3.1.1/3.1.2 Monomers, polymers and carbohydrates
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Monomer
The smallest unit from which larger molecules are made
Condensation
A reaction joining two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond
Produces one molecule of water
Polymer
A large molecule formed by many identical or similar smaller molecules that are linked by bonds
Hydrolysis
A reaction that breaks a chemical bond between two molecules
Eliminates one molecule of water
Monosaccharides and examples
The carbohydrate monomer from which larger carbohydrates are made
Examples include glucose, fructose and galactose
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate polymer. Two monosaccharides joined together with bonds by a condensation reaction.
Examples include maltose, sucrose and lactose
Maltose, sucrose and lactose formation
Glucose + Galactose → Maltose + Water
Glucose + Fructose → Sucrose + Water
Glucose + Galactose → Lactose + Water
Glycosidic bond
During the formation of a disaccharide one molecule of H2O is made, leaving a molecule of oxygen which links the two molecules together. This link is called a ___
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate polymer
Many monosaccharides joined together with bonds by condensation
Examples include
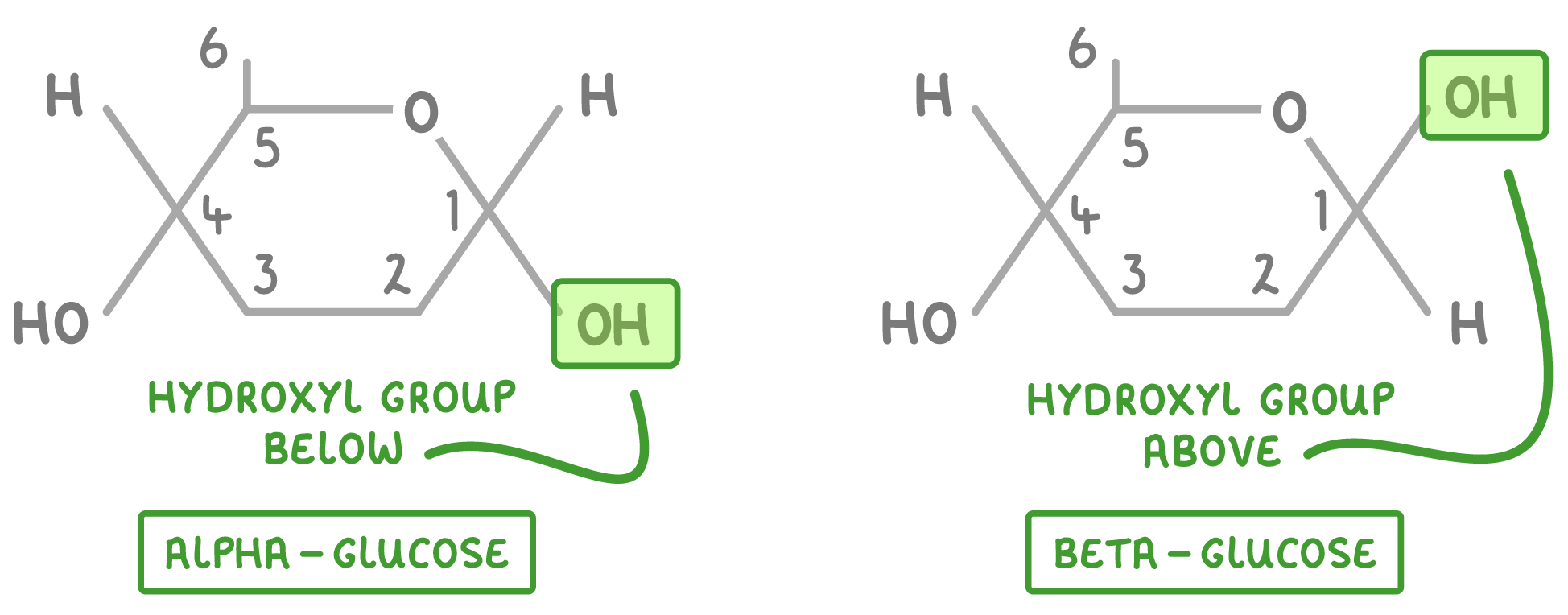
Alpha and beta glucose
Biochemical test for sugars (reducing and non-reducing)
Add Benedict’s solution and heat
No colour change (if non-reducing, such as sucrose)
Boil with hydrochloric acid and then neutralise with sodium hydrogen carbonate
Add Benedict’s solution and heat
A positive result forms a red precipitate
Starch formation and function
Formed by condensation of alpha glucose
Stores energy in plants
Starch biochemical test
Add iodine solution
A positive result turns orange-brown to blue-black
Starch characteristics and the links to its function
Insoluble so does not affect water potential
Large molecule so cannot cross cell membrane to diffuse out of cells
Helical structure so compact so lots of it can be stored in a small space
Branched structure provides lots of ends for enzymes to work on so easily hydrolysed into glucose to more energy
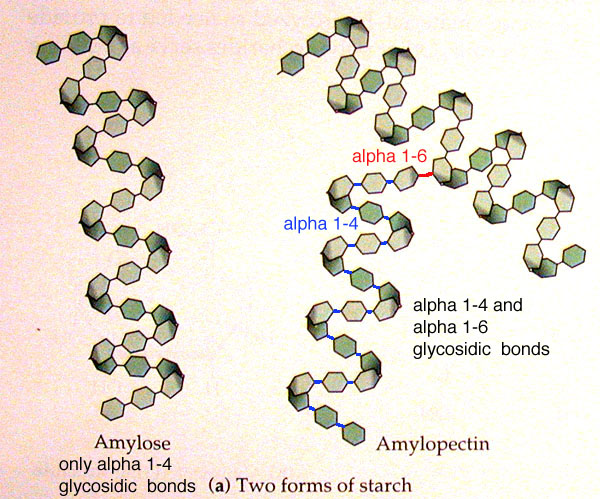
The two forms of starch and their differences
Amylose only has alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Amylopectin has alpha 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Glycogen formation and function
Formed by the condensation of alpha glucose
Energy storage in animals
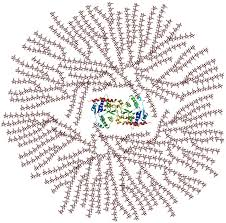
Glycogen characteristics with links to its function
Tight branches and short chains so there are more free ends for enzymes to act on so it is quicker to hydrolyse into glucose for a higher metabolic rate.
Helical structure so its compact so lots of it can be stored in a small space
Formation and function of cellulose
Formed by the condensation of beta glucose
Prevents cell bursting in the plant cell walls
Characteristics of cellulose with links to its function
Long, straight, unbranched chains which are joined together by many hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils. Microfibrils join to form cellulose fibres which join to form cell walls
Large number of hydrogen bonds make the structure very strong, preventing cell bursting
Gives mechanical strength to plants due to the presence of microfibrils which allow water to pass through the cell
Glycogen structure
Cellulose structure
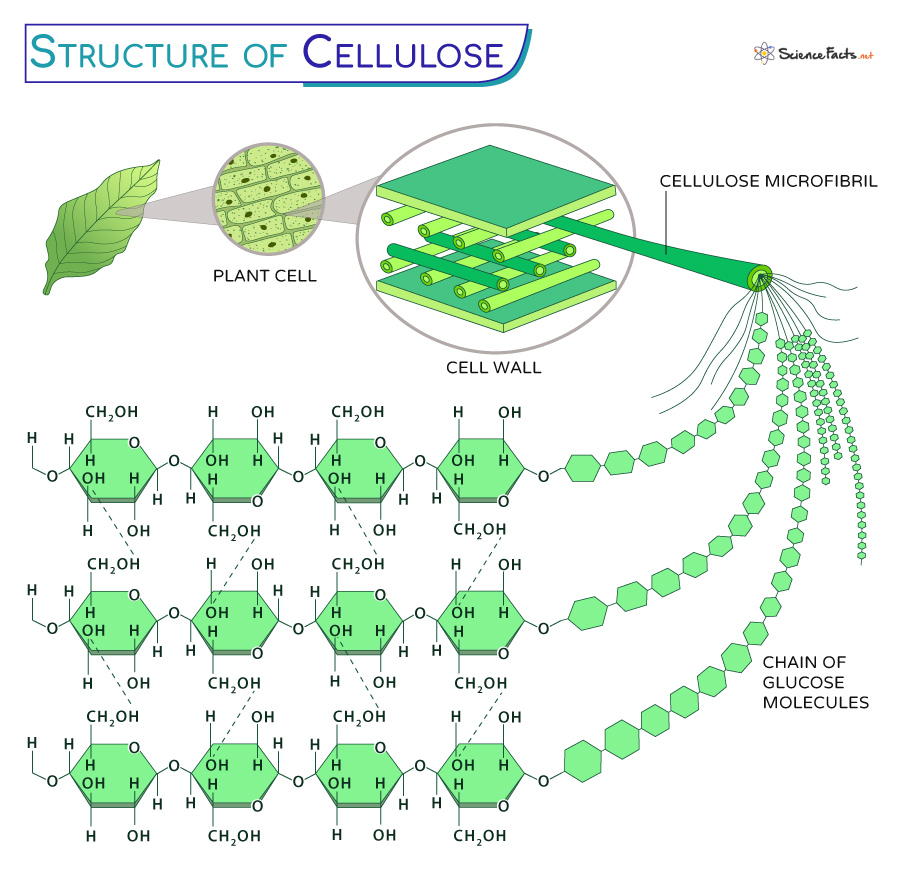
Cellulose structure
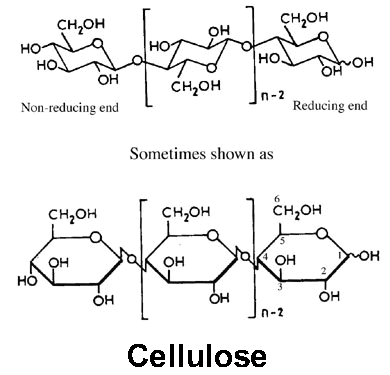
What type of bond provided strength in the cellulose?
Hydrogen bond