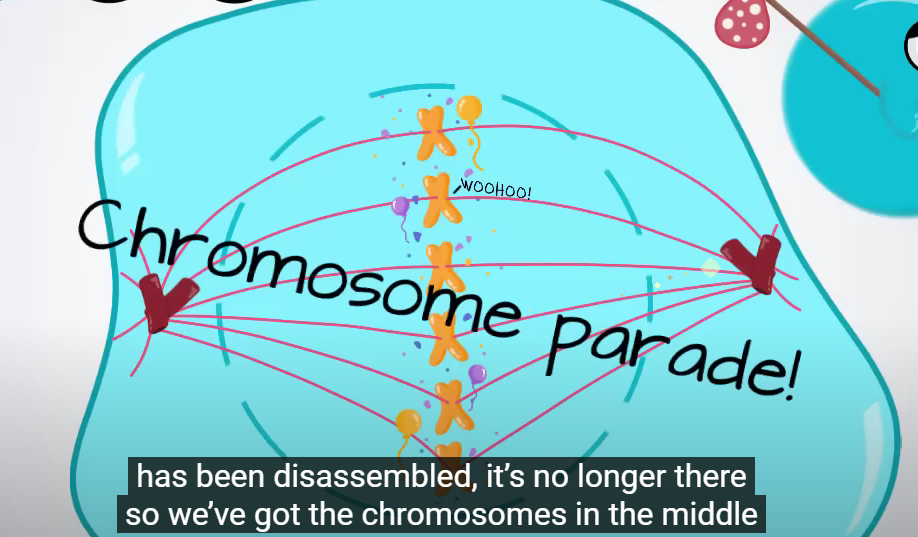
awaay,chromosones move away opposites sides of the cell
anaphase
chromosones at complete opposites ends two nuclei form on opposite ends
telophase
final seperation into two cells by spliting the cytoplasm
cytokinesis