Monopolistic competition
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Characteristics of monopolistic competition:
There are a large number of small firms: each one is relatively small and can act independently of the market
There are low barriers to entry and exit from the industry: firms can start-up or leave the industry with relative ease which increases the level of competition
The products are slightly differentiated: this structure exists as consumers have different desires e.g. two nail bars can differentiate their product through either an express or pampered service. Some consumers may want a quick service, while others want more attention. A relatively homogenous product has now been differentiated
There is a low degree of market power and some price setting ability
Profit Maximising Equilibrium in the Short and Long-run
In order to maximise profit, firms in monopolistic competition produce up to the level of output where marginal cost = marginal revenue (MC=MR)
The firm does have some market power and is able to influence the price and quantity
The firm is a price maker
This is due to the fact that they have a differentiated product that is desirable by certain consumers
The firm can make supernormal profit in the short-run
In the long-run, the firm will return to a long-run equilibrium position in which they make normal profit
This is due to inability to defend against new competitors who enter the market and copy the products of existing sellers
Firms will attempt to find new ways to differentiate their product to prolong the period of supernormal profit, e.g. a barber shop may add in a pool table and beer fridge for their customers to enjoy, thus making them different from the competition (for a period of time)
Monopolistic Competition DiagramsShort-run profit maximisation
Firms in monopolistic competition are able to make supernormal profit in the short-run
The AR curve is the demand curve of the firm and it is downward sloping
The firm has some market power due to the level of product differentiation that exists
To sell an additional unit of output, the firm will have to decrease its price
The marginal revenue (MR) curve will fall twice as quickly as the AR
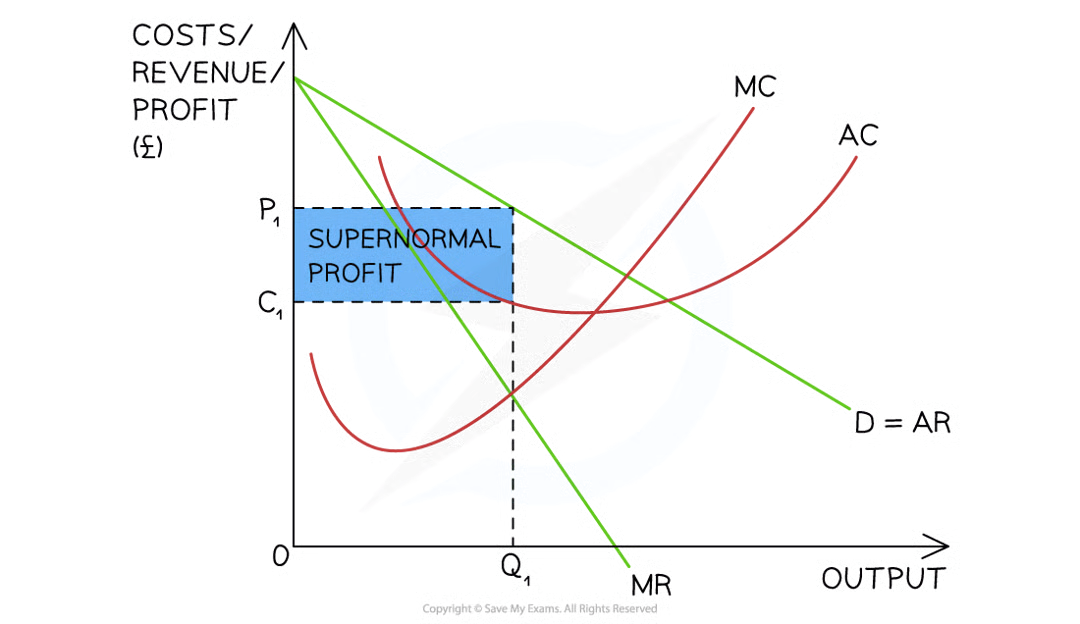
A diagram illustrating a monopolistically competitive firm making supernormal profit in the short-run as the AR > AC at the profit maximisation level of output (Q1)
Diagram analysis
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where MC = MR (Q1)
At this level the AR (P1) > AC (C1)
The firm is making supernormal profit
= (P1-C1)XQ1
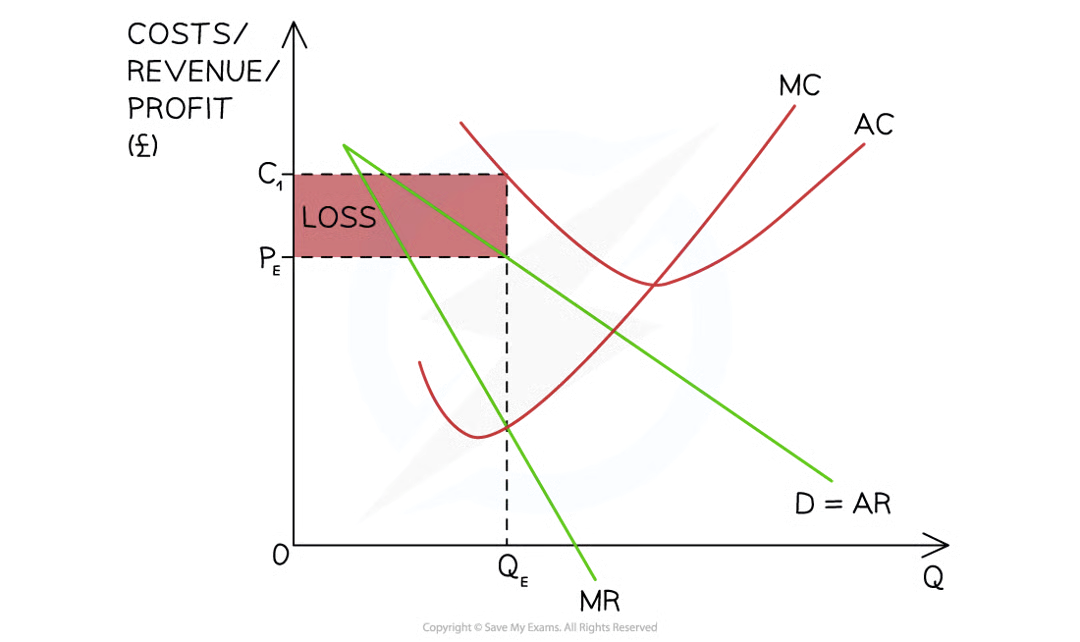
Short-run losses - Firms in monopolistic competition are able to make losses in the short-run
Diagram analysis
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where MC = MR (QE)
At this level of output, the AR (PE) < AC (C1)
The firm's loss is = (PE-C1)XQE
From Supernormal to Normal Profit
If firms in monopolistic competition make supernormal profit in the short-run, new entrants are attracted to the industry and the number of sellers increases
They are incentivised by the opportunity to make supernormal profit
There are low barriers to entry
It is easy to join the industry
Supernormal profit will be eroded and the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
From Losses to Normal Profit
If firms in monopolistic competition make losses in the short-run, some will shut down
The shut down rule will determine which firms shut down
There are low barriers to exit, so it is easy to leave the industry
For the remaining firms, losses will be eliminated and the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
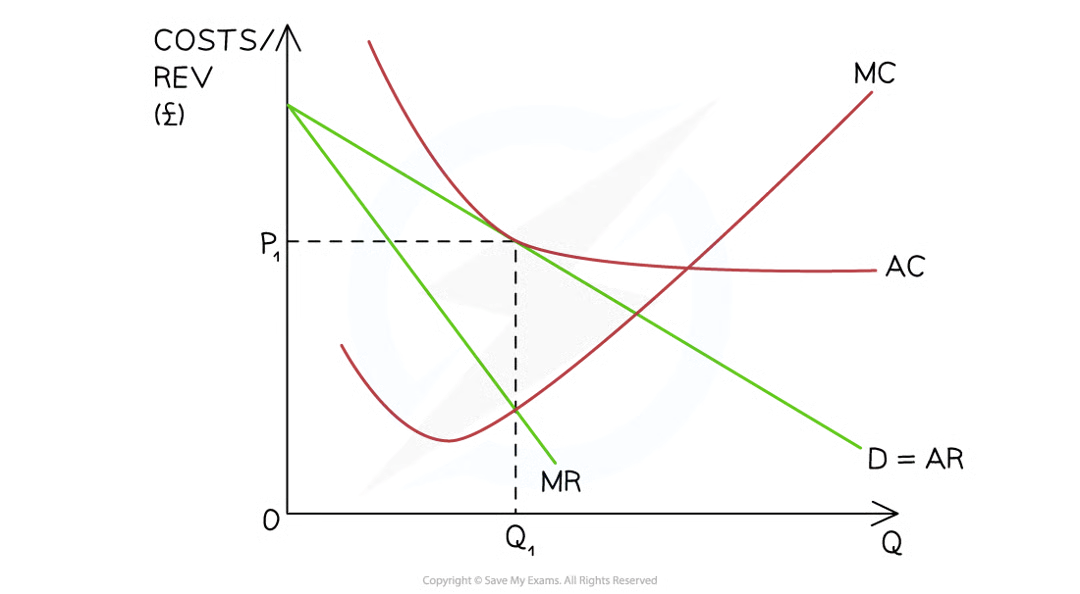
A diagram illustrating the long-run equilibrium position for a monopolistically competitive firm which is making normal profit. AR (P1) = AC at the profit maximisation level of output (Q1)
Diagram analysis
The firm is initially producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
At this level of output P1 = AC and the firm is making normal profit
In the long-run, firms in monopolistic competition always make normal profit
Firms making a loss leave the industry
Firms making supernormal profit see it slowly eradicated as new firms join the industry