EXAM SUN/SAT (6-7)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What causes more brain injury?
Vehicular crashes result in more brain injuries than any other cause.
Two broad categories based on the mechanism by which the injury is produced
impact injuries, Acceleration/ deceleration
Acceleration and deceleration injuries are?
caused by sudden movement of the head immediately after injury, with the resultant production of intracranial pressure gradients and subjecting of the brain to both shearing and tensile force
Injuries from impact tramuas?
Soft tissue: lacerations, abrasions, and contusions of the scalp
o Fracture of the skull
o Contusions of the brain
o Epidural hematomas
o Intracerebral hemorrhage
Skull fractures depend upon?
o The thickness of the scalp, amount of hair
o The configuration and thickness of the skull
o The elasticity of the bone at the point of impact
o The shape, weight and consistency of the object impacting or impacted by the head
o The velocity at which either the blow was delivered, or the head strikes the obje
Diffuse Axonal Injuries:
Shearing of the axons results in the breaking of the nerve connections
Subdural Hematomas:
The most common lethal injury associated with head trauma
Injuries produced by Acceleration or Deceleration Trauma:
Subdural hematomas
Diffuse axonal injury.
Epidural Hematomas
Primary impact injuries. Always a coup injury; never a contrecoup.
Relatively infrequent
ex: falls and accidents by vehicle; present at the point of impact.
o The bleeding usually produces a disk shape and originates from the rupture of an artery.
o Symptoms usually occur 4–8 hours after the injury.
Contrecoup Contusions:
Occur in areas of the brain directly opposite to the point of impact due to tensile force
injuries caused by the brain rebounding backward from the skull following impact. (fall)
Coup Contusions
: Occur at the site of the impact and result from the inbending bone
snapping back causing tensile force injuries to the brain. Coup contusions are less common than contrecoup contusions
Costusions of the Brain?
o 1. Coup Contusions
o 2. Contrecoup Contusions
o 3. Fracture Contusions
o 4. Intermediary Coup Contusions
o 5. Gliding Contusions
o 6. Herniation Contusion
Basilar Skull Fractures?
Occur to the base of the skull. Maybe hinge fractures that completely bisect the base of the skull, creating a “hinge
Depressed Skull Fracture:
Occurs when the skull is struck with an object having a relatively large amount of kinetic energy but a small surface area
impacts only a small area of the skull. Example: Hammer strike to the head
No linear fractures radiate from the circular depression in the scalp
Simple Linear Fractures:
Seen in low-velocity impacts with a large area of contact between the head and the impacting object. Example: Fall to pavement.
Production of a single linear fracture requires approximately 33.3 to 75 ft-lbs of energy.
Is there a correlation between the severity of a brain injury and the production of a linear skull fracture?
There is no correlation between the severity of brain injury and the production of a linear skull fracture.
Skull fracture means?
the degree of deformation and the extent of any fractures is dependent
upon
Subdural hematomas
(Under the dura) - Secondary to tearing of the subdural bridging
veins
Diffuse axonal injury?
secondary to the injury of axons
Can skull fractures occur without a detectable brain injury? And can death without a skull fracture happen?
Yes, Skull fractures can occur without any detectable brain injury
Yes, death may result from extensive brain injury without a skull fracture
Four Types of Wounds Caused by Pointed and Sharp-Edged Weapons:
1. Stab Wounds
2. Incised Wounds
3. Chop Wounds
4. Therapeutic/diagnostic wounds
STAB WOUNDS:
Produced by pointed instruments.
Most are homicidal.
The depth of the wound into the body is greater than its length on the skin surface.
Edges of the wound are sharp, without abrasion or contusion.
Never to be confused with a laceration
The sharper, needle like the instrument is the more readily?
it will perforate the skin.
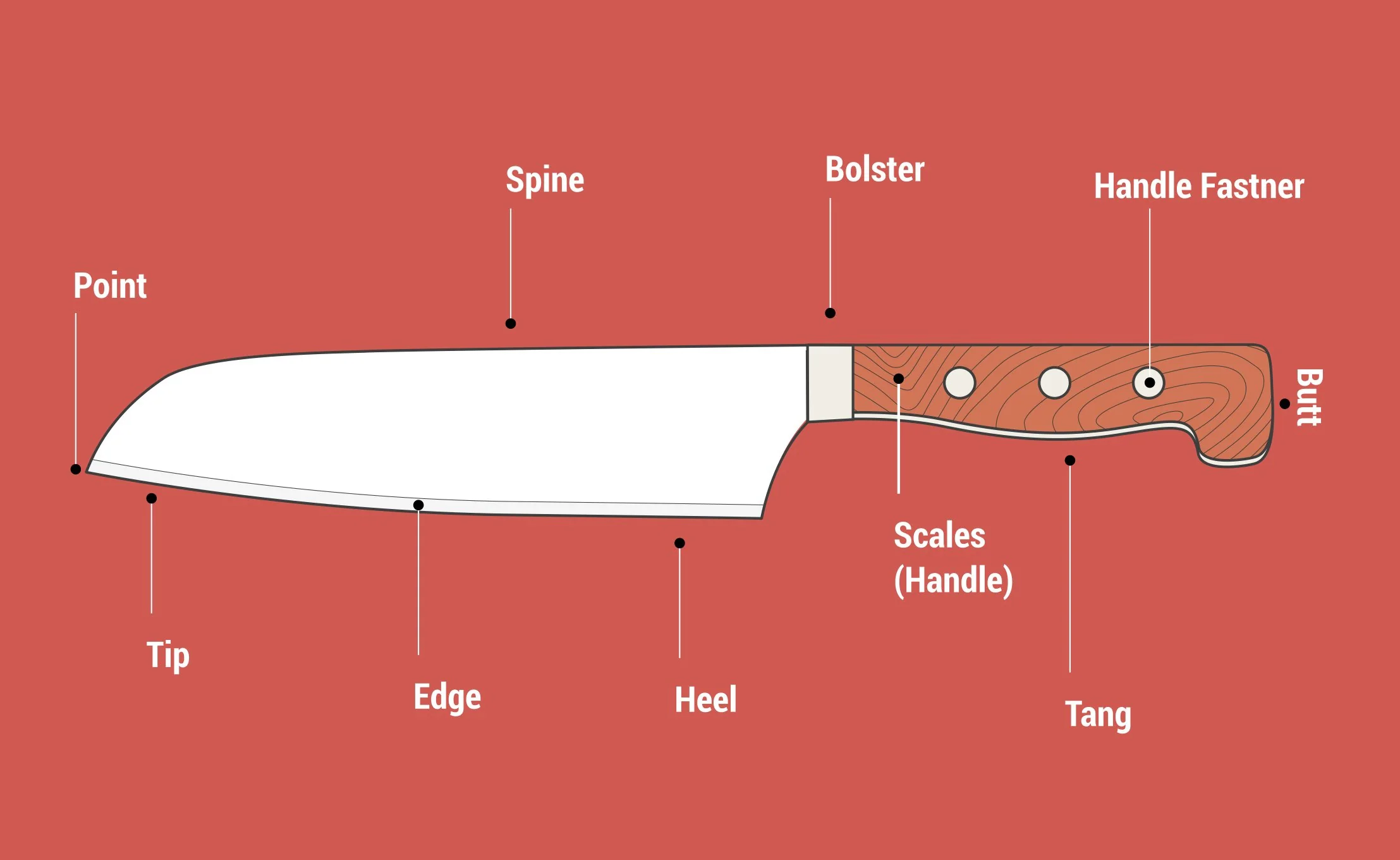
Knife Anatomy?
Look at image
Stab Wounds: What is true about the width and length of a knife?
The length of the wound on the skin surface can be equal to, less than or greater
than the width of the knife.
The depth of the stab wound can be equal to, less than, or greater than the length
of the knife blade.
Stab Wound Appearance is Dependent upon
nature of the stabbing instrument
– Sharpness of weapon will determine appearance of the wound margins
direction of the thrust
movement of the blade in the wound
movement of the individual stabbed
state of relaxation or tension of the skin
Langer’s Lines
– “A pattern of elastic fibers in the dermis of the skin, which is
approximately the same from individual to individual.” (Text, p. 190)
Stab wounds perpendicular to the fibers
will produce gapping wounds.
Stab wounds parallel to the fibers will produce
“narrow slit-like wounds”
What are langer's lines?
A pattern of elastic fibers in the dermis of the skin which is approximately the same from individual to individual
a blow with an axe causes a _______ cut with fine abrasion of the wound edges due to the ________ of the blade
sharp & heaviness
The length and depth of the incised wound _________ yield information about then weapon
will not yield information about the weapon
What are cut or incised wounds?
C- produced by sharp-edged weapons or instruments
IW- weapon drawn over the skin with sufficient pressure to produce an injury that is longer than it is deep