Electrochemistry
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is electrolysis
The use of electricity to bring about a chemical reaction in an electrolyte
Electrolyte
A compound which when molten or dissolved in water will conduct an electric current
Battery
Provides energy for the reaction to occur
What do electrodes do
Dip into the electrolyte and make chemical contact
What are inert electrodes
They do not react with the electrolyte
What are active electrodes
They react with the electrolyte
What charge is an anode
Positive
What charge is a cathode
Negative
What elements make up inert electrodes
Graphite (carbon) and platinum
What elements are in active electrodes
Copper and iron
Outline the main events during electrolysis
Anode attracts to anions from the electrolyte
Energy from the battery allows the anions to lose electrons to the anode (oxidation of anions)
Cathode attracts the cations from the electrolyte
Energy from the battery allows the cations to gain electrons from the cathode (reduction of cations)
Using electrolysis on a solution of potassium iodide, with added phenolphthalein using inert electrodes
Observation: Brown colour around anode, pink colour around cathode
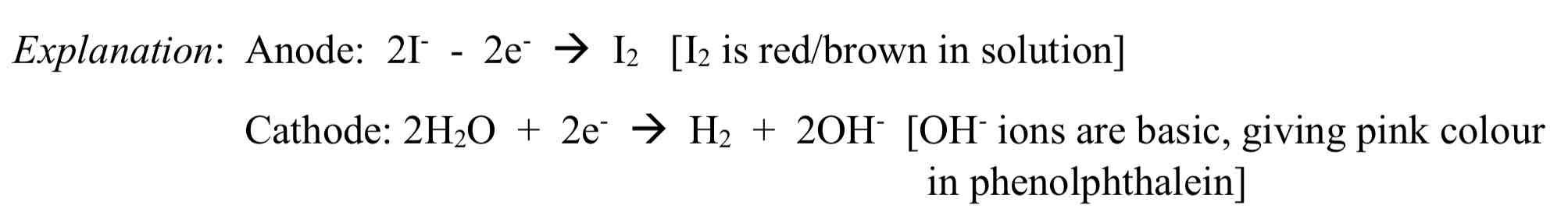
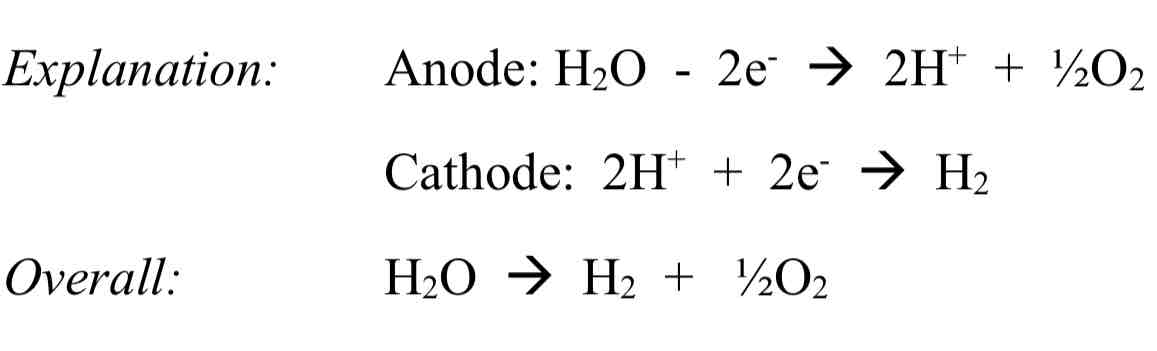
Using electrolysis on acidified water using inert electrodes
Small amount of H2SO4 is added to allow the water to conduct electricity.
Observation: one volume of oxygen gas is produced at anode, two volumes of hydrogen gas are produced at cathode
Using electrolysis on a solution of sodium sulphate with universal indicator using inert electrodes
Observation: Solution turns red in anode, solution turns blue in cathode
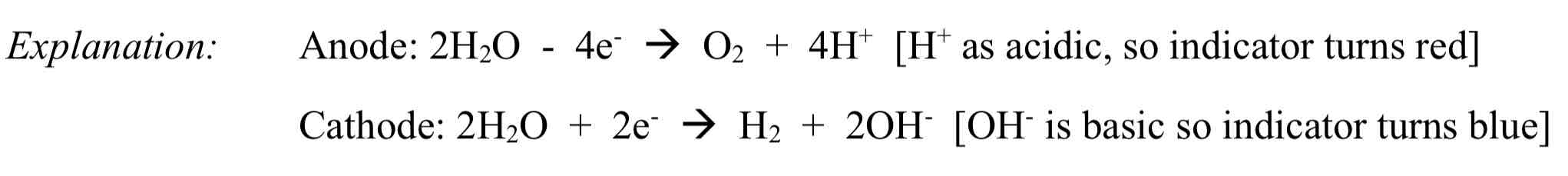
Using electrolysis on a solution of copper (II) sulphate using copper electrodes
Observation: Cathode becomes smaller, anode grows
This process is used to purify copper in industry for electrics
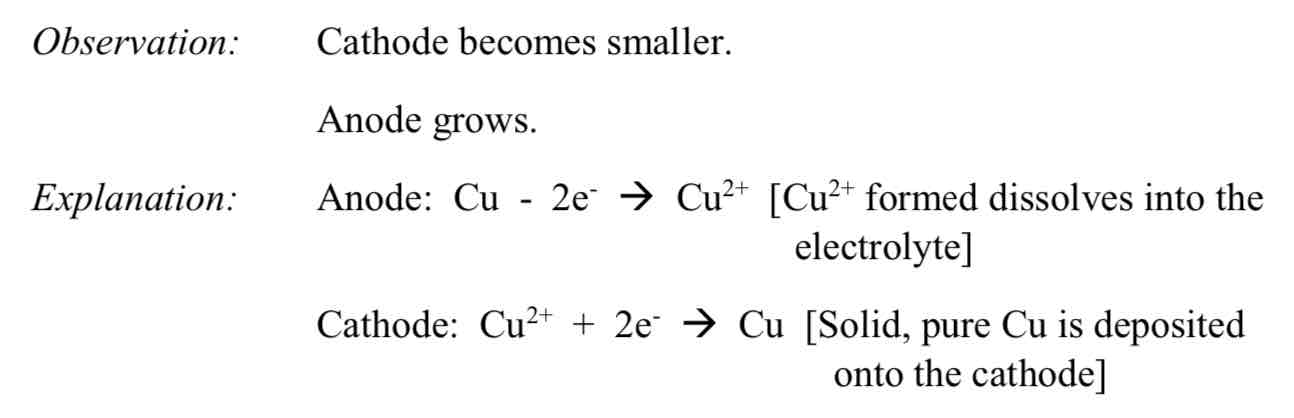
Showing the movement of electrons due to an electronic field
Copper chromate is green in solution, as it is made up of blue Cu2+ and yellow CrO4 2-.
If put into an electronic field, the Cu2+ is attracted to the cathode and the CrO4 2- is attracted to the anode. The movement of electrons results in visible colour separation.
What is electroplating
Where electrolysis is used to put a layer of one metal onto the surface of another
Uses of electrolysis
Used to make coins or cutlery more attractive
Used to prevent rust by plating reactive and less reactive metals
Conditions needed for electrolysis
The metal to be plated must be the cathode
The metal to be plated with must be the anode
The electrolyte must contain ions of the metal we are plating with
What is the electrochemical series?
Series of metals arranged in order of their ability to be oxidised
What is the acronym for the electrochemical series
Please Send Lions Cats, Monkeys And Zebras Into Lovely Hot Countries Signed General Penguin
Please Send Lions, Cats, Monkeys And Zebras Into Lovely Hot Countries, Signed General Penguin
Potassium, Sodium, Lithium, Calcium, Magnesium, Alluminum, Zinc, Iron, Lead, Hydrogen, Carbon, Silver, Gold, Platinum