Structure and bonding
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
A bond formed when two positive nuclei are being held together by their electrostatic attraction for the shared pair of electrons
When are polar covalent bonds formed?
When the attraction of the atoms for the pair of bonding electrons is different
What can these be used to indicate?(δ+, δ-)
The partial charges on atoms which give rise to a dipole
What does δ+ mean?
Slightly positive
What does δ- mean?
Slightly negative
What are Ionic bonds?
The electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
What do ionic compounds form?
Lattice structures of oppositely charged ions
What is the order of bonding in the bonding continuum from left to right and the electronegativitys?
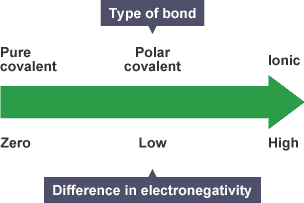
The difference in electronegativities between bonded atoms gives?
an Indication of the ionic character
The larger the difference in electronegativity, The more ……?
Polar the bond will be
What will happen if the difference in electronegativity is large?
Then the movement of bonding electrons from the element of lower electronegativity to the element of higher electronegativity is complete, resulting in the formation of ions
Are compounds formed between metals and non metals always ionic?
Not always but often
Physical properties of a compound, such as ————, should be used to ….. in the compound?
State at room temperature, melting point, boiling point, solubility and electrical conductivity
Deduce the type of bonding and structure
Which type of elements and compounds condense and freeze at sufficiently low temperatures?
All molecular elements and compounds and monatomic elements
For all molecular elements and compounds and monatomic elements to be able to condense and freeze at sufficiently low temperatures, What must exist?
Attractive forces between the molecules or discrete atoms
Intermolecular forces acting between molecules are known as?
van der Waals forces
What are types of van der Waals forces?
Intermolecular forces, London dispersion forces and permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions that include hydrogen bonding
What is the weakest van der Waals force?
London dispersion forces
What are London dispersion forces?
Forces of attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules.
When are London dispersion forces formed?
They are formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles caused by movement of electrons in atoms and molecules.
The strength of London dispersion forces is related to…..?
The number of electrons within an atom or molecule
An increased number of electrons leads to bigger temporary dipoles which causes …?
Larger London dispersion forces
A molecule is described as polar if it has a ..?
Permanent dipole
The spatial arrangement of polar covalent bonds can result in?
A molecule being polar
What are permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions?
Additional electrostatic forces of attraction between polar molecules
Pd-pd interactions are stronger than LDFs for …..?
Molecules with similar numbers of electrons
Bonds consisting of a hydrogen atom bonded to an atom of _____ ___________ ________ such as …….? Are highly polar
strongly electronegative element
Fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen
What are hydrogen bonds?
Electrostatic forces of attraction between molecules that contain highly polar bonds
A hydrogen bond is stronger than other forms of _________ but weaker than a __________
permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
Covalent bond
The melting and boiling point of a substance depends on the …..?
strength of the intermolecular forces between its molecules
The mpt and bpts of polar substances are ______ than the mpt and bpts of non polar substances with similar numbers of electrons
Higher
Substances will tend to be most soluble in solvents with the …?
Same type of intermolecular forces as themselves
What statement can be said about solubility in terms of intermolecular forces to help you remember?
Like dissolves Like
Non polar substances tend to be soluble in?
non polar solvents
Polar substances and Ionic compounds tend to be soluble in
Polar solvents
Highly polar molecules can be strongly attracted to _______ or _______ __________ _____
Positively
Negatively
Charged ions
To predict the solubility of a compound, key features to be considered are the:
• presence in molecules of O-H or N-H bonds, which implies hydrogen bonding
• spatial arrangement of polar covalent bonds, which could result in a molecule possessing a permanent dipole
What is viscosity ?
A measure of how thick a liquid is or how slow it is to move
Thick liquids have ___?
High viscosities
Runny liquids have …?
Lower viscosities
The stronger the intermolecular forces in a liquid are the ………?
Greater the viscosity
Substances with hydrogen bonding will tend to be _____ viscous than substances without hydrogen bonding
More
The inconsistency of the bpts of ammonia, water and hydrogen fluoride are a result of
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding between molecules in ice results in?
an expanded structure that causes the density of ice to be less than that of water at low temperatures.