M4 SKM: section 2 moleclaur basis of muscle contractions
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
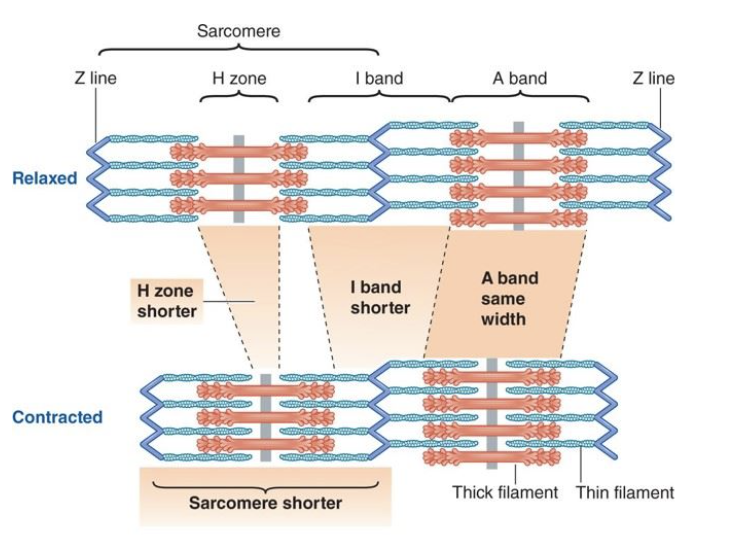
when a muscle contracts it shortens or lengthens
shortens
what brings on muscle contractions
sliding filament mechanism (basis of it is the cross-ridge btw actinc and myosin)
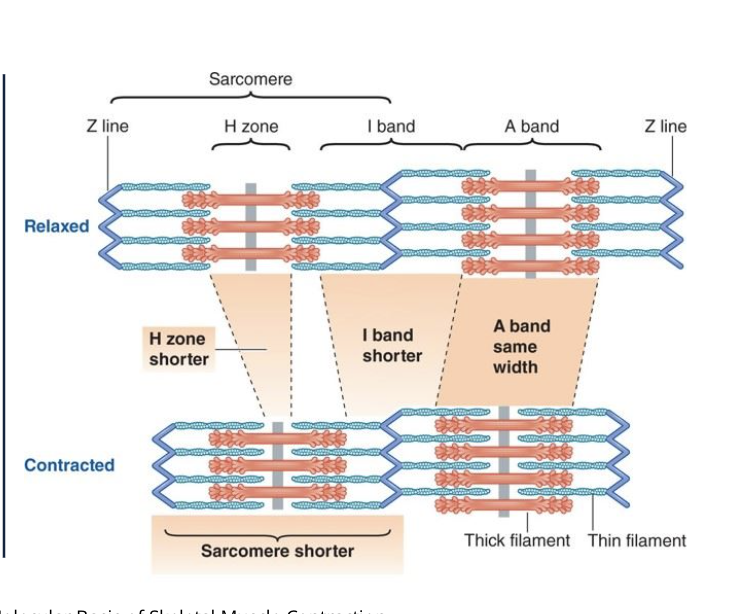
T or F : a sacromere has thin filiements on the outside and thick filiments on the inside
T
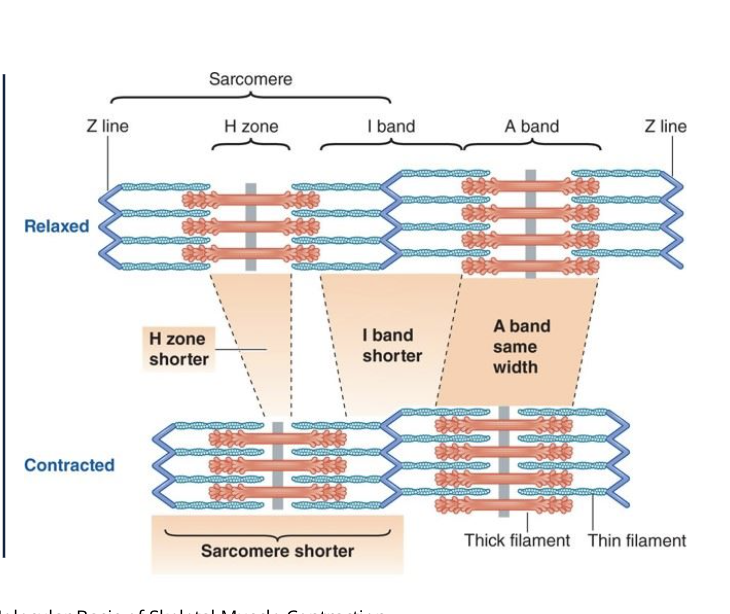
T or F: when a muscle contracts the actin and myosin shorten
F: the sacromeres shorten due to the increase overlapping of the thick and thin filiments
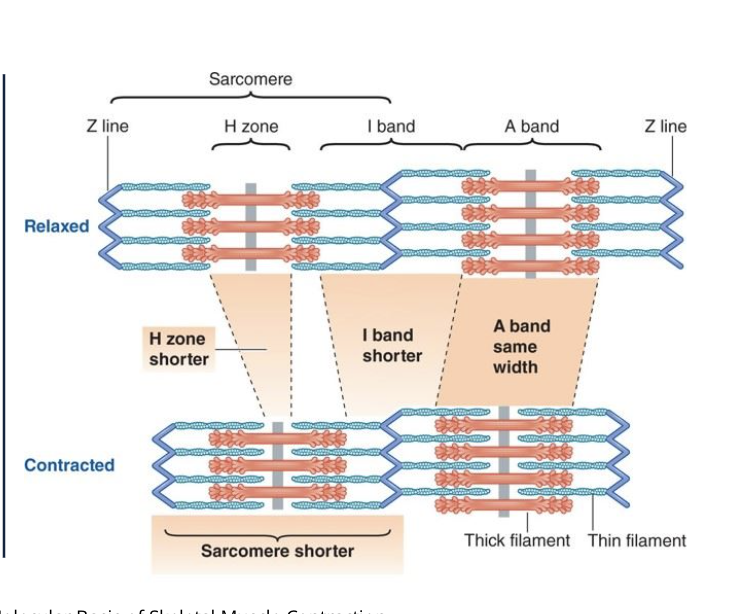
T or F: all sacromeres shorten to the same degree and across the entire fibre
T
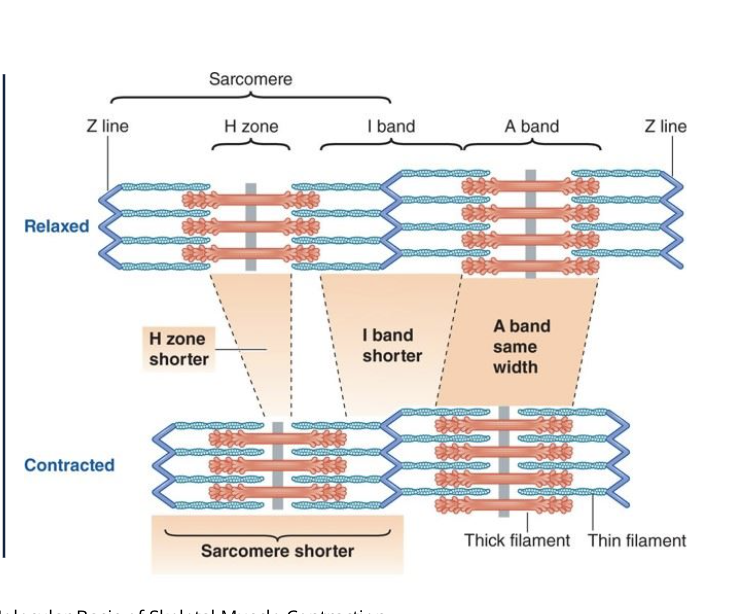
T or F: when a muslce contracts the A band shortens
F: A band stays the same
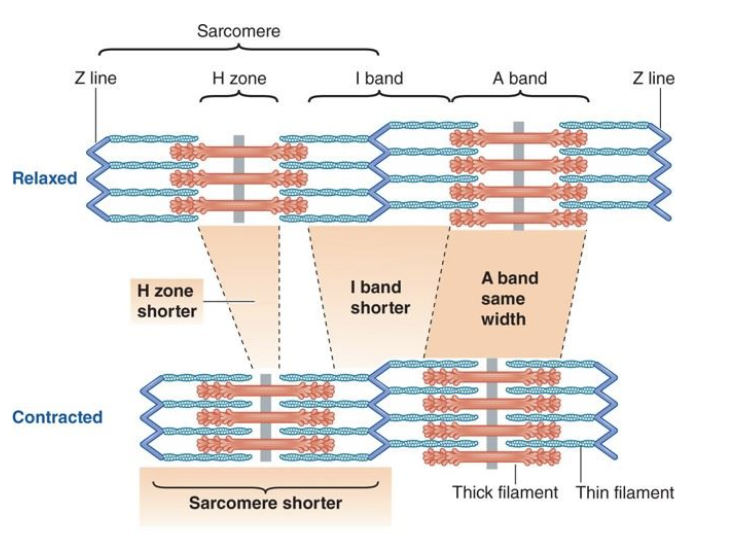
T or F: when a muslce contracts the I band shortens
T
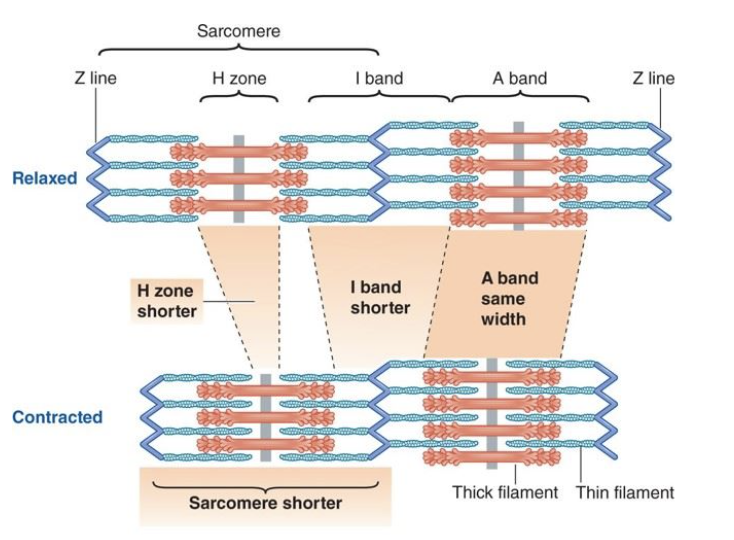
T or F: when a muslce contracts the H zone shortens
T
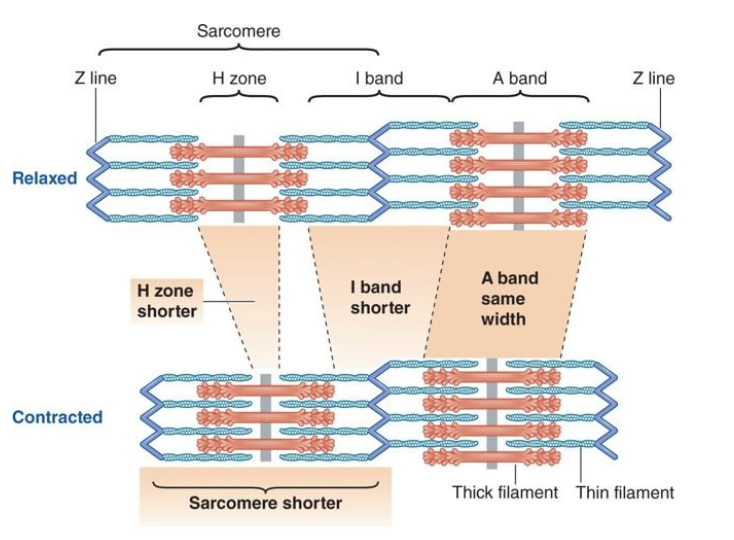
T or F: when a muslce contracts the sacromere shortens
T
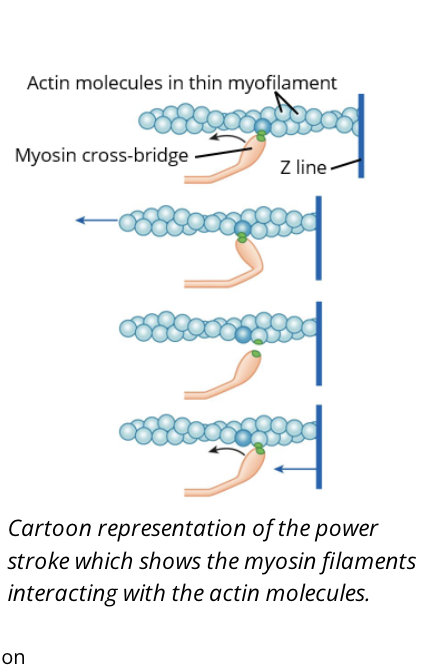
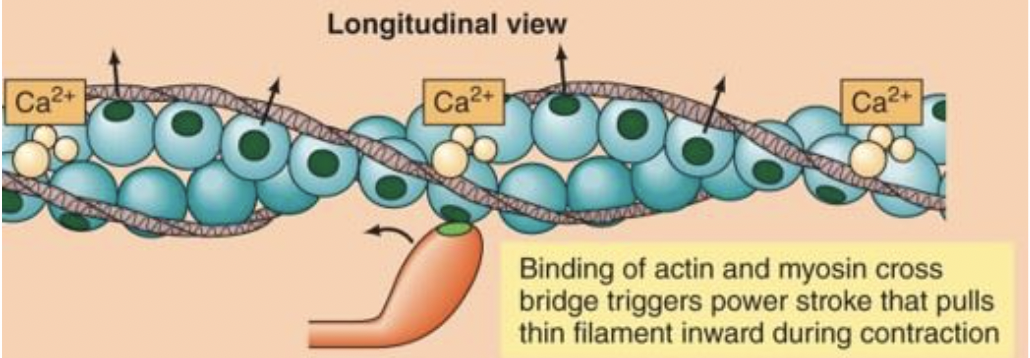
what is the power stroke?
the interaction btw myosin and actin that leads to the shortening of the sacromere
T or F the thin filiment is pulled towards the middle of the thick filiment during the power stroke
T
what are the four stages of the cross-bridge cycle?
Binding
Power Stroke
Detachment
Binding
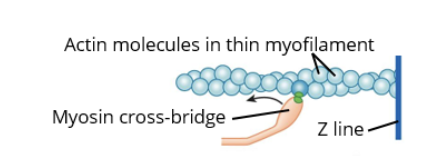
What step is this of the cross-bridge cycle? Myosin cross-bridge binds to actin molecule.
binding
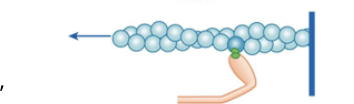
What step is this of the cross-bridge cycle? the myosin head bends pulling thin myofilament inwards
Power Stroke
What step is this of the cross-bridge cycle? cross-bridge detaches at end power stroke and returns to original conformation
Detachment
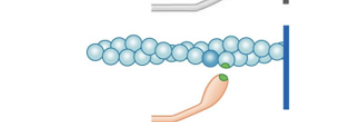
What step is this of the cross-bridge cycle? cross bridge binds to more distal actin molecule: cycle repeats
binding pt 2
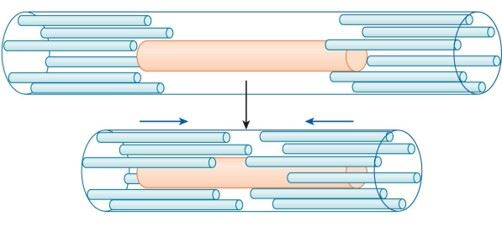
what is the result of the power stroke?
actin molecules being pulled closer to the center of the myosin molecules
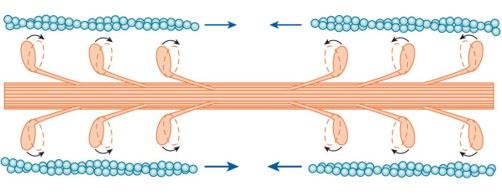
each myosin molecule is surronded by how many actin molecules?
6 actin molecules
T or F: both myosin heads can be attached to actin at a time
F only one head can be attached to actin at a time
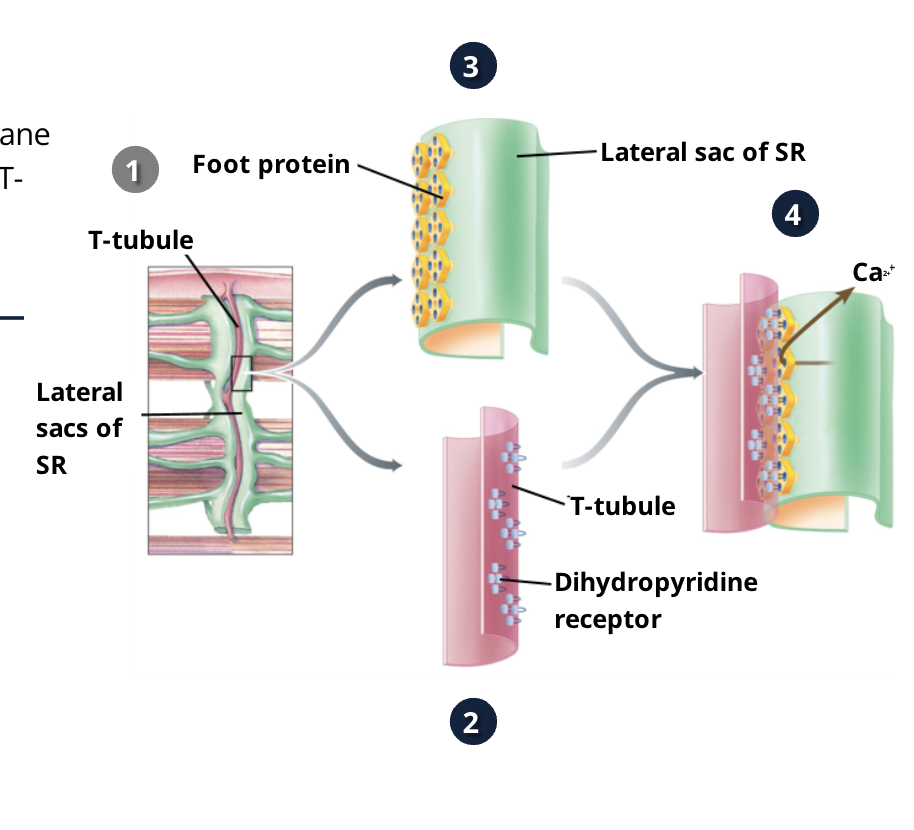
When the plasma membrane is depolarized where does the wave of depolarization spread?
the plasma membrane AND deeper into the cells by spreading down the T-tubles which is then transmitted to the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
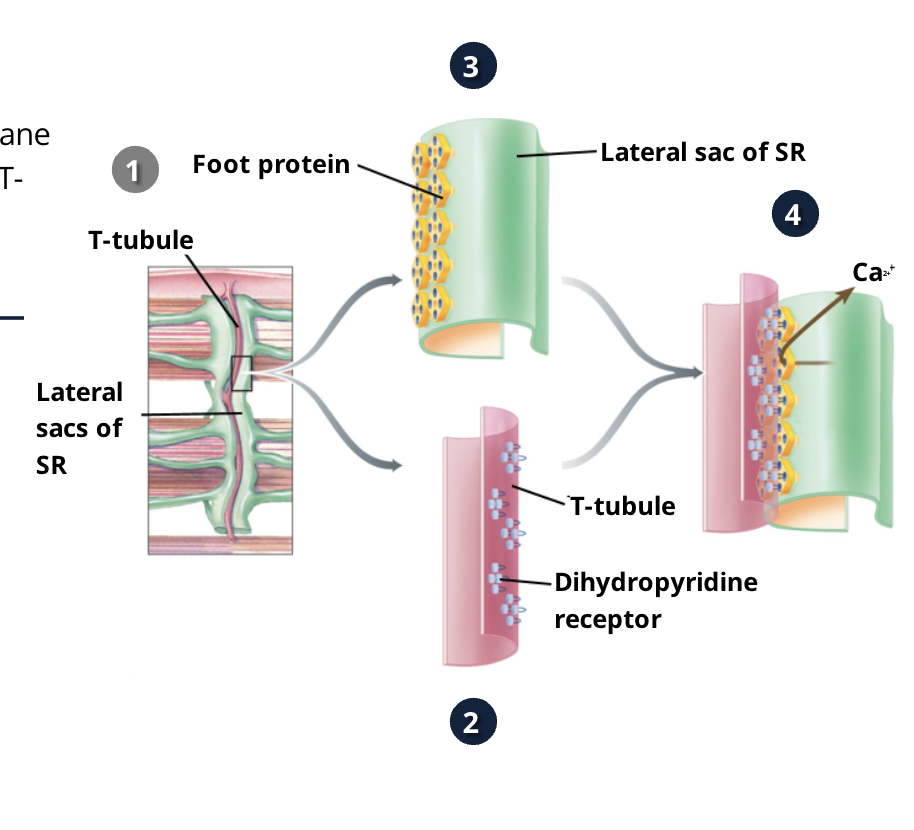
the depolarization is spread to the plasma membrane then ——— which is transmitted to ————
deep into the cell down the T-tubules which is transmitted to the SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum)
where does the energy come from to do the power stroke?
excitation-contraction coupling
what is the process of converting an electrical signal into an actual contraction called?
excitation-contraction coupling
what happens at the motor end plate?
In brief, acetylcholine (Ach) is released into the neuromuscular junction where it causes permeability changes and initiates an action potential that is conducted across the entire muscle membrane. Skeletal muscle cells have two membrane structures that help to transmit this signal to the muscle fibres.(Sarcoplasmic Reticulum and T-Tubles)
what two structures are in SKM membrane help to transmit the signal to the muscle fibres
sarcoplasmic Reticulum
T-tubles
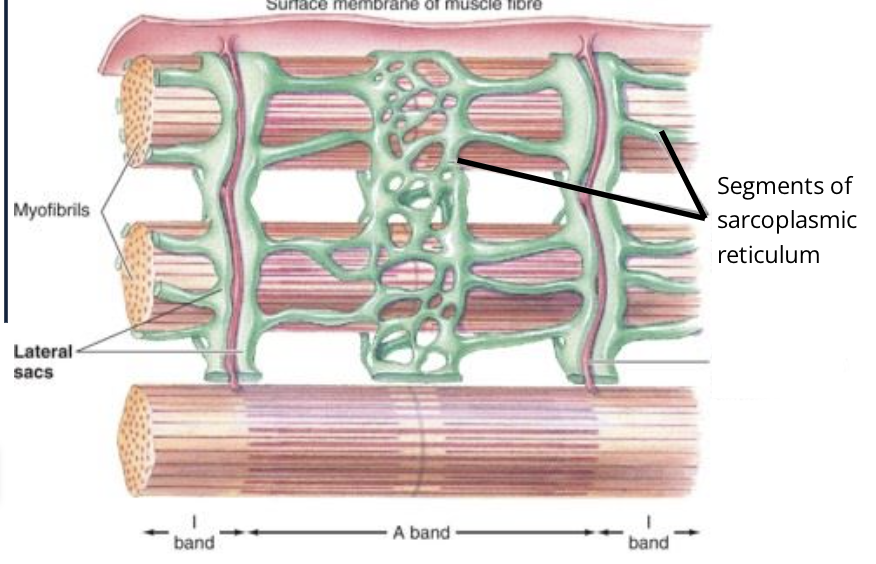
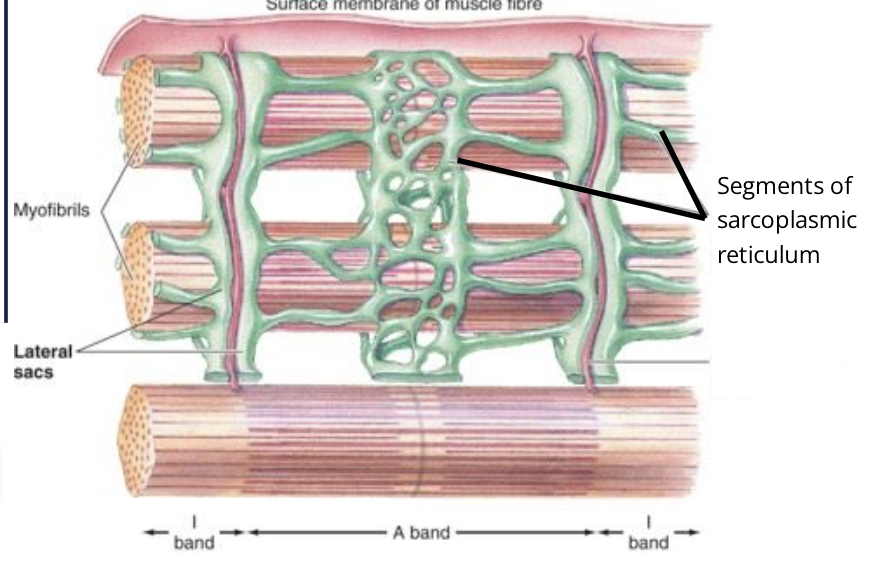
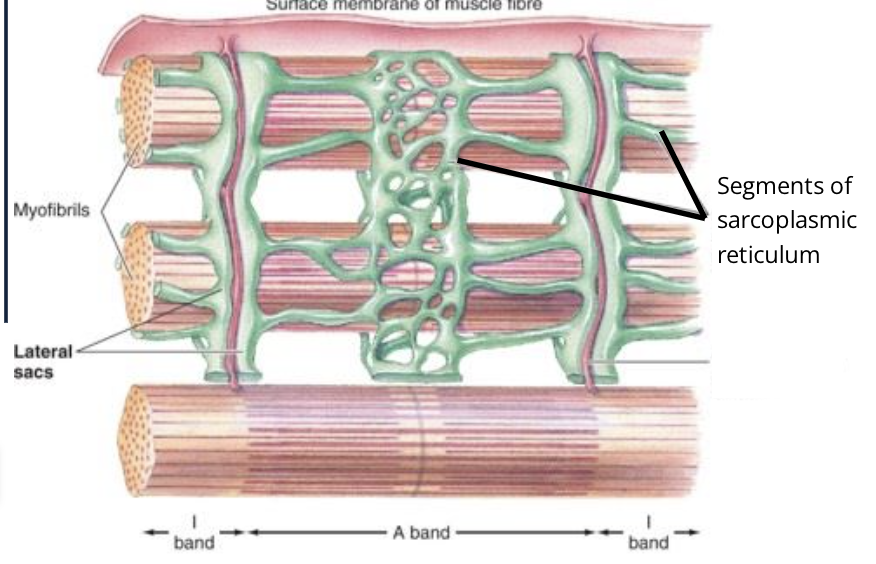
What way does the SR run with the muscle fibres
parallel
what stores Ca2+ in muscles?
the SR
what is the SR called in non musulce cells
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
what is at the end of the SR and is close to the T-tubles?
the lateral sacs of the SR
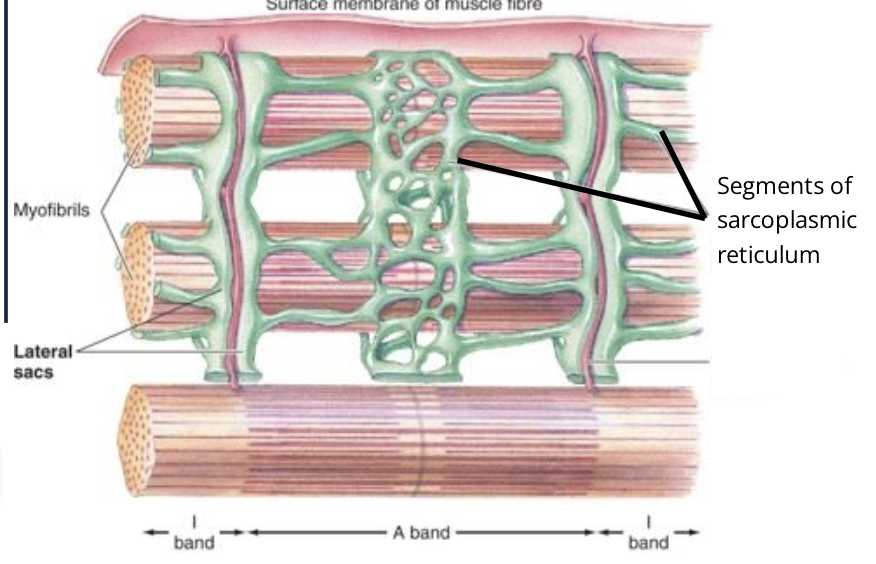
what are T-tubles called
Transverse Tubles
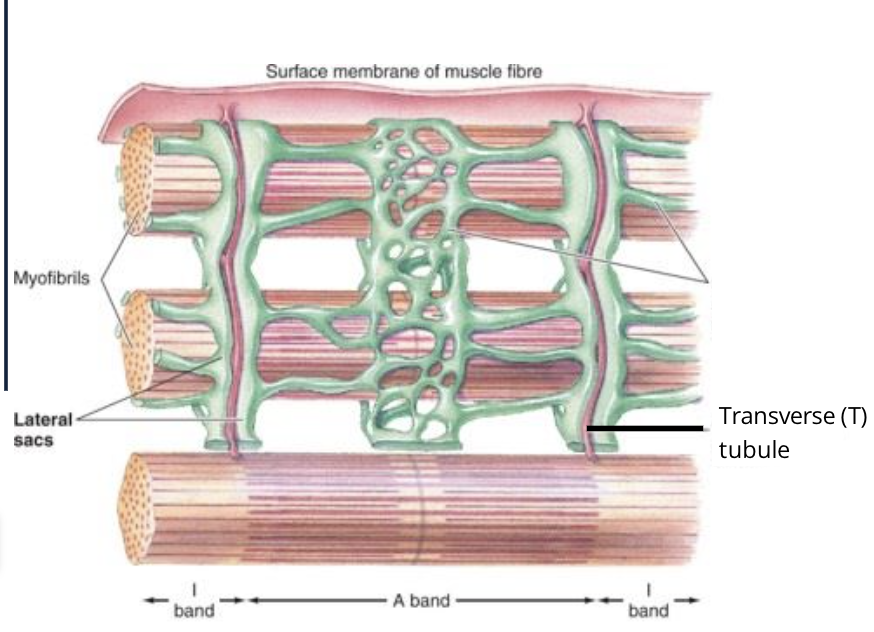
what way do T-tubles run with the muscle fibres
perpendicular to the fibres and are at the junctions of the A and I bands
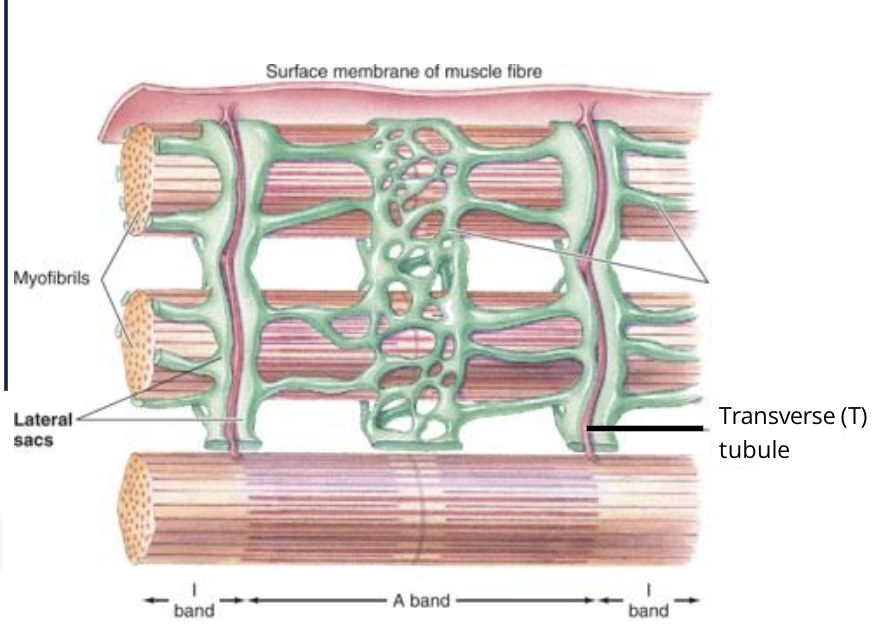
Where does the T-tubles dip into the muscle fibres?
at the junction between A and I bands of the myofibrils
what is on the surface of the T-tubles?
dihydropyridine receptors (essentailly voltage sensors)
what do dihydropyridine receptors onthe T-tuble surface sense?
they sene the wave of depolarozation as it makes its way down the T-tubles
What senses the wave of depolarozation as it makes its way down the T-tubles
dihydropyridine receptors
what is opposite of the what do dihydropyridine receptors on the T-tuble surface on the SR?
ryanodine receptors
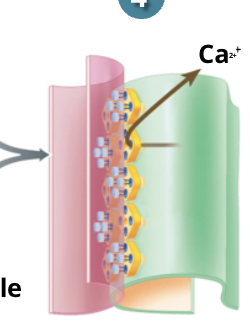
what are ryanodine receptors?
a form of Ca+ channel on the SR that are influenced by the dihydropyridine to undergo a conformational change, when they are activated they open and Ca+ enters the cyctomplasm
what happens when ryanodine receptors are activated by dihydropyridine?
when they are activated they open and Ca+ enters the cyctomplam
what is realsed from the SR when there is a depolarization
Ca2+
what is the primary trigger to allow skeletal muscle to contract
Ca2+
why can contractions not take place when the muslce is relaxed?
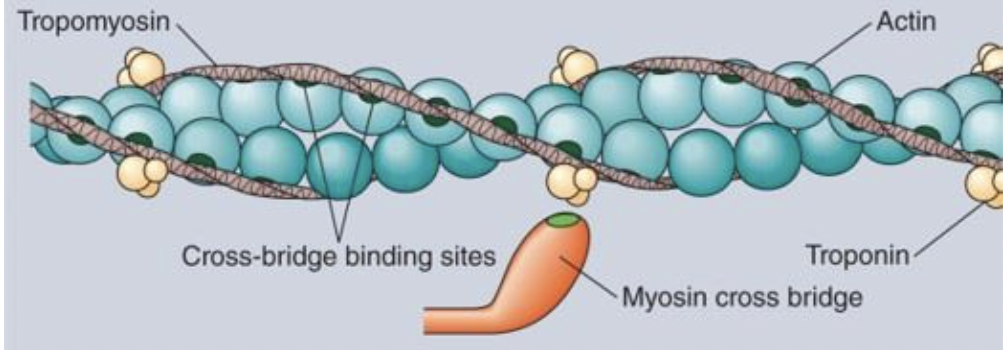
because tropomyosin and troponon are positioned to prevent cross-bridging by blocking the mysoin binding site on the actin molecule.
what happens when Ca2+ enters the muscle fibre?
Ca2+ binds to troponin, which moving tropomysin out of the way and exposes the myosin sites on the actin molecules
what causes relaxatin of the muscle?
when there is decreased nerve activity at the neuromuscular junction, when Ach is no longer realised, acetylcholinesterase can remove any remaining Ach from the neuromuscular junction. this stops the generation of action potentials in the SKM fibre
T or F: once Ca2+ is realsed in to the cystosl is can be activily pumped back in to the SR for when it is needed.
T is pumped activly be the Ca2+-ATPase
T or F: ATP is required for Ca2+ reabsorption into the SR
T
where is Ca2+ realsed from
the lateral sacs of the SR
T or F: for the cross bridge to remain ready to fire there must be Ca2+
F: there must be ATP
Recall that the myosin heads have an actin binding site and an ATPase site. The ATPase site can bind ATP and when it does, it splits it into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). By removing the P, from the ATP, stored energy is released and transferred to the myosin cross-bridge. Using a gun analogy, the cross-bridge is now "cocked" and ready to fire when the trigger is pulled.
During the power stroke the —-; is released and when the power stroke is complete, the —- is also released leaving the ATPase site empty yet the cross-bridge is still bound to the actin.
During the power stroke the P; is released and when the power stroke is complete, the ADP is also released leaving the ATPase site empty yet the cross-bridge is still bound to the actin.
how does the cross-bridge return to the “un-cocked” shape?
binding of a new ATP
igor mortis occur why?
After death, rigor mortis occurs. This is because, due to a poorly understood mechanism, Ca2+ concentration increases it cells. Because the cross-bridges were already "cocked" the muscles will start contracting until they run out of ATP after which they remain contracted. Eventually (after several days) sufficient muscle proteins decay and relaxation occurs again.
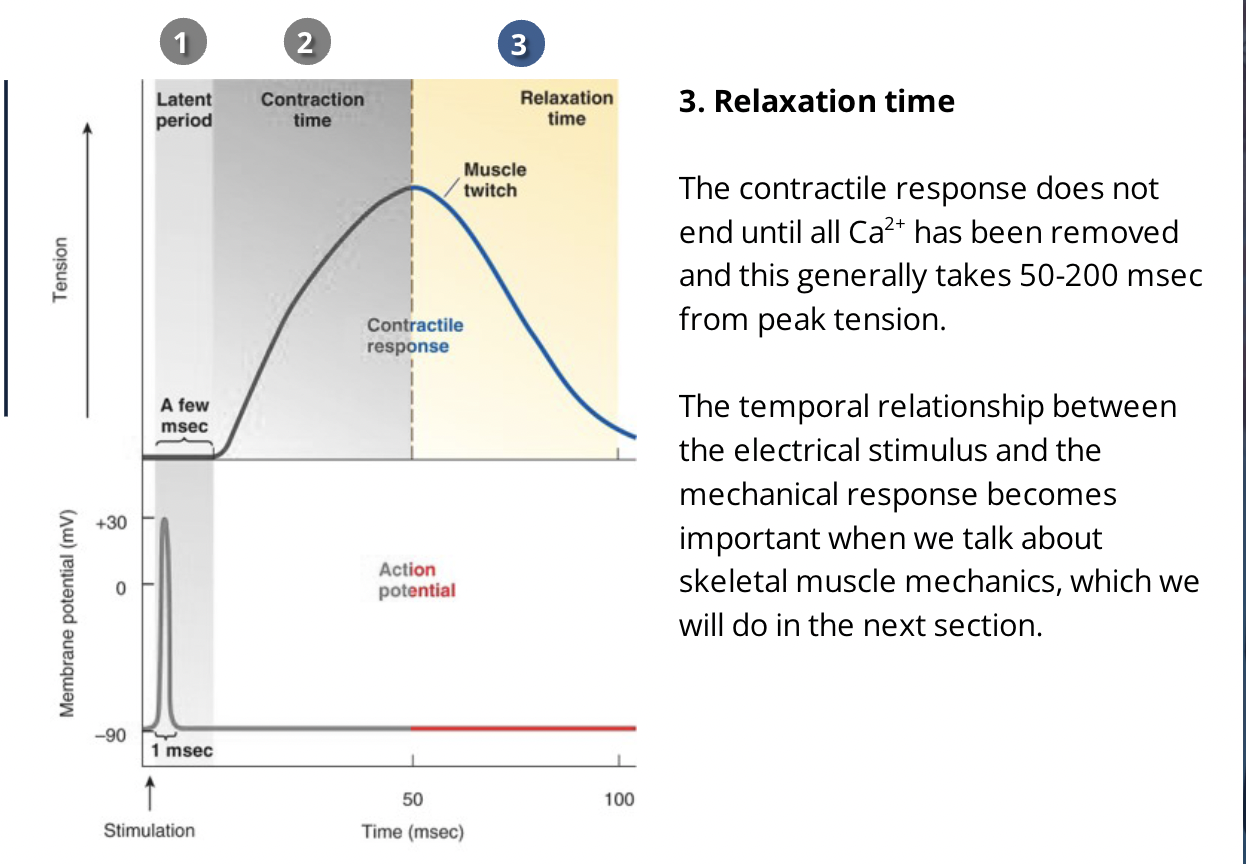
what is a muslce twitch?
the minimum contraction of a whole muscles caused by a single action potential in the nerve exciting the musle
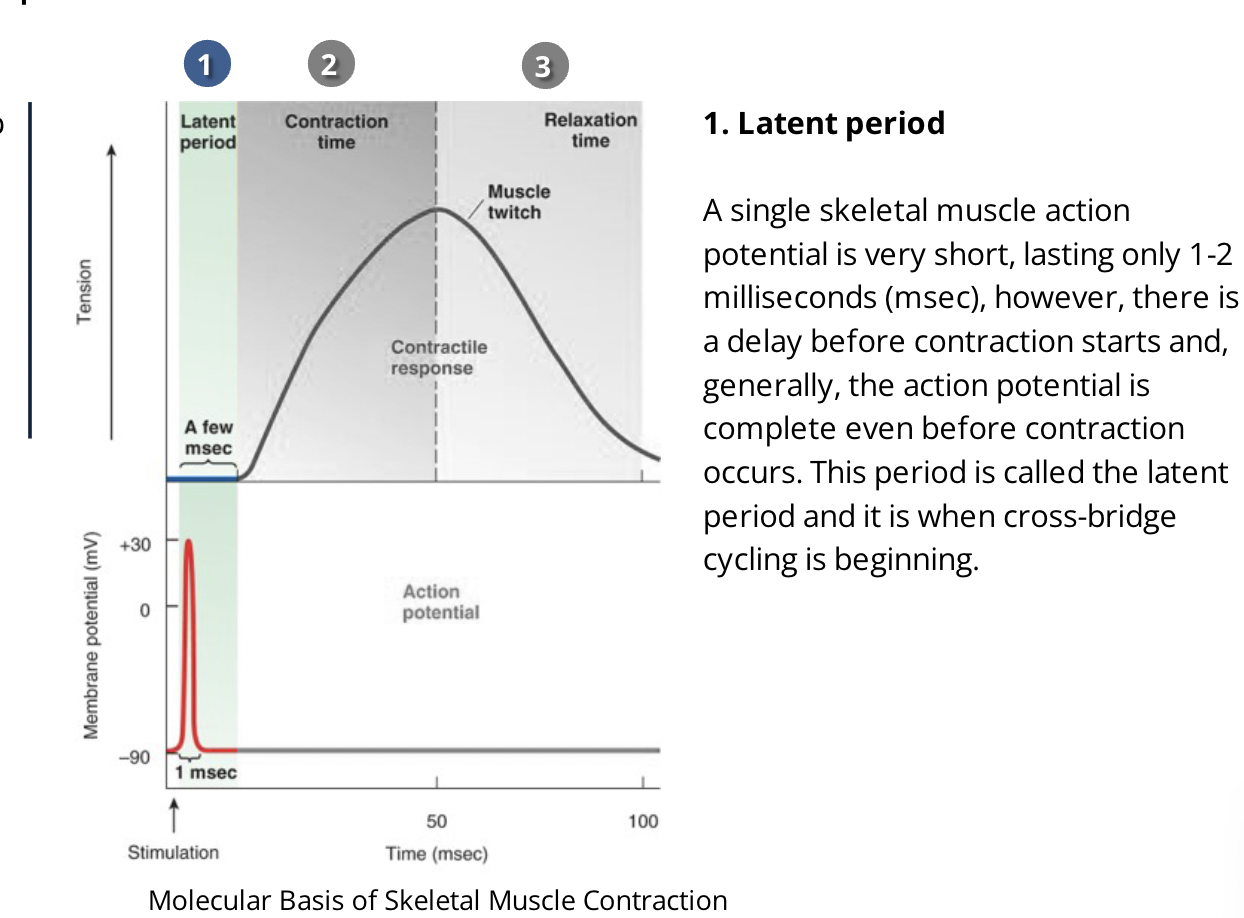
what is the latent period?
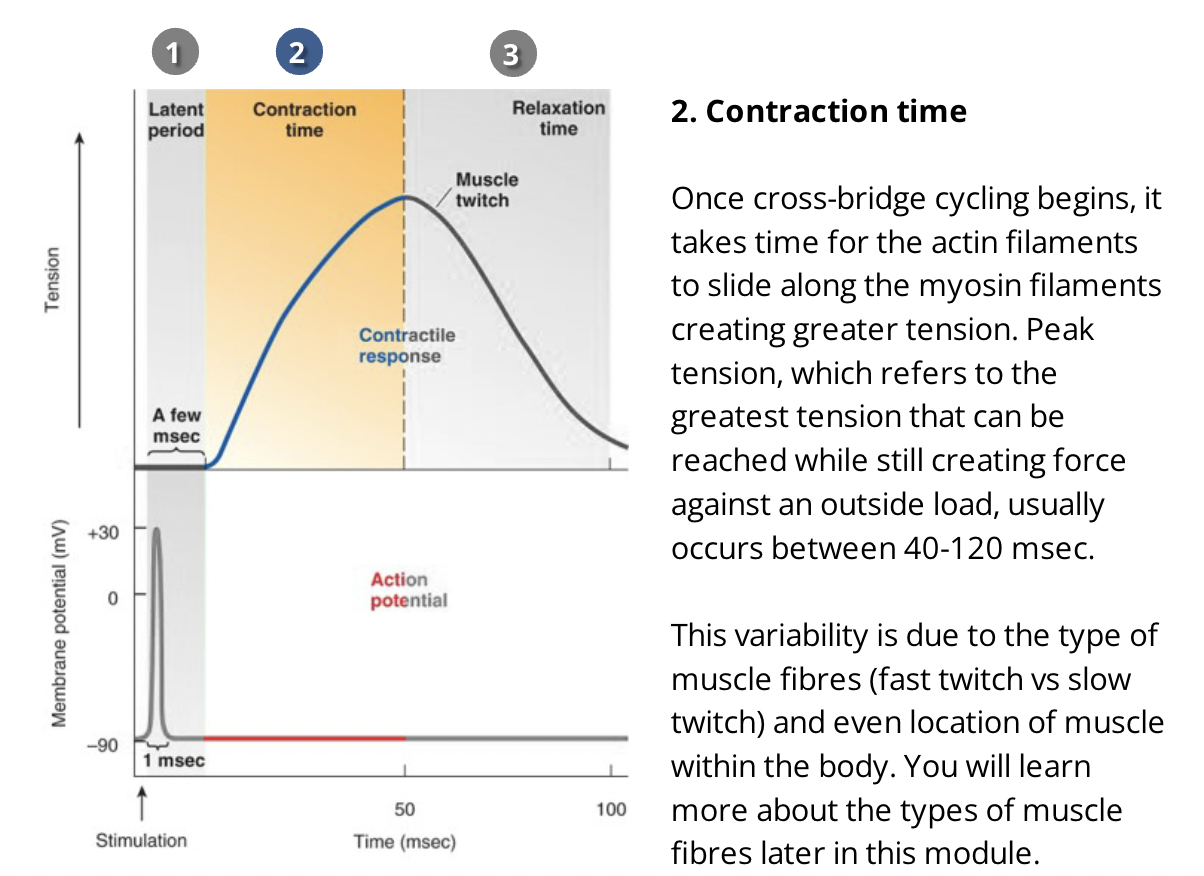
what is the contraction time?
what is relaxtion time?