Basic vs. Applied Research in Educational Psychology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Basic Science
Goal: Understand knowledge about a topic for the sake of knowledge itself.
Applied Science
Goal: Study issues related to a topic in psychology/education to apply the findings to help solve problems.
Basic Science
Aimed at increasing the knowledge of a scientific field like psychology/education.
Applied Science
Aimed at solving practical problems or generating solutions that apply to real-world settings (teaching; classroom instruction).
Basic Science
Tends to be theory-driven or data-driven, often uses hypothesis testing, can help strengthen theories or develop new ones.
Applied Science
Real-world application of science to provide info that will help solve problems that have immediate practical consequences for children.
Basic Science
Focus on description.
Applied Science
Focus on change.
Example of Basic Science
How do students memorize vocab? How high can young children count at different ages?
Example of Applied Science
Spacing-out practice could help students learn better.
Experimental Group
80 5-year-olds in intervention study on analogical reasoning with 30 items.
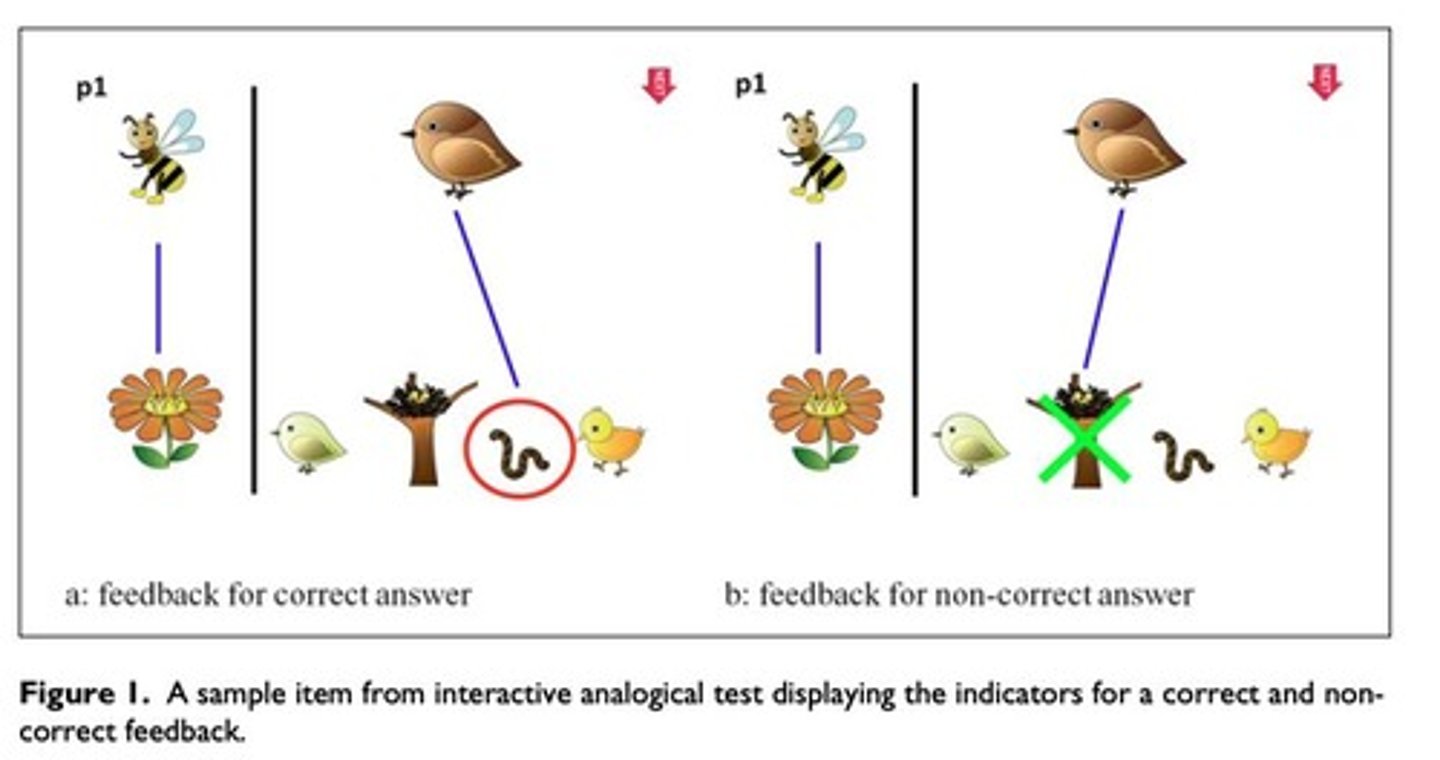
Control Group
No feedback; after each selection, instructed to click 'next' button.
Performance Differences
Experimental Group did better than control group & responded more consistently.
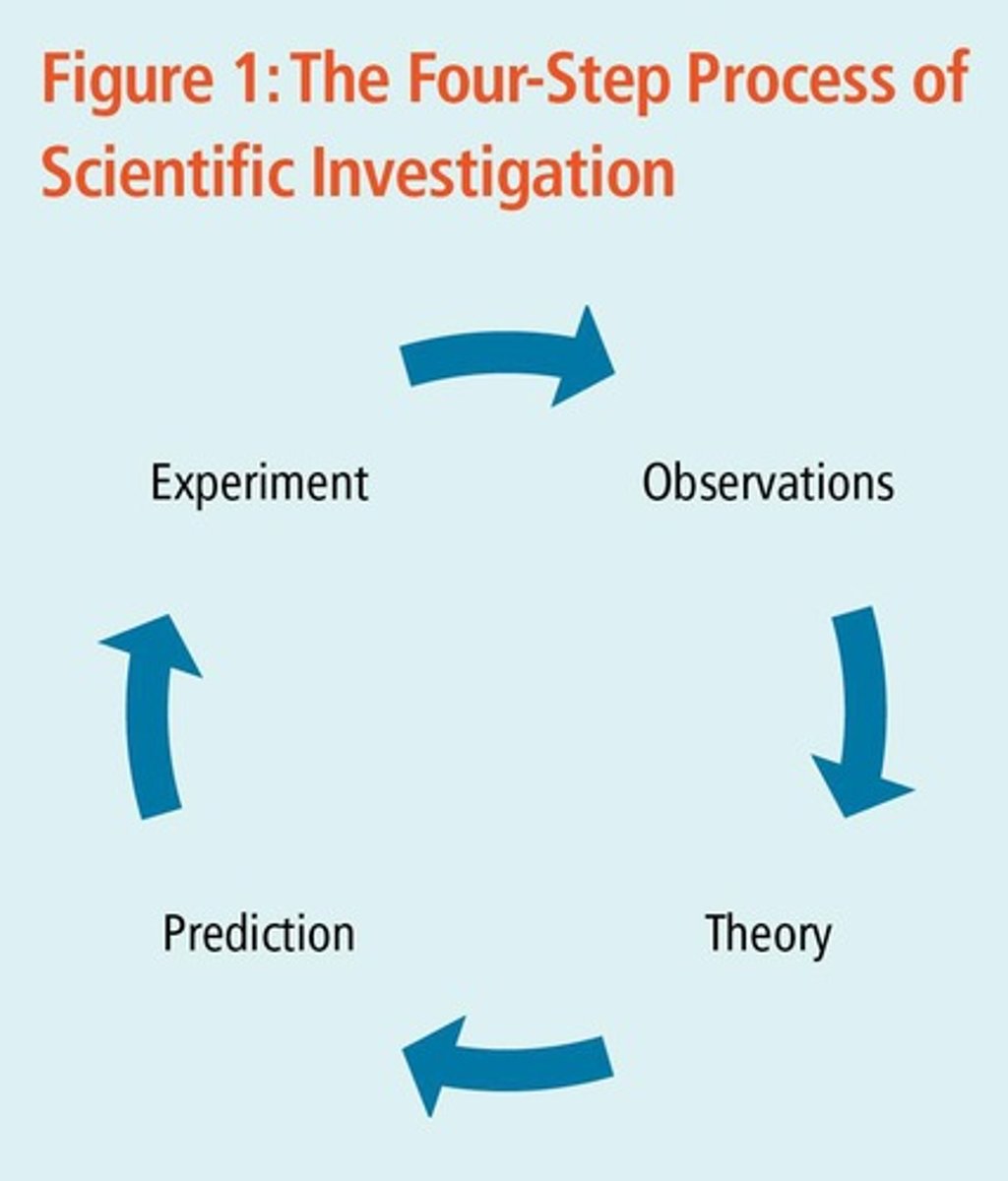
The Scientific Method
Gather observations about the world, summarize observations with a small set of general statements (theory), use theory to generate predictions about some unobserved phenomena, conduct experiments to test prediction.
Empirical Generalizations
About observations of the world (here: how kids learn).
Theoretical Statements
Claims made about how students consistently think, feel, or behave in particular circumstances after observing different samples of students.
Epistemic Assumptions
Assumptions about the nature and scope of knowledge.
Utility of Empirical Generalizations
Of the 3 types of scientific statements, this has the most potential utility for educators.
Example of Empirical Generalization
Task performance improves with practice is a commonly accepted assumption about students that is useful for educators.
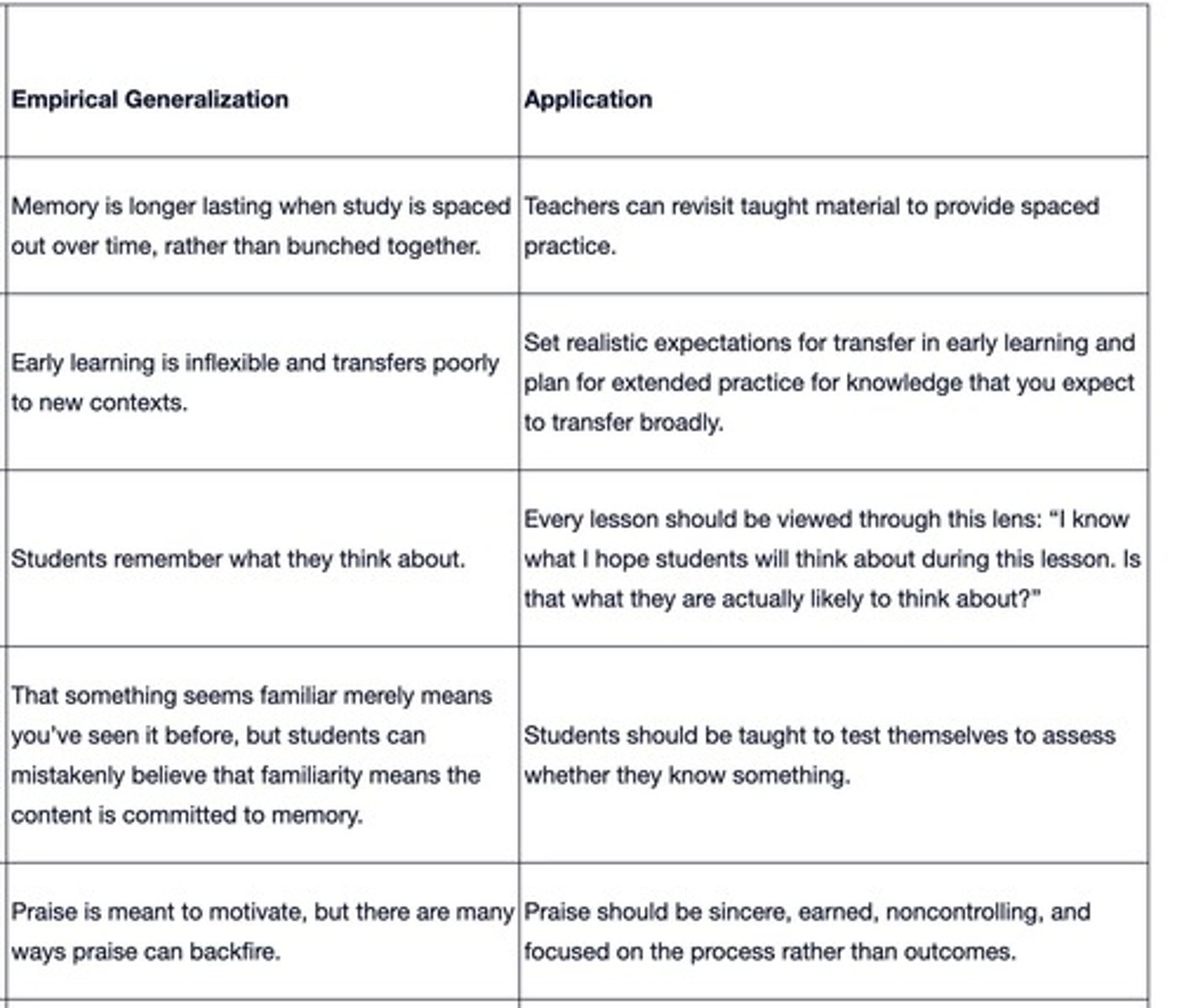
Empirical generalizations
Can help educators understand and predict how children might respond in given educational situations.
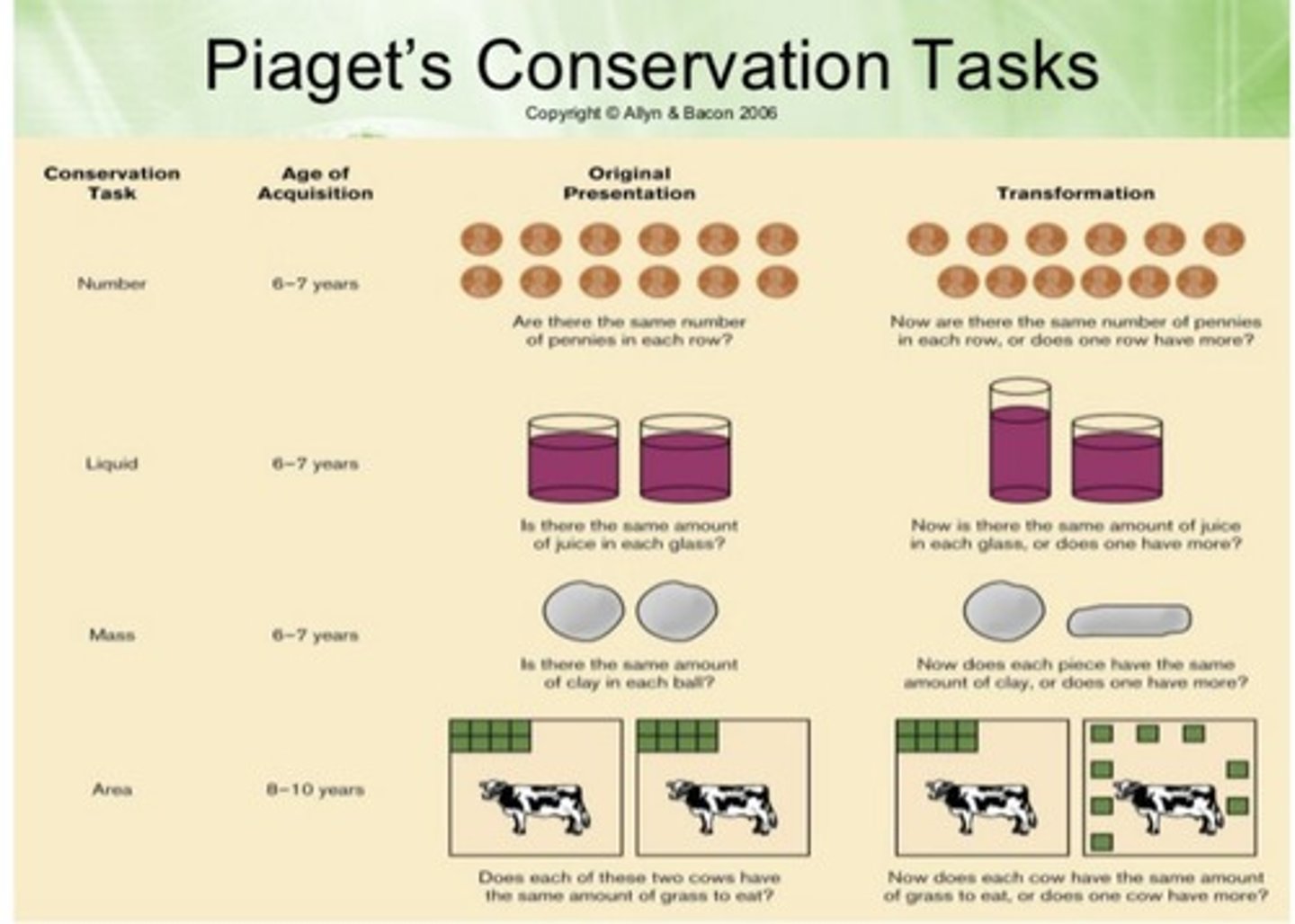
Piaget Conservation Tasks
Test a child's ability to see that some properties are conserved or invariant after an object undergoes physical transformation.
Issues with Empirical Generalizations
They might work most times but not every time for every student.
Guideline for educators
Consider a wide variety of factors that may influence learning in an educational context.
Theoretical Statements
Much more abstract & general statements compared to empirical observations.
Purpose of Theoretical Statements
Summarize & integrate many empirical generalizations and make new predictions about what might happen in novel situations.
Issues with Theoretical Statements
Some novel predictions from a theory will eventually be proven wrong as data accumulates & theory testing continues with time.
Epistemic Assumptions
Statements about the nature and thought of knowledge.
Examples of Epistemic Assumptions
"Learning is social," "Everyone learns differently," "Knowledge is constructed."
Issues with Epistemic Assumptions
Not proven and unlike empirical generalizations, not based on multiple observations of what kids actually do.
Distinguishing Between Empirical Generalizations
Often describe how two things go together & based on data.
Distinguishing Between Theoretical Statements
More general than empirical generalizations.
Distinguishing Between Epistemic Assumptions
Simple statements about the nature of learning or knowledge.
Big Takeaways for Teachers
Examine your beliefs as a teacher and consider whether your beliefs about how kids/people learn align with findings from basic science.
Lack of Basic Science
Doesn't mean practice is bad; likely won't be basic science research related to every instructional approach.
Keep Learning
Resources online; professional development workshops; webinars.