Age Related Macular Degeneration
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
80, 90
____% of pts have non-neovascular AMD, yet neovascular form is responsible for ____% of severe vision loss
increases
prevalence, incidence, & progression of AMD ______ with age
Caucasian
observations from the Barbados Eye Study, the Baltimore Eye Study & MPS suggest late-stage AMD is more prevalent in _______ individuals
European
meta-analysis in a systematic review reported higher prevalence of AMD in ________ individuals compared to Asian & African
age
northern European ancestry
genetic factors
smoking
HTN & CV disease (mixed results)
theoretically: hormonal status, sunlight exposure, alcohol use, vitamins B & D
what are the risk factors for AMD?
complement factors H (leads to defective regulation of alternative complement pathway)
what genetic component has been shown to have a strong association with higher risk of AMD?
RPE cells age & accumulate residual bodies with lipofuscin
decreased RPE function & changes in permeability of Bruch’s membrane may lead to drusen
drusen may initiate inflammatory cascade that can contribute to AMD progression
disrupt RPE function
loss of RPE & PRs
dysfunction in Bruch’s
VEGF
CNVM
describe the pathogenesis of AMD
non-exudative
characterized by deep yellow deposits called drusen, RPE pigmentation changes, & atrophy
exudative
characterized by development of macular neovascularization which leak & bleed into surrounding tissue ultimately leaving a fibrovascular scar or disciform scar
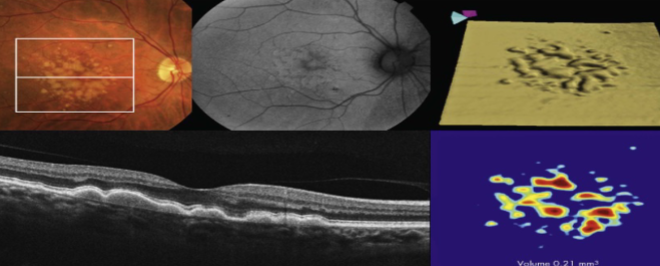
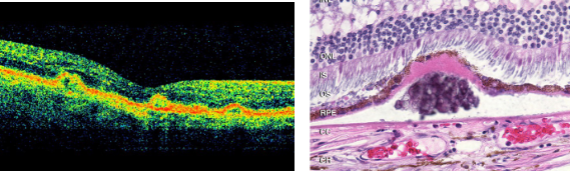
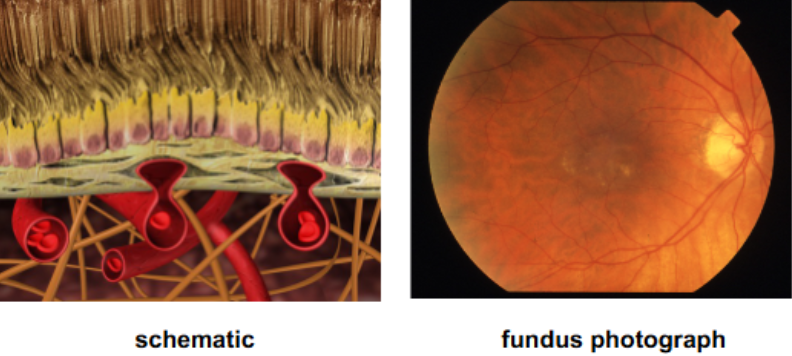
drusen
multilpe, discrete, round, slightly elevated, variable sized, yellow/white sub-RPE deposits in the macula & posterior pole b/t the RPE & Bruch’s membrane
bilateral
clustered in macular or paramacular area
tend to increase in # & size but can fade from view & decrease in number
change in size/shape/distribution/color/consistency w/ time
less than 63um
what are the size of small drusen?
63-125um
what is the size of intermediate drusen?
greater than or equal to 125um
what is the size of large drusen?
compare to the width of a major retina vein
how do you estimate the size of drusen?
hard drusen
yellow, punctate, calcific
can become crystalline in appearance or occasionally polychromatic or golden sparkling indicative of cholesterol deposits
low risk of MNV
FA shows early, well defined focal hyperfluorescence w/o leakage
often clustered & can extend out of the vascular arcades & into the equatorial retina
soft drusen
larger, pale yellow or gray-white, placoid or dome-shaped, less well-defined
may coalesce to appear similar to a serous detachment of the RPE
FA demonstrates early hyperfluorescence that does not leak & fades midway through
increased risk of MNV
reticular pseudodrusen
subretinal drusenoid deposits
best imaged w/ AF, infrared reflectance, OCT
appear to be a meaningful risk factor to GA
basal laminar drusen/cuticular drusen
nodular thickening of the BM of the RPE
uniformly small, discrete, round, slightly raised, yellow subretinal nodules that appear as early as early adulthood w/ equal frequency in blacks, Latinos, & whites
can give an orange peel appearance when they cluster
predispose pts to the development of the more typical drusen
younger, slower, higher, lower, better
how do basal laminar/cuticular drusen differ in regard to AMD?
onset is in ______(younger/older) pts, rate of visual loss is ____(slower/faster), incidence of GA is ______(lower/higher), risk of neovascularization is _____(lower/higher), & prognosis for retention of useful central vision is _____(better/worse)
large, soft, confluent
what type of drusen have been found to put pts at a higher risk for vision loss?
loss of choroidal vessels & fibrous replacement of choroid stroma
what can pseudodrusen indicate?
no AMD (AREDS category 1)
AREDS severity scale
characterized by no or few small drusen, aka drupelets
early AMD (AREDS category 2)
AREDS severity scale
characterized by a combination of multiple small drusen, few intermediate drusen or mild RPE abnormalities
intermediate AMD (AREDS category 3)
AREDS severity scale
characterized by numerous medium drusen or at least 1 large druse
advanced AMD (AREDS category 4)
AREDS severity scale
characterized by 1 or more of the following in 1 eye:
GA of the RPE fovea involving & not involving fovea
1
the presence of intermediate drusen in both eyes is __ risk factor
2
the presence of advanced AMD in 1 eye is __ risk factor
4
the contralateral eye to the eye of advanced AMD has large drusen & pigmentary changes is __ risk factors
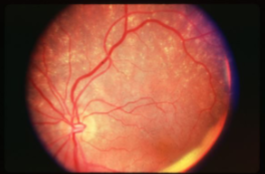
geographic or central areolar RPE atrophy
a form of dry AMD consisting of large areas of GA of the RPE
histologic: the area of GA is associated w/ focal loss of the retinal receptor cells, RPE, & choriocapillaris
5-10% of pts w/ AMD lose central vision as a result of this form of AMD
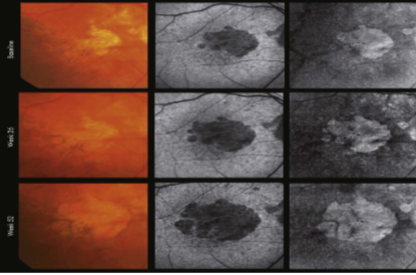
one or more sharply circumscribed geographic areas of atrophy of the RPE & retinal in the posterior pole
central vision is slow & progressive as the atrophic concentric area enlarges
bilateral, symmetric
20% of these pts will develop CNVM in the 2nd eye
FA shows varying degrees of loss of the choriocapillaris w/in the area of GA
AREDS
double-masked clinical trial that studied the effects of zinc &/or antioxidants on pts w/ cataracts & those w/ varying stages & types of AMD
19
AREDS found that high levels of antioxidants & zinc can reduce the risk of vision loss from advanced AMD by about ____% in high-risk patients (pts w/ intermediate AMD or advanced AMD in 1 eye but not the other)
F
T/F: AREDS found that supplements do provide significant benefits to pts w/ minimal AMD
T
T/F: AREDS found that nutritional supplements do not prevent the initial development of AMD, nor do they improve vision already lost to AMD
F
T/F: AREDS found that nutritional supplements do seem to prevent cataracts & keep them from getting worse over time
vitamin C
vitamin E
beta-carotene
zinc
copper
what were the things included in the AREDS1 supplements?
AREDS2
primary objective was to evaluate the effect of dietary xanthophylls &/or omega-3 on progression to advanced AMD
F
T/F: AREDS 2 found that there was a benefit from adding omega-3 fatty acids or a 5:1 mixture of lutein & zeaxanthin to the formulation
T
T/F: AREDS2 found that there was some benefit to pts who took an AREDS formulation with lutein & zeaxanthin but no beta-carotene
T
T/F: AREDS 2 found that there was no benefit to lowering the zinc dosage compared to AREDS1
vitamin C
vitamin E
lutein & zeaxanthin
zinc
copper
what was included in the new formulation of AREDS?
people at a high risk for developing advanced AMD:
intermediate AMD in 1 or both eyes
advanced AMD in 1 eye but not the other
who should consider taking a combination of antioxidants and zinc like those examined in AREDS & AREDS2?
drusen
drusen
hard drusen
soft drusen

soft drusen
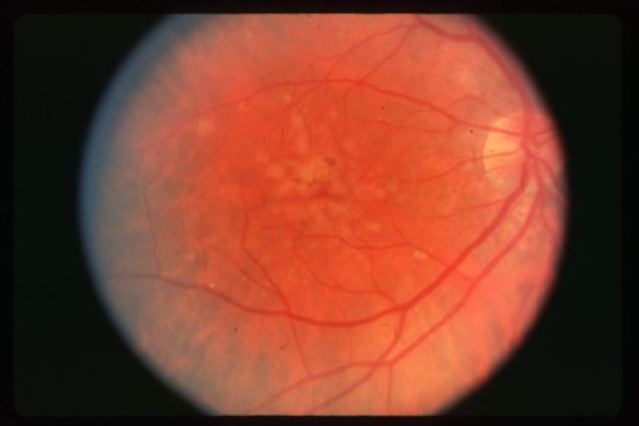
soft drusen
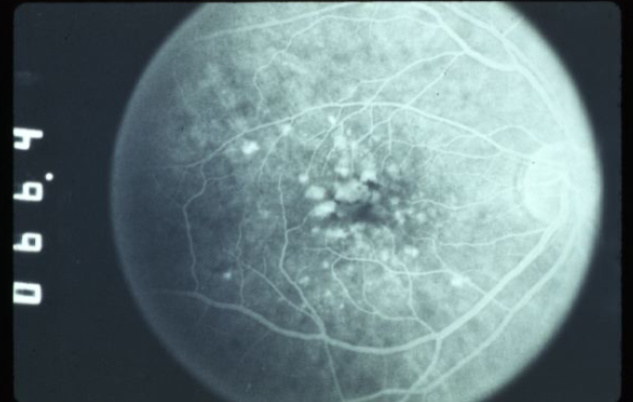
soft drusen
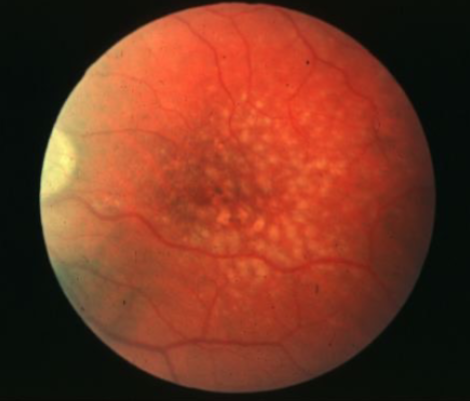
reticular pseudodrusen
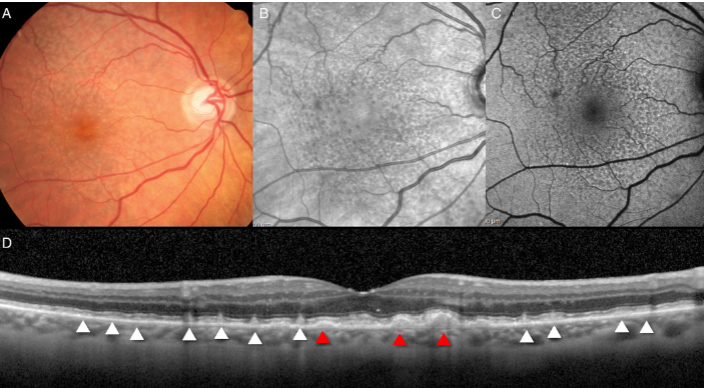
basal laminar/cuticular drusen
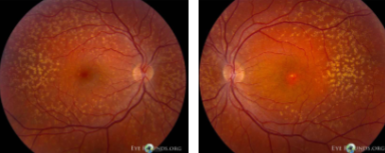
GA
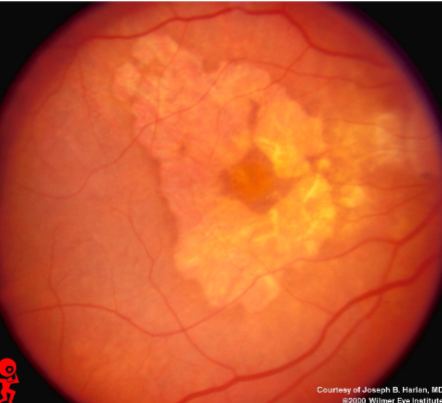
GA
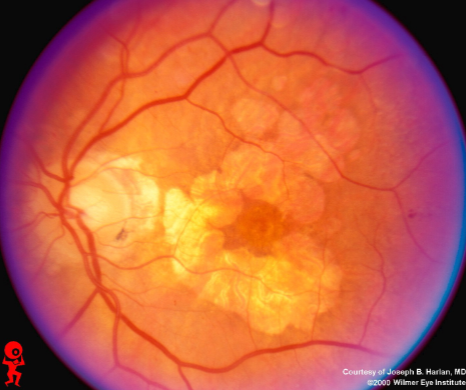
GA
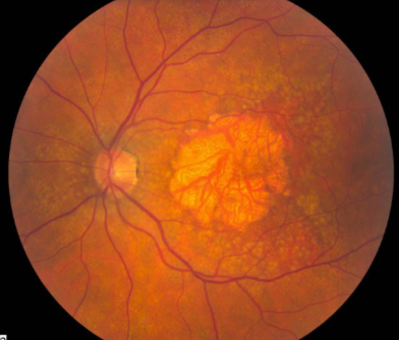
GA
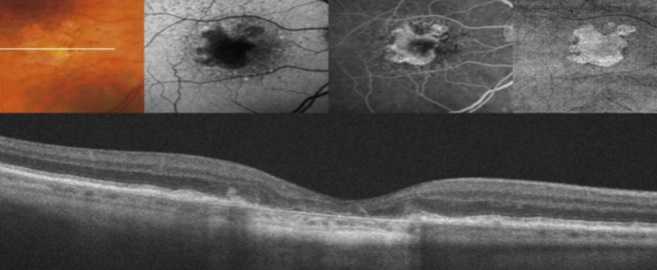
GA
maybe loss of vision, distortion, or blur
acute hemorrhage or insidious (fluid & PEDS) in onset
bilateral but often asymmetric
can have a hx of loss of vision in other eye
stable central scotoma in which VA falls below reading & legal driving level
peripheral vision retained
what are the signs/sx of neovascular AMD?
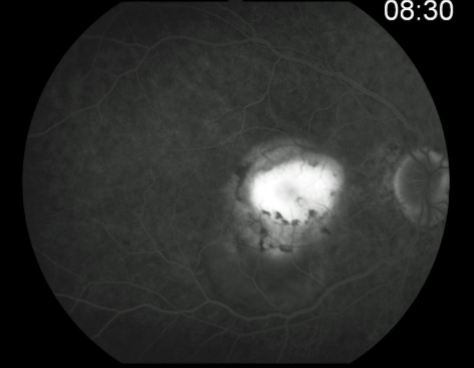
CNV
ingrowth of new vessels extending from the choroid into sub-RPE space in one or more areas
neovascular buds invade & penetrate the degenerated Bruch’s membrane & proliferate beneath the RPE
occult stage/Gass type 1
initial blood flow is very slow through CNVM
fibrovascular PED or late leakage of underdetermined source
breaks through Bruch’s but staying sub-RPE
classic CNV/Gass type 2
CNVM
well defined hyperfluorescence
cartwheel or sea fan appearance
thought to break through RPE & staying sub-retinal
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV)
polypoid lesions
more evident on ICG
bridges AMD discussion & pachychoroid syndrome
growth of abnormal choroidal vessels
new vessels grow into & break through Bruch’s
new vessels continue to grow under RPE
drusen are resorbed
new vessels continue to grow under RPE
exudation due to vessels leaking fluid into sub-RPE space
fluid breaks into sub-retinal space through RPE
type 2 CNV develops which may show classic components or remain occult to FA depending on RPE cells’ migration to envelop the membrane
describe the development of wet AMD
under the pigment epithelium
describe type 1 CNVM on OCT
subretinal
describe type 2 CNVM on OCT
retinal angiomatous proliferation
describe type 3 CNVM on OCT
type 1 MNV
fibrovascular PED
late leakage from undetermined source (poorly defined neovascularization)
speckled hyperfluorescence
dye pooling late in study
poorly defined
PCV
similar to type 1 MNV w/ dilated vascular elements (polyps)
type 2 MNV
MNV is now b/t neurosensory retina & RPE making the IVFA more obvious & well defined
IVFA shows lacy, well-group area of neovascularization
hyperfluorescent early in study
late leakage
lacy early fill of the MNV during the choroidal & arterial filling phase
may have hypofluorescence corresponding to RPE hyperpigmentation & blood in the outline of the MNV
progressive hyperfluorescence throughout the FA w/o leakage of the margins of the MNV
type 3 MNV
macular NV originating from deep capillary plexus growing to the outer retina
subretinal hyperreflective material
exudation into subretinal space
composed of serum, fibrin, inflammatory cells
may correspond w/ increased risk of GA
serous fluid
type of PED
dome-shaped detachment of RPE
bright diffuse hyperfluorescence that does not spread
fibrovascular tissue
type of PED
irregular RPE w/ speckled fluorescence
hemorrhagic
type of PED
dark elevation of RPE
blocked fluorescence
coalescence of drusen sub-RPE
type of PED
drusenoid
staining w/ fading of fluorescence w/o leaking
RPE tear
hemorrhagic detachment of the RPE & retina
vitreous hemorrhage
subretinal scar tissue
what are the further complications of MNV
disciform scarring
final stage of MNV in which there is progressive fibrosis & loss of the macular photoreceptors function
seen less often now w/ anti-VEGF therapy
5, 15
over 5y, up to ___% w/ early AMD will progress to late stage, increasing to ___ over 15 years
hard
____ drusen is common & not associated w/ progression
6.5
soft drusen indicates ___% risk of progression to late AMD in 5y
7.1
RPE changes indicate a ___% risk of progression to late in 5y
47.3
if large drusen & pigmentation changes are present, there is a ___% risk of progression to late AMD in 5y
30
wet AMD is often bilateral w/ __% risk of 2nd eye involvement in 6y
exudative macular degeneration
fibrosis
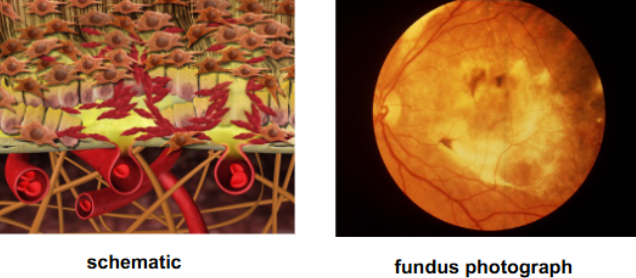
PED
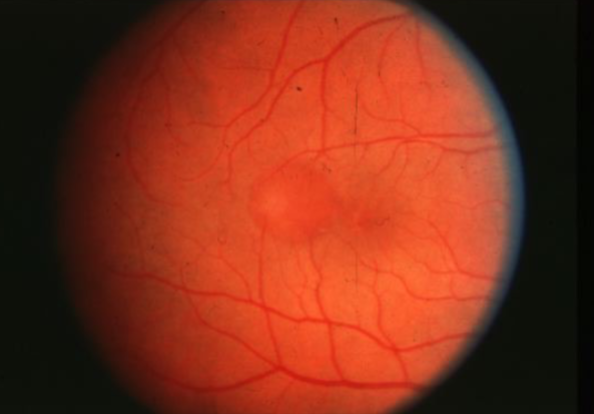
PED
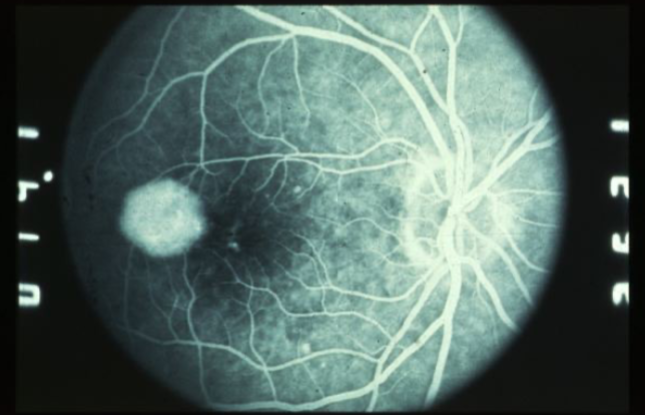
PED

PED
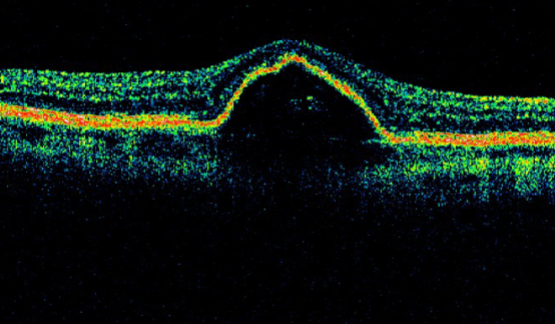
MNV type 1
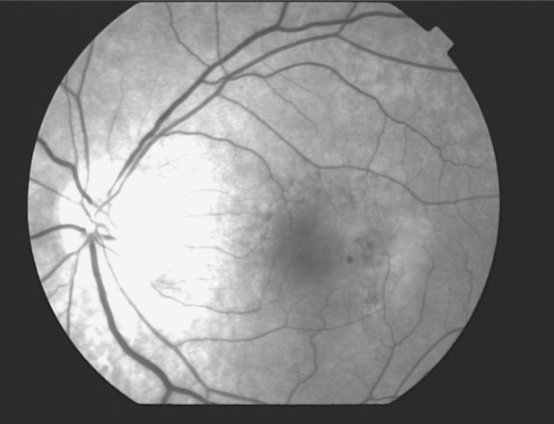
MNV type 1
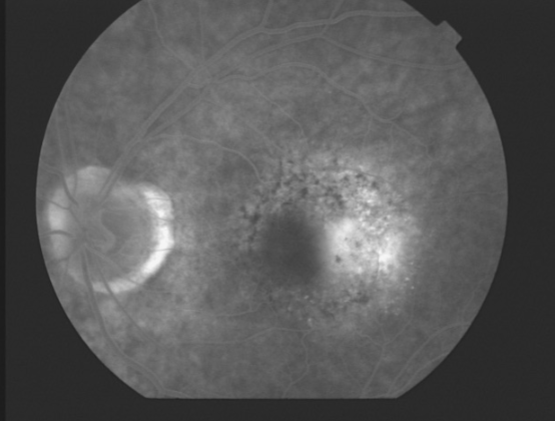
MNV type 1
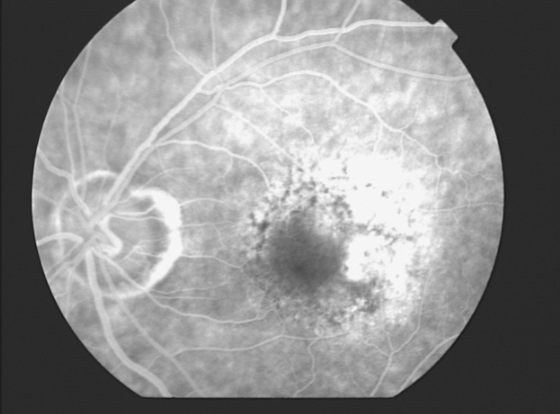
MNV type 1
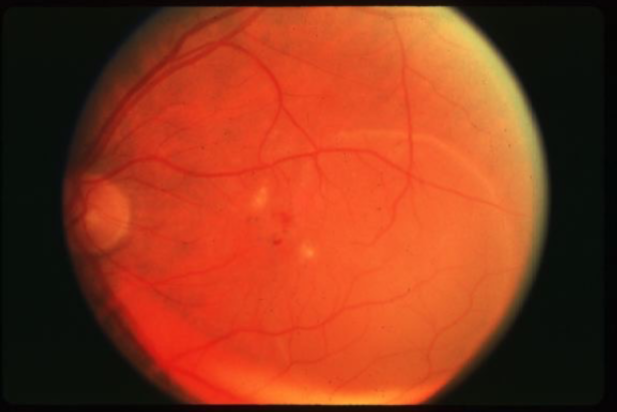
MNV type 1
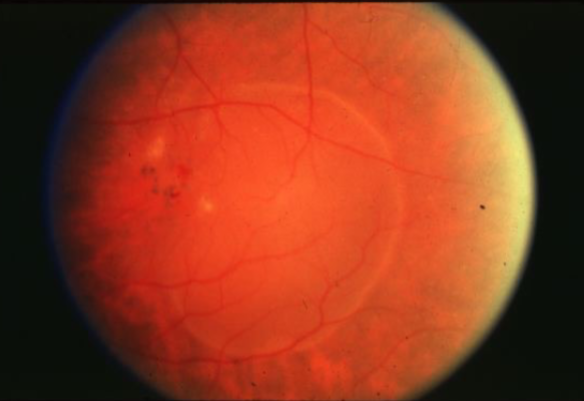
classic CNV
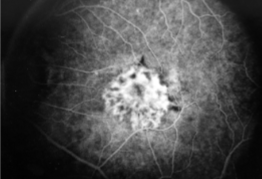
classic & occult CNV
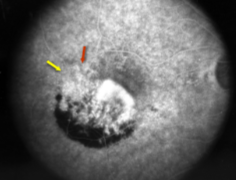
type 2 MNV
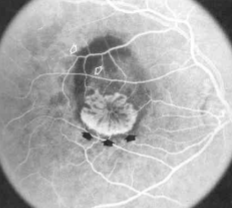
MNV type 2
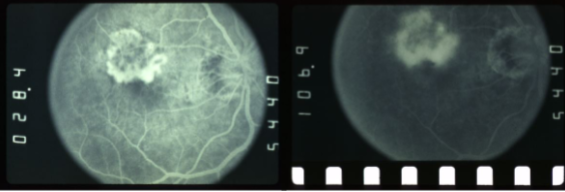
MNV type 2
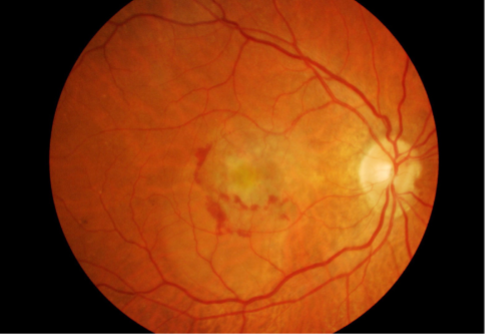
MNV type 2
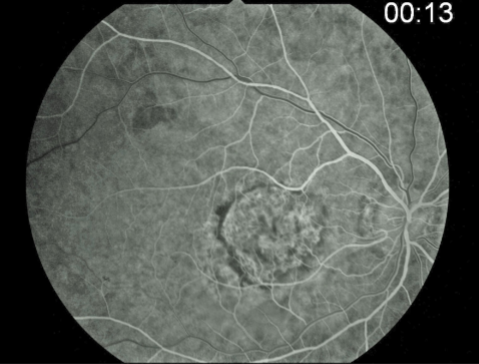
MNV type 2
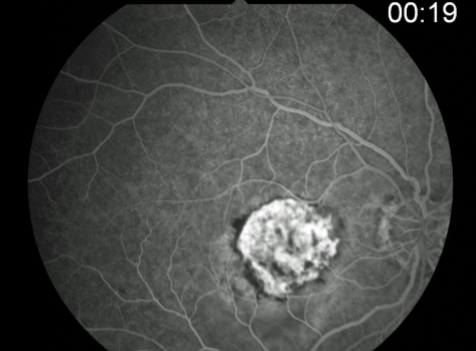
MNV type 2