CH 10 X-ray interaction ROD
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
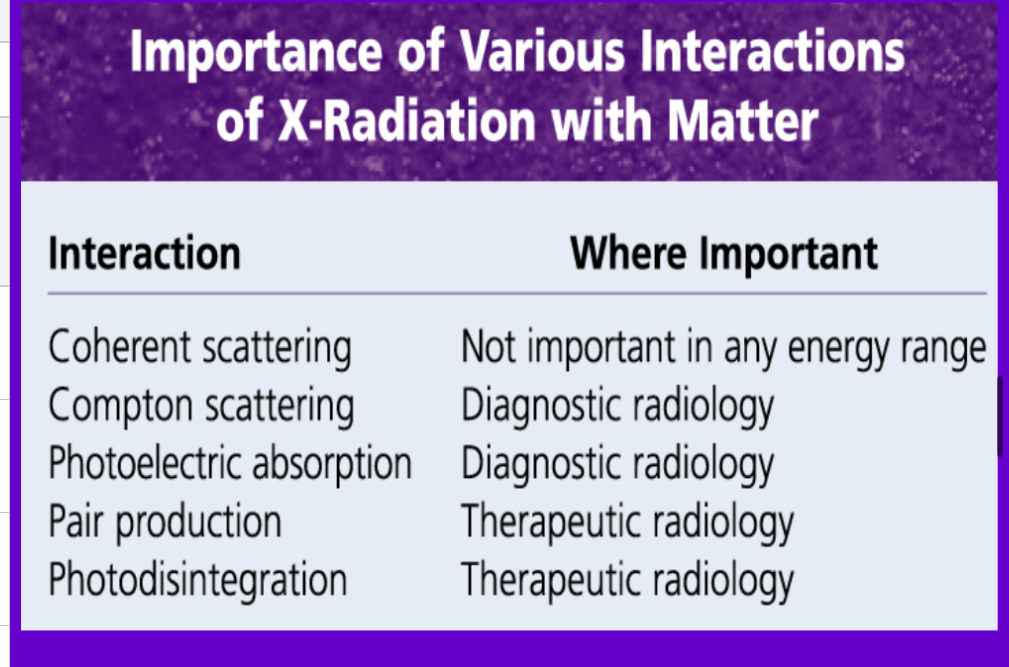
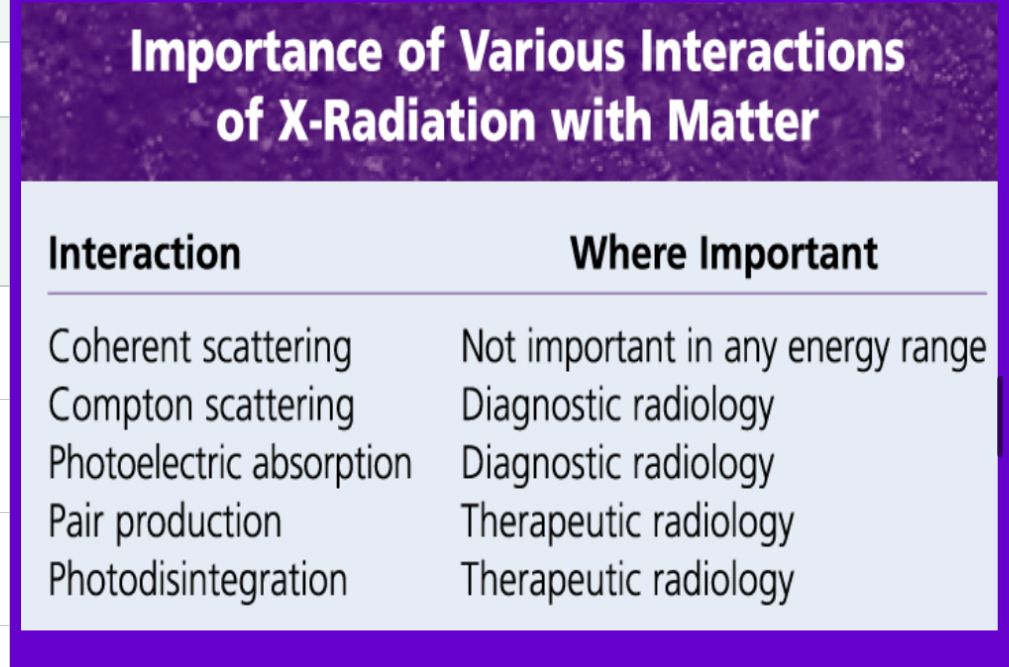
5 interactions w matter include?
Coherent scattering
Compton scattering
Photoelectric effect
Pair production
Photo disintegration
(only COMPTON SCATTERING AND PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT MAKE X-RAY IMAGES)
Photon is the smallest
Smallest quantity of electromagnetic radiation.
Small bundle of energy or quantum traveling at the speed of light
Wavelength;
Frequency;
Wavelength; refers to the distance between two crests
Frequency; refers to the number of cycles per second , unit of measure is hertz
The shorter the wavelength the higher the _____
Frequenncy
When an electron is added or removed from the atom, it is ?
- it is ionized
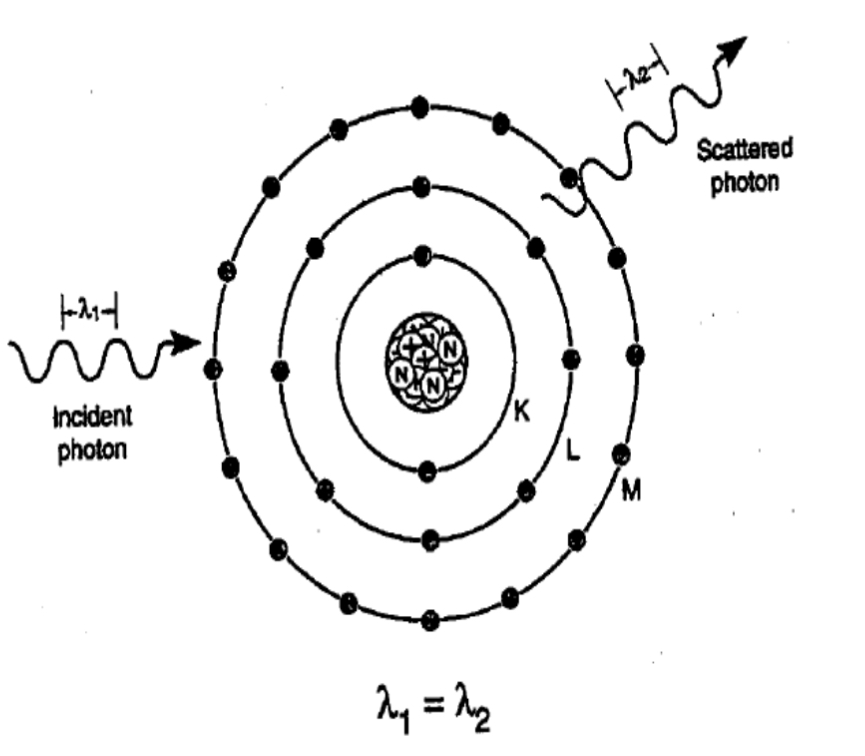
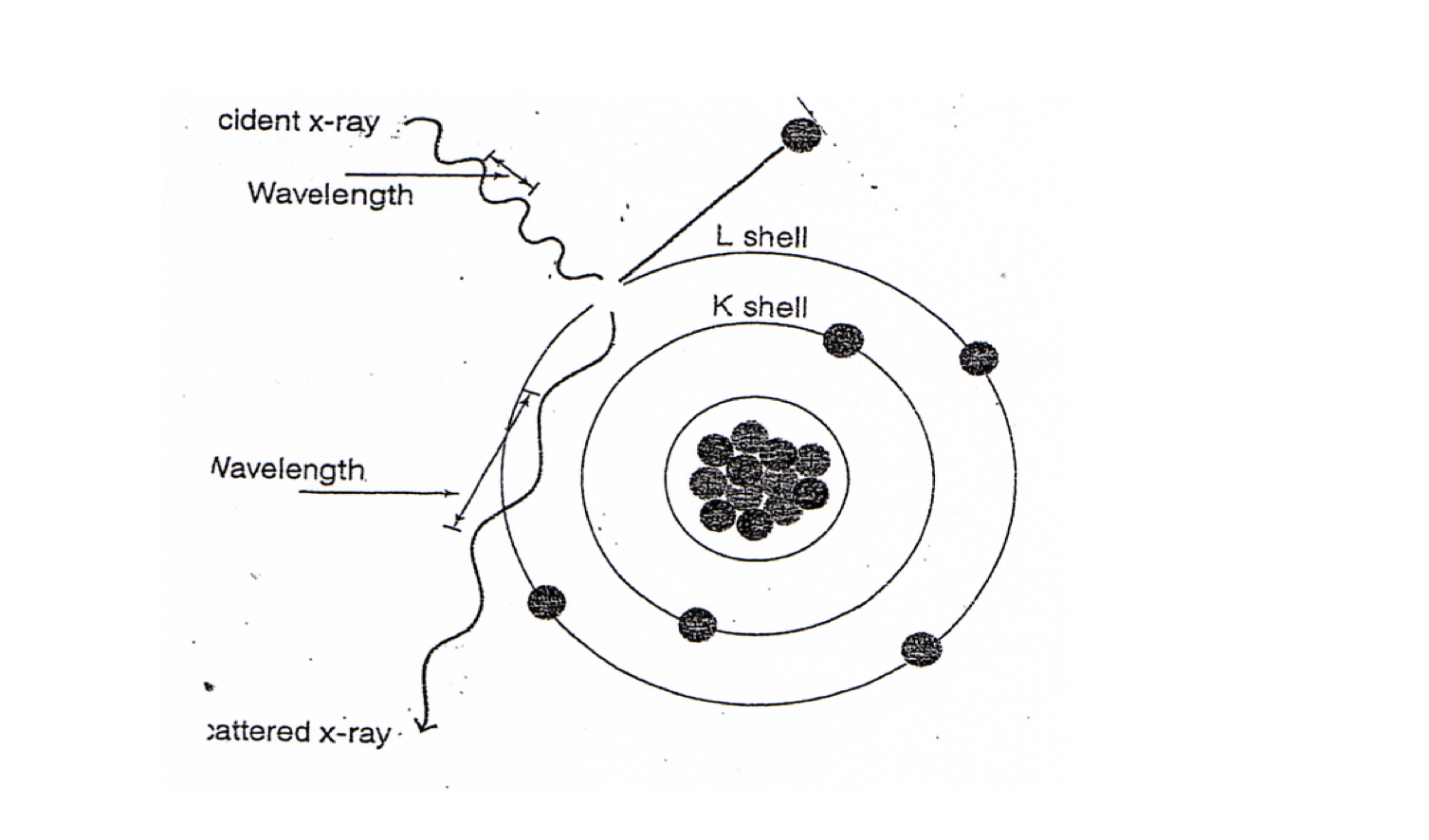
Coherent scattering refers to
Also called: Classical scattering or Thompson scattering
Occurs with energies below 10 keV( involves low energy X-rays)
-Incident x-ray interacts with an atom of matter, causing it to become excited. Immediately the atom releases this excess energy and the scattered x-ray with a wavelength equal to that of the incident X-ray it just changes direction.
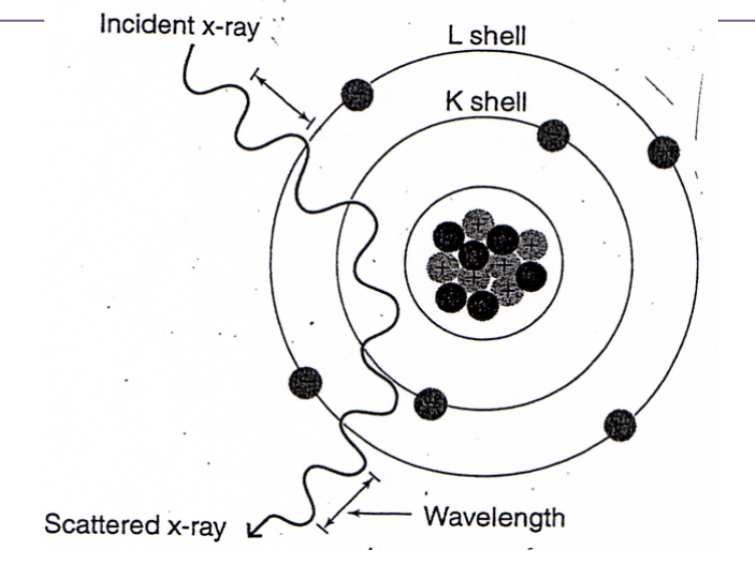
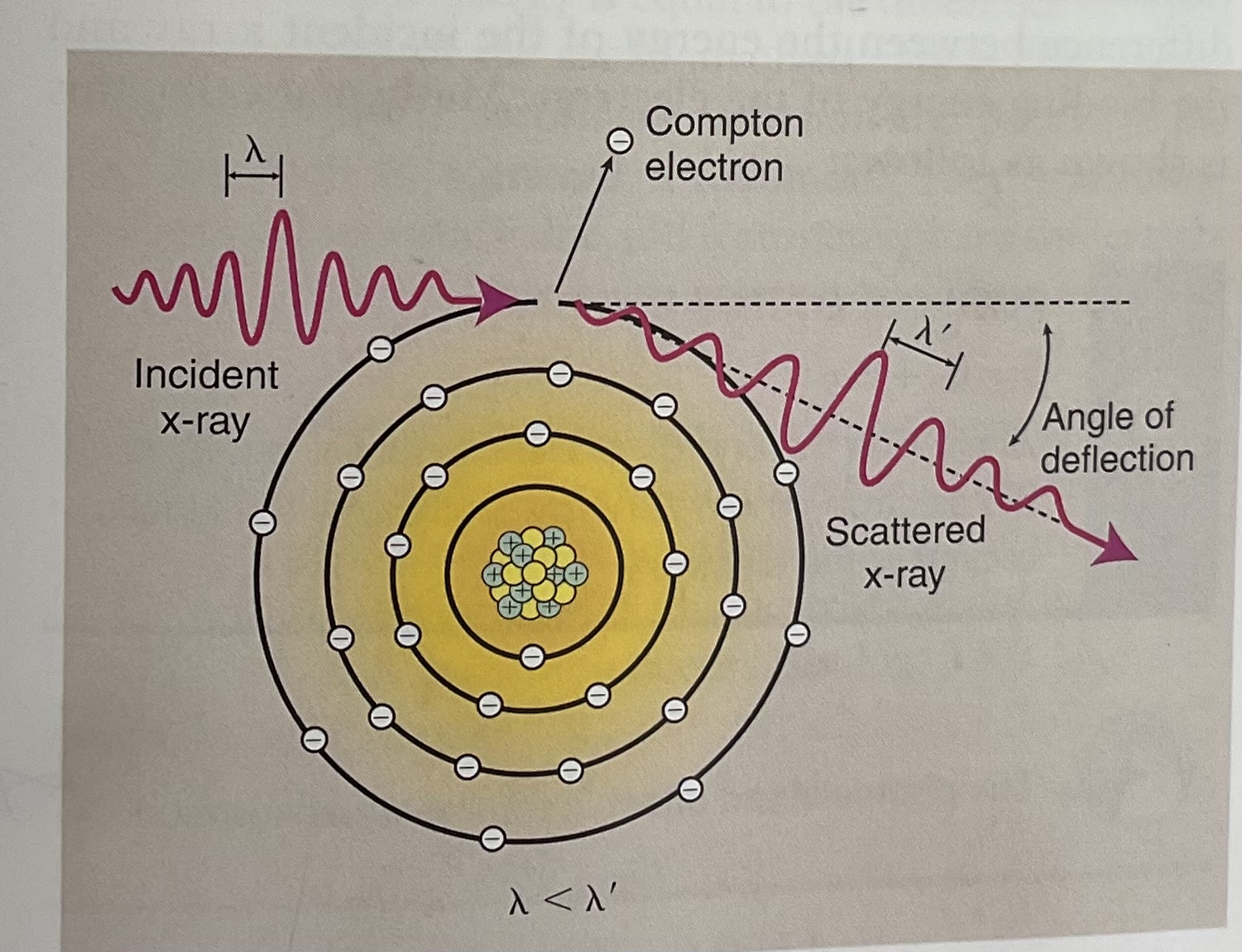
Compton scattering refers to
Occurs throughout the diagnostic imaging range
A fairly high energy (high kVp) x-ray photon ejects an outer shell electron. The incident x-ray interacts with the outer electron shell on an atom of matter, removing it. (Ejecting it) called COMPTON ELECTRON
-It not only causes ionizes it but scatters the incident x-ray causing a reductions in energy and the change of direction.
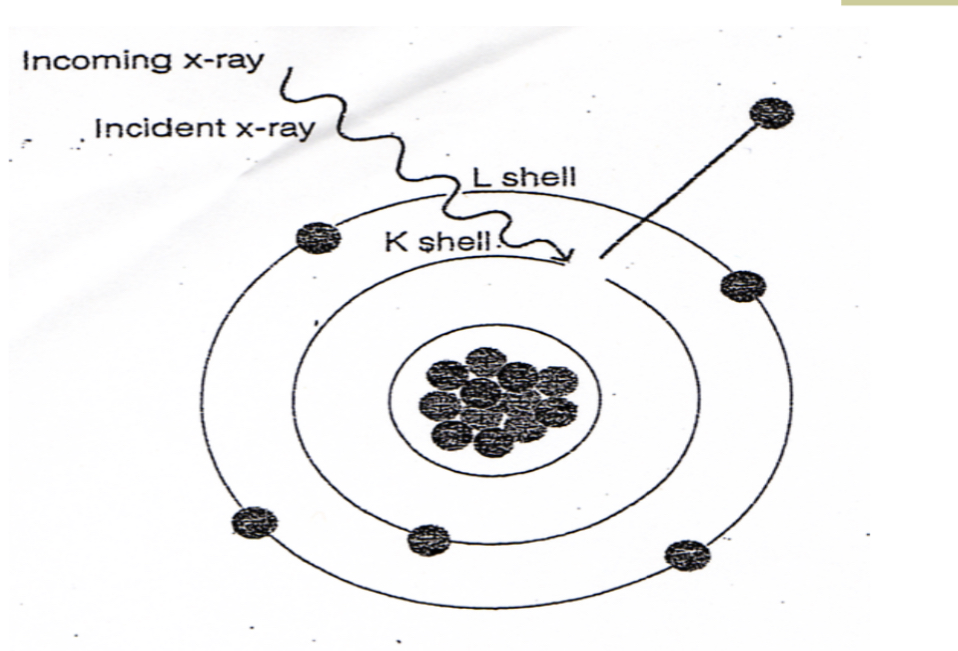
The probability of Compton gathering decreases as______
Decreases as x-ray energy increases
X-rays scattered back in the direction of the incident x-ray beam are called
Backscatter radiation
The probability of Compton scattering is inversely proportional to_________ And not dependent on atomic number
Inverse proportional to x-ray energy
Compton scattering reduces _____
image contrast
Scattered x-rays provide no information on the x-ray image rather they produce unwanted exposure to the image receptor called
X-ray fog,
The result is uniform x-ray intensity on the image, receptor, resulting and reduced image contrast?.
Scattered x-rays from Compton, such a radiation exposure, hydrate and radiography particularly in _____
fluoroscopy
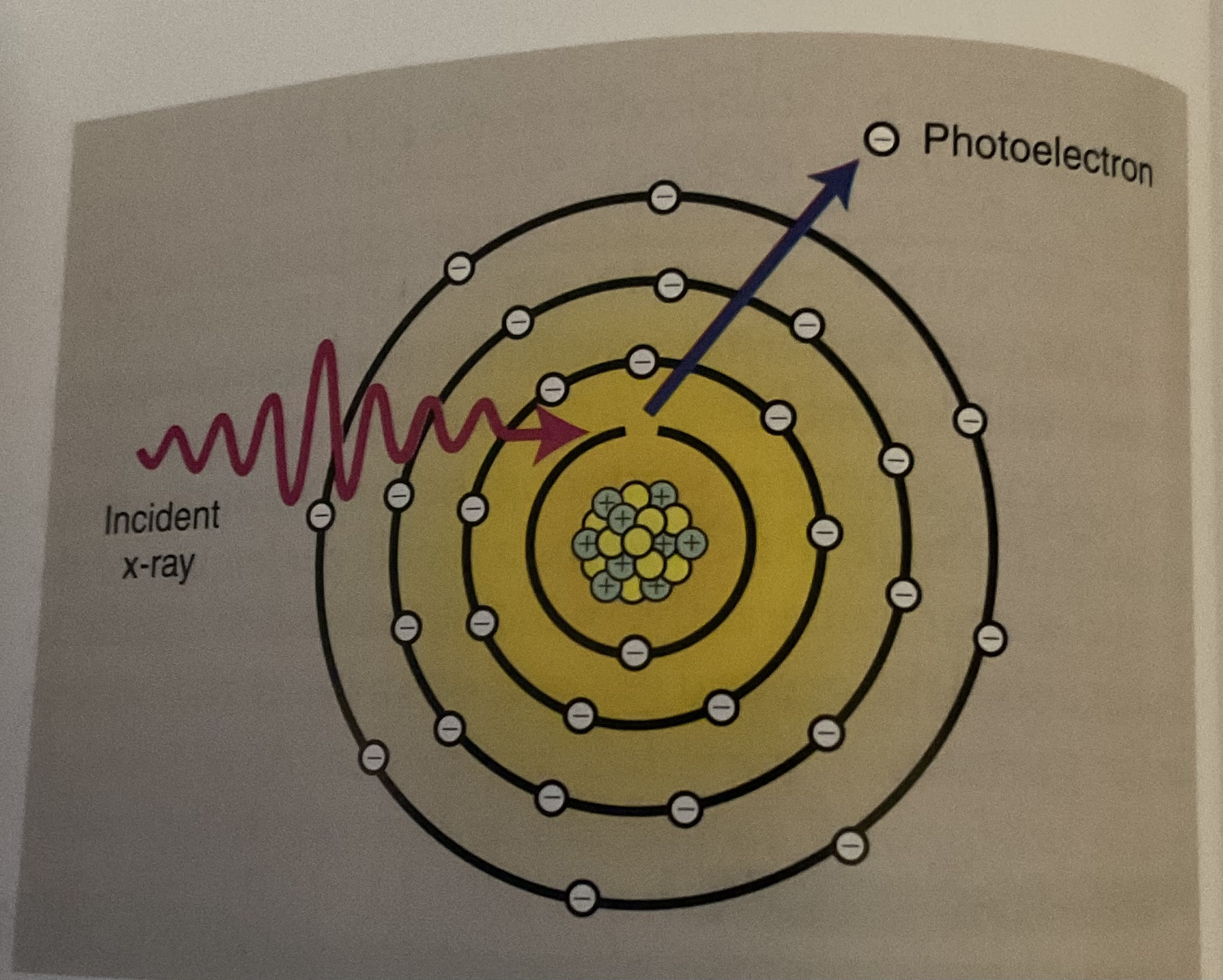
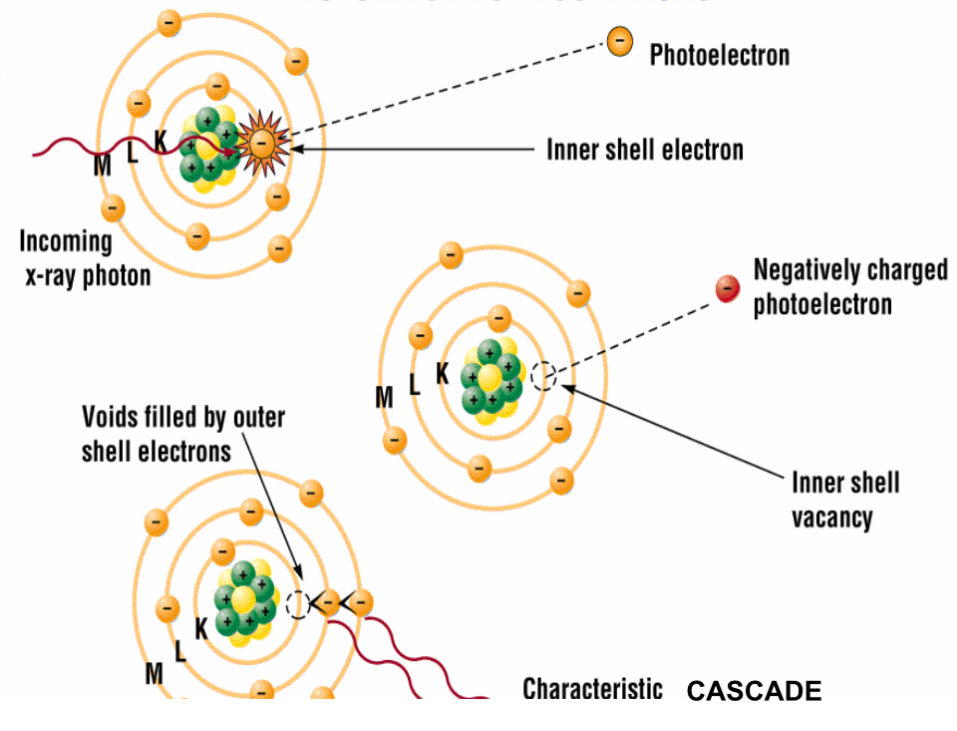
Photoelectric effect refers to
Occurs when an incident X-ray is totally absorbed after interacting with an inner shell electron.
-The incident photon disappear, and the K shell electron is NOW called a photo electron ejected from the atom. (Escapes with kinetic energy equal to the the energy of the incident x-ray, and the binding energy of the electron)
characteristic x-rays are produced after photoelectric interaction
The photo electric effect is total X-ray _______
Absorption
The probability that x-ray will go under the photoelectric interaction is a function of both x-ray _________ and _________
ray energy and the atomic number of the atom in which interacts
The photoelectric interaction cannot occur unless the incident x-ray has_________
has equal energy or greater than the electron Binding energy(kshell)
A photo electric interaction is more likely to occur with ________
with high Z atoms than low Z atoms ?
Type and effective atomic numbeR
Fat
Soft tissue
Lung
Bone
Air
Iodine
Barium
Tungsten
Lead
Fat ; 6.3
Soft tissue; 7.4
Lung; 7.4
Bone; 13.8
Air: 7.6
Iodine 53
Barium: 56
Tungsten: 74
Lead: 82
Pair production ______ occur in X-ray imaging
DOES NOT OCCUR
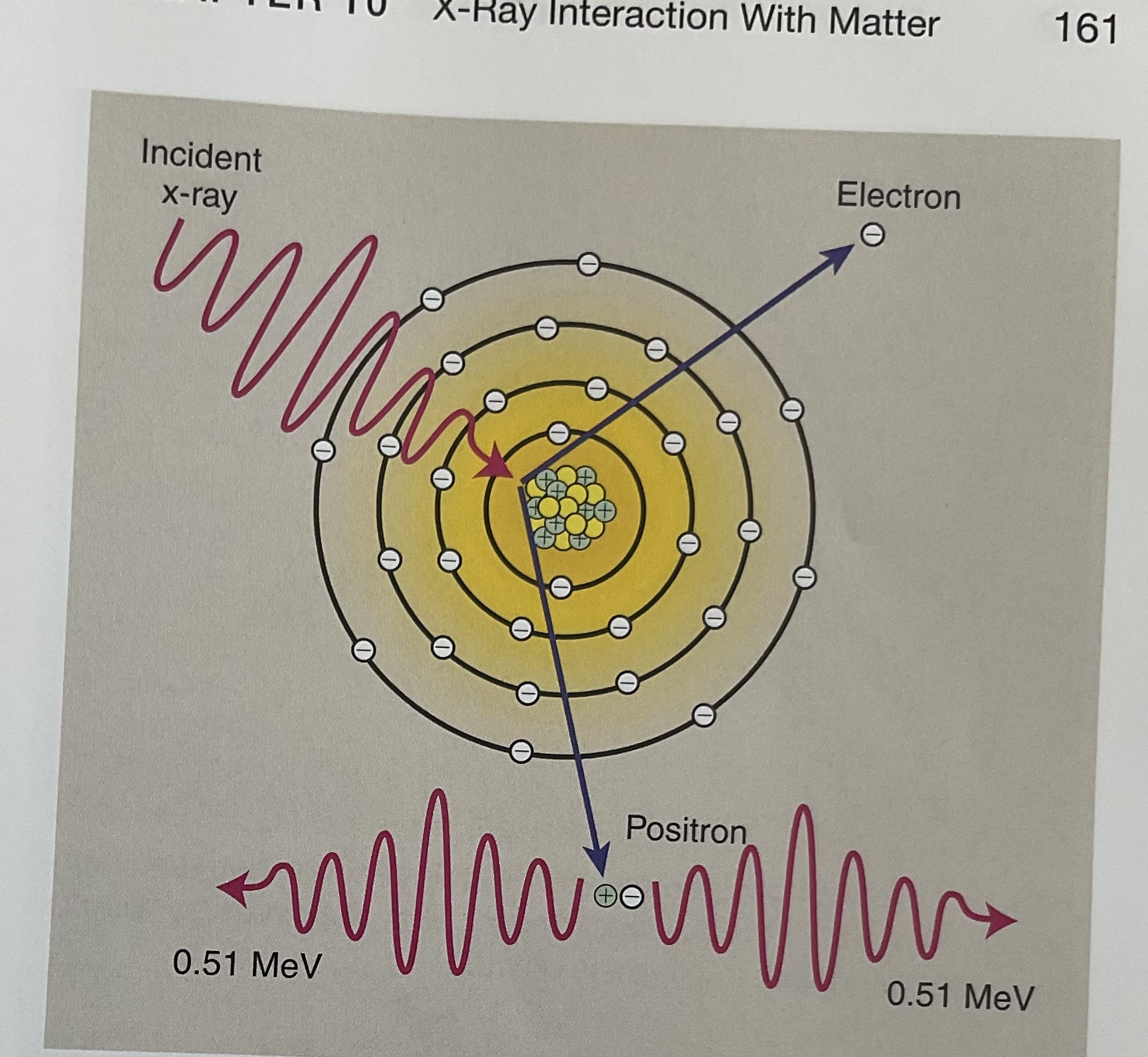
Pair production refers to
occurs with x-rays have energy is greater than 1.2 MEV the x-ray interacts with the nuclear field and two electrons that have opposite electrostatic charges are created.
electron that result from pair production loses energy through excitation and ionization vacancy in atomic orbital shell.
Photodistenegration refers to
X-rays with greater than 10 MEV , nuclear field is raised right now and excited and instantly admit a nuclear called photo disintegration
The difference in which x-rays interact and or absorb food electrically and transmitted to the image receptor is called
Diffferential absorption
Differential absorption occurs because of ______, ______ and ___________
compton scattering, photoelectric effect and x-rays transmitted to the patient.
approximately ________ of x-rays that passed through the patient reach the image receptor
1%
Differential absorption increases as KVP is ________
Reduced.
Compton scattering is __________________ of tissues. The probability of Comptons scattering for bone atoms and for soft tissue atoms is approximately _______ and decreases with _____________
not dependent on atomic number, equal and decreases with increasing energy.
The capability of continent scattering with inversely proportional to
Inversely proportional to x-ray energy
At low energy, most xray interactions with tissue are
Photoelectric interactions
At high energy’s _______ occurs
Compton scattering occurs
We know that we could image bone even if differential absorption would not be Z-related because bone has a higher mass density than soft tissue. What is mass density?
Density is a quantity of matter per unit volume specified in units of kilograms per cubic meter. (Kg/m*3)
The interaction Of x-rays with tissue is ________________
proportional to the mass density of a tissue, regardless of type of interaction
Characteristics of differential absorption
As x-ray energy increases;
As tissue atomic number increases:
As tissue mass density increases
As x-ray energy increases;
-fewer Compton interactions,
Many fewer for photoelectric interactions, - More transmission tissue
As tissue atomic number increases:
No change in Compton interactions, More photoelectric, interactions, less x-ray transmission
As tissue mass density increases:
proportional increase in Compton interactions , proportional increase in photoelectric, interactions, proportional reduction in x-ray transmission
Attenuation refers to
The reduction in the number of x-rays remaining in the x-ray beam after penetrating through a given thickness of tissue.
Barium and iodine compound are used to aid imaging of x-rays. The atomic number of barium and iodine is.
Barium;56
Iodine:53
He has a much higher atomic number and greater mass density than soft tissue.
Called contrast agents, They are positive contrast agents