(l-m) Nitrogen cycle ad rate of decompostion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Give some example of biological molecules which have nitrogen in them?
proteins (amino acids), most nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
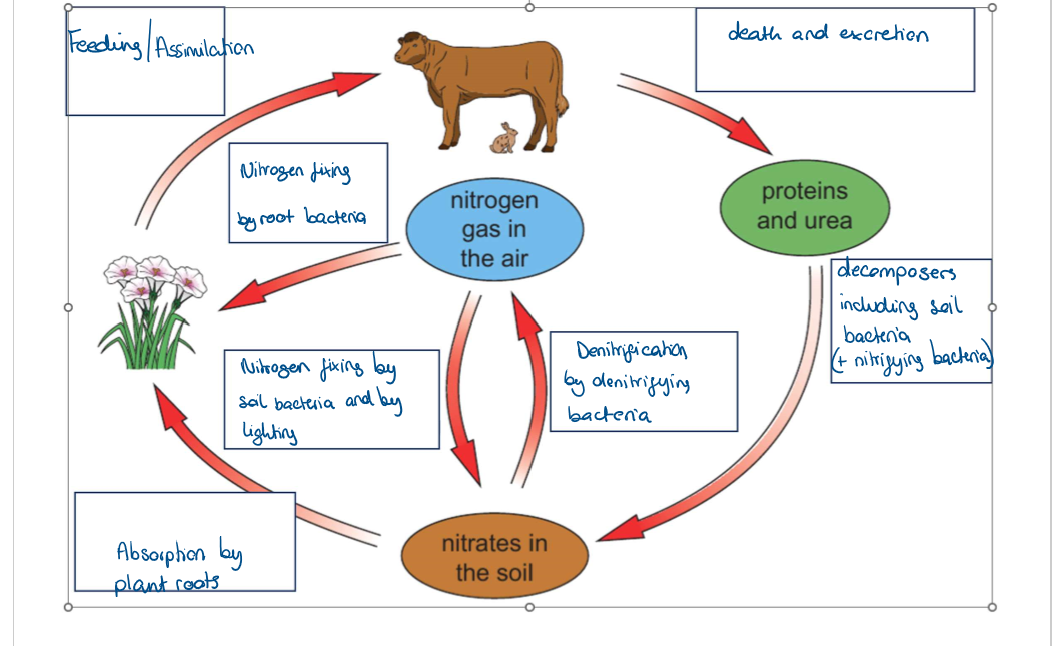
What are the 4 types of bacteria that are vital to the nitrogen cycle?
nitrogen-fixing bacteria
decomposers
nitrifying bacteria
denitrifying bacteria
What is the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
they convert unreactive nitrogen gas in the air into reactive nitrogen compounds such as nitrates which can be used by plants
they are good as they help plants get the nutrients (nitrogen) they need
"What is the role of decomposers?
fungi and bacteria are examples of decomposers
they break down dead organic matter and excreting waste to release nitrogen compounds (e.g ammonia)
they are a good thing
What is the role of nitrifying bacteria?
they convert ammonia compounds into nitrates.
these bacteria need oxygen as they carry out aerobic respiration
they are good because they enable plants to up taken the nutrients they have broken down
What is denitrifying bacteria?
bacteria in soil which turns nitrates back to nitrogen gas through the process of denitrification.
they occur in very water logged soil (water low in oxygen)
How do nitrates get into plants?
through the roots via active transport
What is crop rotation?
growing different crops to make the soil more fertile
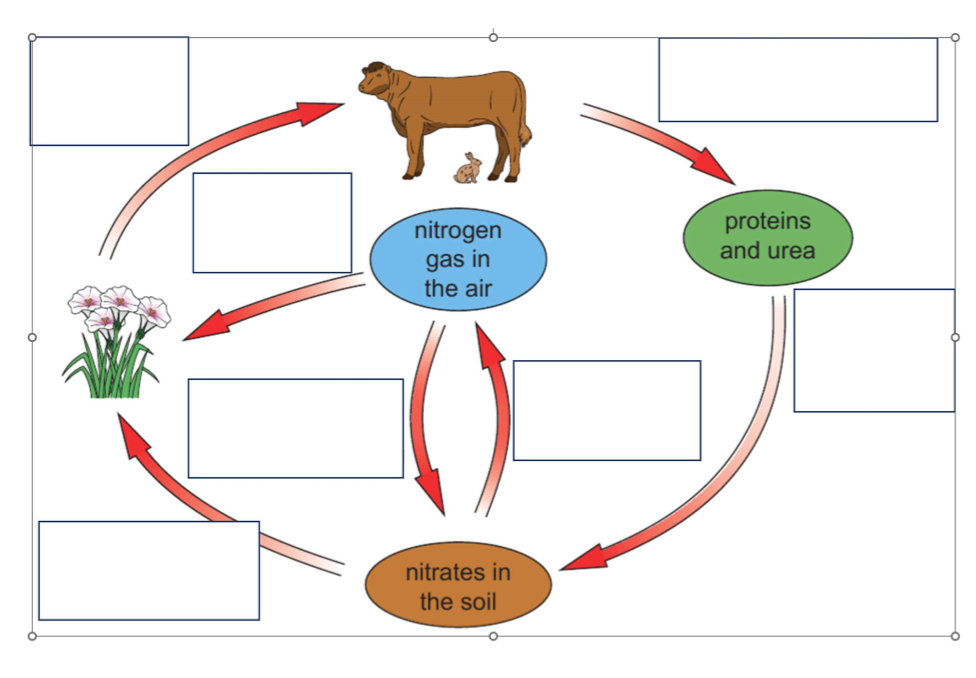
Complete this diagram with the following words: nitrogen-fixing bacteria, feeding, death and execration, decomposers, denitrification
Why do plants need nitrates?
to make proteins (amino acids) to grow
state 2 ways nitrogen is fixed into nitrates?
-By lighting
-nitrogen-fixing bacteria
State 3 ways farmers increase the concentration of nitrates in the soil
Crop rotation
fertilisers (organic)
fertilisers (inorganic)
Explain the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle
some convert nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds such as nitrates
some are decomposers and break down dead organic matter into ammonia
Explain why waterlogged soils reduce the growth of plant
They contain denitrifying bacteria
which convert soluble nitrates into nitrogen gas, so there are no nitrates available for growth
What is soil fertility maintained by?
Decomposers such as bacteria in soil.
these organisms release nitrogen compounds together with carbon compounds when they decompose dead plants and animals and their waste
Give an example of a plan that have a mutualistic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Pea and bean plants.
the bacteria are protected inside nodules in the plant roots,
and the plant gets nitrogen compounds directly from the bacteria
What is crop rotation?
Planting a sequence of crops in different wheats, such as wheat followed by potatoes followed by peas, is called crop rotation
How can farmers make use of the mutualistic relationship between pea and bean plants and nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
farmers can can make use of this relationship to keep their soil fertile.
by planting a crop of peas (or related plants) and then digging in the root after the crop has been harvested.
the following year a different crop will benefit from the additional nitrogen compounds in the soil.