Pharynx and Nasal Cavity
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the subdivisions of the oral cavity?
Oral vestibule (between lips/cheeks and teeth) and oral cavity proper (internal to teeth).
What are the surface landmarks of the oral cavity?
Hard and soft palate, uvula, palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches, tonsillar fossa, tongue, sublingual folds.
What are the subdivisions of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx.
What muscles form the pharyngeal wall?
Three constrictors (superior, middle, inferior) and three longitudinal muscles (stylopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus).
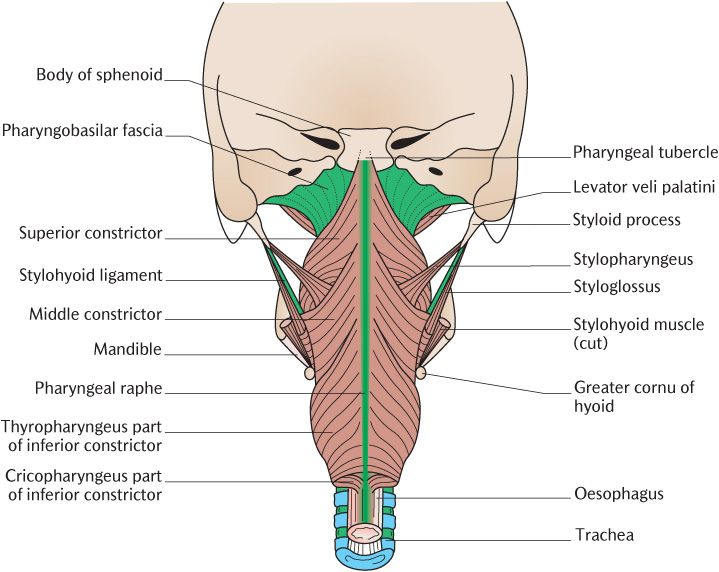
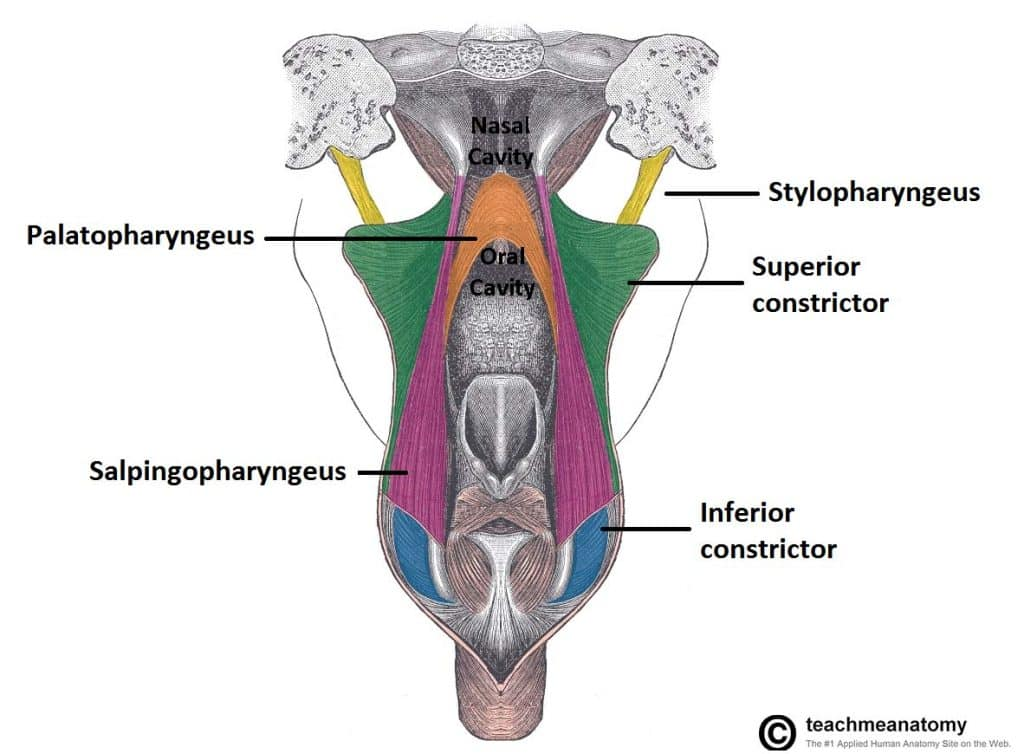

What is the innervation of the pharyngeal constrictors?
Pharyngeal plexus: primarily CN X (vagus); stylopharyngeus by CN IX.
What is the afferent limb of the gag reflex?
CN IX (glossopharyngeal).
What is the efferent limb of the gag reflex?
CN X (vagus).
What is the course of CN IX in the pharynx?
Exits jugular foramen → descends between internal and external carotid arteries → joins pharyngeal plexus → innervates stylopharyngeus and mucosa.
What is the course of CN X in the pharynx?
Exits jugular foramen → travels in carotid sheath → gives pharyngeal branches, superior laryngeal nerve, and recurrent laryngeal nerve.
What are the prevertebral muscles of the neck?
Longus capitis, longus colli, rectus capitis anterior and lateralis.
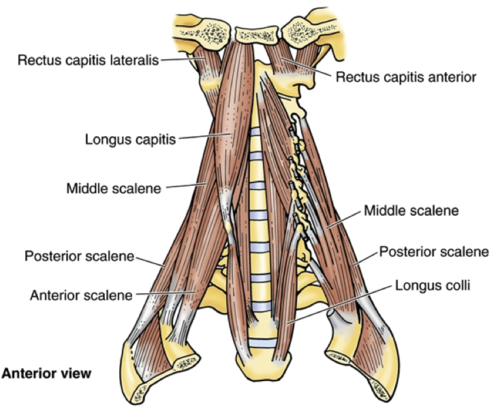

What fascia surrounds the prevertebral muscles?
Prevertebral fascia; forms posterior boundary of retropharyngeal space.
What is the clinical significance of the retropharyngeal space?
Potential space for infection spread from pharynx to mediastinum.
Where is the cervical sympathetic trunk located?
Posterior to carotid sheath, anterior to prevertebral fascia; contains superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia.
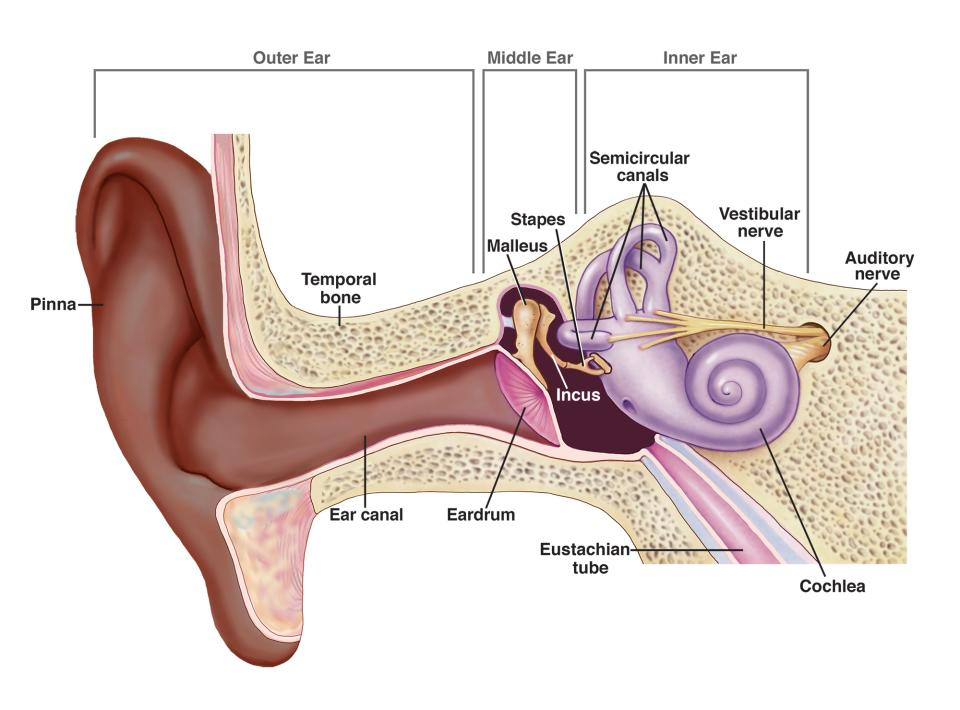
What are the components of the outer ear?
Auricle (pinna), external acoustic meatus.
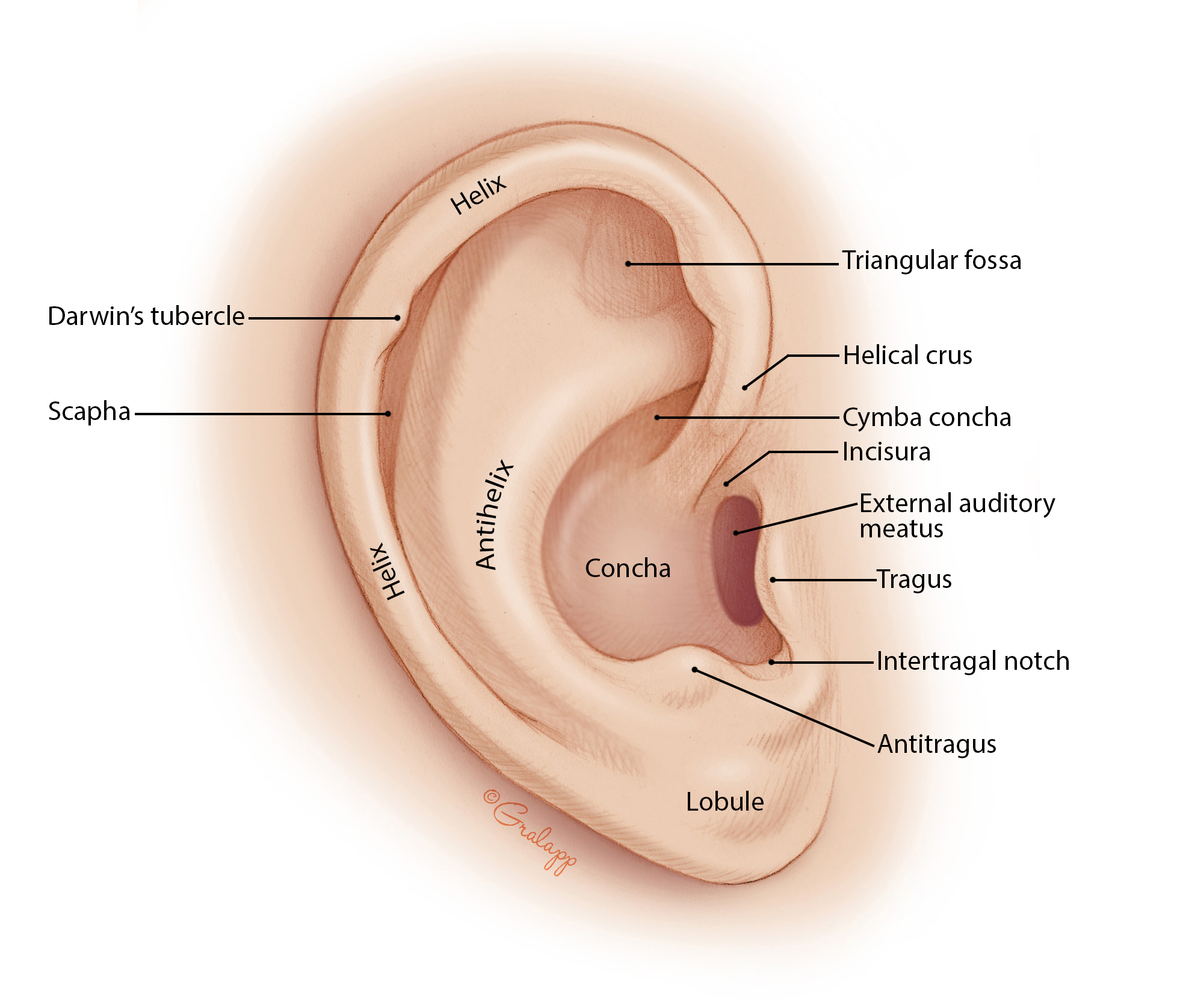

What are the components of the middle ear?
Tympanic cavity, ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), pharyngotympanic tube.
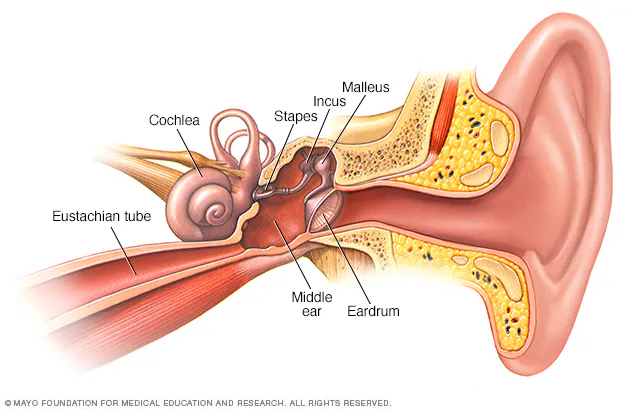

What are the components of the inner ear?
Cochlea (hearing), vestibule and semicircular canals (balance).

What is the embryologic origin of the external ear?
First pharyngeal groove and auricular hillocks from arches 1 and 2.
What is the embryologic origin of the middle ear cavity?
First pharyngeal pouch.
What is the embryologic origin of the ossicles?
Malleus and incus from arch 1; stapes from arch 2.
What is the embryologic origin of the inner ear?
Otic placode (ectodermal thickening).
What forms the nasal septum?
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid, vomer, septal cartilage.
What forms the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
Superior, middle, and inferior conchae; ethmoid, maxilla, palatine, lacrimal bones.
What are the four paranasal sinuses?
Frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, maxillary.
Where does the frontal sinus drain?
Into middle meatus via frontonasal duct.
Where do the ethmoidal sinuses drain?
Anterior and middle into middle meatus; posterior into superior meatus.
Where does the sphenoidal sinus drain?
Into sphenoethmoidal recess above superior concha.
Where does the maxillary sinus drain?
Into middle meatus via semilunar hiatus.
What are the regions of the nasal cavity?
Vestibule, respiratory region, olfactory region.
What are the meatuses of the nasal cavity?
Superior, middle, and inferior meatuses beneath corresponding conchae.
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
Increase surface area; warm, humidify, and filter inspired air.
What is the pterygopalatine fossa?
Small space posterior to maxilla; contains pterygopalatine ganglion, maxillary nerve (V2), and branches of maxillary artery.
What are the communications of the pterygopalatine fossa?
Foramen rotundum (to middle cranial fossa), sphenopalatine foramen (to nasal cavity), inferior orbital fissure, palatine canals.
What is the course of the maxillary artery in the fossa?
Passes through infratemporal fossa → enters pterygopalatine fossa → gives off sphenopalatine, descending palatine, infraorbital, and pharyngeal branches.
What is the distribution of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)?
Exits foramen rotundum → enters pterygopalatine fossa → gives off infraorbital, zygomatic, superior alveolar, and palatine nerves.
What is the blood supply to the palatine tonsils?
Tonsillar branch of facial artery; also contributions from ascending palatine, dorsal lingual, and ascending pharyngeal arteries.
What muscles form the soft palate?
Palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, levator veli palatini, tensor veli palatini, musculus uvulae.
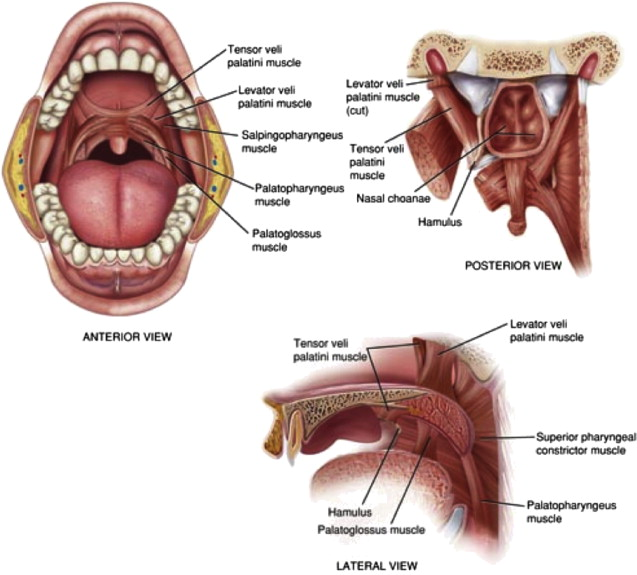

What is the motor innervation of the palate muscles?
All by CN X via pharyngeal plexus except tensor veli palatini (CN V3).
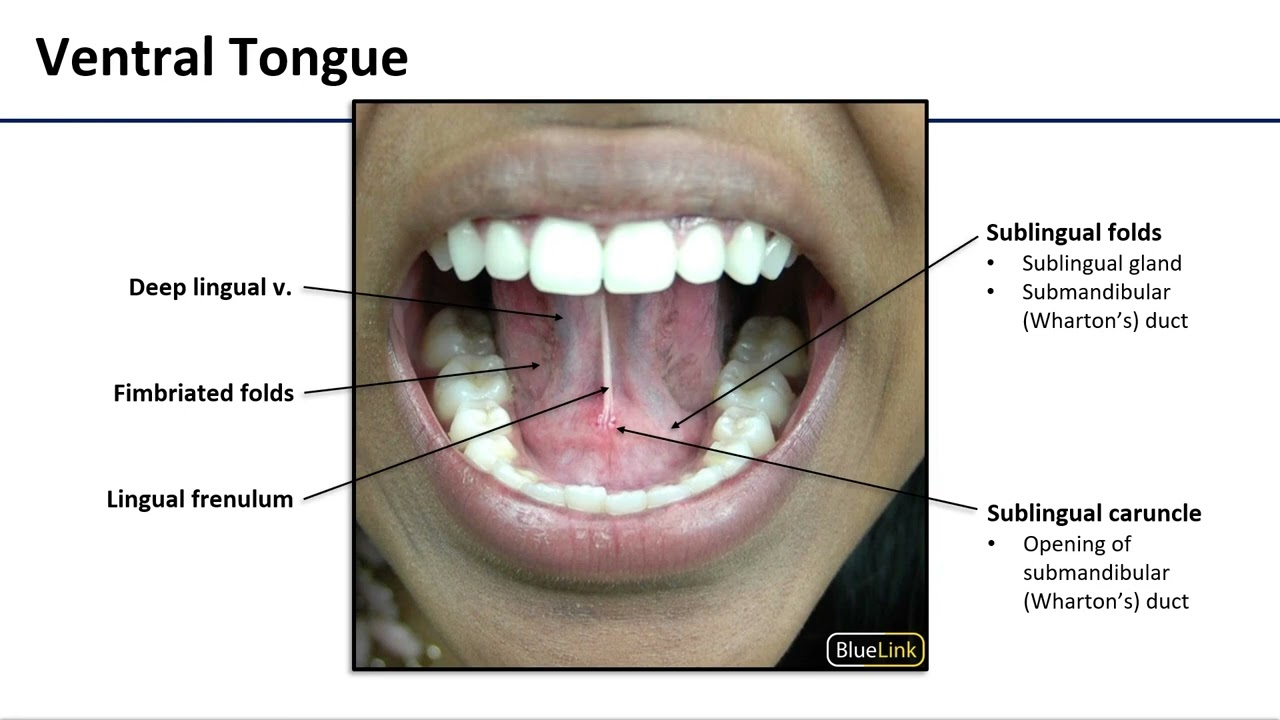
What are the surface features of the sublingual region?
Sublingual folds, submandibular duct openings, lingual frenulum.

What are the surface features of the tongue?
Anterior 2/3: papillae (filiform, fungiform, circumvallate); posterior 1/3: lingual tonsil.
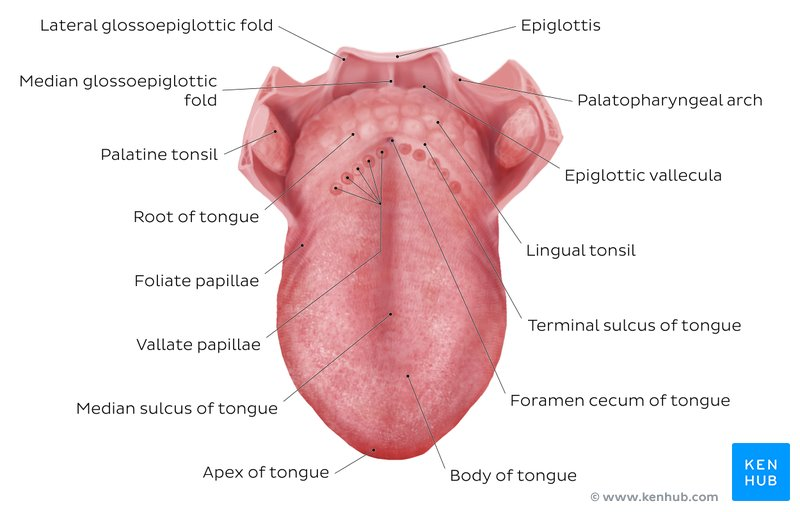

What is the sensory innervation of the tongue?
Anterior 2/3: general sensation via CN V3 (lingual), taste via CN VII (chorda tympani); Posterior 1/3: both via CN IX; root and epiglottis via CN X.
What is the motor innervation of the tongue?
CN XII (hypoglossal); all intrinsic and extrinsic muscles except palatoglossus (CN X).
What are the actions of the tongue muscles?
Intrinsic: shape changes; Extrinsic: protrusion (genioglossus), retraction (styloglossus), elevation (palatoglossus), depression (hyoglossus).
What is the lymphatic drainage of the oral cavity?
Submental, submandibular, and deep cervical lymph nodes; midline structures drain bilaterally.
What is the embryologic origin of the tongue?
Anterior 2/3: first pharyngeal arch; Posterior 1/3: third arch; root: fourth arch.
What is the embryologic origin of the palate?
Primary palate from intermaxillary segment; secondary palate from lateral palatine processes.
What is the embryologic origin of the pituitary gland?
Anterior lobe: Rathke’s pouch (oral ectoderm); Posterior lobe: neuroectoderm of diencephalon.