Physics: Space Physics (P8)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The solar system is:
everything that orbits the sun
In the solar system there are:
the Sun, eight planets dwarf planets that orbit around the Sun. Natural satellites, the moons that orbit planets, artificial satellites
How is a star formed
dust and gas pulled together by gravitational attraction
life cycle of a star (start with sun size then bigger than sun)
protostar
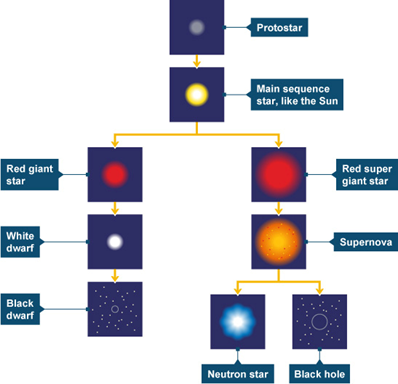
main sequence star red giant white dwarf black dwarf red super giant supernova neutron star black hole
1) Stars initially form from a _______ called a (_______)
2) _____ pulls the ____ and _________ to form a _____. The _____ ______ as the star gets _______ and more _____ ______. When the ________ is _______ enough ________ _______ undergo ______ _____. This forms _____ ____ which gives out ________ which keeps the _____ of the star _____.
cloud of dust and gas nebula, gravity dust gas protostar temperature rises denser particles collide star hot hydrogen nuclei nuclear fusion helium nuclei lots of energy core hot,
3) Star enters a ____ ____ period. The _____ _____ from _____ _____(radiation pressure remember this is what the MS scheme says) ______ the _____ _____ of ______. They are at e_________. This is called a ____ _____ star. lasts _____ __ ____.
4)____ begins to _____ ____. Star ____ into a _____ _____(same size as sun) or a ___ _____ ____(bigger than sun) it becomes _____ because the _____ _____. Then _____ elements up to iron created in ______. n_______ f_______ of ___
long stable outward pressure nuclear fusion balances inward force gravity equilibrium main sequence billions of years, Hydrogen run out swells red giant super red giant red surface cools down heavier core nuclear fusion heleim
5)(sun size star) becomes ______, ____ _____ ____ ____. leaving behind a ___ ___ ___ ___ - a ___ ____. This ___ down, ____ less ____ and becomes a ____ ____.
6) (bigger star) starts to ___ _____, undergo more n_____ F______, ____ and _____ several times. EAVENTUALY EXPLODE INTO A ________ forming elements ____ than _____ and _______ then into the universe to ______ new ______ and ______.
7) (bigger stars) This leaves behind a ___ ___ ___ called a ____ ____. If the star is d____ enough it will become a ___ ___ - super dense point in space.
unstable ejects outer layers of dust and gas hot dense solid core white dwarf cools emits energy black dwarf glow brightly nuclear fusion expand and contract supernova heavier iron ejecting form planets stars dense hot core neutron star dense black hole
nuclear fusion
Why is it important?
when nuclei combine to form a single atomic nucleus
energy producing process
Why is the presence of elements heavier than iron evidence solar system came from a star exploding?
elements heavier than iron can only be formed when a missive star explodes
satellite-
natural satellite-
artificial satellite-
body that orbits the planet not man amde humans have built
when a satellite orbits the plane the ___ remains ____ but the satellite is ____ _____ ______ so it is ____ ____ ____. The force that keeps an object moving in a circle is called a _____ force .This force acts ….
planet speed constant constantly changing direction constantly changing velocity centripetal towards the centre of the earth
2 factors that determine the size of the centripetal force
speed/velocity of satellite radius of orbit
Explain why the velocity of the satellite changes as it orbits the planet?
gravity causes the satellite to accelerate acceleration causes a change in direction velocity changes because direction changes
the ____ you get to a star or planet the ______ the _____ ____ is. . ____ the force, _______ the orbiting so it _____ in orbit.
If the _____ changes the ___ of the orbit must too.
closer stronger gravitational force stronger faster remains speed size
explain why a star remains stable
gravitational forces inward balances radiation pressure outwards
polar orbits-
a satellite path that passes over or near the Earth's North and South Poles high speeds used for close monitoring of earth military.
geostationary -
atellite orbits the Earth directly above the equator at the same speed the Earth rotatess orbit higher travel slower, sued for most weather applications and mobile internet
wavelength-
length of one complete wave. this effects the pitch of sound and colour of light.
red shift
the increase in the observed wavelength of a light source when it moves away from an observer; the spectral lines move toward the red end
blue shift
the decrease in the observed wavelength of a light source when it moves towards an observer; the spectral lines move toward the blue end
Doppler effect
When the car moves towards you, the wavelength ______ so sounds _____ ____
when the car moves away from you the wavelength so sounds _____ _____
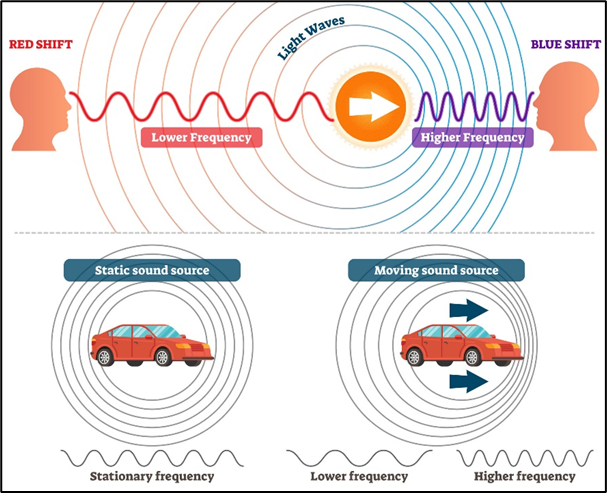
decreases higher pitch increases lower pitch
The universe is
When scientists observe ________—- from distant , they find the ______________-has _________-
They are _______________ — they have to the of the spectrum.
This suggests the source of the ____ is _________________.
More _____________galaxies have greater ____________ than closer galaxies.
expanding light galaxies wavelength increased red shifted shifted red end light is moving away distant red shifts
Bing bang theory is a theory that …
describes the early development of the earth. The discovery of red shift led to the development of the bbt
The bang theory states that …
1 all matter occupied verry small space that was verry dense and so verry hot. 2 it exploded and space started expanding - still happenign
_____ ____ is the substance scientists believe ____ ____ ____ ______.
D____ ____ is the substance scientists believe responsible for the …..
dark matter holds the galaxy together dark energy universe expanding
Cosmic microwave background radiation
remains of thermal enrgy from bbt can only be explained by bbt so provides strong support for the theory.
big crunch
gravitational attraction between all objects will slow to a stop, attracting everything back together in a 'Big Crunch'.
HOW TO REMEBR PLANETS
MY VERY EASY METHOD JUST SPEEDS UP NAMING PLANETS