W7: Understanding Conflict and Negotiation in Organizations
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Conflict
A process that begins when one party perceives another party has negatively affected something they care about.
Key Elements of Conflict: Perceived Incompatibility
A belief that goals, interests, or values clash.
Key Elements of Conflict: Interdependence
The need for parties to interact for conflict to occur.
Key Elements of Conflict: Emotional Involvement
Conflict often brings frustration, stress, or defensiveness.
Types of Conflict: Task Conflict
Differences in ideas, viewpoints, or work-related decisions.
Types of Conflict: Relationship Conflict
Emotional or personal clashes between individuals.
Types of Conflict: Process Conflict
Disagreements over how work should be done.
Types of Conflict: Intra-personal Conflict
Conflict that occurs within an individual.
Types of Conflict: Inter-personal Conflict
Conflict that occurs between individuals.
Types of Conflict: Inter-group Conflict
Conflict that occurs between different groups.
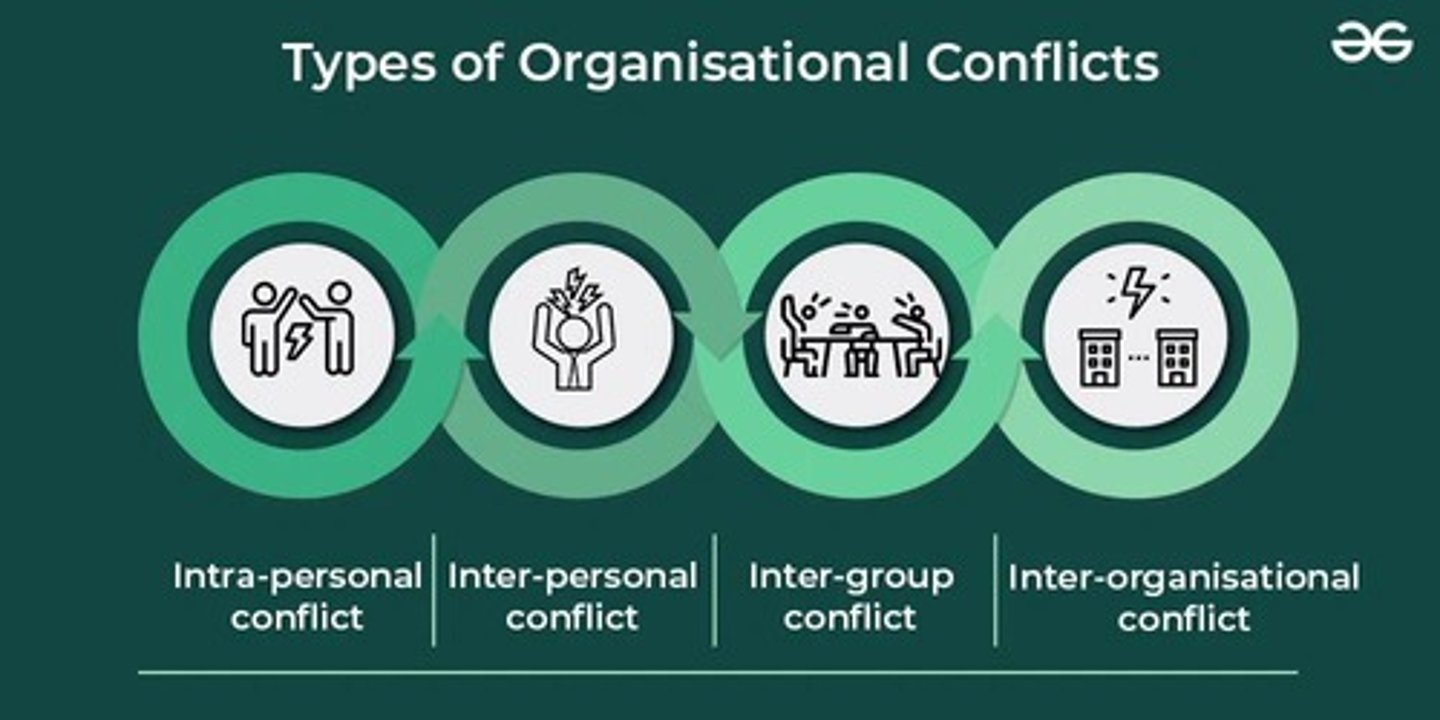
Types of Conflict: Inter-organisation Conflict
Conflict that occurs between different organizations.
Functional Conflict
Encourages creativity, challenges assumptions, and enhances performance. Leads to better decision-making.
Dysfunctional Conflict
Distracts from goals, damages relationships, and reduces efficiency. Causes stress and disengagement.
Conflict Process Model: Potential Opposition
Conflict triggers arise (e.g., communication issues, differing values, resource allocation).
Conflict Process Model: Cognition & Personalization
Conflict is perceived and emotions get involved.
Conflict Process Model: Intentions
Individuals determine their approach to handling conflict.
Conflict Process Model: Behavior
The conflict becomes visible through communication, negotiation, or confrontation.
Conflict Process Model: Outcomes
The resolution may be constructive (improved relationships) or destructive (worsened tensions).
Conflict Resolution Approaches (Thomas-Kilmann Model): Competing
High assertiveness, low cooperation. Used when quick action is necessary.
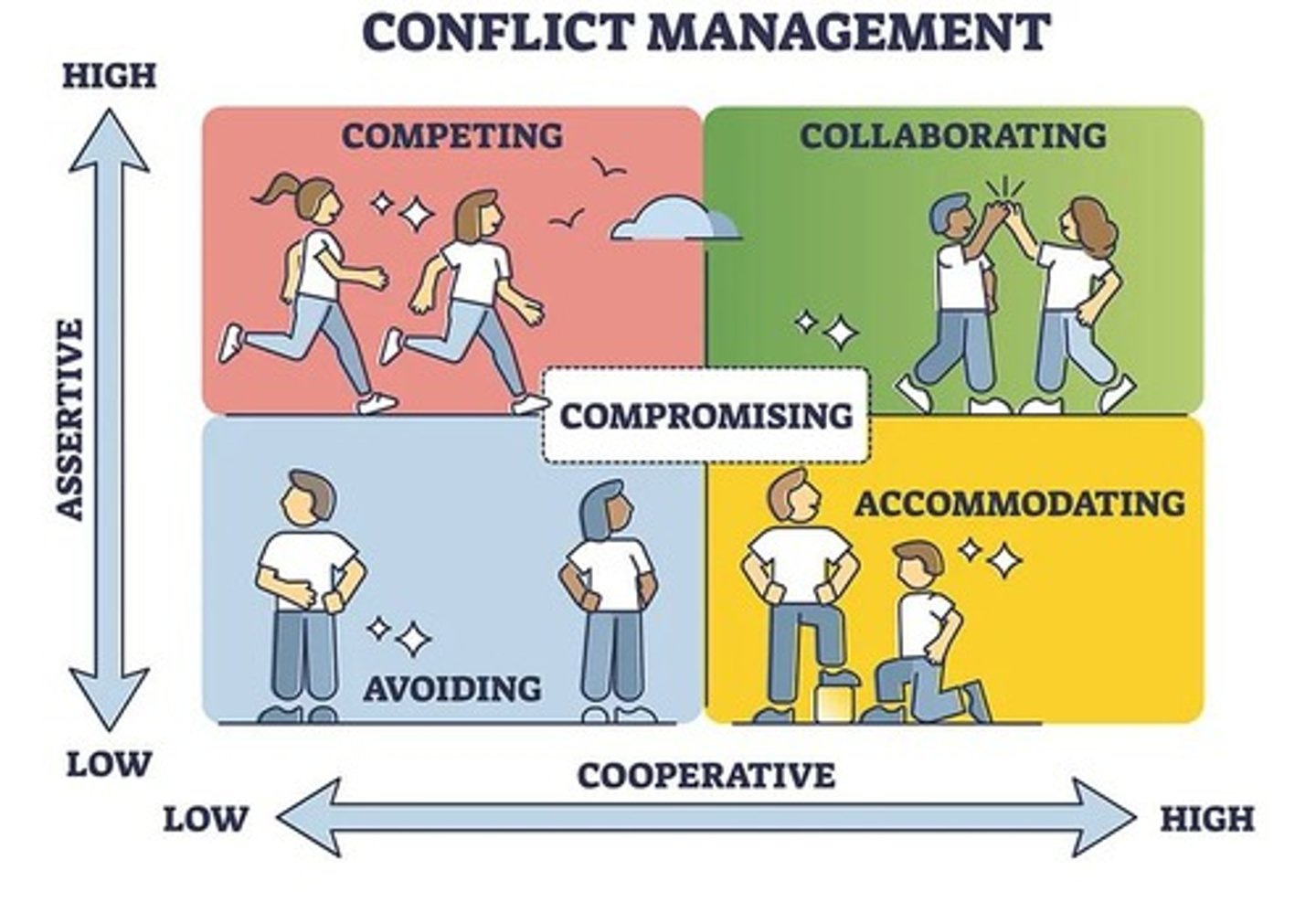
Conflict Resolution Approaches (Thomas-Kilmann Model): Collaborating
High assertiveness, high cooperation. Seeks win-win outcomes.
Conflict Resolution Approaches (Thomas-Kilmann Model): Compromising
Moderate assertiveness, moderate cooperation. Both sides give something up.
Conflict Resolution Approaches (Thomas-Kilmann Model): Avoiding
Low assertiveness, low cooperation. Ignoring or delaying the conflict.
Conflict Resolution Approaches (Thomas-Kilmann Model): Accommodating
Low assertiveness, high cooperation. Letting the other party win.
Negotiation
1.A process in which two or more parties exchange goods or services and attempt to agree on the exchange rate
2.Occurs in both formal and informal situations
3.Involves interdependence: both sides have something the other wants
Steps in Negotiating:
1. Preparation & Planning
Research interests, set goals, anticipate challenges.
Steps in Negotiating:
2. Definition of Ground Rules
Set guidelines for discussions.
Steps in Negotiating:
3. Clarification & Justification
Share perspectives and justify positions.
Steps in Negotiating:
4. Bargaining & Problem-Solving
Make offers, counteroffers, and reach agreements.
Steps in Negotiating:
5. Closure & Implementation
Finalize and execute the agreement.
BATNA
Best Alternative To a Negotiated Agreement. Determines your walk-away point The stronger your BATNA, the more power you have
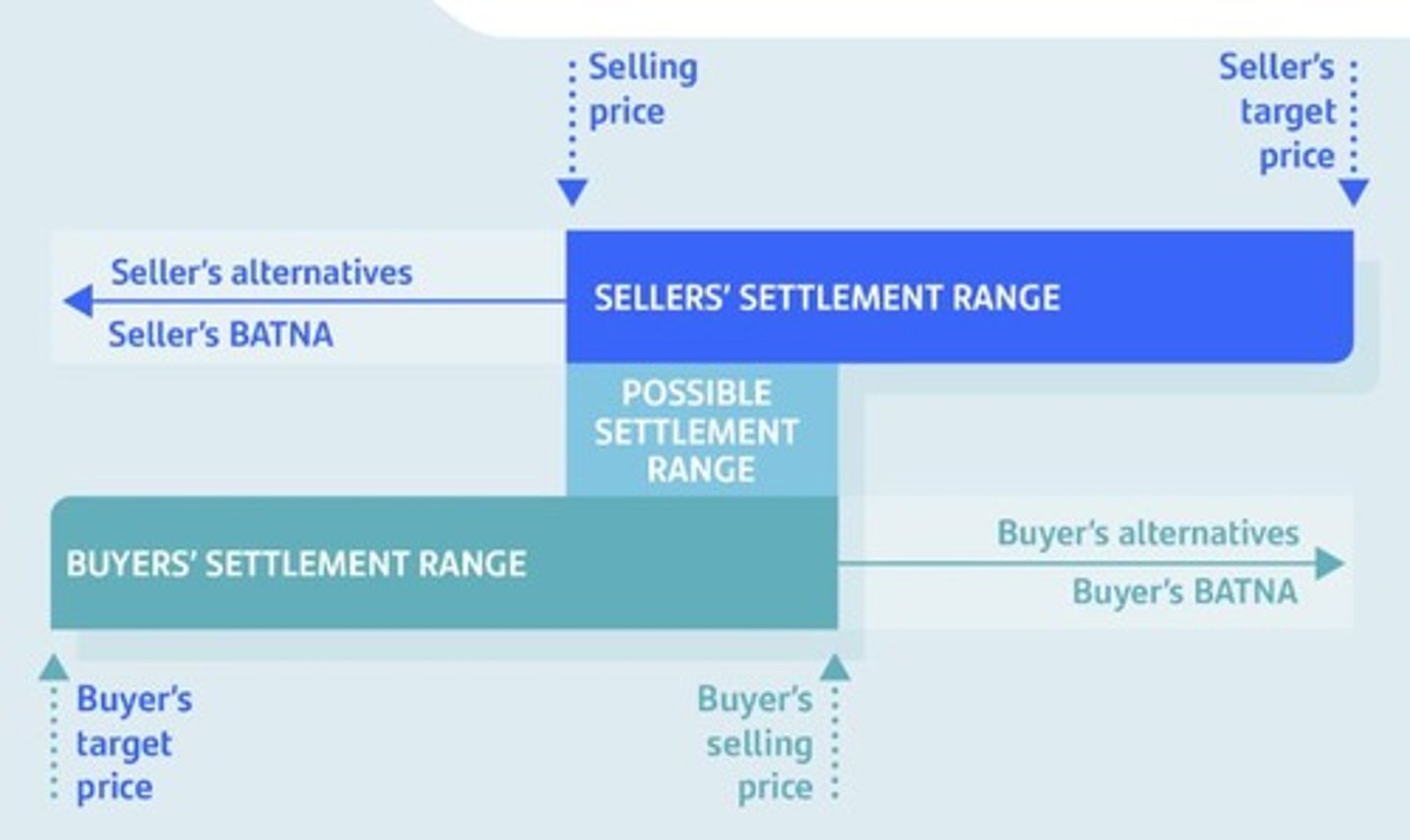
BATNA Common Tactics: Anchoring
Setting the tone with the first offer.
BATNA Common Tactics: Framing
Presenting options to shape perception.
BATNA Common Tactics: Silence
Letting discomfort work for you.
BATNA Common Tactics: Bundling
Combining issues to create tradeoffs.
BATNA Common Tactics: Deadline pressure
Creating urgency.
Common Negotiation Mistakes
Failing to prepare, letting emotions control decisions, overvaluing initial offers, ignoring the other party's interests.
Ethical Negotiation Practices
Transparency and honesty, avoiding deception, respecting long-term relationships.
Unethical Behaviors
Misrepresenting information, using intimidation tactics, taking advantage of uninformed parties.