Chapter 7: Formed elements in urine
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
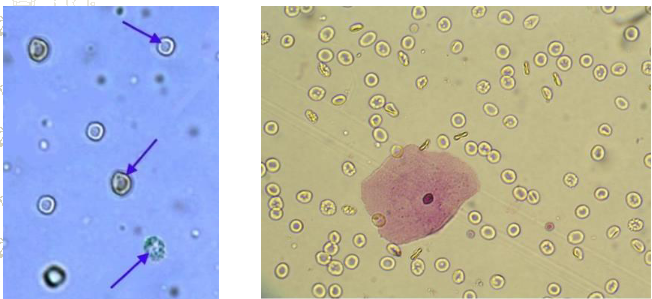
RBCs
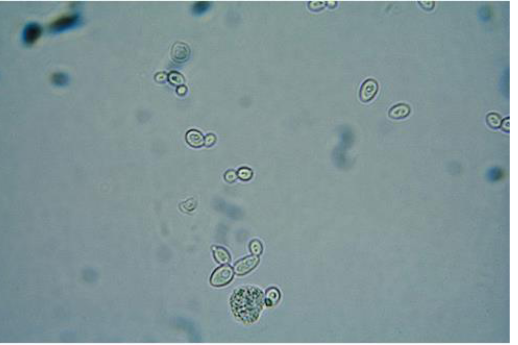
Yeast
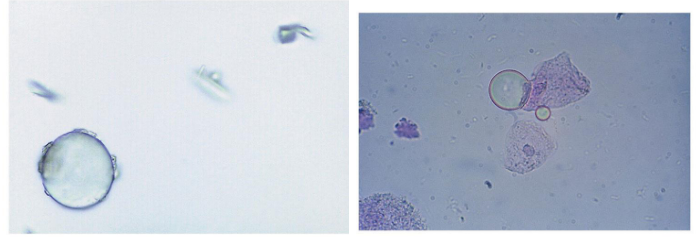
Aire bubble and oil droplet
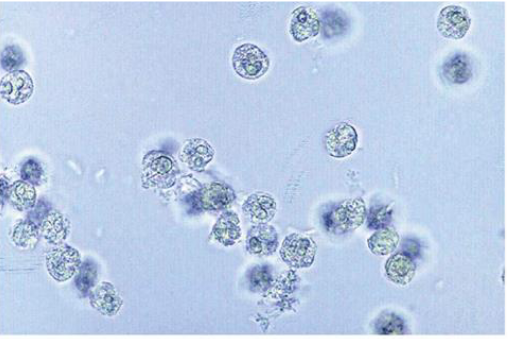
WBC 0-8 per field of view is normal
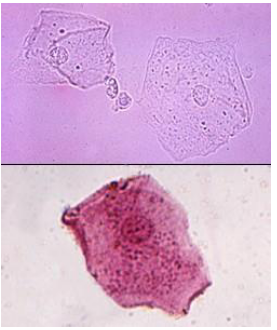
Squamous cells, small centrally located nucleus, most frequent and least significant.
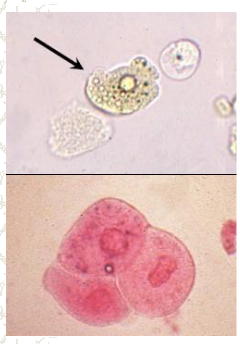
Transitional cells, round or pear shaped, central nucleus, large numbers are unusual and should be reported.
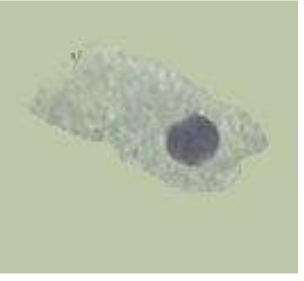
Renal Tubular, relatively large, oblong, eccentric nucleus, large numbers mean tubular necrosis.
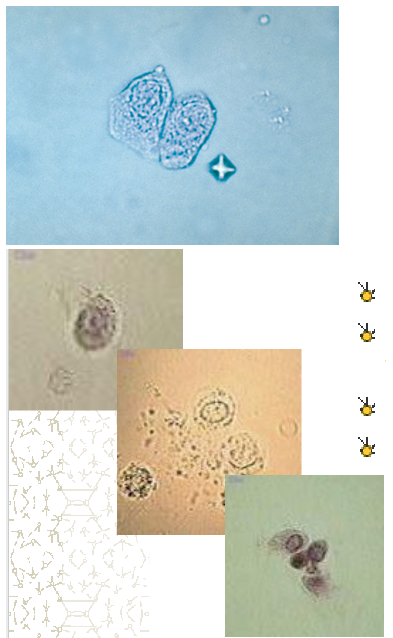
Renal tubular cells: collecting ducts, single large nucleus, large number means renal disease often accompanied by increased RBCs
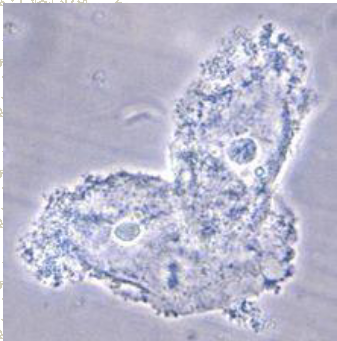
Clue cell, epithelia cell with bacteria on it , usualy vaginal secretions, bacterial vaginosis.
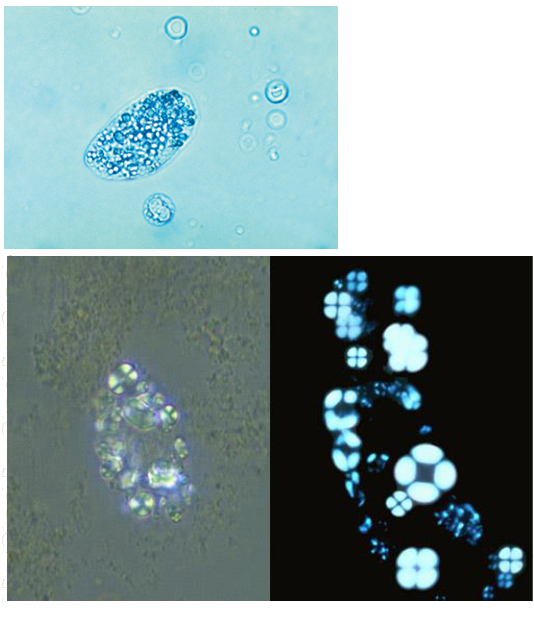
Oval Fat bodies, renal tubular cell containing fat, stain with Sudan III or oil Red O, polarized light see Maltese cross, indicate glomerular dysfunction and renal tubular cell death, increased protein and cast formation.
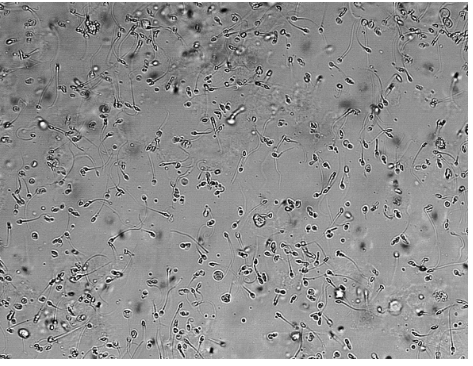
Sperm, not really a concern but check the age and sex of the patient, young patients it can be sexual abuse.
Casts
Formed in distal and collecting tubules, not normally present. Cylindroiduria- Presence of casts in urine
Tamm-Horsfall Protein
Mucoprotein that is secreted by renal tubular cell, forms matrix of cast.
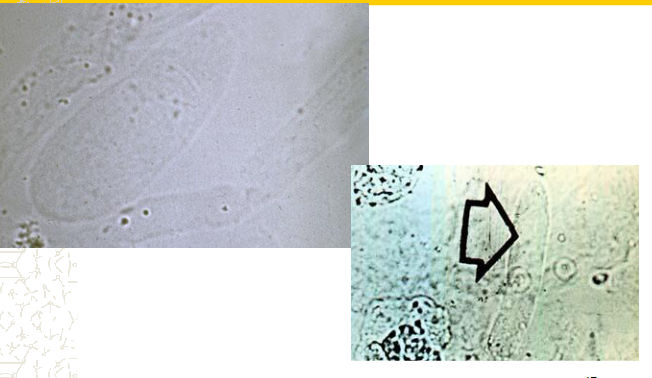
Hyaline casts
strenuous exercise, stress, dehydration
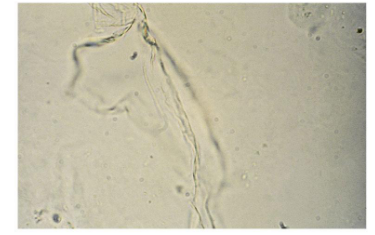
Mucus
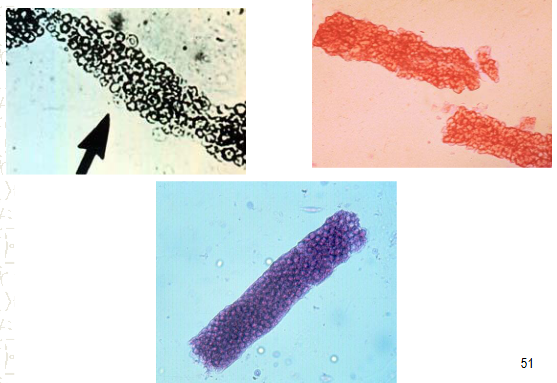
RBC cast
Accompanied by blood and protein on chemical test, associated with glomerular diseases, maybe sometimes sports.
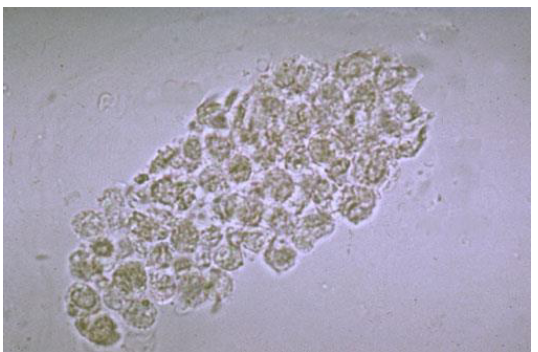
WBC cast
Seen with protein+, LE +, blood ±, nitrite ±, associated with infectious diseases.
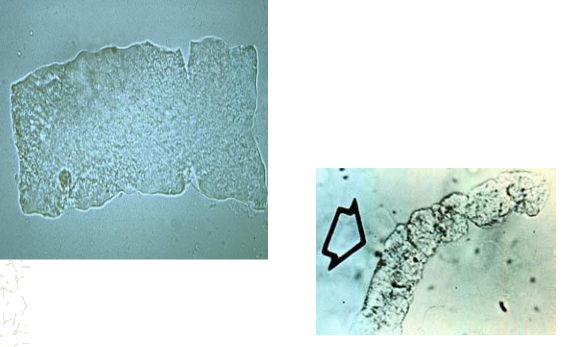
Waxy Cast
Ground glass appearance, seen with protein + and blood ±, associated with nephrotic syndrome and chronic renal disease.
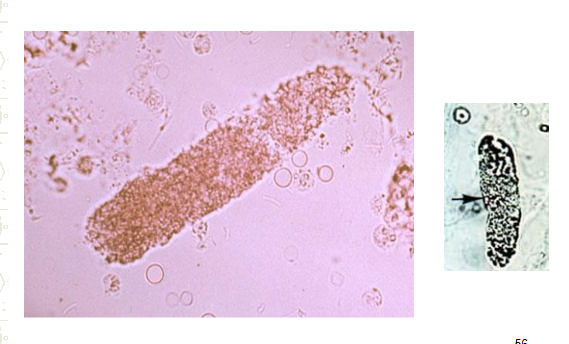
Granular cast, can be blood cast of brown cast, hemoglobin and RBC breakdown.
Fine granular- protein ± and blood ±, associated with strenuous exercise, stress, dehydration, fever
Coarsely granular cast- protein + and blood ±, not associated with anything specific, accompanied by other pathologic casts
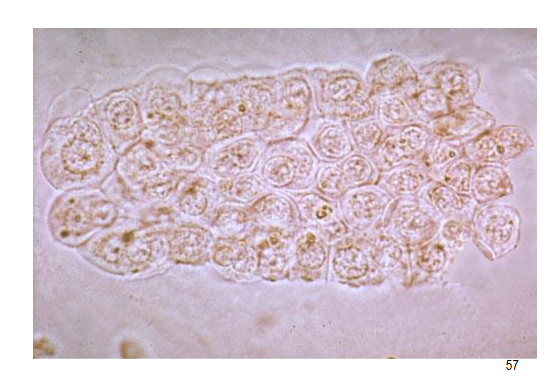
Renal tubular cell cast
protein + and blood ±, most associated with acute tubular necrosis and all renal diseases.
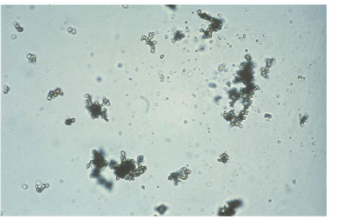
Amorphous
-urate= acidic
-phosphates= Alkaline
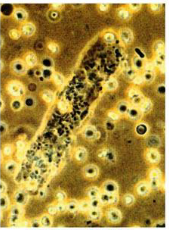
Bacterial cast, hard to distinguish, diagnostic for pyelonephritis, mixed with EBC’s, can gram stain to ID
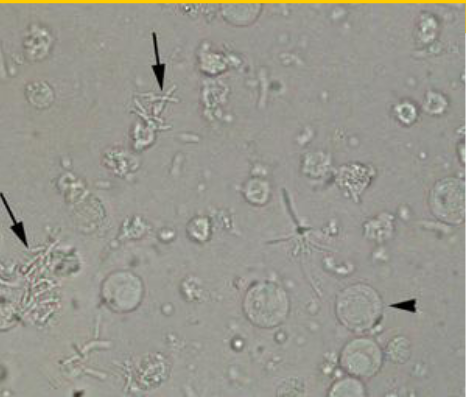
Bacteria
most common shape bacilli, motility distinguishes from amorphous
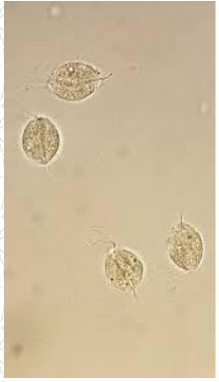
Trichomonas vaginalis
Most clinically significant crystals in urine?
Cystine, Leucine, and Tyrocine
Calcium oxalate- Acid/alkaline
Envelopes or dumbells
most common form of kidney stone, ingestion of Ethylene glycol, vegetarian diet.

Monosodium Urate- Acidic
thin needles, pencil like small clusters
Gout
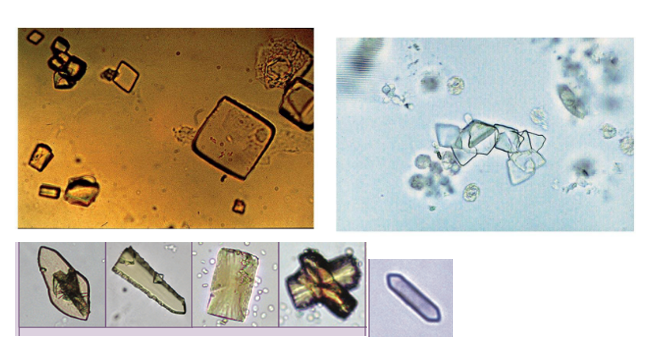
Uric acid- Acidic
Rhombic plates,
Can be seen after chemotherapy or gout
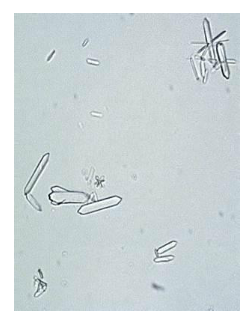
Hipuric acid- colorless
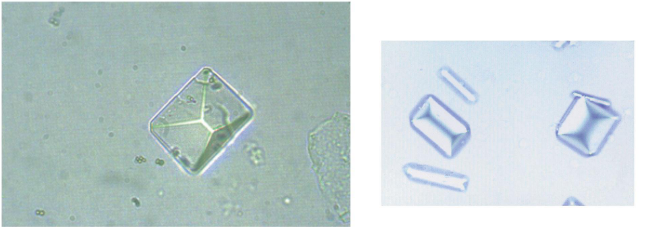
Triple phosphate- Alkaline

Calcium carbonate- Alkaline
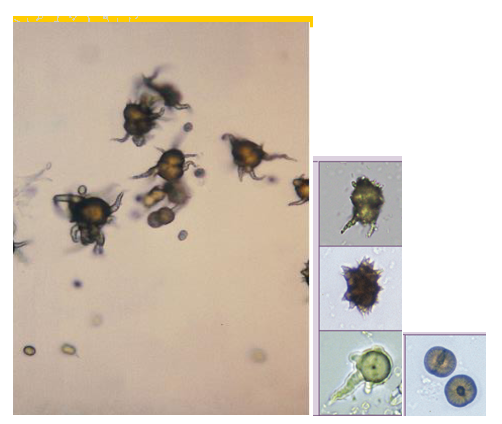
Ammonium Biurate- Alkaline
Old urine, in fresh its clinically significant, frenal tubular damage
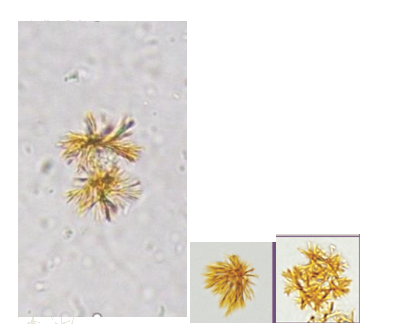
Bilirubin- Acidic
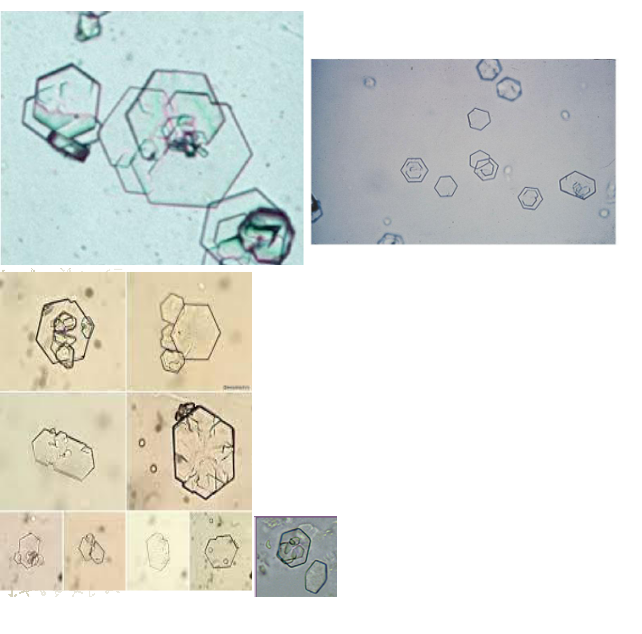
Cystine- Acidic/Alkaline
Clinically significant, hereditary cystinosis or cystinuria, renal damage, confirmatory test needed.
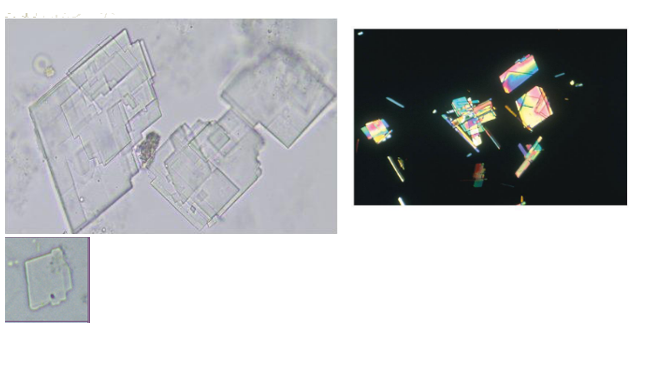
Cholesterol- Acidic

Tyrosine- Acidic
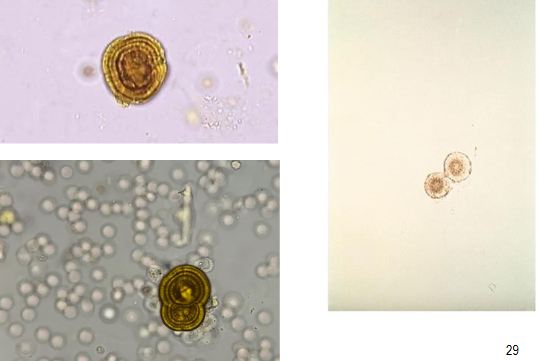
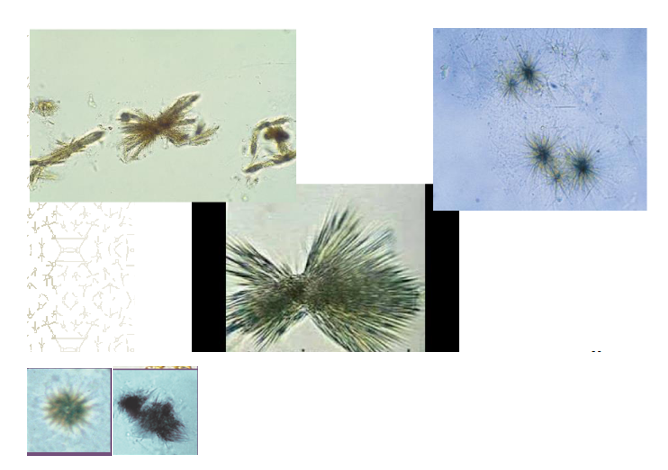
Leucine- Acidic
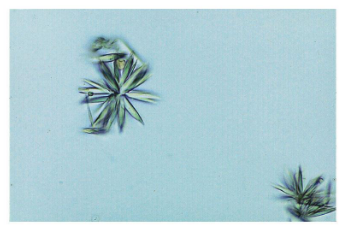
Sulfa crystals
Ionic X-ray media- acidic

Starch granules- Acidic/Alkaline