MODULE 15B - [Anatomy 3.0] BRAINSTEM ONLY (NO CN)
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
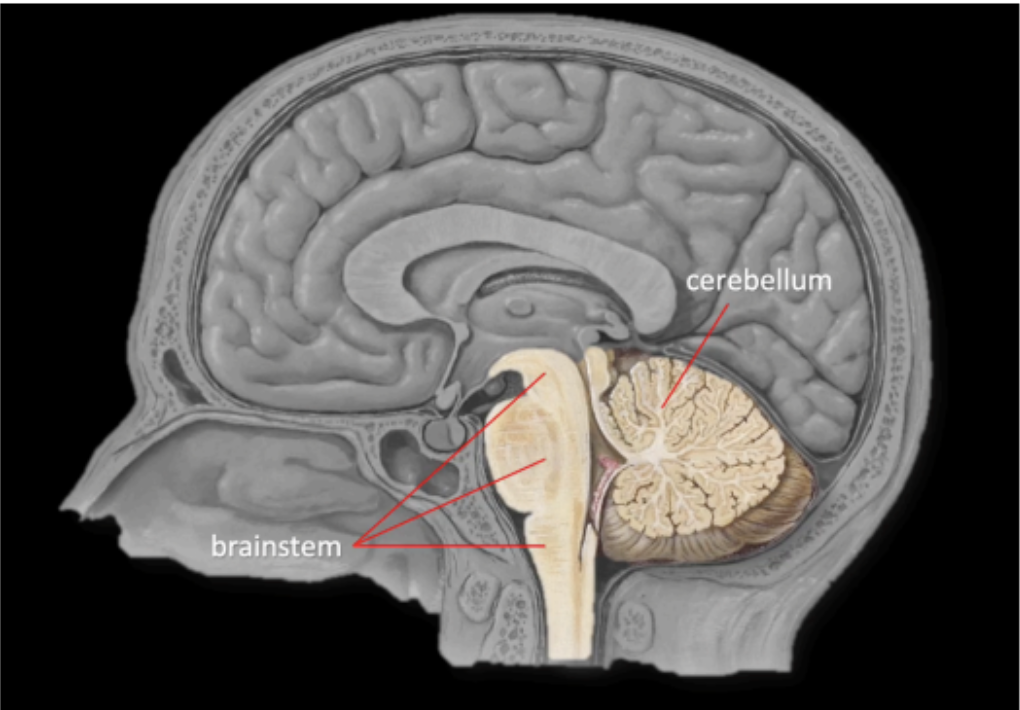
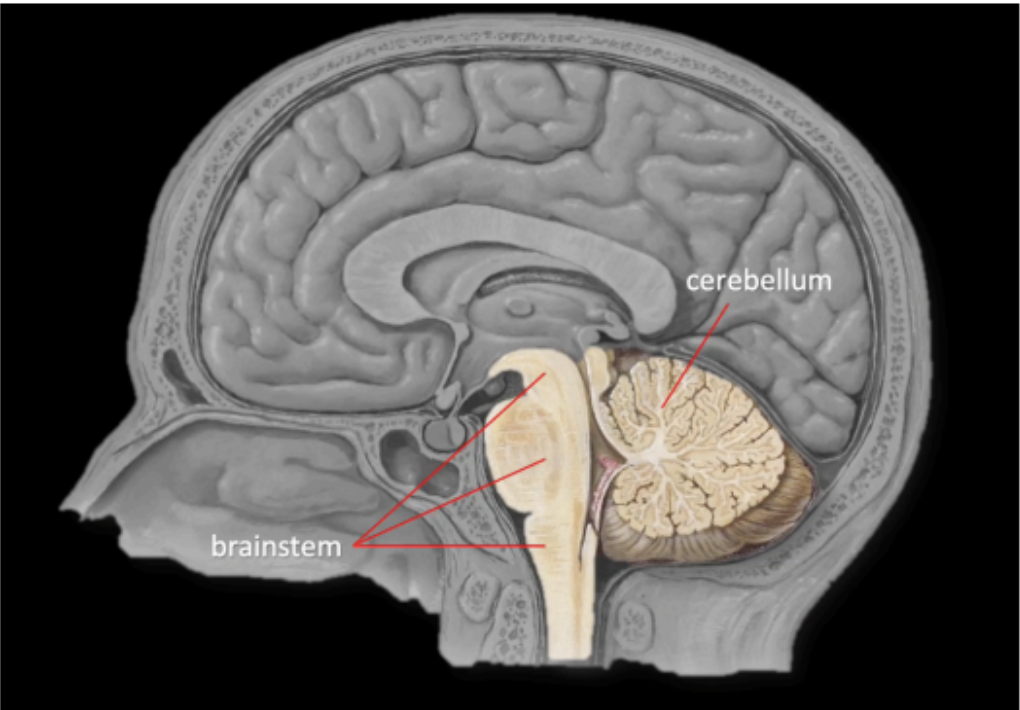
The brainstem, together with the cerebellum, are structures that occupy the _____
posterior cranial fossa
The brainstem is located _____ to the cerebellum
anterior
The Brainstem is continuous with the diencephalon _____, and the spinal cord ____
continuous to the diencephalon superiorly
continuous to the spinal cord inferiorly
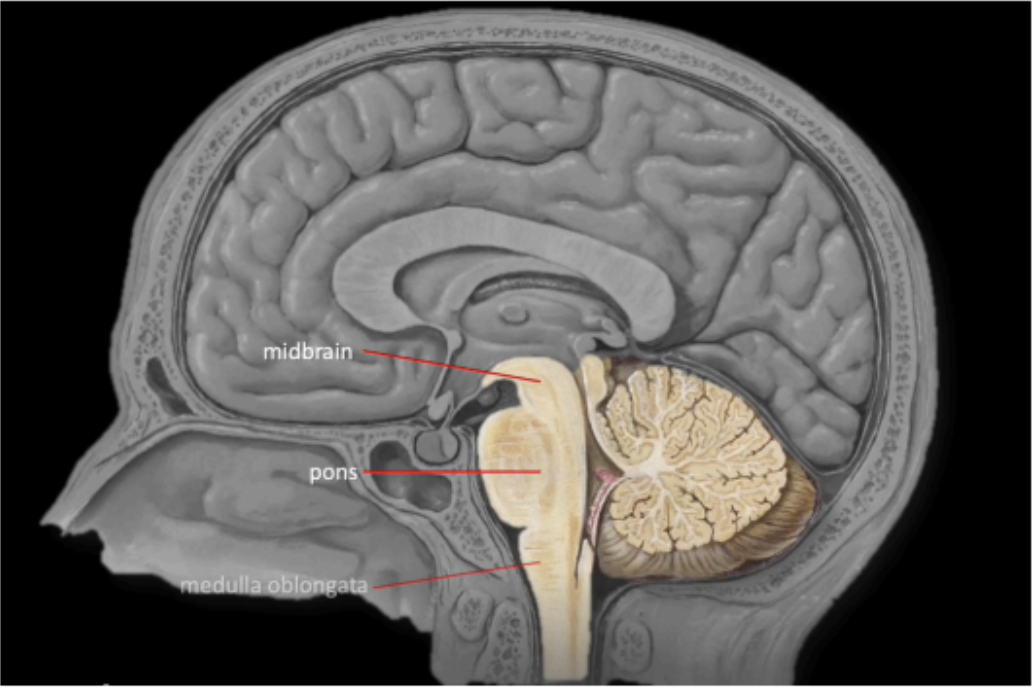
Enumerate the segments of the Brainstem (SUPERIOR TO INFERIOR)
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
The brainstem receives sensory information coming from the cranial structures and through the _____ controls the muscles of the ____
cranial nerves; head
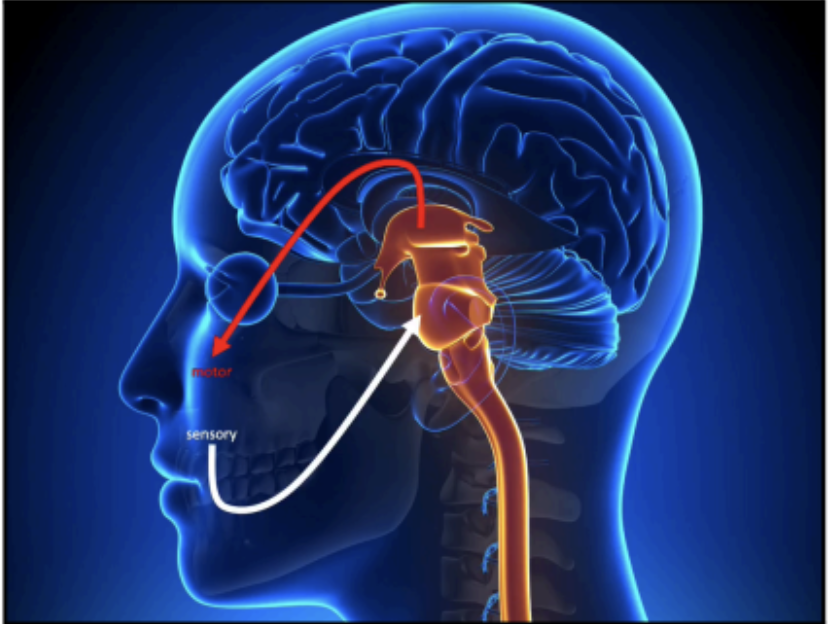
The function of the brainstem is comparable to what the spinal cord is doing in relation to the _____ and _____.
trunk and extremities
Embedded in the brain stem
Give rise to CN III - CN XII
CRANIAL NUCLEI
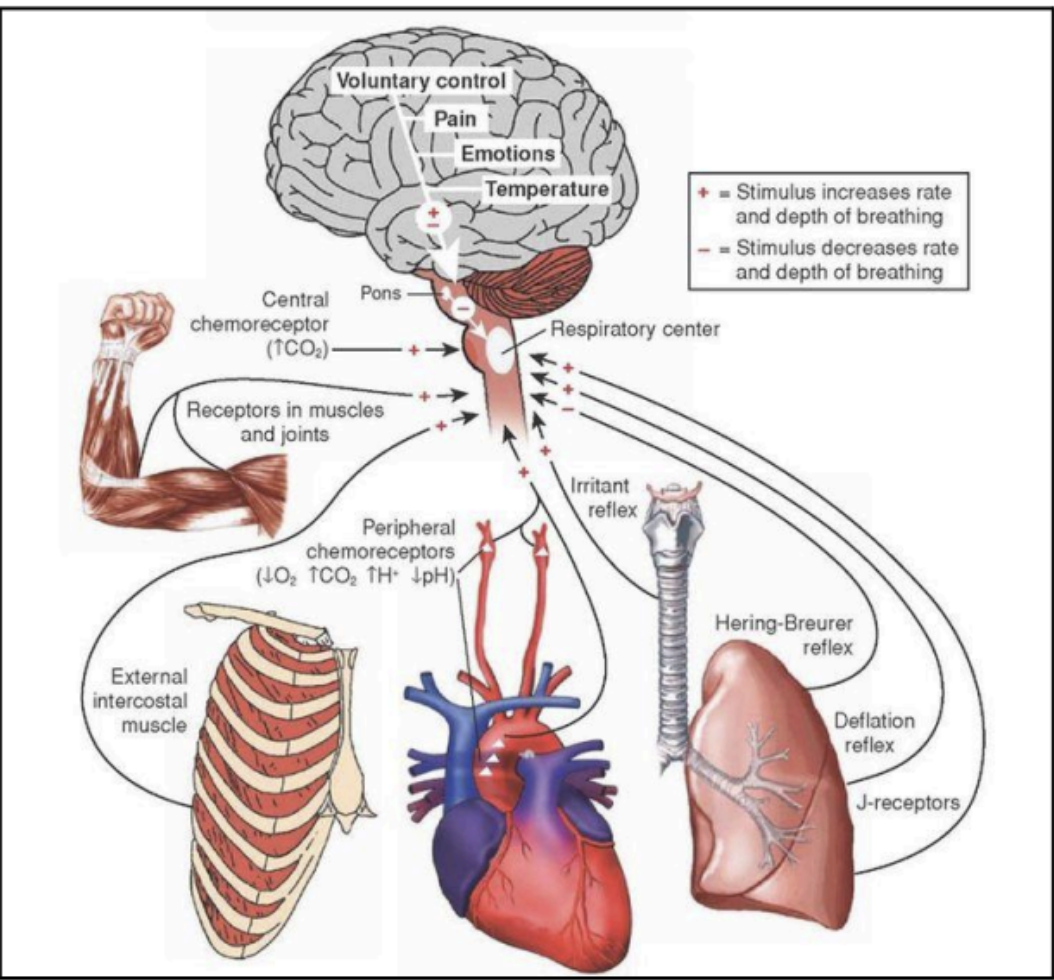
Various divisions of the brainstem subserve specific functions that _____ and ______.
control blood pressure and respiratory regulatory mechanisms
Long fiber tracts that enter and exit the brain via the brainstem
ASCENDING AND DESCENDING PATHWAYS
Carry sensory information coming from the trunk and extremities that will be processed in the cerebrum, where we appreciate sensations like pain, light touch, pressure
Ascending Pathway
Carry motor fibers that control the skeletal muscles of the trunk and extremities, thereby allowing an individual to move
Descending Pathway
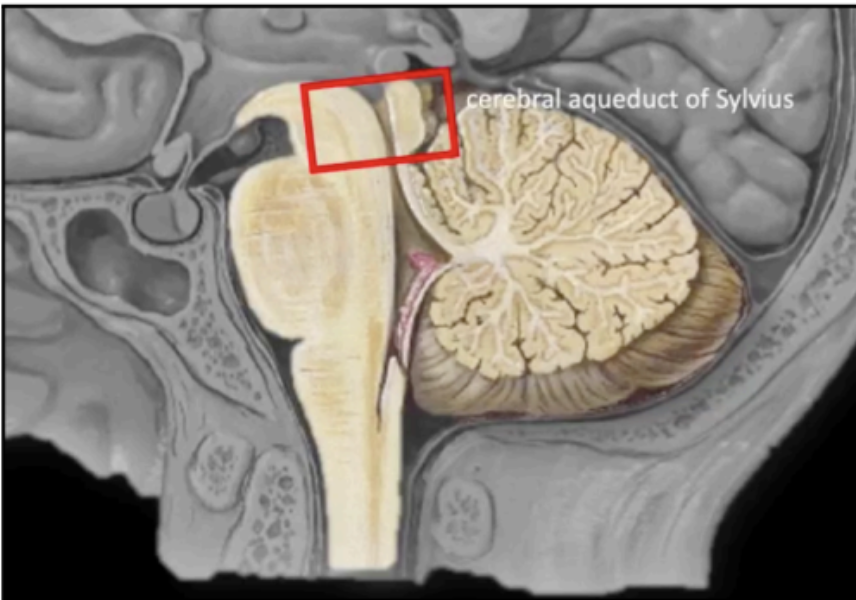
In the sagittal section of the brainstem, cavitation can be appreciated on its posterior region. This is the part of the ventricular system that will contain ____.
cerebrospinal fluid
The cavity traversing the midbrain
becomes continuous with the triangular cavity of the 4th ventricle, which can be appreciated at the levels of pons and upper medulla.
Cerebral Aqueduct of Sylvius
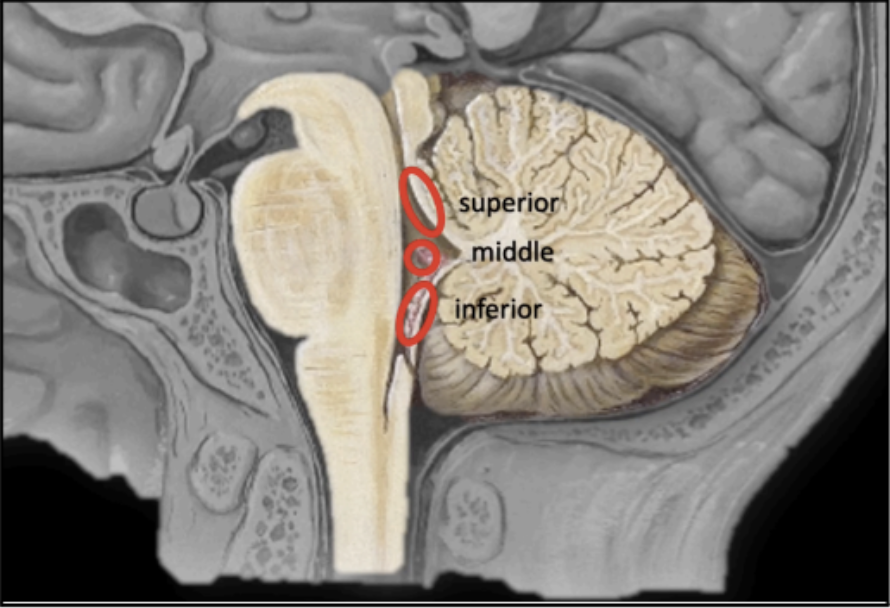
The connection of the brainstem to the cerebellum
posteriorly
It serves as the pathway through which the cerebellum connects to other parts of the central nervous system, such as the brain and spinal cord
Since there are 3 segments of the brain stem, therefore, there are also 3 separate cerebellar peduncles
CEREBELLAR PEDUNCLES
Enumerate the 3 separate cerebellar peduncles and their other terms:
Superior Cerebellar Peduncles - Brachium Conjunctivum
Middle Cerebellar Peduncles - Brachium Pontis
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncles - Restiform Body
In the actual cadaveric specimen, the adult brainstem is around ____ in length and its diameter is about the size of a pinky finger.
2.5 centimeters
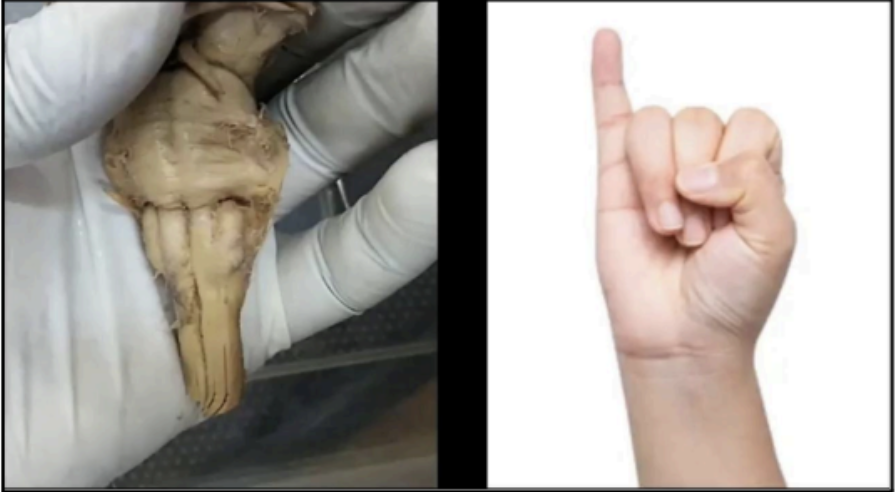
Signs and symptoms that points to brainstem affectation unless proven otherwise
affectation of motor and sensory of the head
involvement of the cranial nerves
alteration of the sensorium
association with cardiorespiratory abnormalities
long tract signs
external structures of the Midbrain
ANTERIOR SURFACE OF THE MIDBRAIN
POSTERIOR SURFACE OF THE MIDBRAIN
The Anterior surface of the Midbrain contains the
Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncles
Interpeduncular fossa
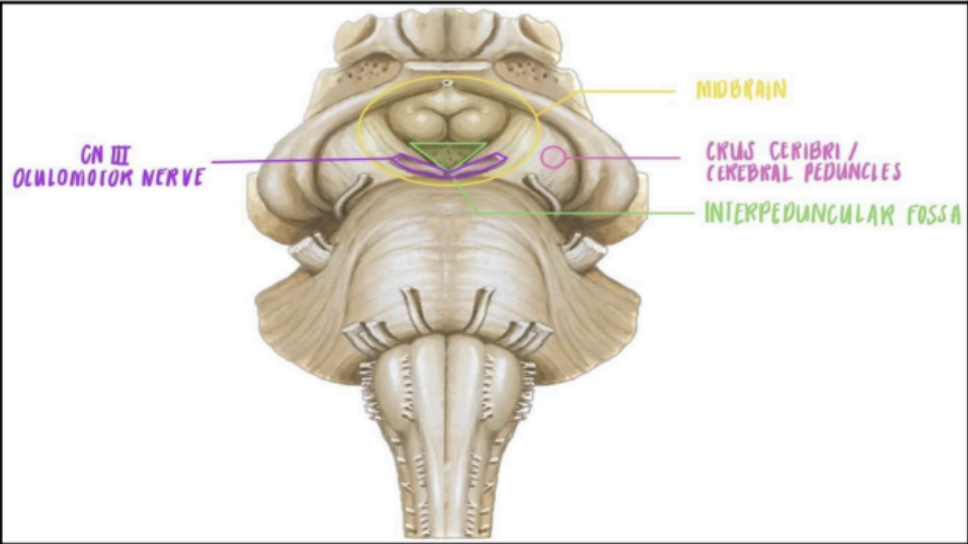
Two pillar-like structures that emerge from the pons
Crus cerebri of cerebral peduncles
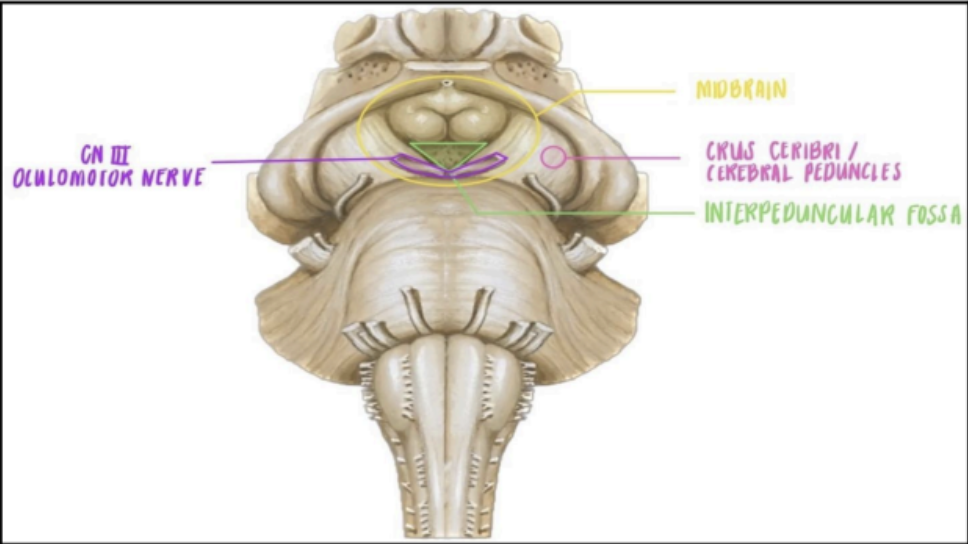
A hollow groove or depression in between the two
crus cerebri
Interpeduncular fossa
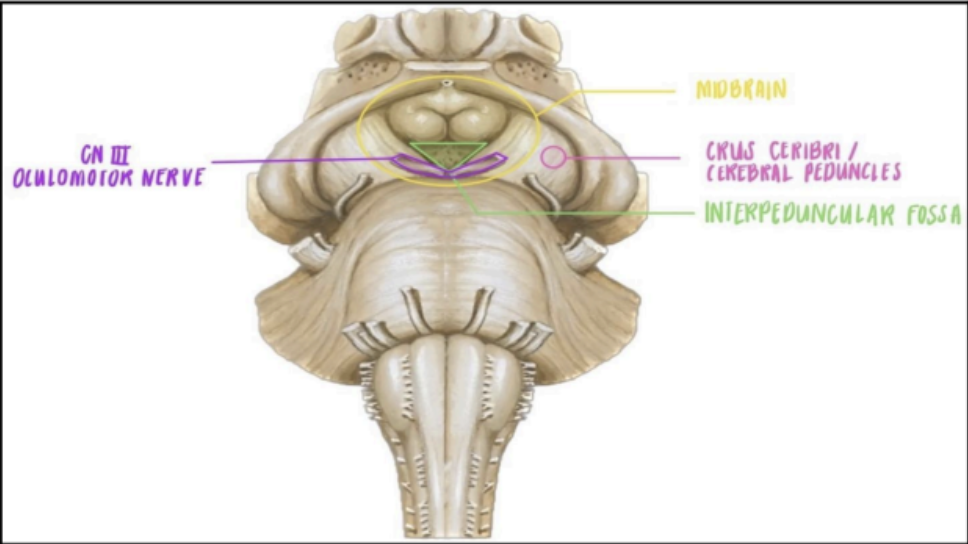
From the interpeduncular fossa, this is where the _____ can be appreciated.
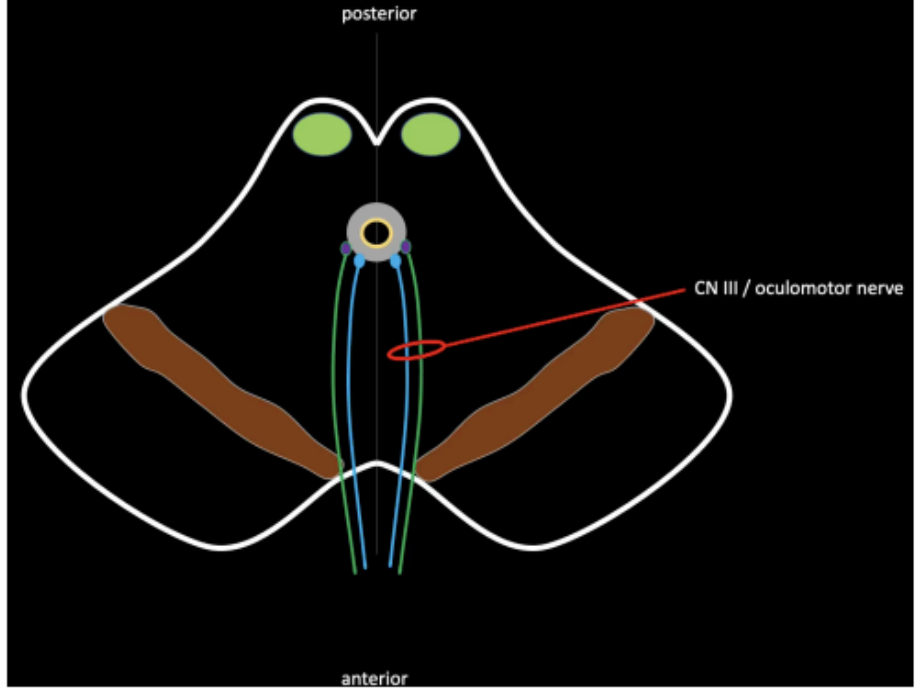
oculomotor nerve (CN III) can be appreciated in the interpeduncular fossa
Enumerate the structures in the posterior surface of the midbrain
Corpora quadrigemina
superior colliculi
inferior colliculi
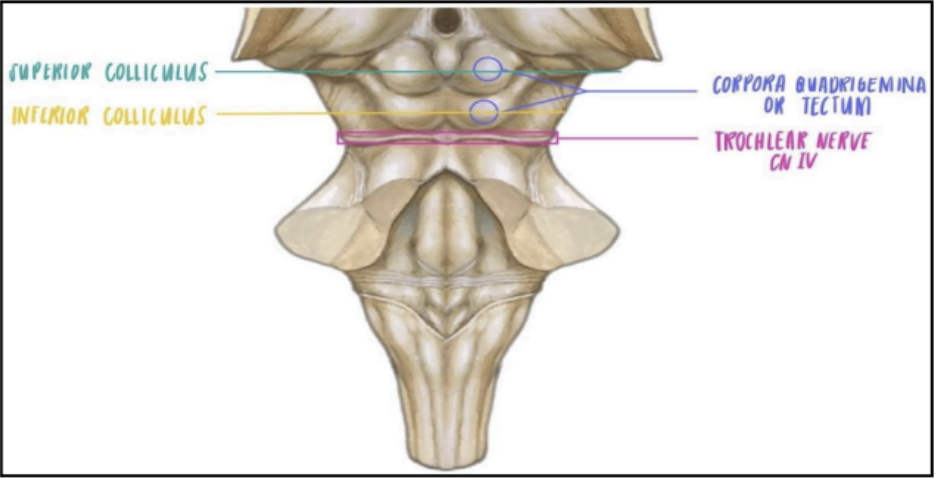
Two pairs of swelling on the posterior side of the midbrain
Corpora quadrigemina or Tectum
superior paired swellings in the posterior surface of the midbrain
superior colliculi
inferior paired swellings in the posterior surface of the midbrain
inferior colliculi
Just inferior to the inferior colliculi in the midline is where the _____ will emerge from the brainstem, coursing its way to the lateral side of the crus cerebri.
trochlear nerve (CN IV) will emerge inferior to the inferior colliculi
Enumerate the two levels of the midbrain internal stucture
Level of the superior colliculus
Level of the inferior colliculus
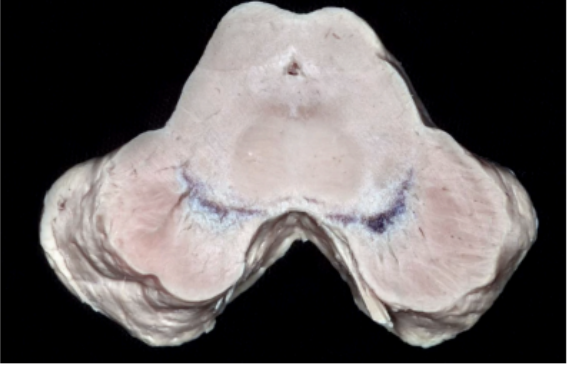
In the Level of Superior Colliculus an imaginary line can be placed in the middle to designate the midline, dividing the midbrain into left and right side
Posteriorly is the ______
Anteriorly is the _____
Posteriorly is the superior colliculus
Posteriorly is the superior colliculus
Colliculus for visual reflex
Superior colliculus
Colliculus for auditory pathway
Inferior colliculus
What are the structures found in the level of the superior colliculus of the midbrain
Substantia Nigra
Cerebral Aqueduct
Tectum
Motor Nucleus of CN III and Edinger-Westphal Nucleus
Pretectal Nucleus
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
Mesencephalic Nucleus of CN V
Ascending Tracts
Ascending Tracts
Red Nucleus
A dark pigmented region that plays an important role in movement and reward function.
Part of the Superior Colliculus Level
Substantia Nigra
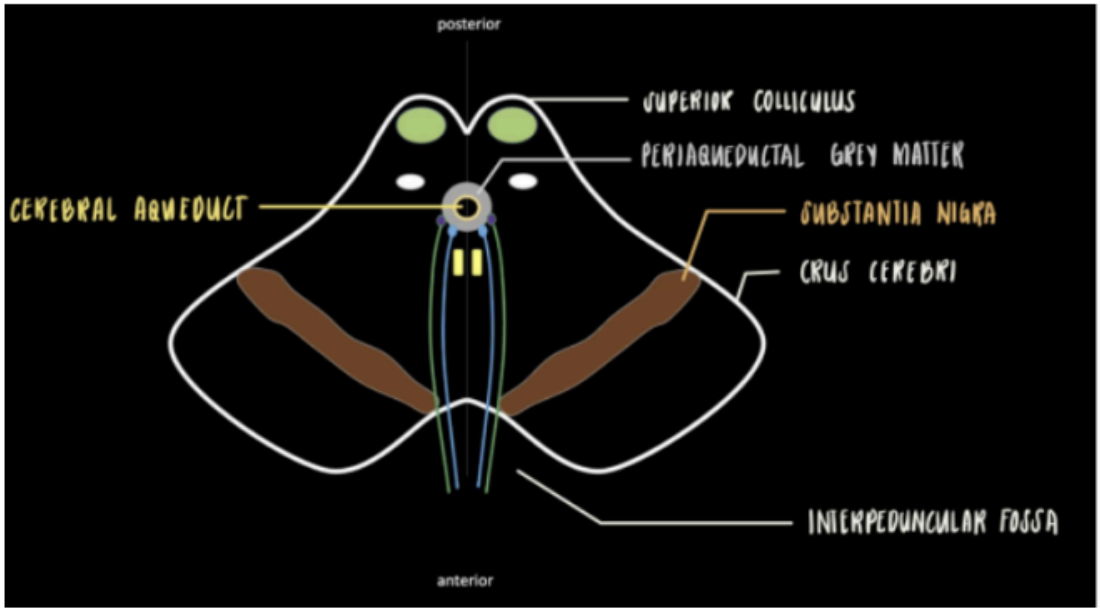
In the midline of the midbrain
This is surrounded by an area called the periaqueductal grey mater
Part of the Superior Colliculus Level
cavity of the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius
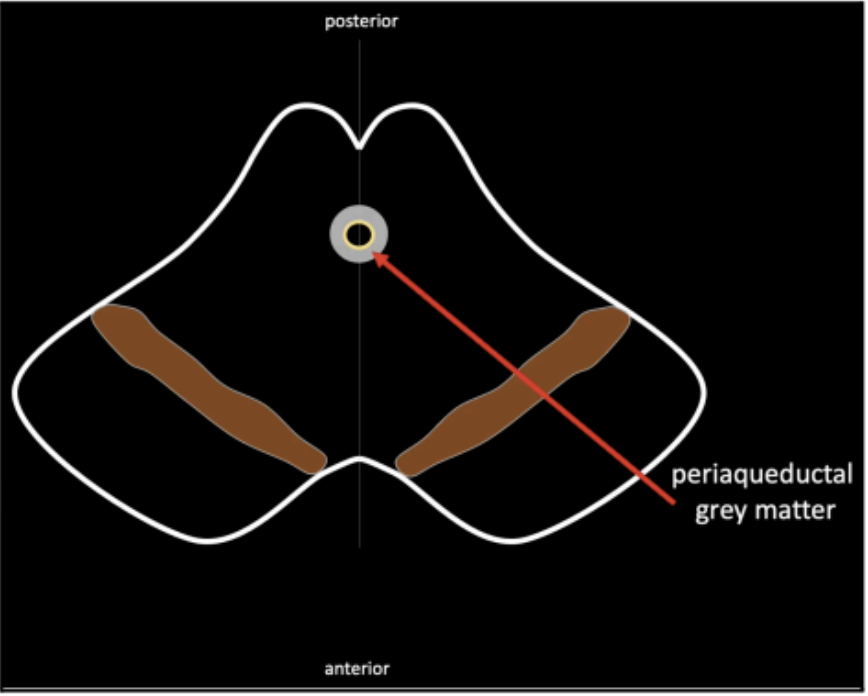
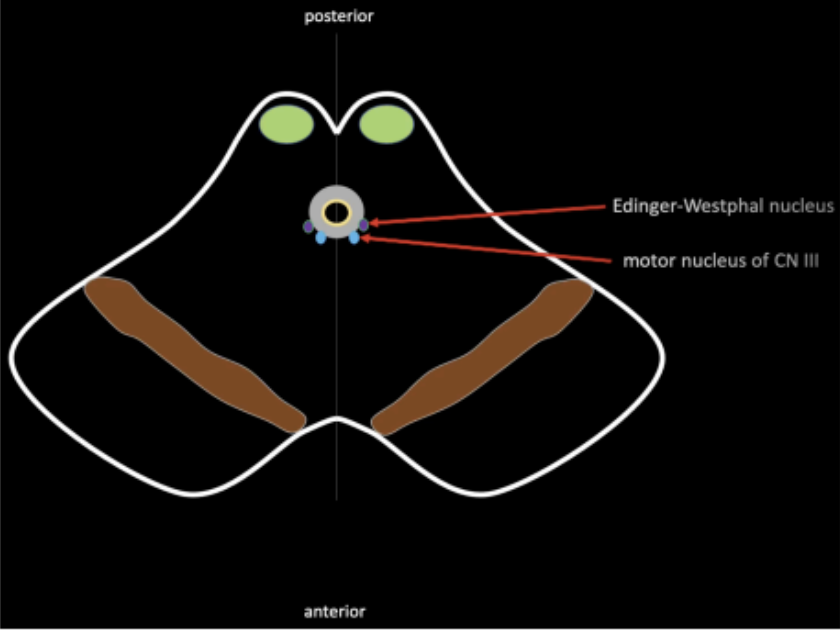
In the area of the periaqueductal grey mater, lies the
motor nucleus of cranial nerve III and its accessory
nucleus, called the _____
This accessory nucleus also carries the parasympathetic function of cranial nerve III
Edinger–Westphal nucleus
Midbrain area posterior to the periaqueductal grey mater and also contains the colliculi.
Tectum
The Tectum contains the nucleus of the ______, which is important in the control of visual reflexes
superior colliculus

The presence of substantia nigra further subdivides the midbrain into the _____ anteriorly and the rest of the area into the _____
crus cerebri (anteriorly)
tegmentum (rest of the area)
Fibers of the motor nucleus of the oculomotor and Edinger-Westphal nucleus will give rise to CN III that exits at the ____
interpeduncular fossa
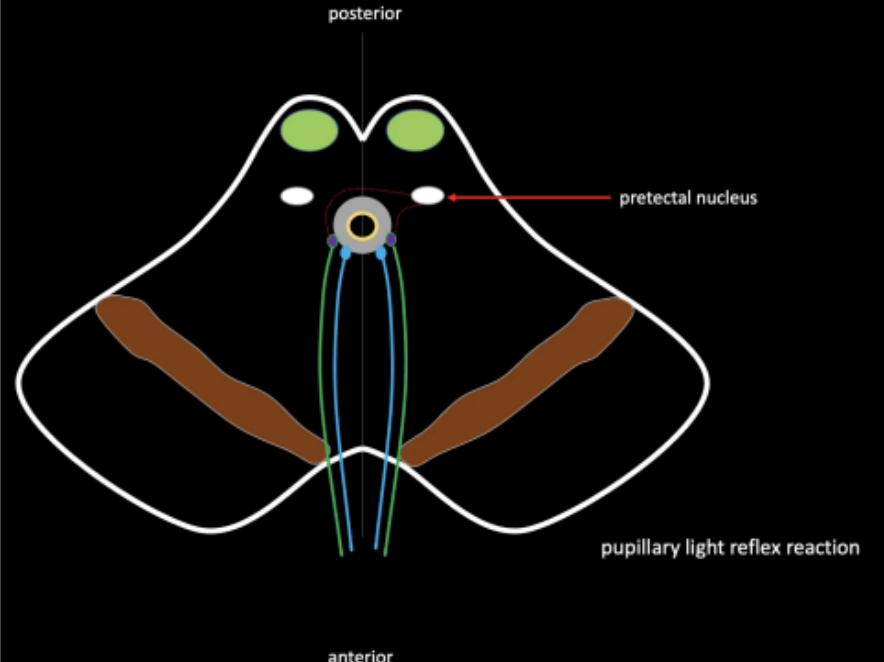
Controls the Edinger-Westphal on both sides
Plays a role in the pupillary light reflex reaction
Pretectal Nucleus
Bundle of white mater in the middle region of the tegmentum
Links the three cranial nerves that control the eyeball
○ CN III - Oculomotor
○ CN IV - Trochlear
○ CN VI - Abducens
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
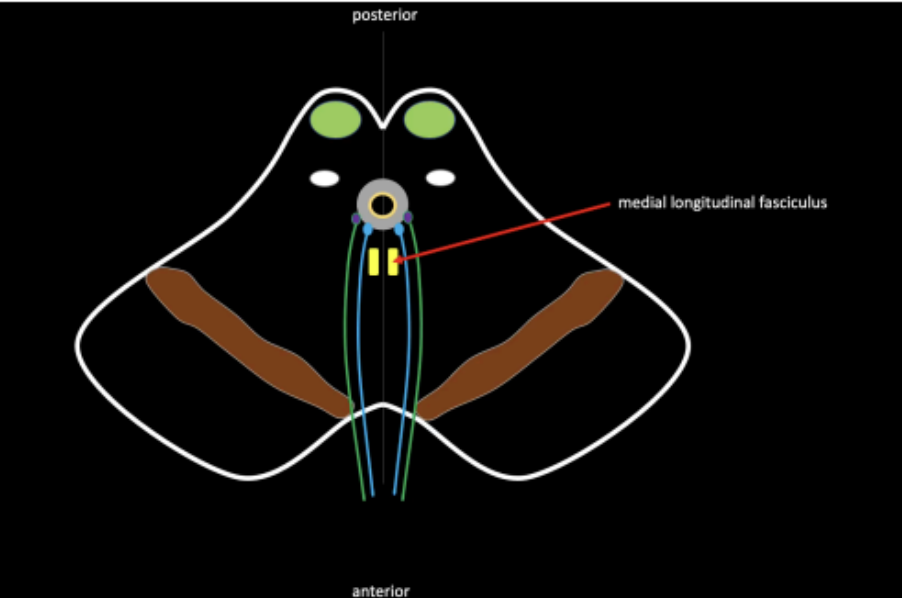
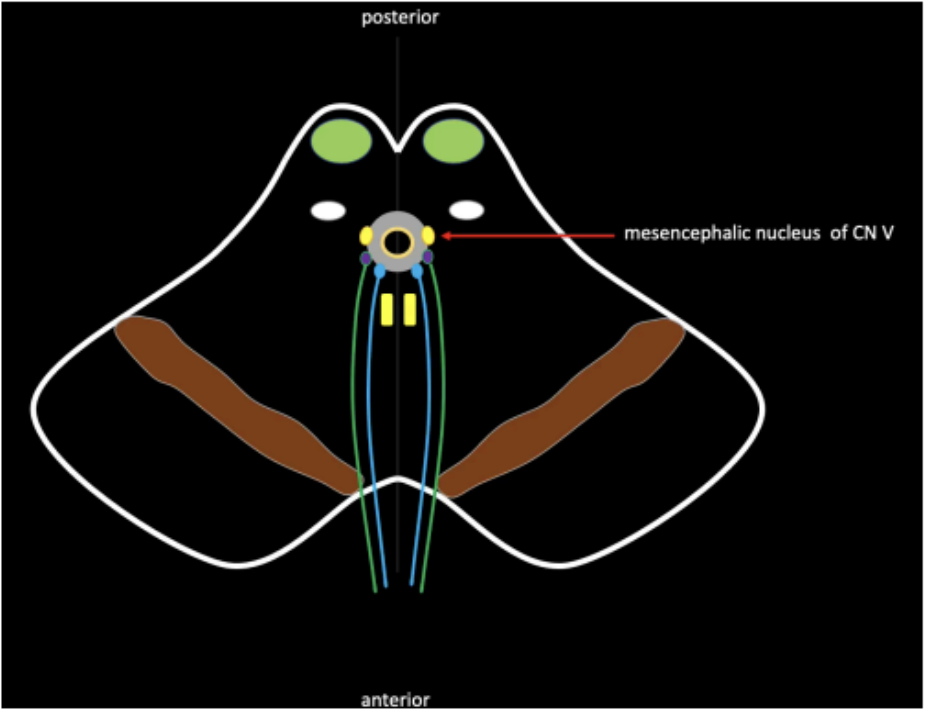
Present in the midbrain
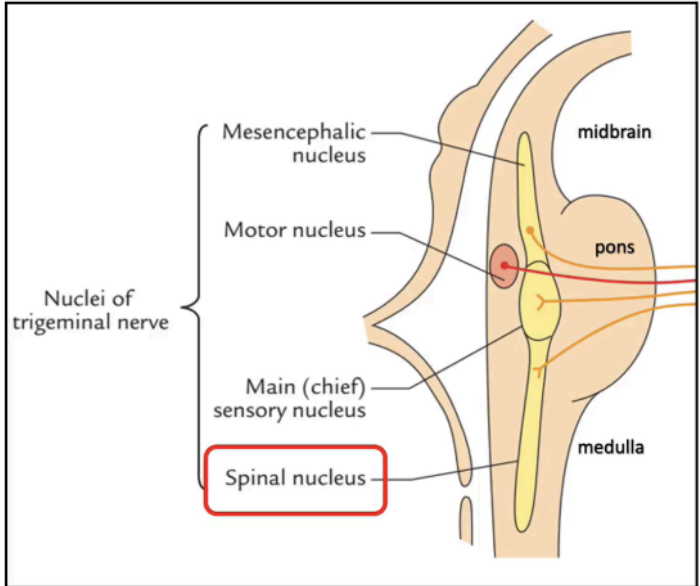
One of the sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve
Mesencephalic Nucleus of CN V
Long tracts will pass through the brainstem in order to connect the spinal cord to the cerebrum and vice versa.
These fibers originating from the spinal cord will form a bundle of white mater on the lateral side of the tegmentum.
Ascending Tracts
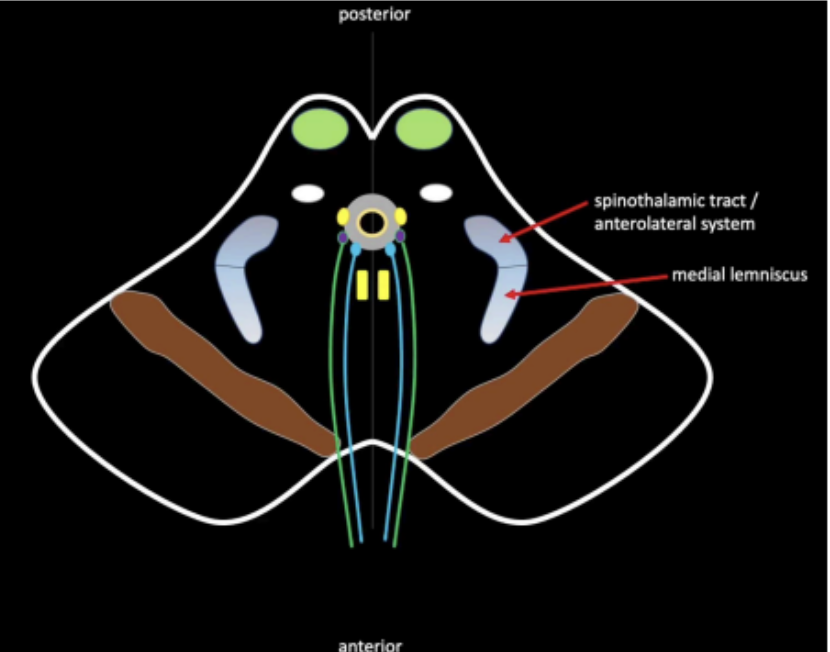
What are the ascending tracts that originate from the spinal cord and forms a bundle of white mater on the lateral side of the tegmentun
Spinothalamic Tract
Medial Lemniscus.
Descending motor pathways are organized in the
crus cerebri
Descending Tracts
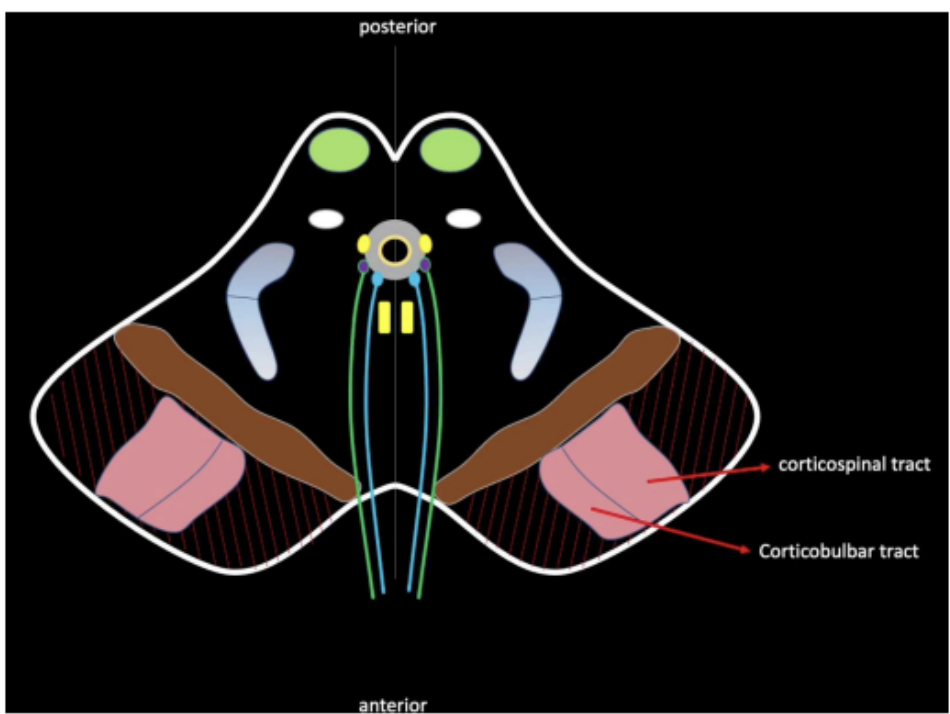
Enumerate the descending tracts that organize in the crus cerebri
corticospinal tract
corticobulbar tract
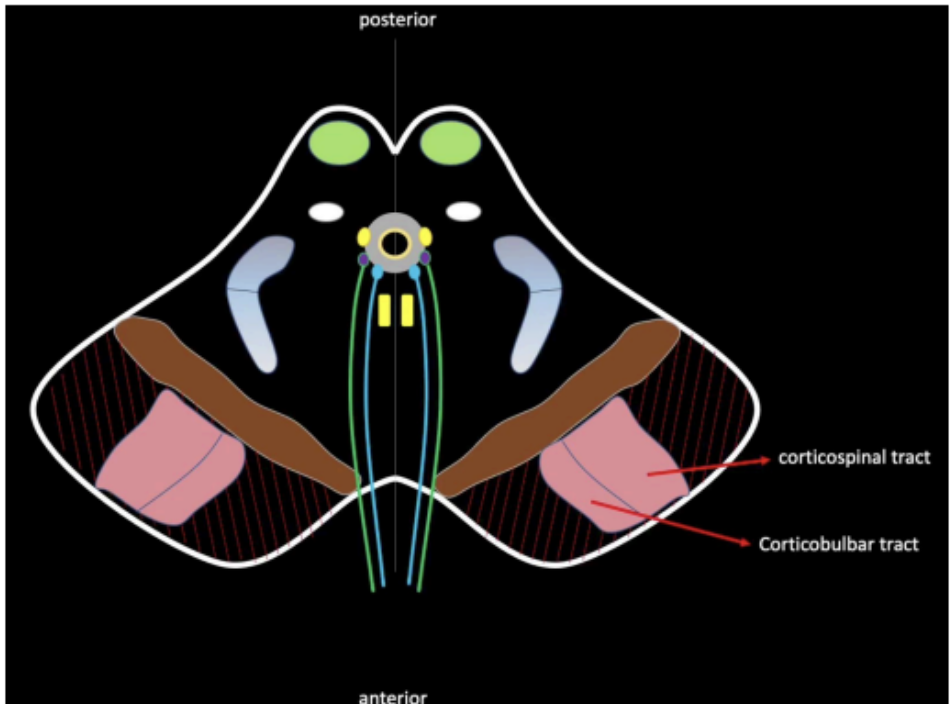
are pale pink structures present in the area which is usually involved in motor coordination.
The fibers of CN III traverses this structure
Patients with affectation of the red nucleus may also involve the third cranial nerve.
Red Nucleus
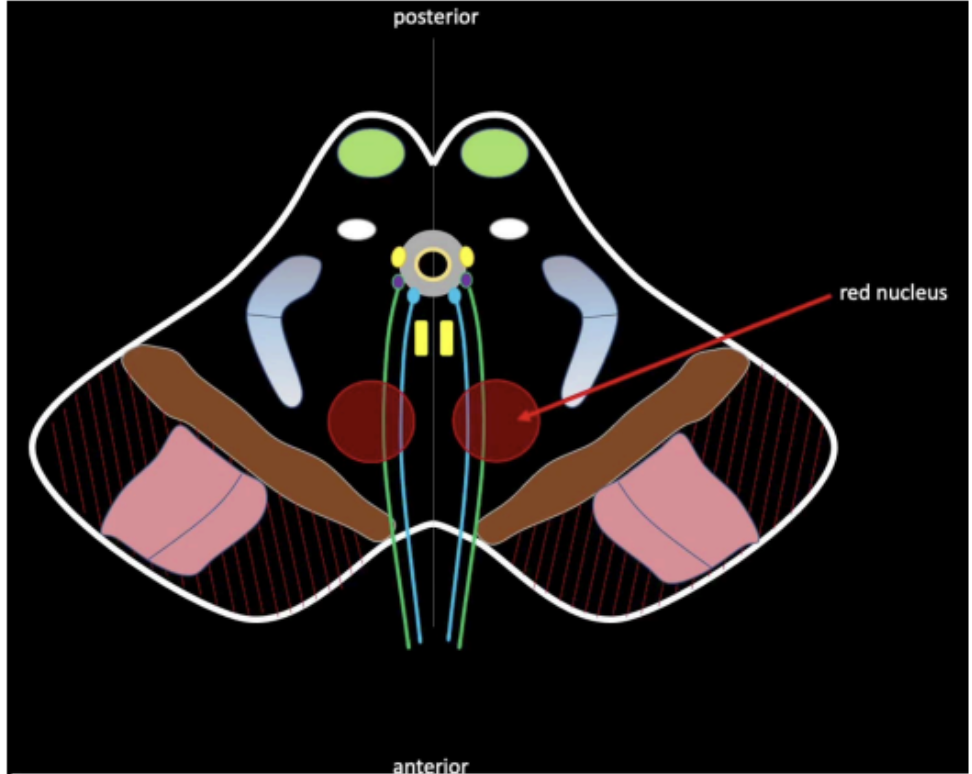
What are the structures found at the level of the inferior colliculus of the midbrain
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
Motor of the Nucleus of CN IV
CN III is absent in this level
Sometimes, the red nucleus can no longer be appreciated in the lower level
The inferior colliculus is present at this level, rather than the superior colliculus
These nuclei will be part of the auditory pathway
Main highlight: presence of the motor nucleus of CN IV
Inferior colliculus of the midbrain
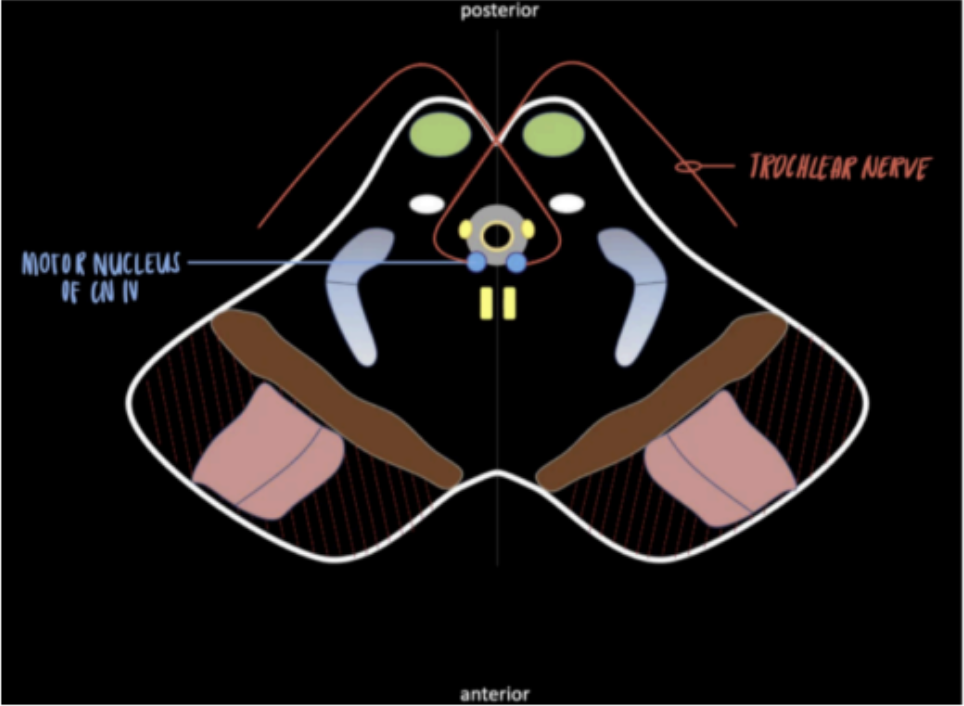
The longest cranial nerve intracranially
The ONLY cranial nerve that exits at the posterior side of the brainstem
The ONLY crossed cranial nerve
Origin: motor nucleus
Innervates: superior oblique muscles (one of the extraocular muscles of the eye)
Arises from: behind the midbrain
Exits: posteriorly and prior to its exit the fibers crosses the midline
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) (Midbrain)
Enumerate the external structures of Pons
PONTINEPROTUBERANCE
BASILAR GROOVE
CN V or TRIGEMINAL NERVE
PONTO-MEDULLARY JUNCTION
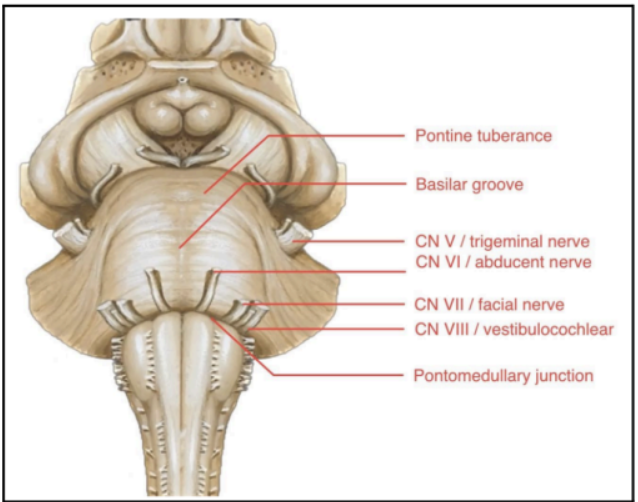
Large bulging structures at the anterior brainstem
Identifying feature of the pons
PONTINEPROTUBERANCE
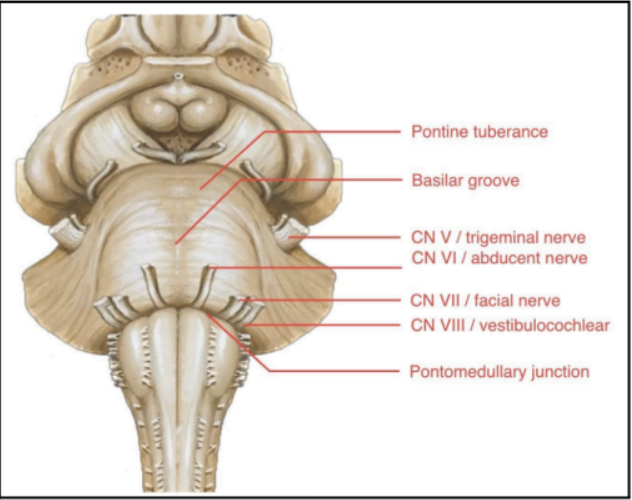
At the middle of the pontine protuberance
Central depression/groove
Occupied by the basilar artery, which is one of the main arteries of the brainstem
BASILAR GROOVE
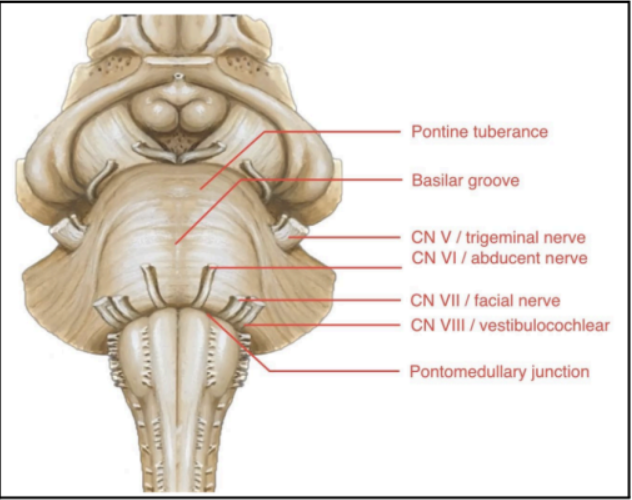
Found at the lateral sides of the pontine protuberance
CN V or TRIGEMINAL NERVE (Pons)
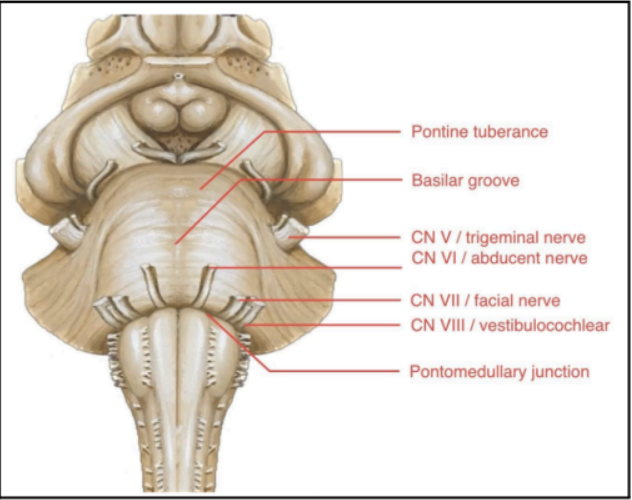
Junction between the pons and medulla
A sulcus where several cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem:
Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
PONTO-MEDULLARY JUNCTION
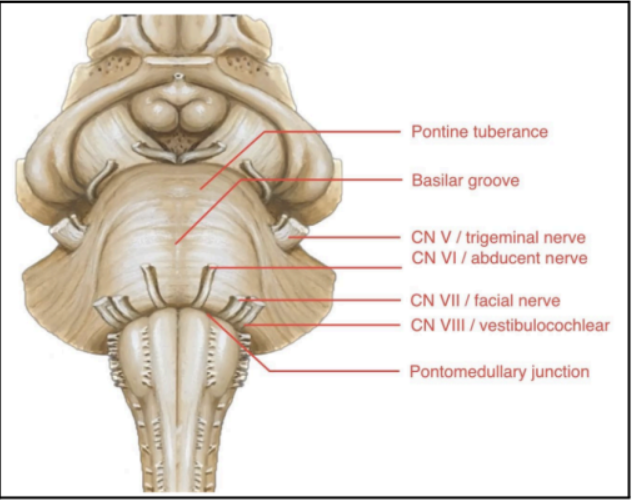
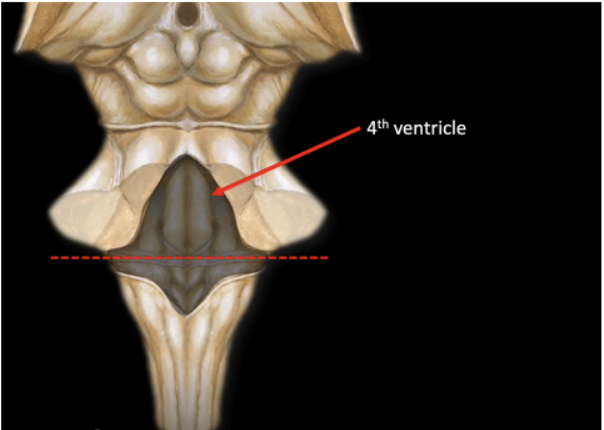
Enumerate the structures found ant the posterior surface of Pons
Upper Half of the floor of the 4th Ventricle
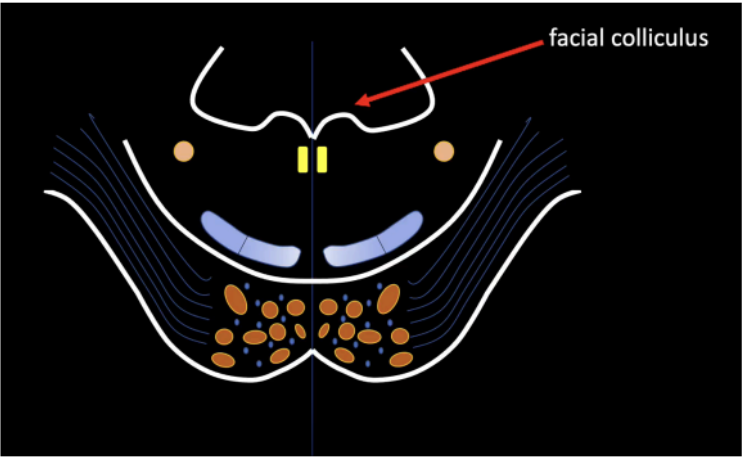
Facial colliculus
Forms the upper half of the floor of the 4th ventricle.
Triangular in shape
The 4th ventricle cavity can be clearly seen if the cerebellum is removed.
POSTERIOR SURFACE OF THE PONS
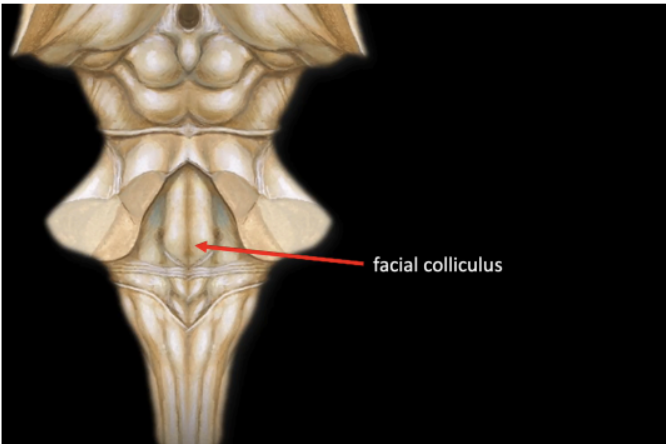
Prominent swelling
Produced by the root of the Facial nerve (CN VII) winding around the nucleus of the Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Facial colliculus
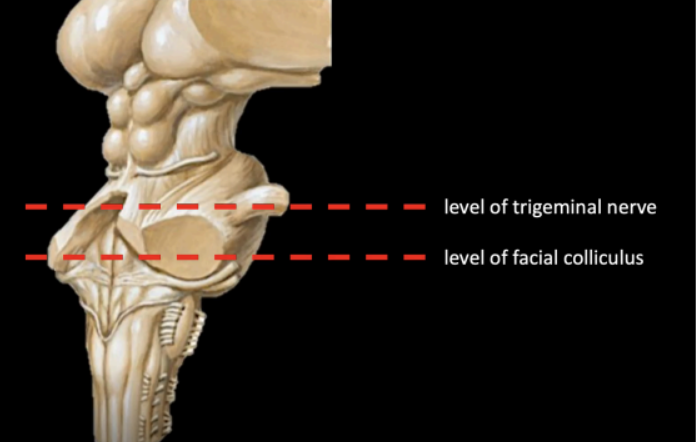
To study the internal structure of Pons we would need to transect at the level of ____ and ____
level of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
level of the Facial colliculus
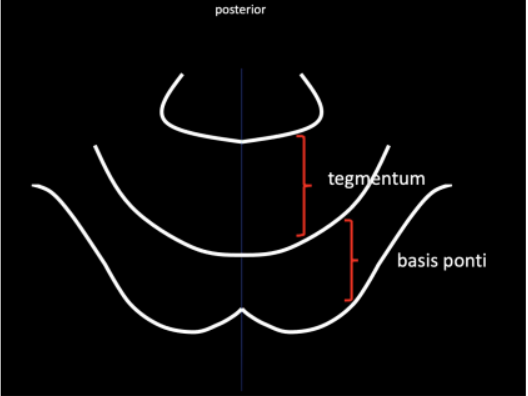
Enumerate the two (2) regions of the internal surface of the Pons
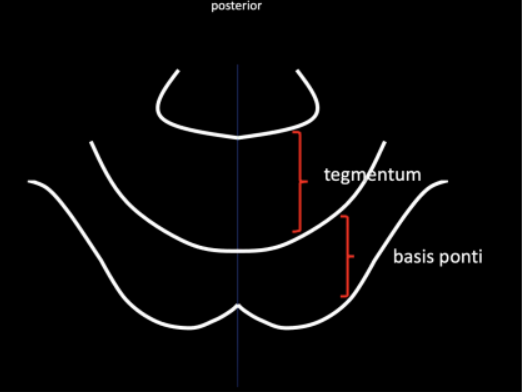
Basis ponti (anteriorly)
Tegmentum (posteriorly)
Region that is the continuation of the crus cerebri (found in the midbrain) in the internal structure of the Pons
Basis Ponti
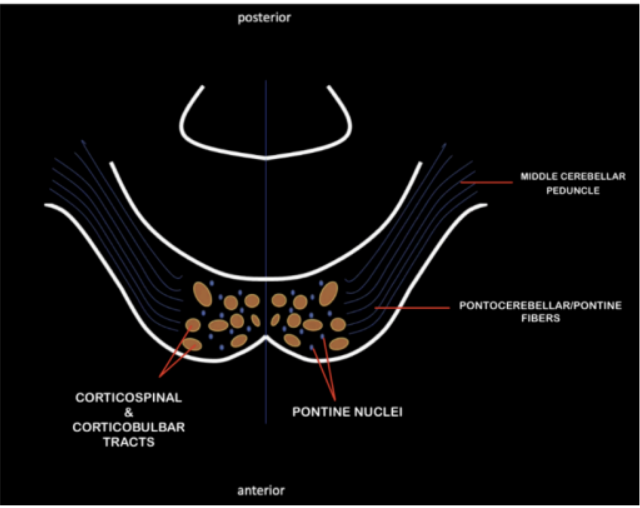
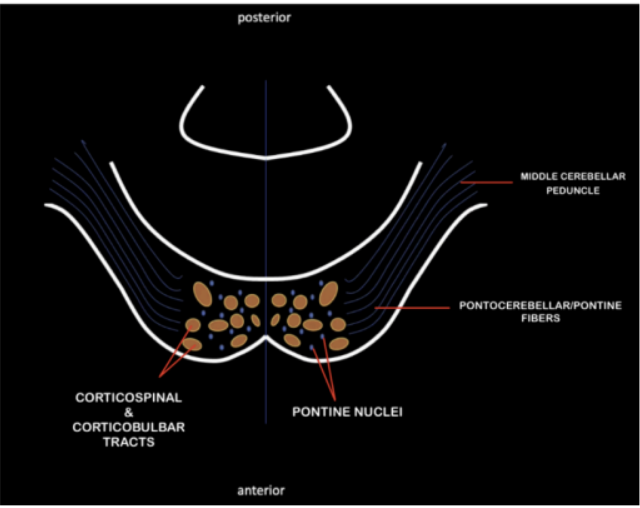
Enumerate the structures found in the Basis Ponti
Pontine Nuclei
Pontocerebellar /Pontine fibers
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tract
Scattered at the middle of the basis ponti
Pontine Nuclei
Horizontally arranged
Arise from the pontine nuclei
Externally, horizontally arranged fibers can be appreciated as it courses laterally and forming the middle cerebellar peduncle
Pontocerebellar/Pontine fibers
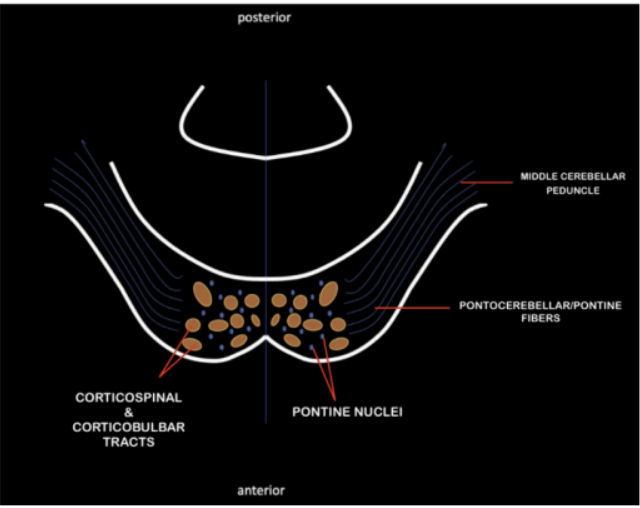
Input pathway that connects the pons’ pontocerebellar/pontine fibers to the cerebellum
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
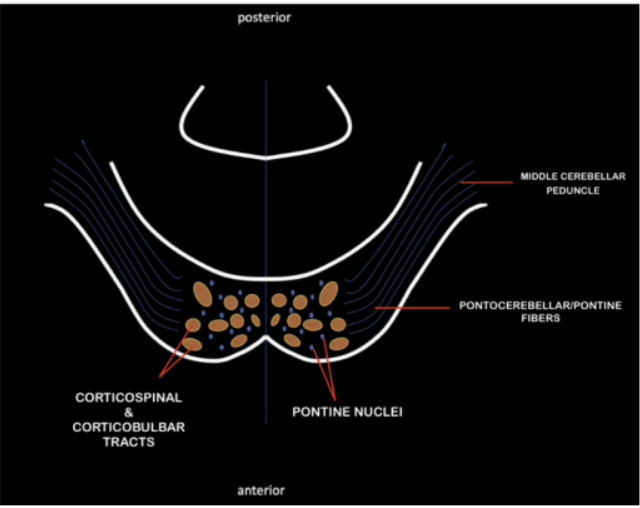
Interspersed within the basis ponti are bundles of descending motor tracts coming from the crus cerebri of the midbrain
Organized in crus cerebri, and continues to descend in the pons, inserting in bundles of fascicles among fibers of pontine nucleus until it reaches the medulla oblongata
Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tract
Continuation of the tegmentum of the midbrain
Contains ascending pathways that originated from the
spinal cord
This contains the fibers of:
Medial lemniscus
Spinothalamic tract
Tegmentum
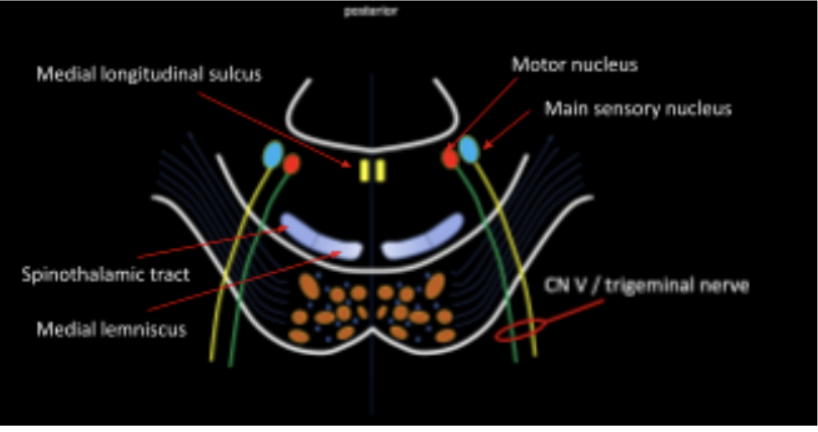
Enumerate the Internal structures of the pons in the tegmentum at the level of CN V
Medial Lemniscus and Spinothalamic Tract
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
Motor Nucleus and Main Sensory Nucleus of CN V
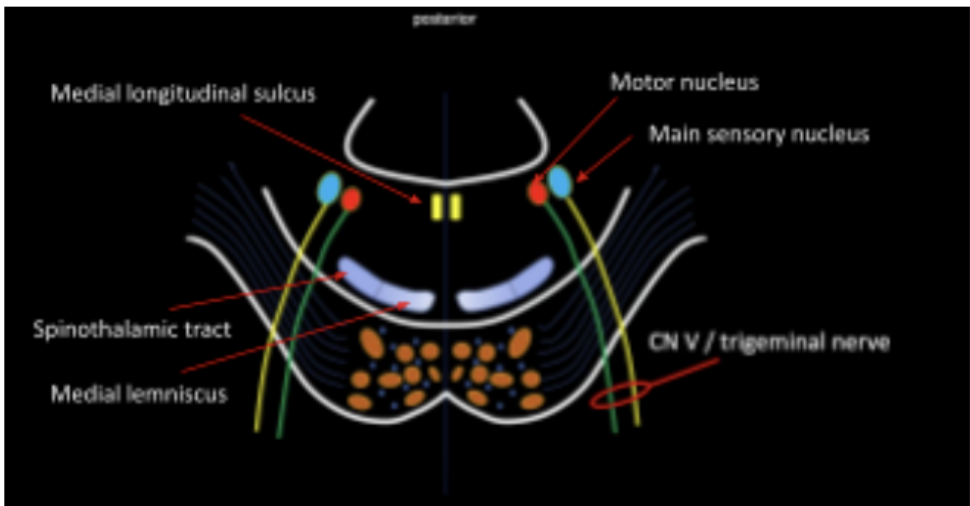
Located in the most anterior part of the tegmentum
Medial Lemniscus and Spinothalamic Tract
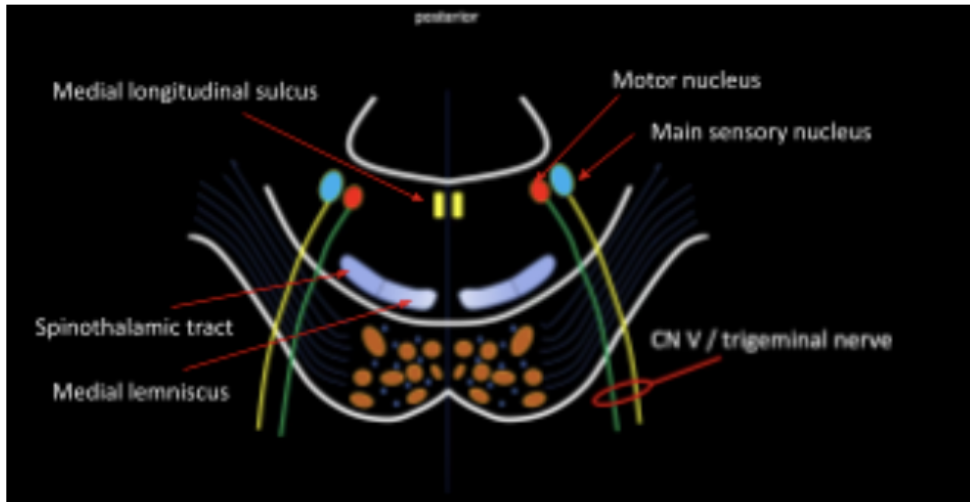
Organized on the medial region of the tegmentum
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
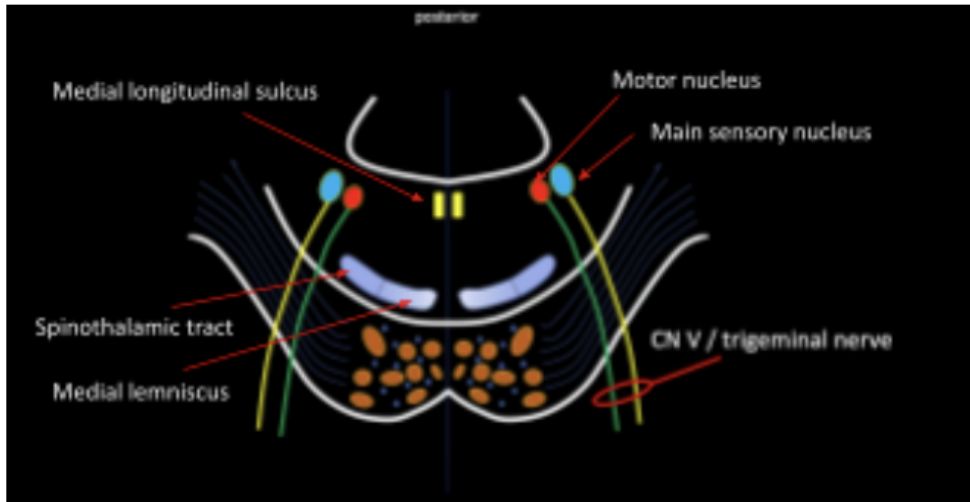
Main motor and sensory nucleus of CN V
Give rise to the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Motor Nucleus and Main Sensory Nucleus of CN V
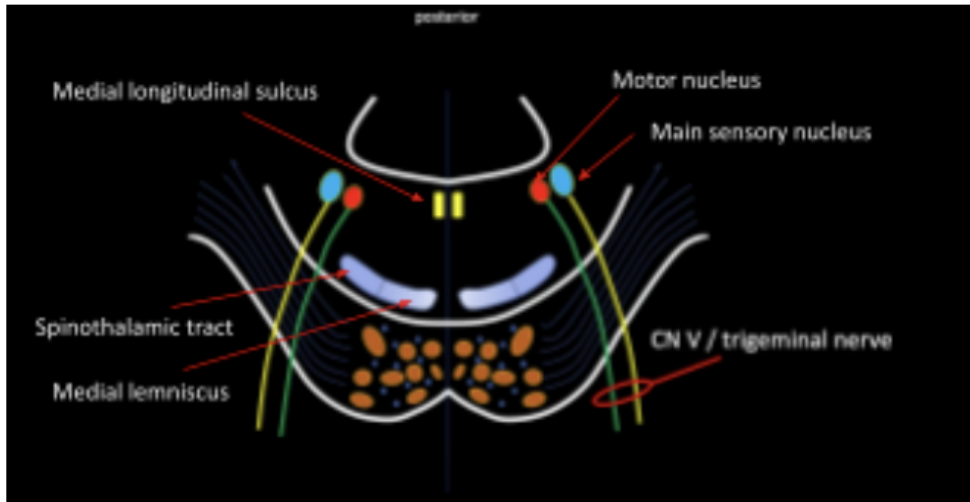
Represented by a bump at the posterior wall of pons
Facial colliculus
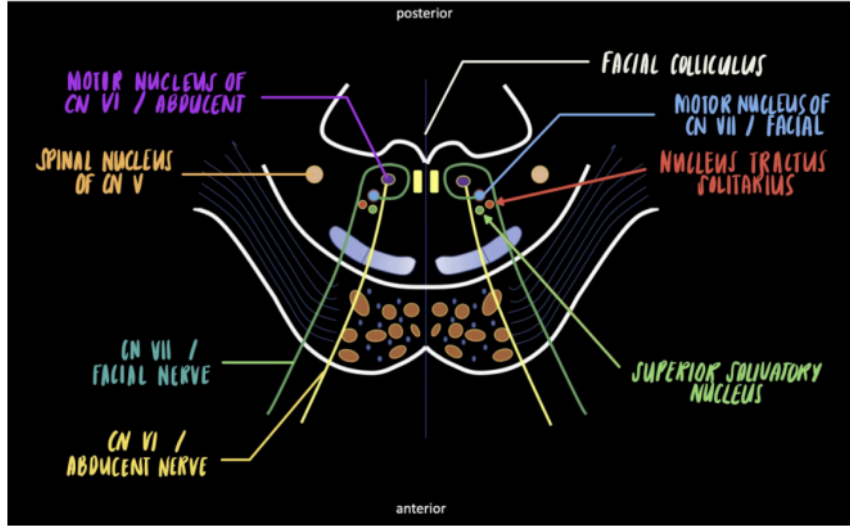
Enumerate the strucutres found at the level of Facial Colliculus
Spinal Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Motor Nucleus of Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
Motor Nucleus of Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Located at the lower regions of the pons and will extend until the medulla oblongata
Spinal Nucleus of Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Main highlight of this level
Will give rise to the Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
Motor Nucleus of Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
Will give rise to the Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Fibers of Facial nerve winds around motor nucleus of abducens, which creates a bump or swelling at posterior wall of pons (Facial colliculus)
Motor Nucleus of Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Enumerate the structures associated with motor nucleus of CN Vii
SUPERIOR SALIVATORY NUCLEUS
NUCLEUS TRACTUS SOLITARIUS
Parasympathetic nucleus of Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Responsible for controlling the secretion of certain salivary glands
SUPERIOR SALIVATORY NUCLEUS
Sensory nucleus of the Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Relay station for the taste sensation, originating from the taste receptors of the tongue and the pharyngeal mucosa
NUCLEUS TRACTUS SOLITARIUS
Last segment and most inferior region of the brainstem
Is divided into two segments
Open Medulla
Closed Medulla
MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Upper half of the medulla that coincides with the lower region of the 4th ventricle.
Open Medulla
Lower half of medulla; the central canal can be seen in its cross section
Closed Medulla
From the midline of the Medulla, the first bump seen is ____
Pyramid
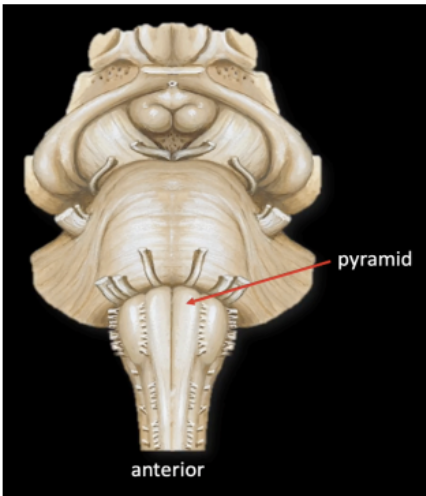
In the Medulla, lateral to the pyramid is another swelling which is called
Olive
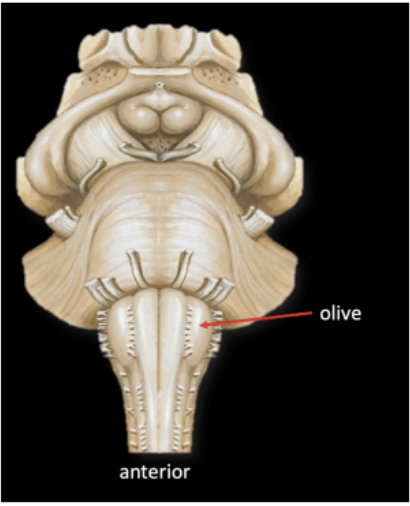
Enumerate the cranial nerves that emerges from the anterior surface of the medulla
CN IX Glossopharyngeal Nerve
CN X Vagus Nerve
CN XI Spinal Accessory Nerve
CN XII Hypoglossal Nerve
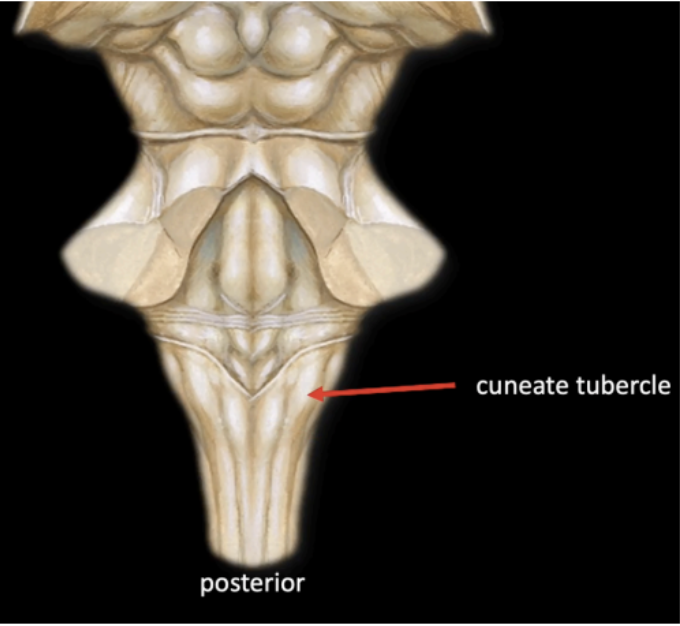
In the posterior of medulla, a series of bumps and swellings can also be appreciated from the Midline
Gracile Tubercle
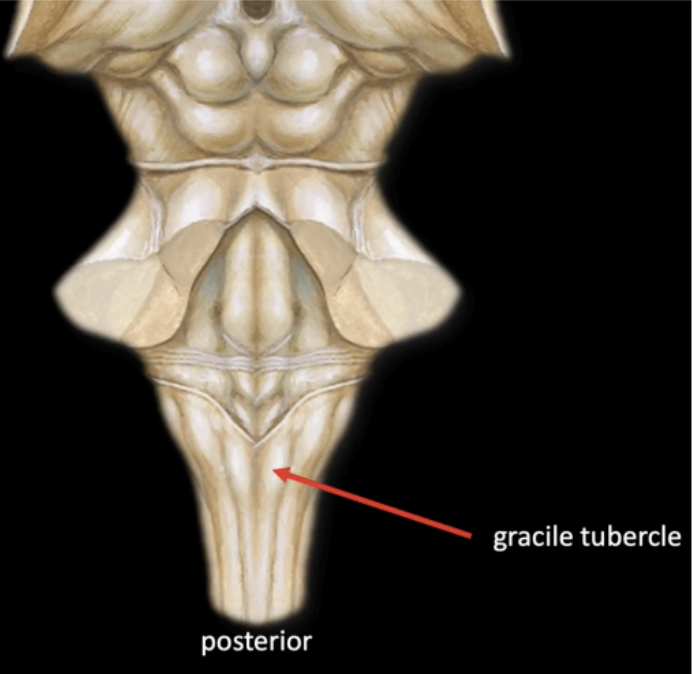
In the posterior of medulla, a series of bumps and swellings can also be appreciated Lateral to the Gracile
Cuneate Tubercle
Enumerate the division of the Dorsal column
Fasciculus gracilis
Fasciculus cuneatus
Matches with the gracile tubercle in the medulla
Fasciculus gracilis (medial)
Enumerate the levels at which the medulla is divided
Level of the olives
The great sensory decussation
The great motor decussation (inferiormost level)
Attaches the medulla to the cerebellum.
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
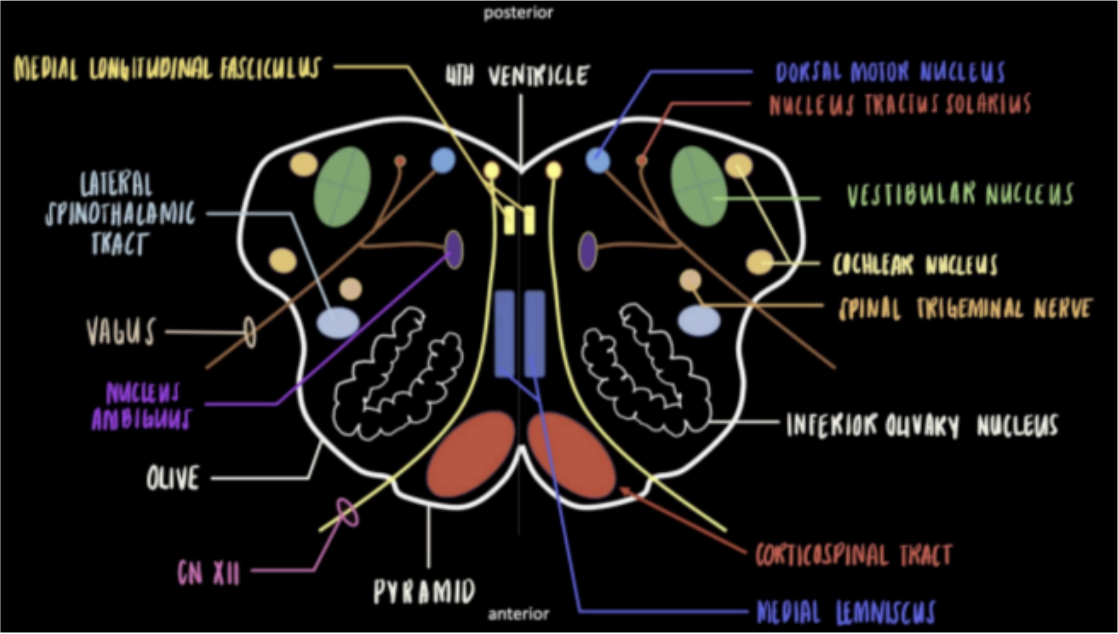
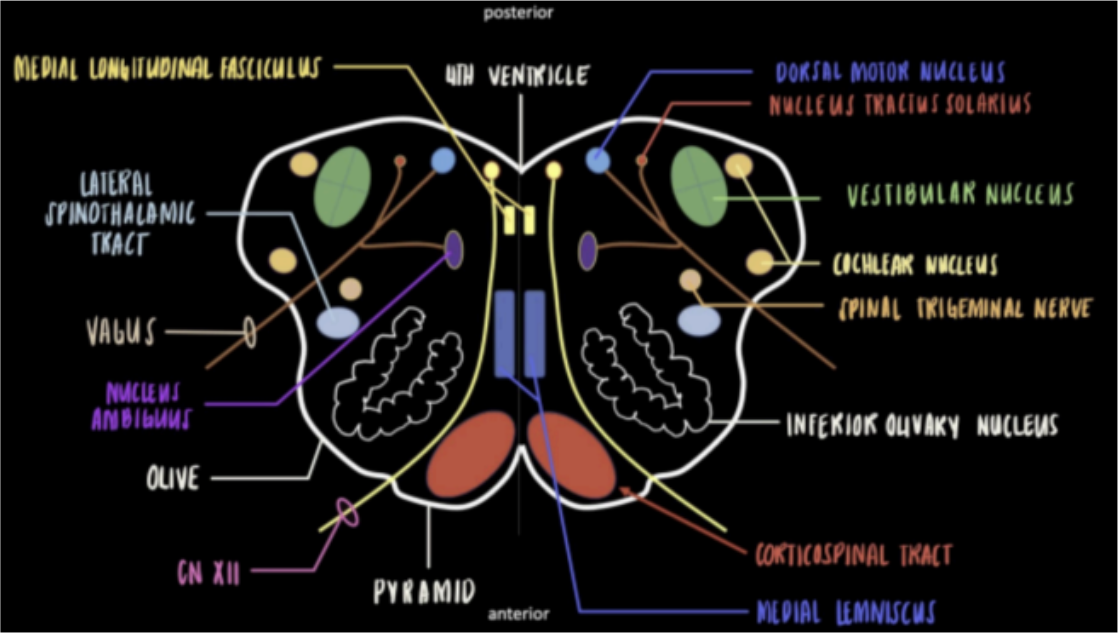
Enumerate the structures at the level of Olives
Inferior Olivary Nucleus
Motor Nucleus of CN XII/Hypoglossal
Vestibular Nucleus and Cochlear Nucleus
Dorsal Motor Nucleus
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
Nucleus Ambiguus
Vagus Nerve
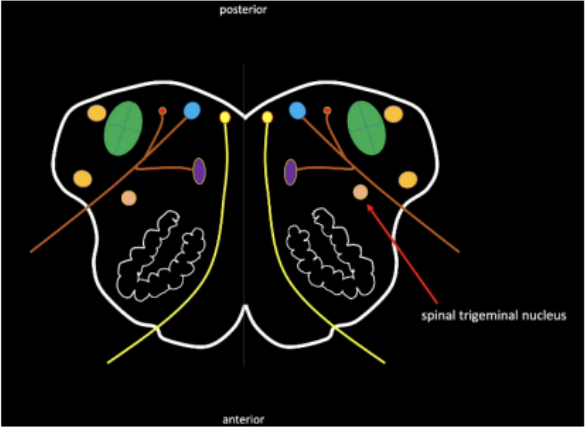
Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
Medial Lemniscus and Lateral Spinothalamic Tract
Corticospinal Tract/Pyramidal Tract
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Most prominent with a crumpled U-shape nucleus.
Forms a projected swelling in the lateral surface of the medulla.
Coordinates movements and is associated with learning
Inferior Olivary Nucleus
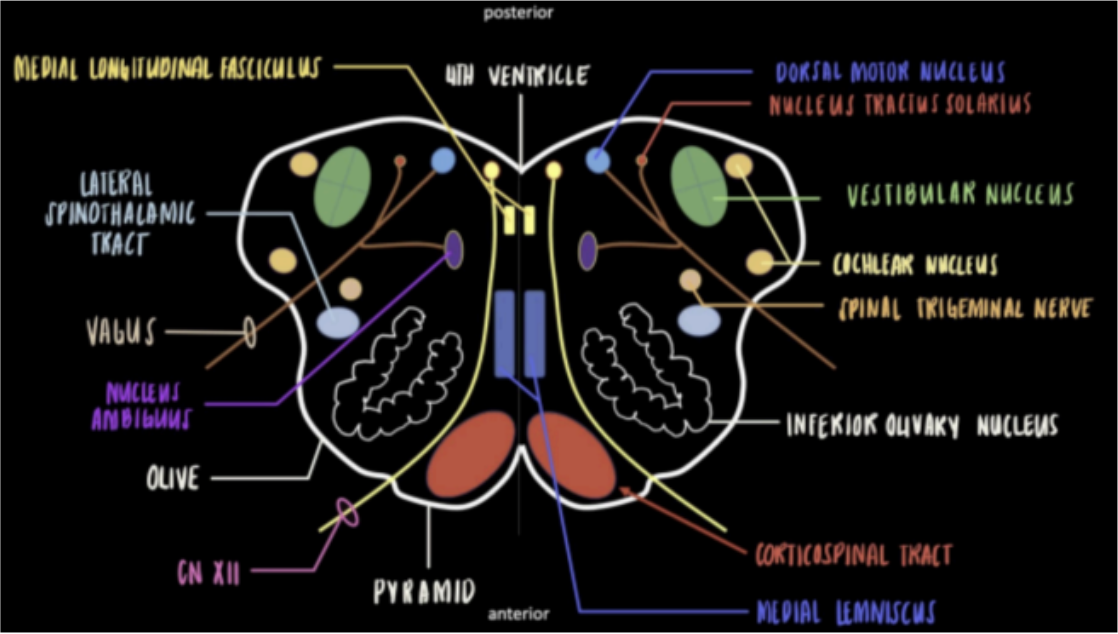
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Located as the posterior wall of the medulla.
Give rise to Hypoglossal nerve CN (XII).
Motor Nucleus of CN XII/Hypoglossal
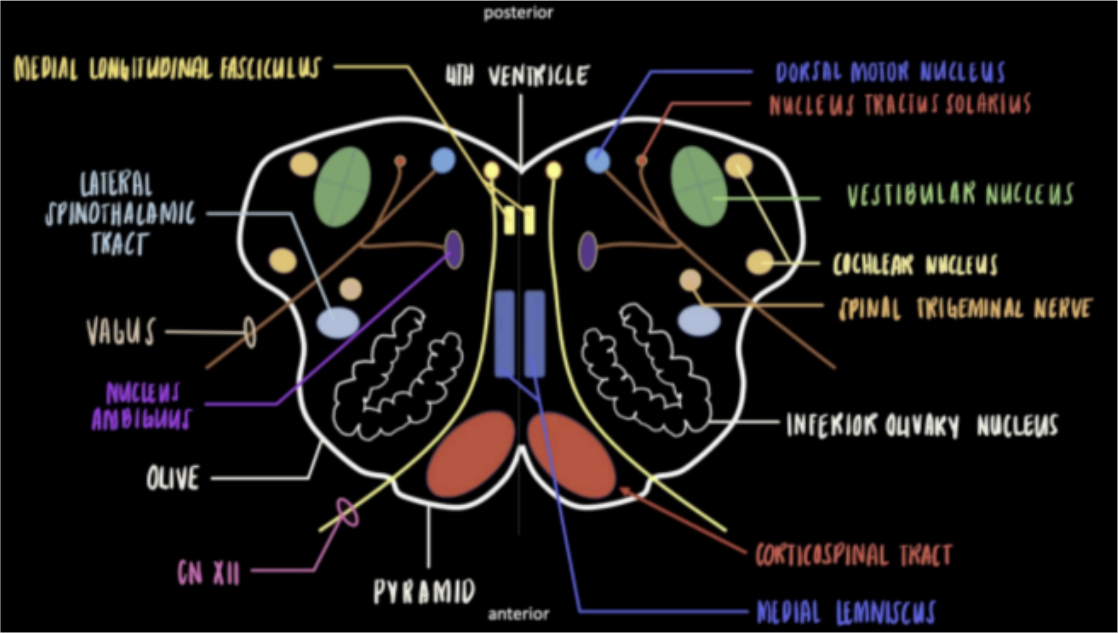
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Near the area of cerebellar peduncle; made up of 4 individual nuclei.
Give rise to the vestibulocochlear nerve CN (VIII); will exit at the anterolateral pontomedullary junction.
Vestibular Nucleus and Cochlear Nucleus
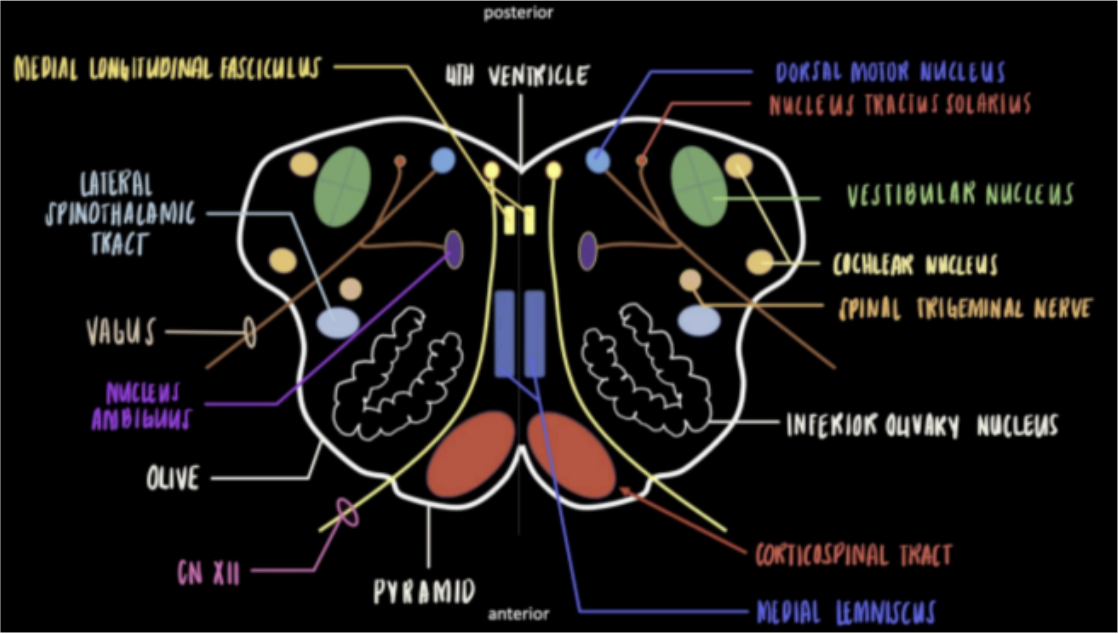
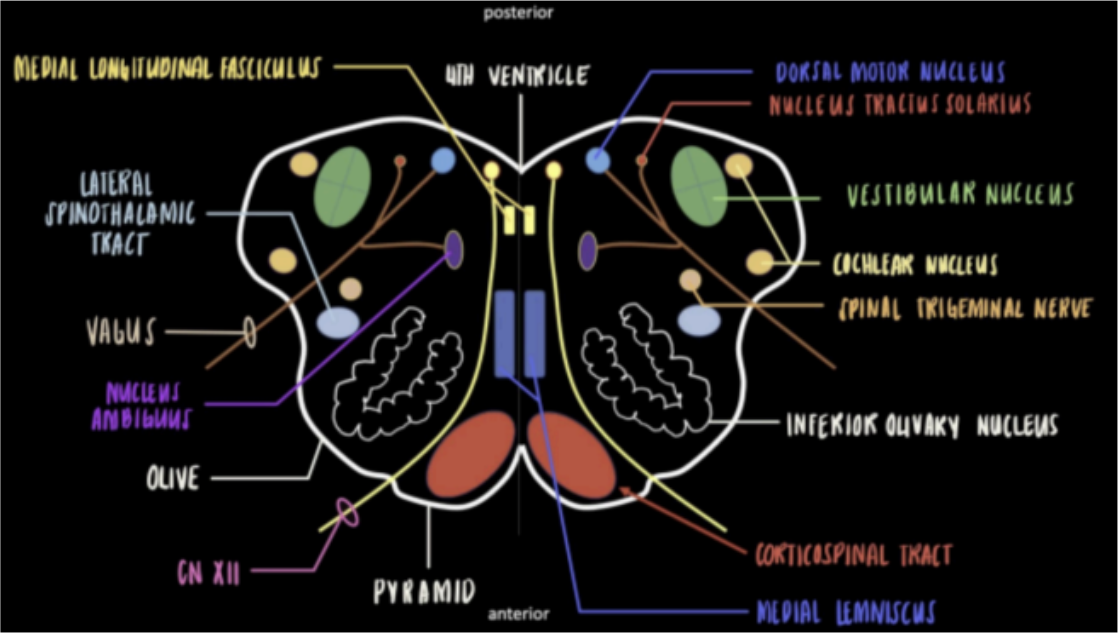
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Adjacent to the hypoglossal nucleus
The parasympathetic component of the vagus nerve.
Dorsal Motor Nucleus
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Process taste sensation coming from the tongue and oropharynx.
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
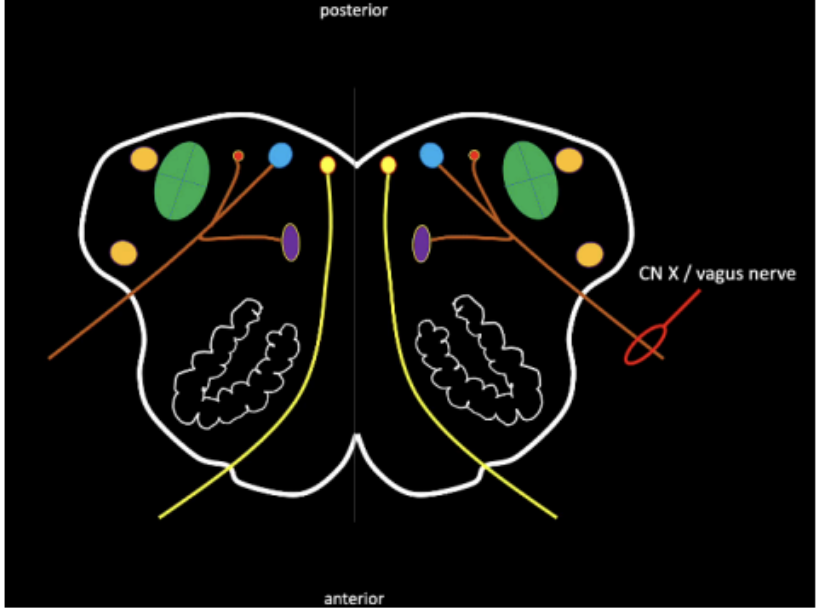
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Shared by several cranial nerves.
The motor nucleus that supplies the muscles of deglutition.
Nucleus Ambiguus
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Contributes nerve fibers for the formation of CN X.
Dorsal Motor Nucleus
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
Nucleus Ambiguus
Vagus Nerve (Medulla)
Seen in the Internal Medulla at the levels of Olives
Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus
Picture of Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus