ATP redox and electron carriers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
metabolism
sum of all catabolic/anabolic reactions
catabolism
break compounds into smaller molecules to release energy
(energy stored within bonds is releasedwhen broken)
anabolism
creates larger compounds by using energy
metabolic pathways
reactions follow a step-by-step sequences called metabolic pathways
in each step of the pathway, enzymes are used to convert substrates to products
organisms do their work at the [__] level through a series of chemical reaction
organisms do their work at the molecular level through a series of chemical reaction
bond energy
energy needed to break/form a bond in kJ
molecular bonds are store energy that can be used by cells to do work if it’s released
whenever a chemical bond form between 2 atoms, energy is RELEASED. to break that bond, energy is ABSORBED
amt of energy released when bonds form is the [__] amt required to break a bond
amt of energy released when bonds form is the same amt required to break a bond
the more energy stored in a bond, the more [__] it is and [__]
the more energy stored in a bond, the more stable it is and harder to break apart
thermodynamics
describes how thermal energy changes in a system & surroundings
energy released during chemical reactions is usually measured as thermal energy
1st law of thermodynamics
total amt of energy in the universe is constant
energy can’t be destroyed but only converted between forms
eg. when running, chemical E → kinetic E
if heat/thermal energy isn’t doing work, then what does it do?
heat increases randomness in the universe
molecules are always moving randomly. Thermal energy causes molecules to move faster → more randomness
2nd law of thermodynamics
during any change that occurs, the universe will move towards disorder/entropy
heat from chem reaction increases entropy & reduces amt of energy that can be used to do work
how is life able to maintain order?
input energy to reduce randomness by using energy in our surroundings to keep us alive (eg photosynthesis, cleaning ur room)
gibbs free energy (G)
a measure of how much energy is available to do useful work in a system
helps determine whether or not reactions will occur spontaneously
gibbs free energy equation
ΔG = ΔH − (T)*(ΔS)
enthalpy (H)
energy stored in bonds in the form of heat
ΔH = change in enthalpy of a reaction (products-reactants)
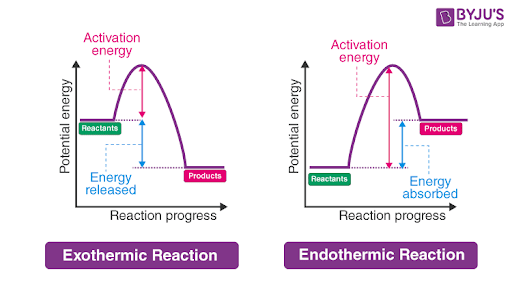
exothermic reaction
more E in reactants than products, thus E is released, ΔH = (-)
draw a graph of exothermic reaction
x axis → reaction progress
y axis → potential energy
energy released
etc
exothermic
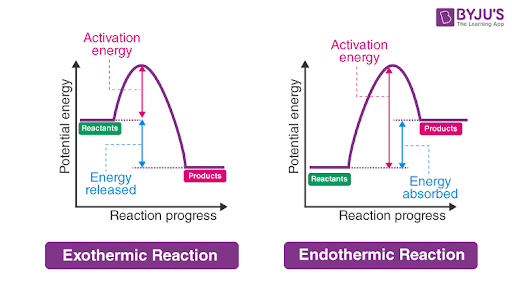
draw a graph of endothermic reaction
x axis → reaction progress
y axis → potential energy
energy absorbed
endothermic
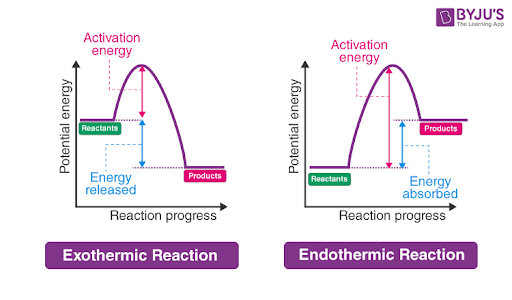
endothermic reaction
less energy in reactants than in products, thus energy absorbed
ΔH = (+)
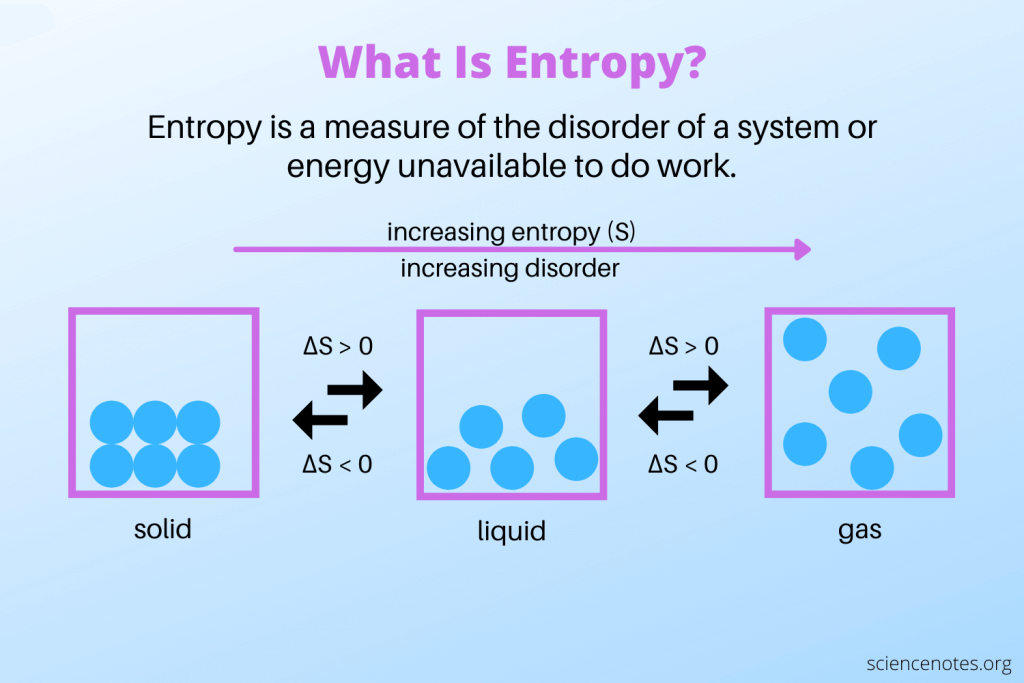
entropy (S)
randomness/disorder in a system
ΔS = (+) → system becomes more disordered during the reaction
ΔS = (-) → system becomes less disordered during the reaction
if reaction is [__], entropy [__]
if reaction is spontaneous, entropy increases
temperature (T)
amount of kinetic E of molecules
higher temps = faster molecule movement, thus entropy increases
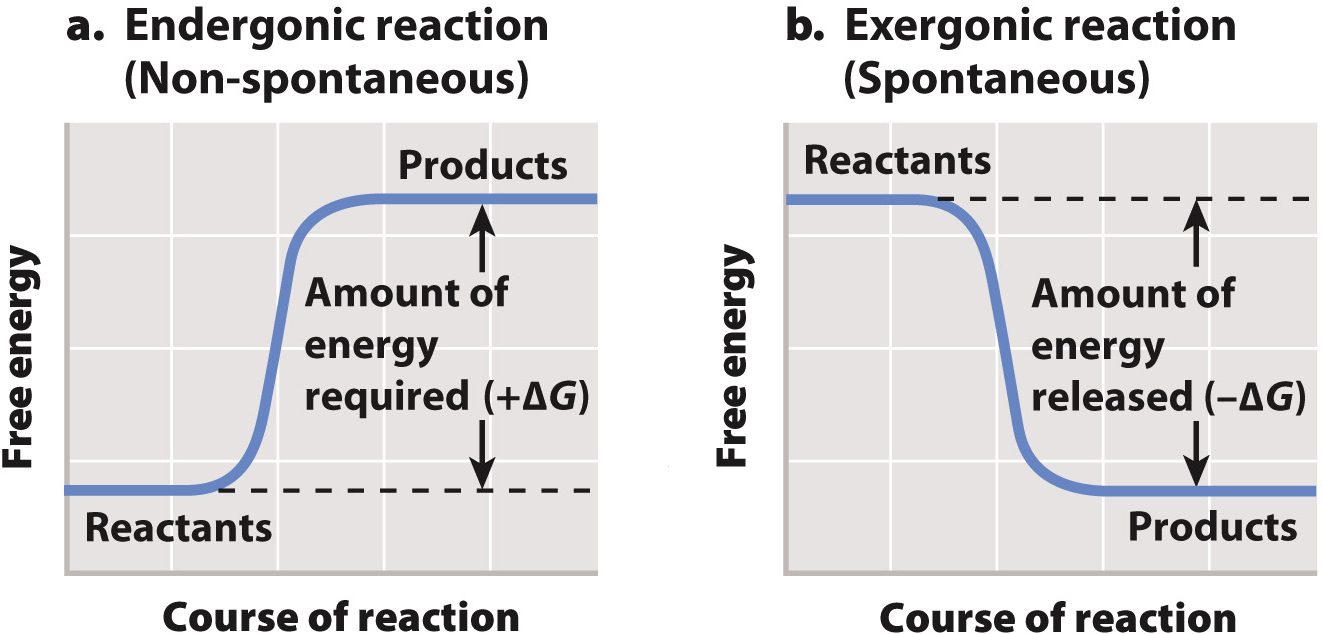
exergonic reaction
release free energy (ΔG = (-)) and increase entropy
reactants have high potential E & are less stable
products have less potential E and more stable
reactions happen spontaneously with a small input of E to get things started
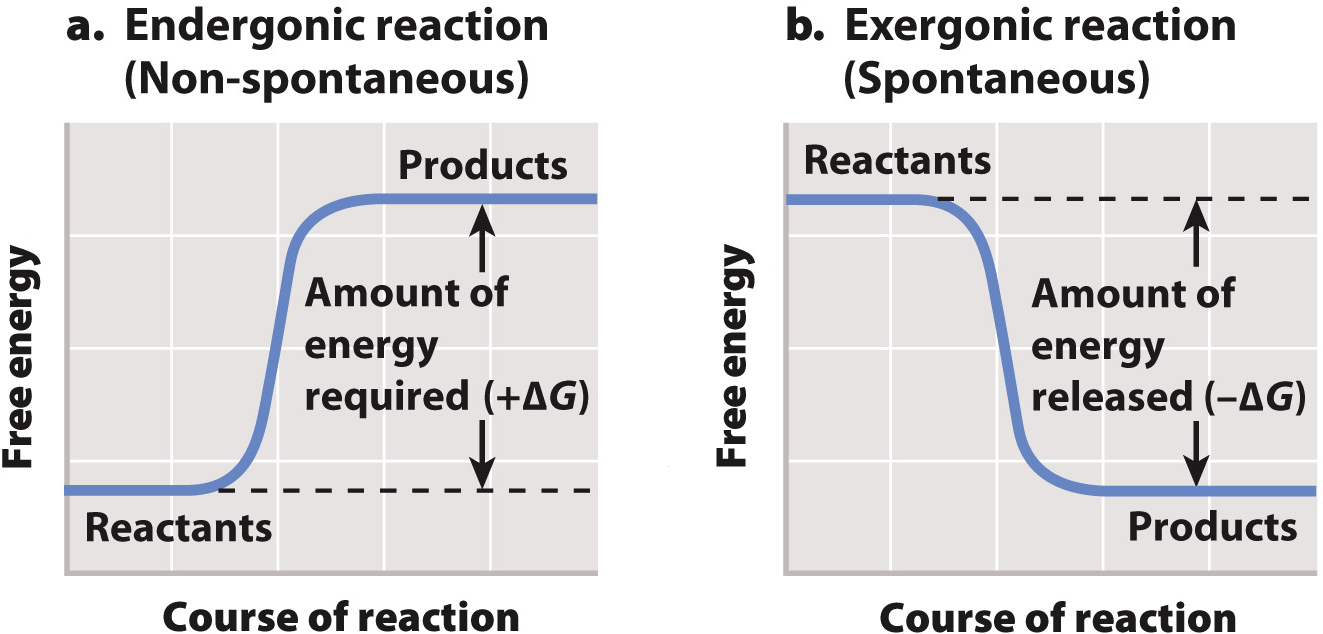
endergonic reaction
uses free energy (ΔG = (+)), decrease entropy
reactants have low Potential Energy & more stable
products have more PE & less stable
reactions need an input of free energy to occur aka not spontaneous
energy coupling in exer/endergonic reactions
endergonic reactions occur due to the free energy released during exergonic reactions (free energy in cells = ATP)