health assesment exam 1
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
what is clinical judgement model used for
assessing/judging a patients situation
list the 6 components of clinical judgement (rapgte)
recognize cues
analyze cues
prioritize hypothesis
generate solutions
take action
evaluate outcomes
ABC stands for
airway, breathing, circulation
what is ADPIE
nursing process
ADPIE (steps of nursing process)
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
what are the 3 steps of the patient centered interview
orientation, working phase, termination phase
What is PICOT
question asking model
what does PICOT stand for
Population
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome
Time
AIDET stands for
acknowledge, introduce, duration, explanation, thank you
what is a primary source
information obtained directly by patient
secondary information
information from chart, family members, other healthcare workers
objective data
information that is seen, heard, felt, or smelled by yourself as the nurse
subjective data
what the person says about himself/herself during history taking
list 3 interview techniques
open ended questions, observation, back channeling
what is back channeling?
prompts such as "go on, I understand"
3 types of assessments
emergency, comprehensive, focused
explain a comprehensive assessment
detailed health history and physical examination of all body systems
activities of daily living
Daily basic tasks fundamental to everyday functioning like hygiene, elimination, dressing
chief complaint definition
main reason for a patients visit
instrumental activities of daily living
daily tasks that allow patients to function independently like, paying bills, preparing meals
main health care needs definition
used to classify what needs the patient feels are most important to address
medication reconciliation definition
comparison of a list of current medications with a previous list
sign definition
Objective data found by the nurse during assessment
symptom definiton
Subjective data that the patient reports (like "I feel dizzy")
what is the joint commission? (TJC)
accrediting agency for health care places, reports data on serious errors
What is the function of the National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators (NDNQI)?
find out how nursing workforce factors like staffing, influence patient outcomes
assessment
hands on data collection
What is cortical bone?
compact bone
What is cancellous bone?
spongy bone
3 types of muscle
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
what acronym can we use to assess pain
PQRST
what does PQRST stand for (questions for assessing pain)
Precipitating cause
Quality
Region
Severity
Timing
palliative definition
relieves the pain
preceptive definition
causes more pain
Wong-Baker FACES scale

A visual pain rating scale, such as Wong-Baker FACES, involves six faces with different expressions, this test is best for:
children
numeric pain scale
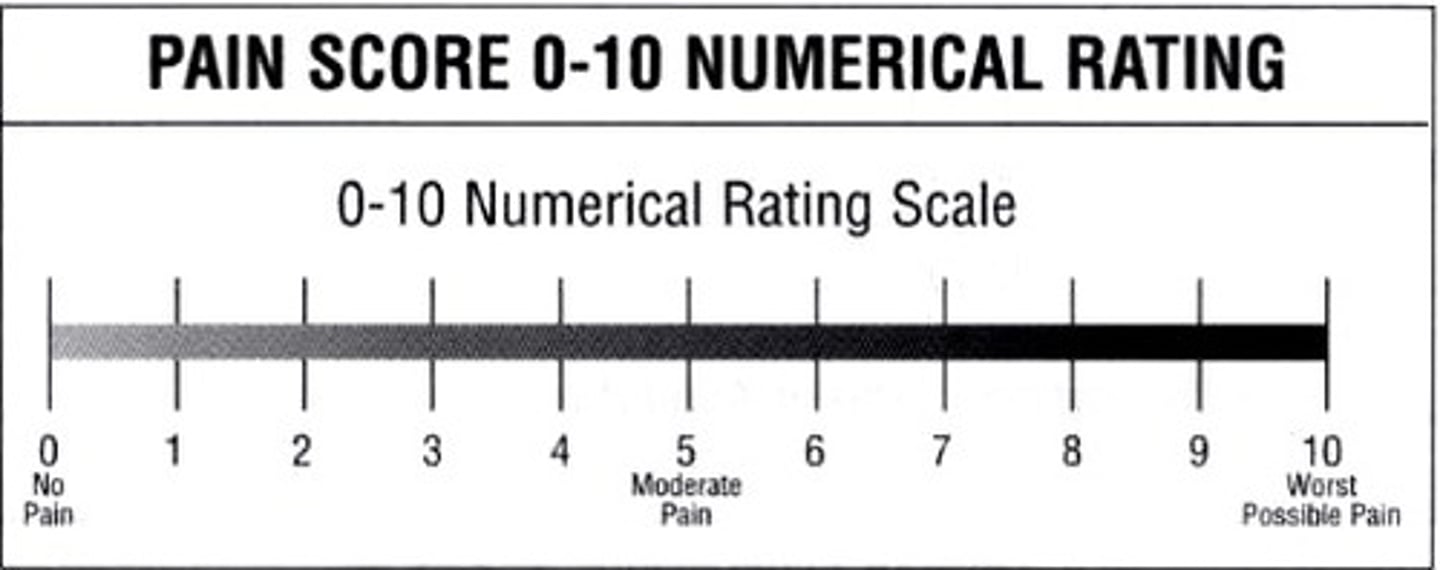
the numeric pain scale is best for:
adults
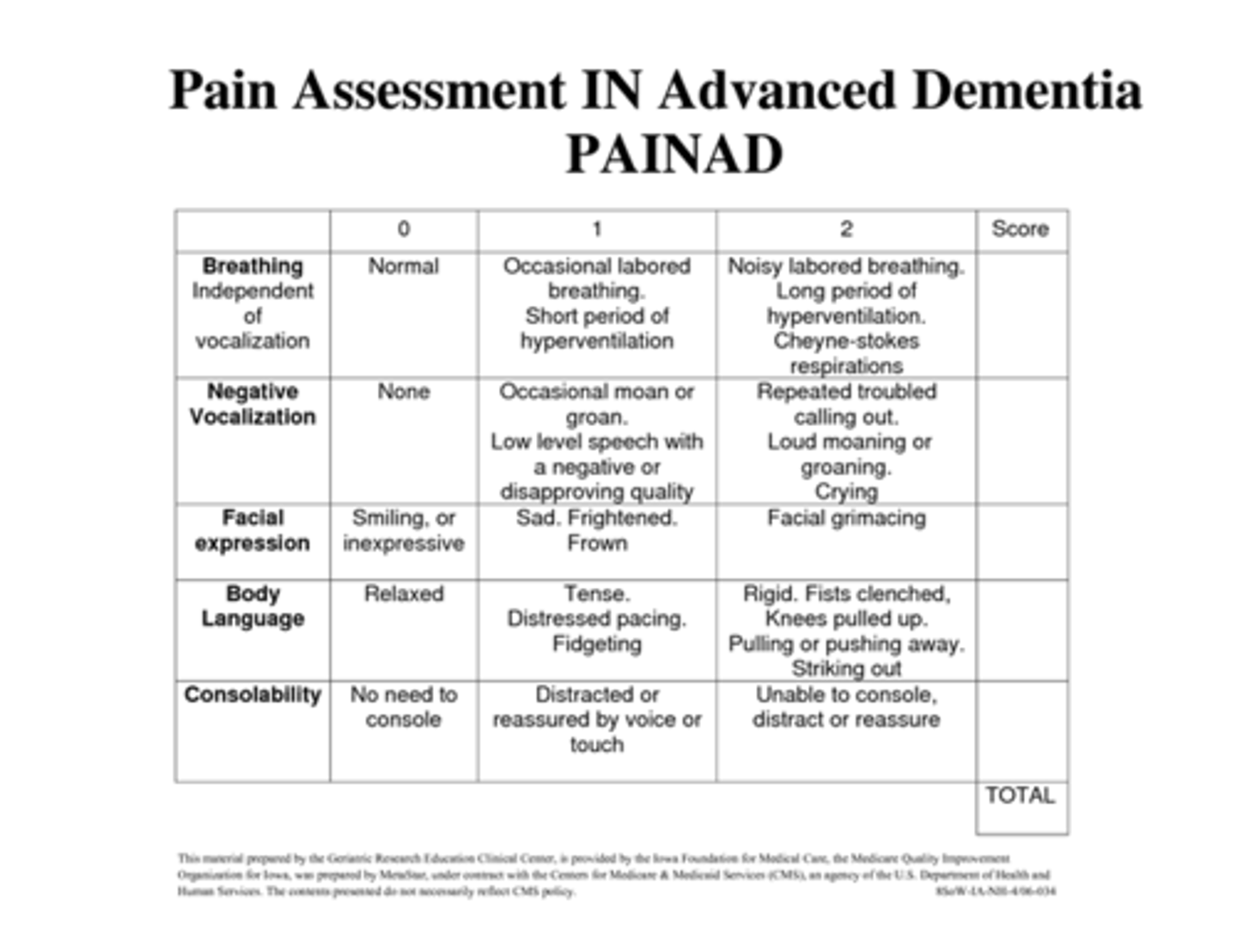
Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD) is best for:
chronically confused/disoriented patients
PAINAD scale
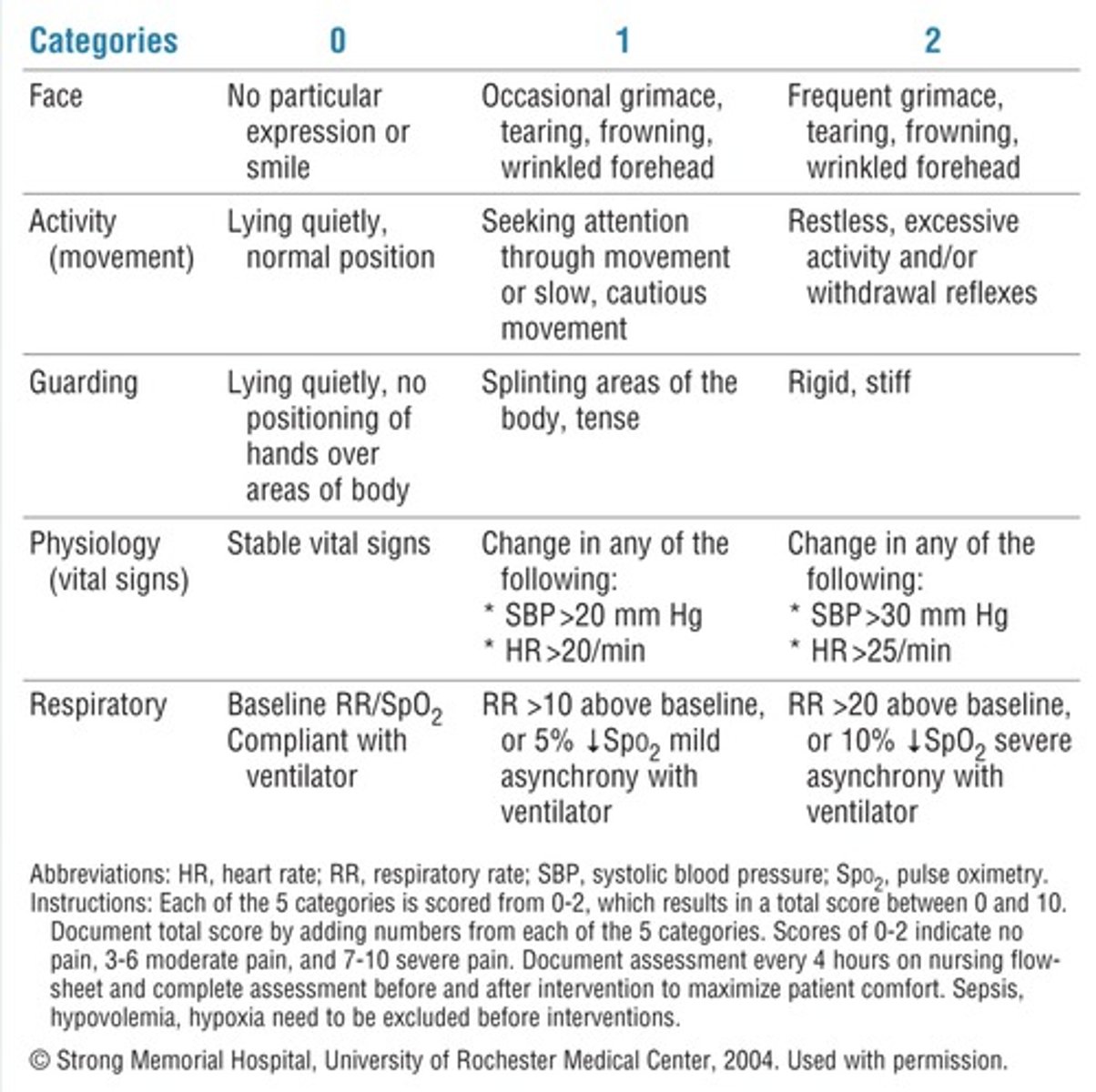
Adult Non-Verbal Pain Scale (NVPS) is best for:
Patients on ventilators/intubated or Inability to speak
NVPS scale
acute pain lasts between a few seconds to ___ months
6
chronic pain lasts ___ months or longer
6
list 3 objective indicators of pain
pale, fainting, guarding area of pain
EAT stands for ____ ____ ___, and can ONLY BE DONE BY A RN
evaluate, assess, teach
function of a tendon
attaches muscle to bone
function of a ligament
attach bones to bones
fascia definition
Layers of connective tissue that provide strength to muscles
bursae definition
sacs of connective tissue found at bony prominences or joints to relieve pressure and decrease friction
long bones
longer than they are wide
short bones
small cube shaped bones
flat bones
thin, flat, slightly curved
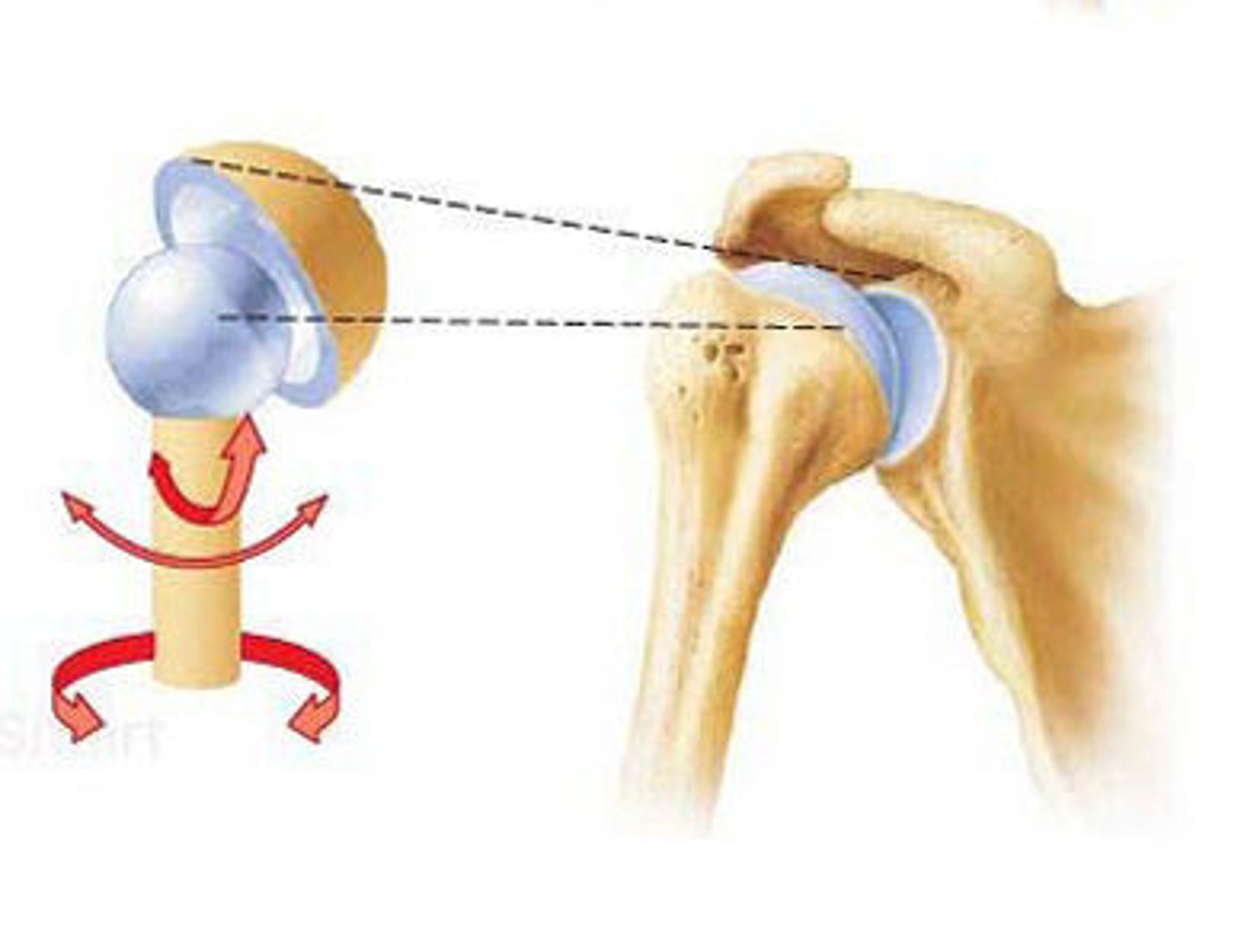
joint definition
articulation of two bones
what is a osteoblast
bone forming cells
what is a osteocyte
mature bone cell
what is a osteoclasts function
breaks down bone
capsule definition
encloses joint in fibrous connective tissue
function of a goniometer
measures ROM
Normal Physical Assessment of the Musculoskeletal System should include
full ROM
normal spinal shape
no atrophy
no joint swelling/tenderness
full muscle strength
3 examples of a diagnostic study of the musculoskeletal system
x-ray, MRI, CT scan
lordosis definition
excessive inward curvature of the spine
Kyphosis definition
upper back is abnormally rounded
5 rights of delegation (tcpcs)
right task
right circumstance
right person
right communication
right supervision
what is gender dysphoria
incongruence between assigned gender and experienced gender
list 3 positions you can use for patient assessment
supine, fowlers, prone
what is fowlers position
sitting in bed slightly elevated (like sitting upright in bed)
flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
extension
increases the angle of a joint
abduction
movement away from the midline
adduction
movement toward the midline
pronation
palm down
supination
Palm up
Circumduction
circular movement at the far end of a limb
rotation
joint movement
inversion
turning sole of foot inward
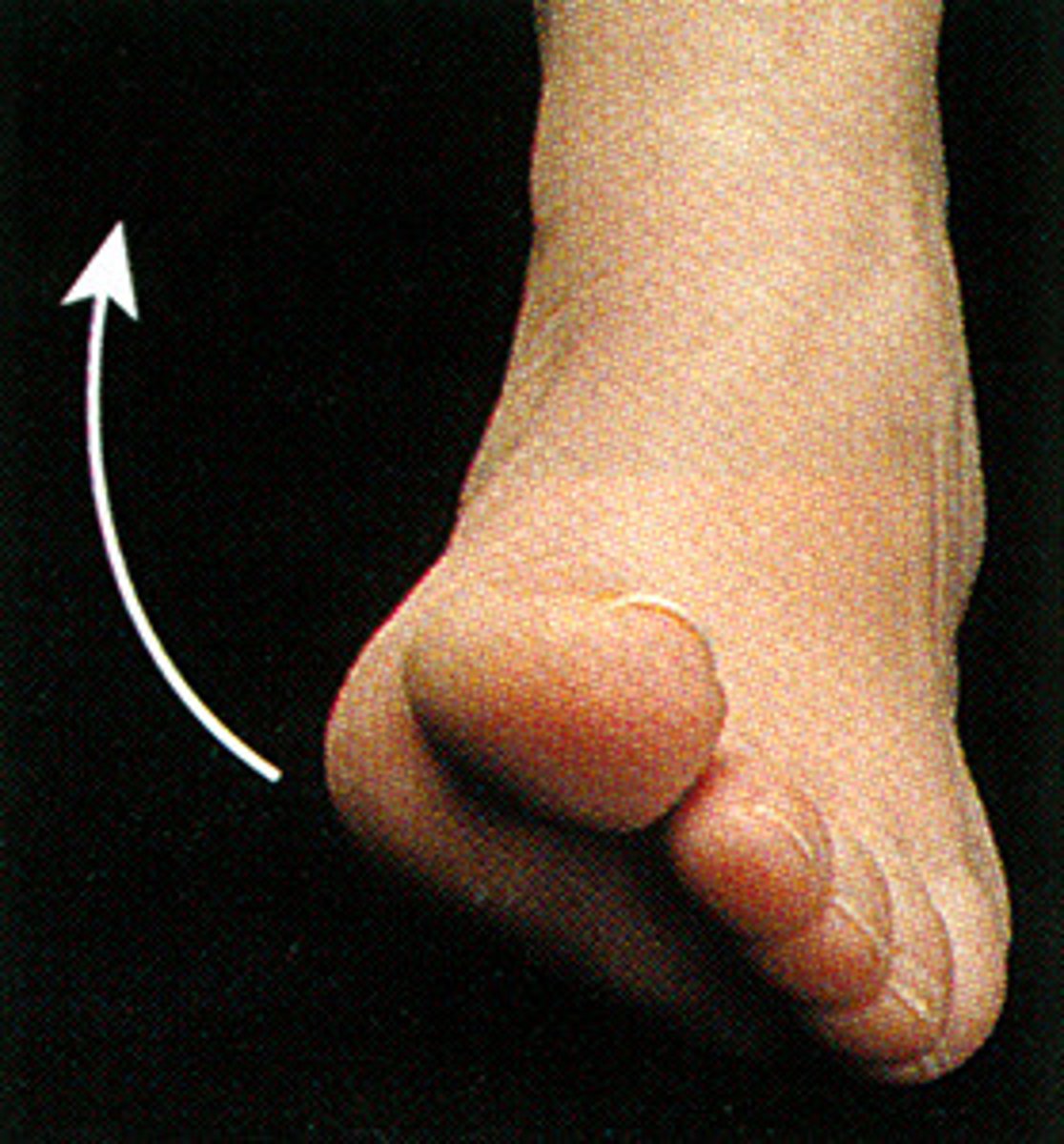
eversion
turning sole of the foot outward
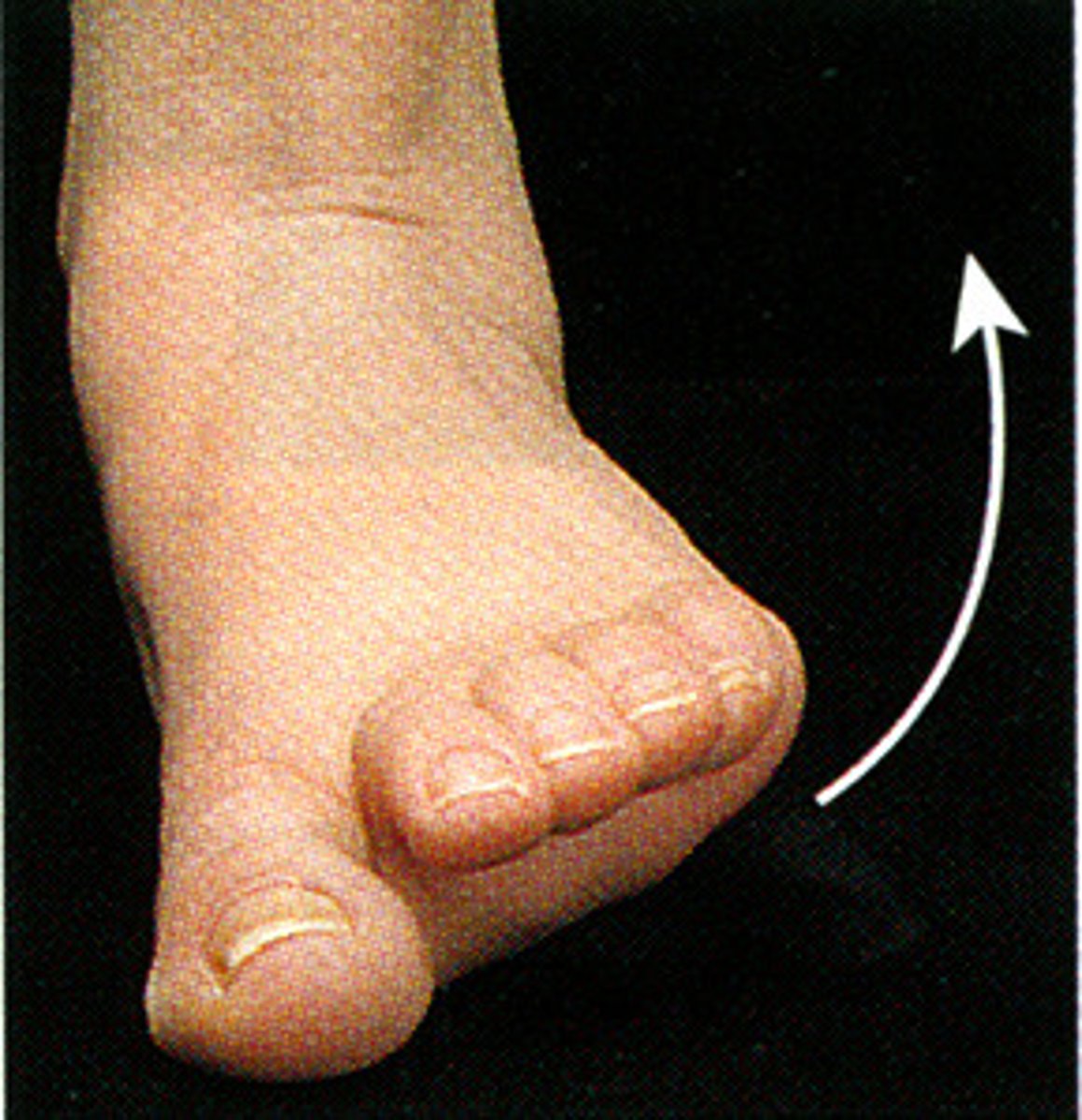
Dorsiflexion
bending the foot/the toes upward
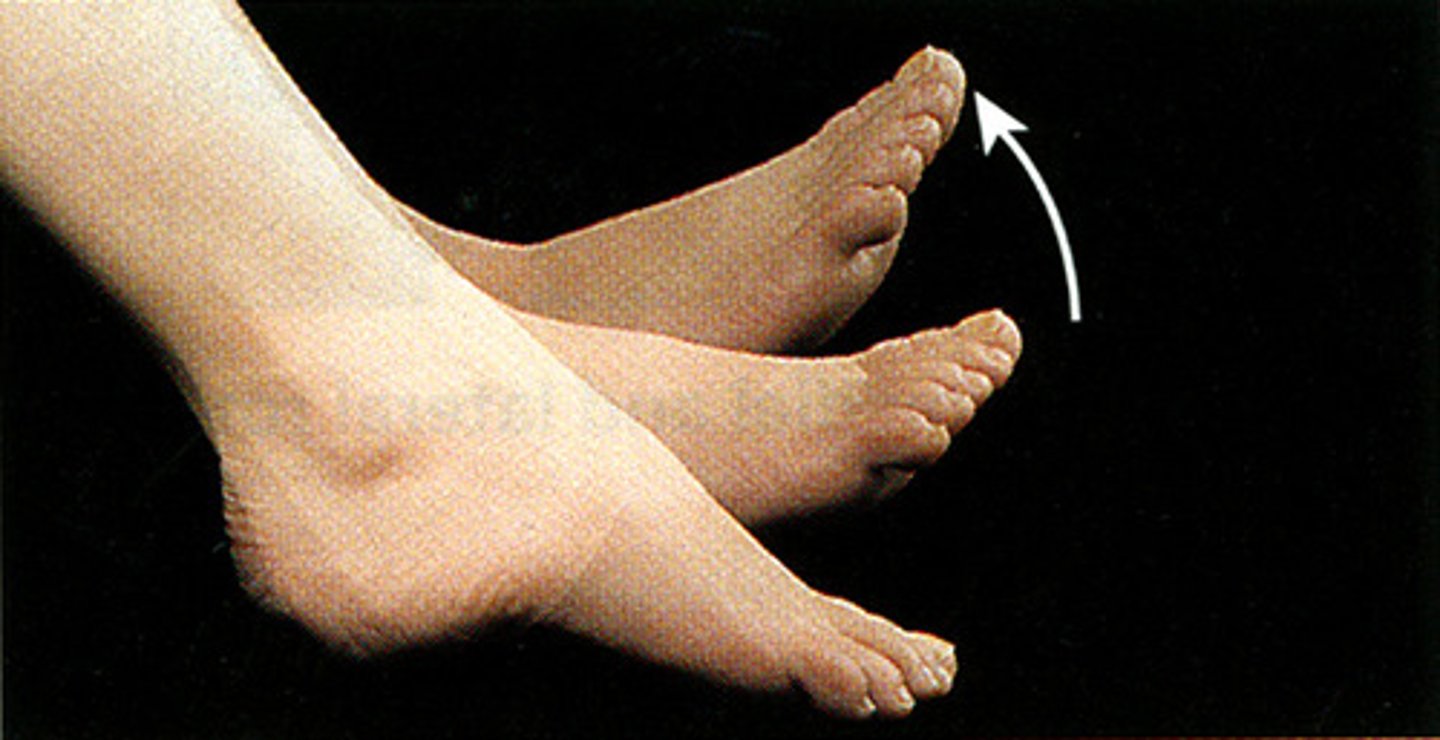
plantarflexion
pointing the foot/toes down
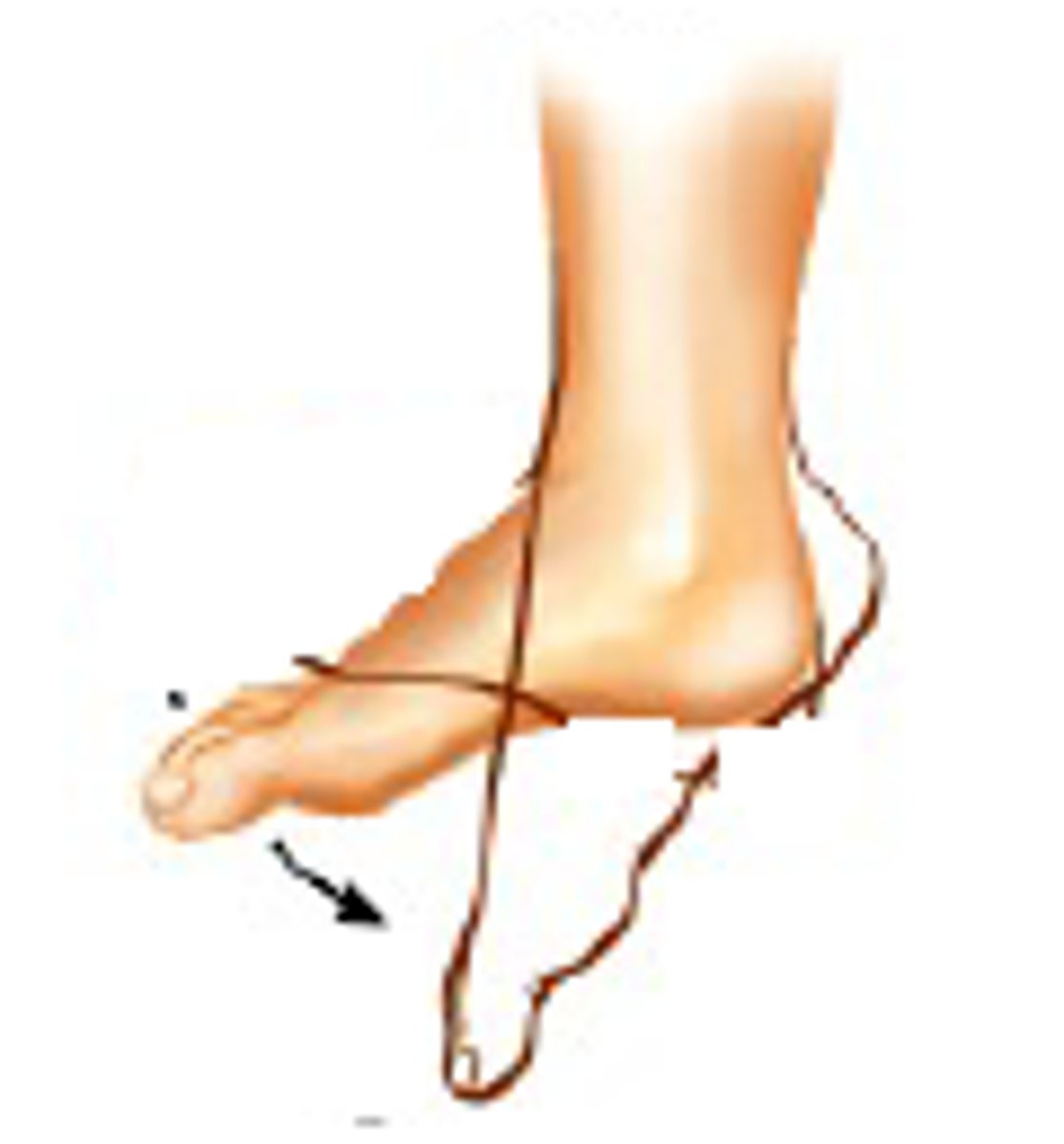
what are the 4 types of physical assessment
inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation
what order do you do a abdominal assessment
inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation
what type of bone is full of bone marrow
cancellous
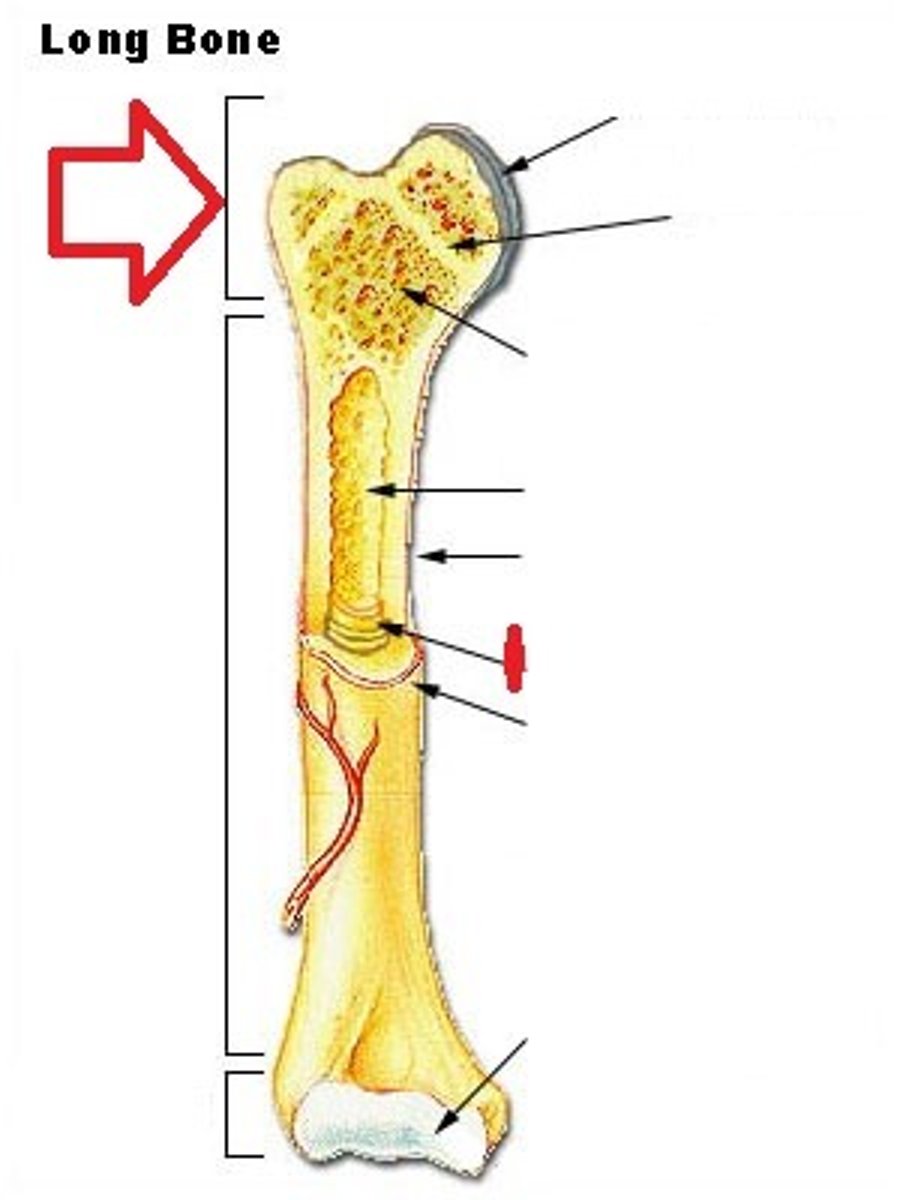
epiphysis of long bone
ends of long bones
Diaphysis (long bone)
shaft of a long bone
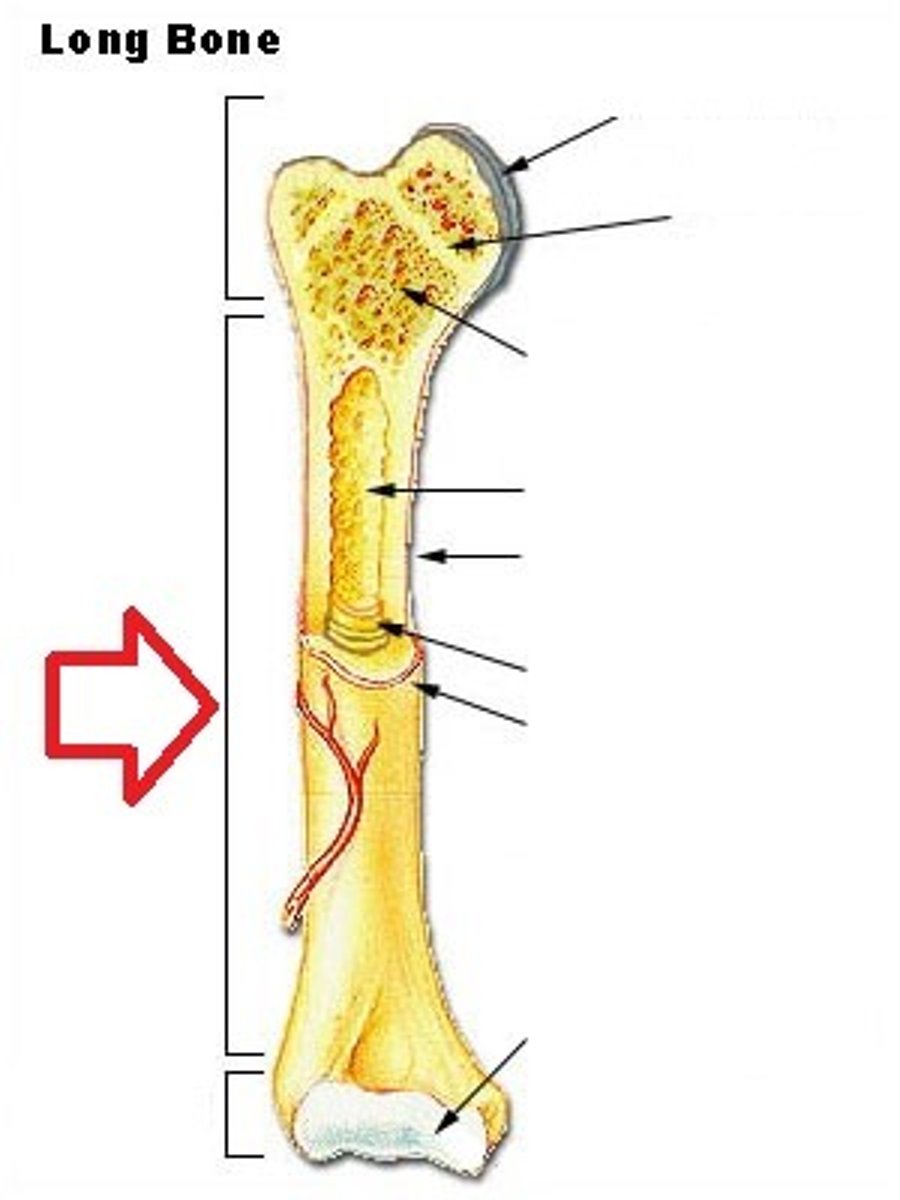
metaphysis
flared portion of a long bone

epiphyseal plate
cartilaginous area between the epiphysis and metaphysis
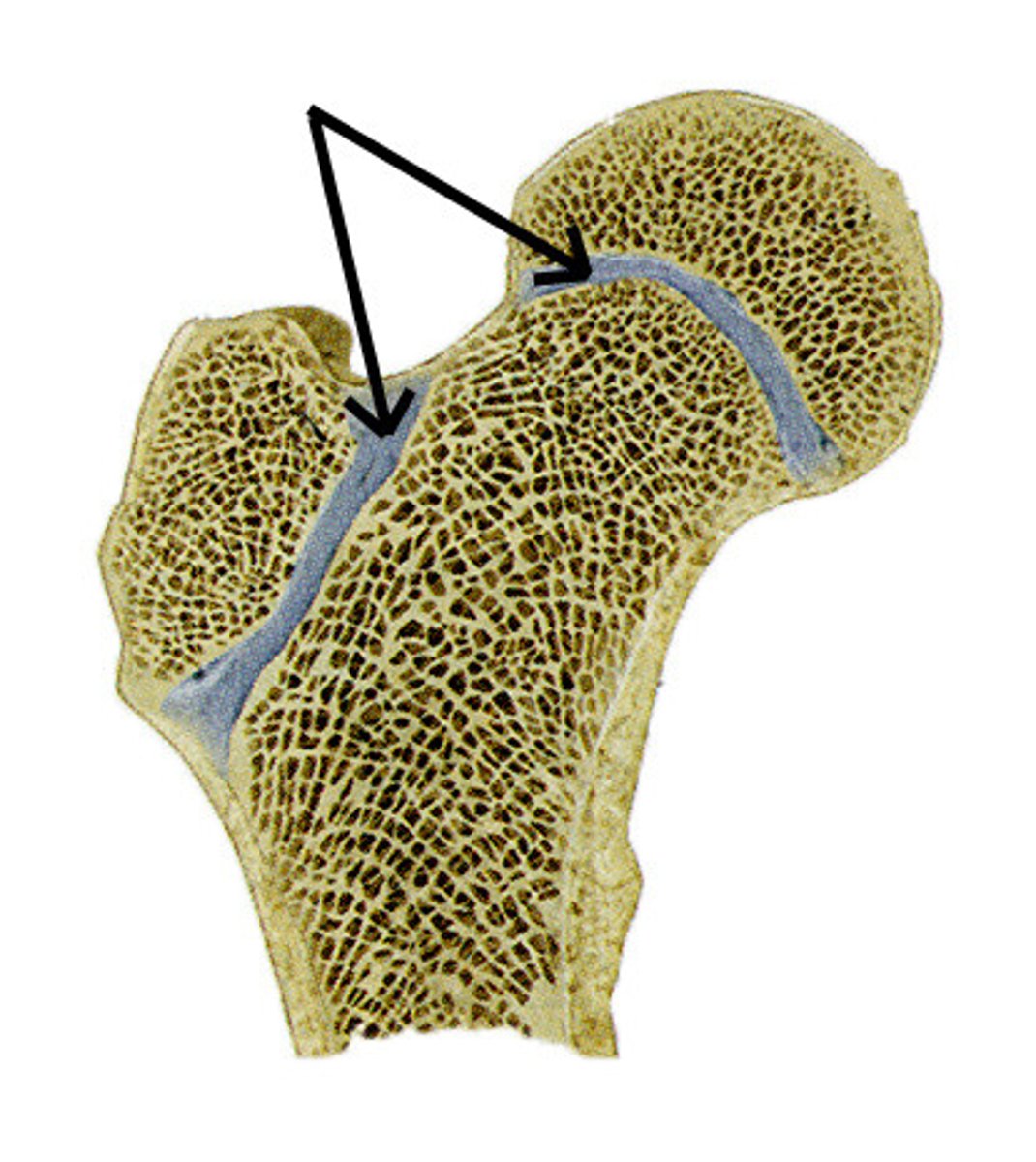
Periosteum
fibrous connective tissue that covers the bone
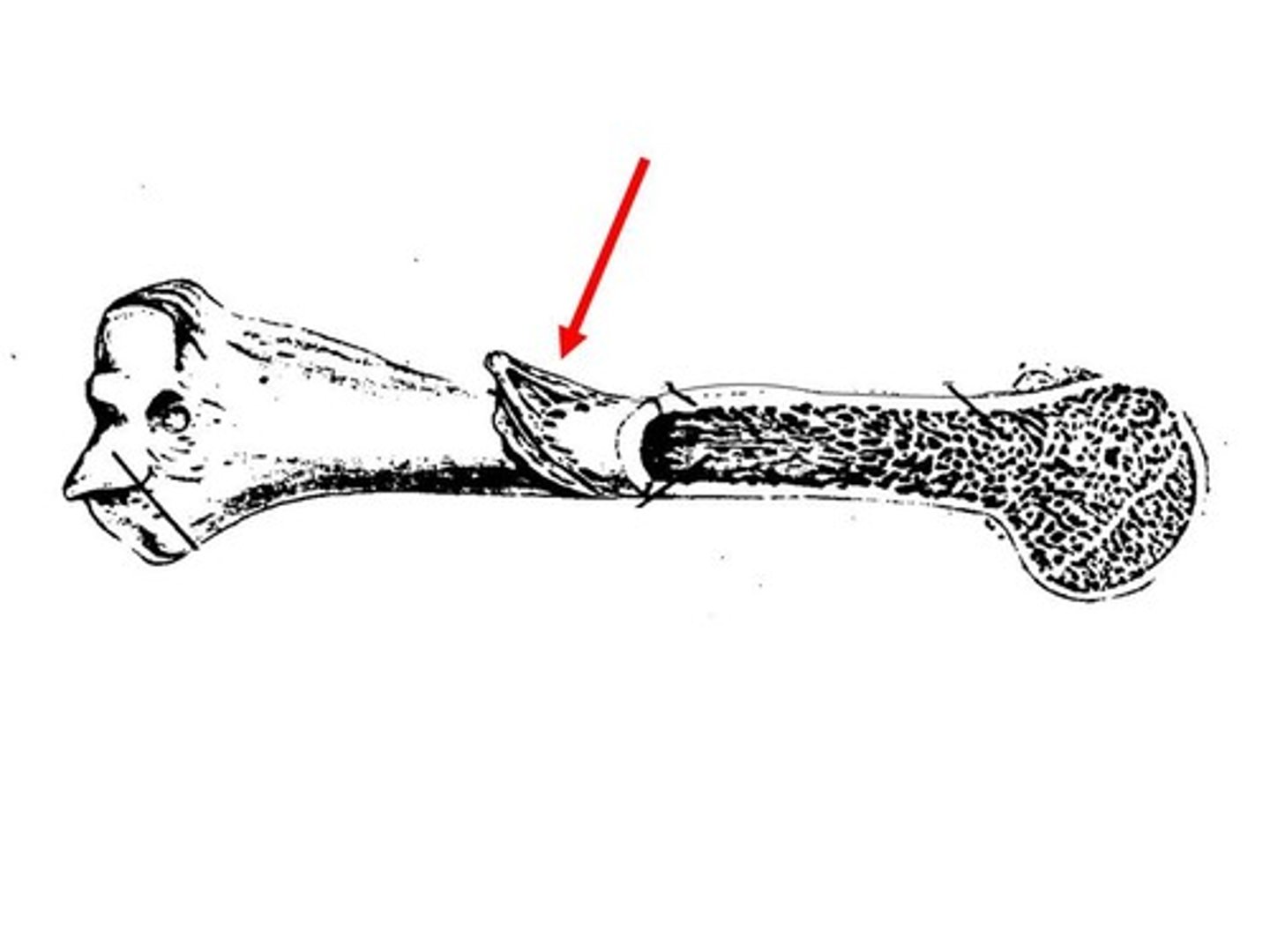
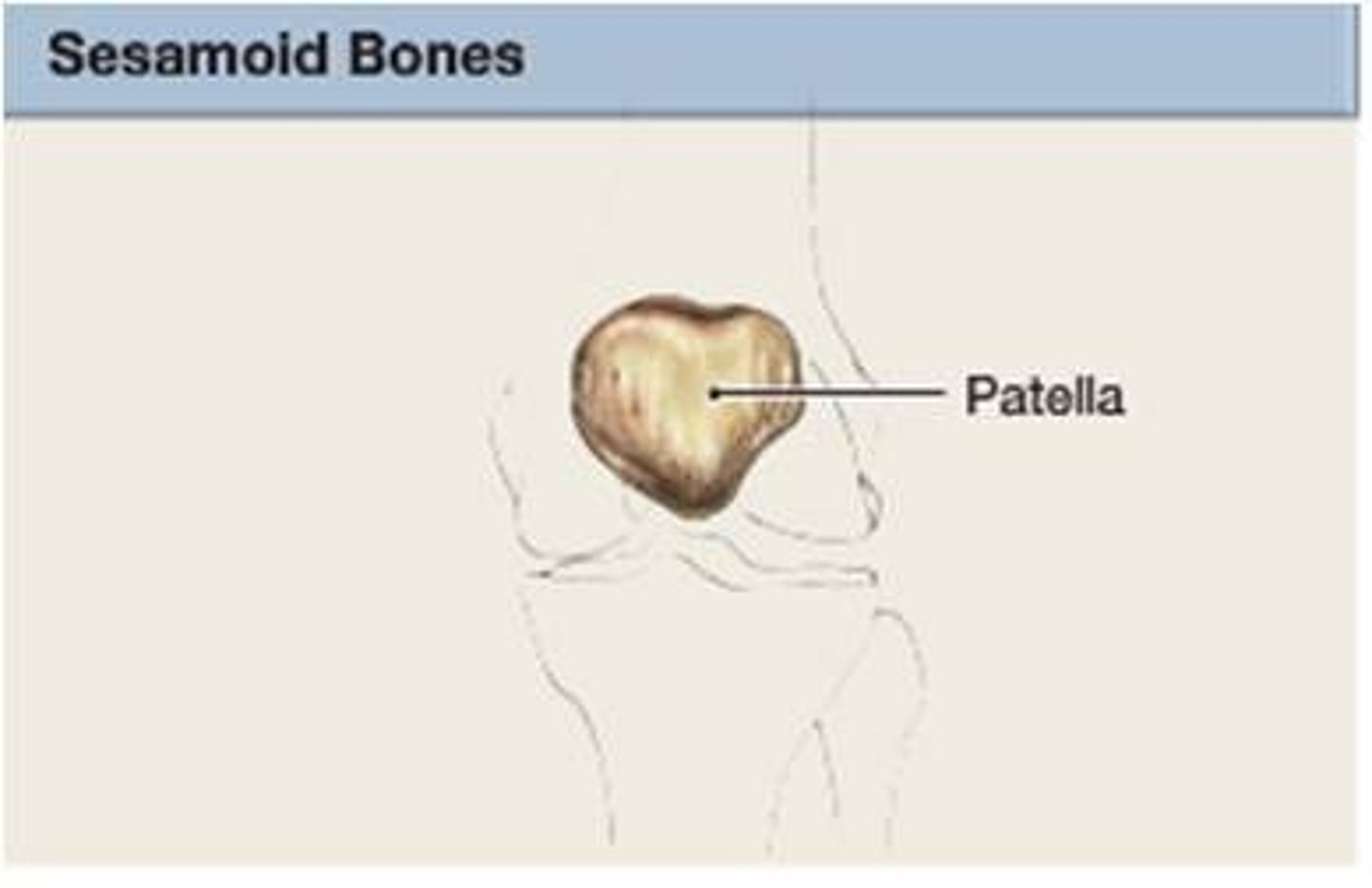
sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
Perimysium
surrounds fascicles
Endomysium
surrounds each muscle fiber
isometric movements do or do not produce movement
do not
isotonic movements do or do not produce movement
do
2 sources of ATP
phosphocreatine and glycolysis
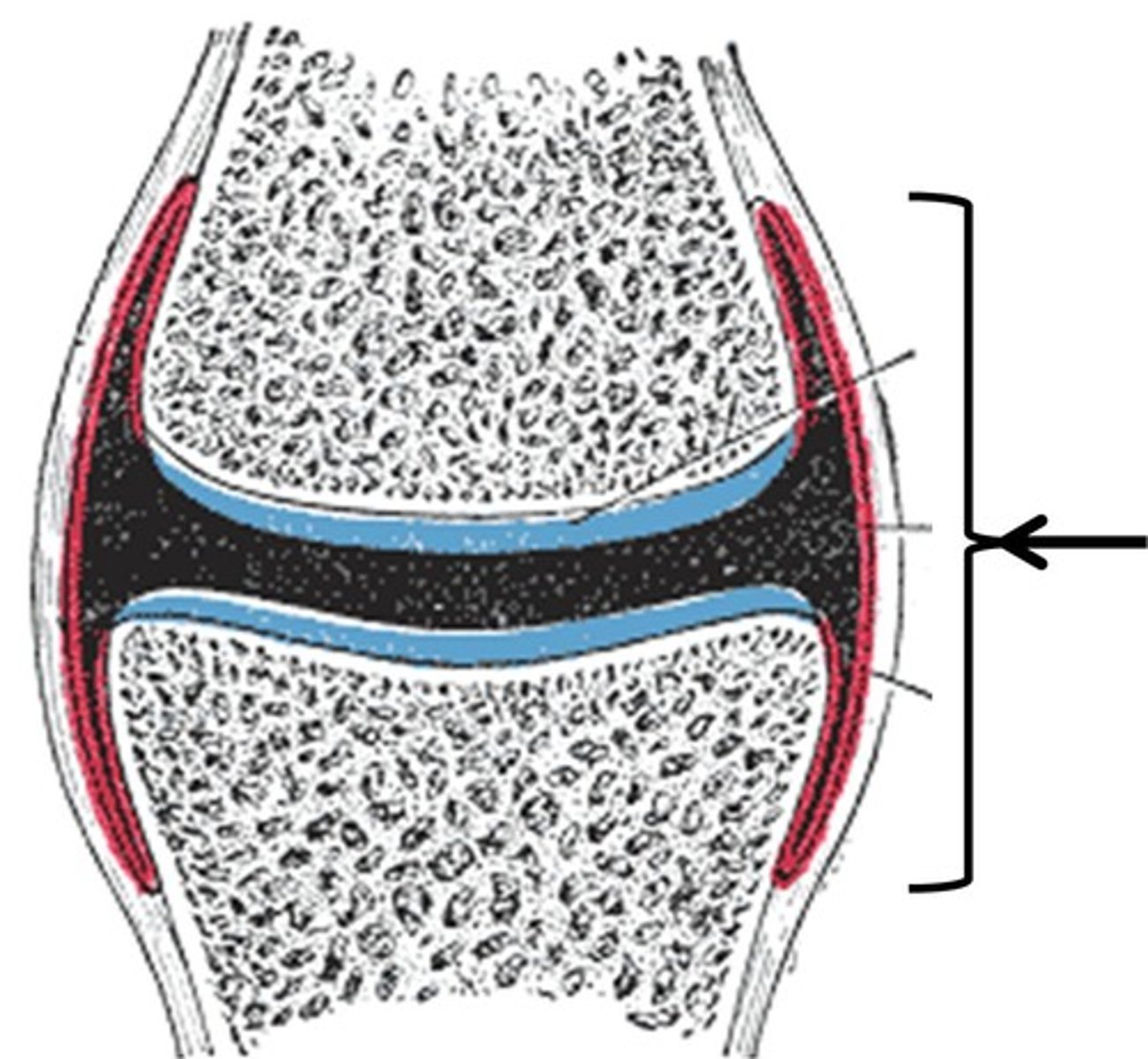
synovial joint (diarthrodial)
freely movable joint
hyaline cartilage
The most abundant cartilage type in the body; provides firm support with some pliability
fibrous cartilage
very tough form of cartilage
doo tendons and ligaments have a good blood supply
no
how does aging affect bones
increased reabsorption of bone, decreasing bone formation
osteoarthritis
cartilage damage