Biology - Intro to Genetics - Test
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What happens when genes are separated?
Gametes are formed
What is non-mendelian genetics?
Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, some traits are controlled by one or more genes
What is Incomplete Dominance?
When one allele is not completely dominant over another.
Is this incomplete dominance or codominance?
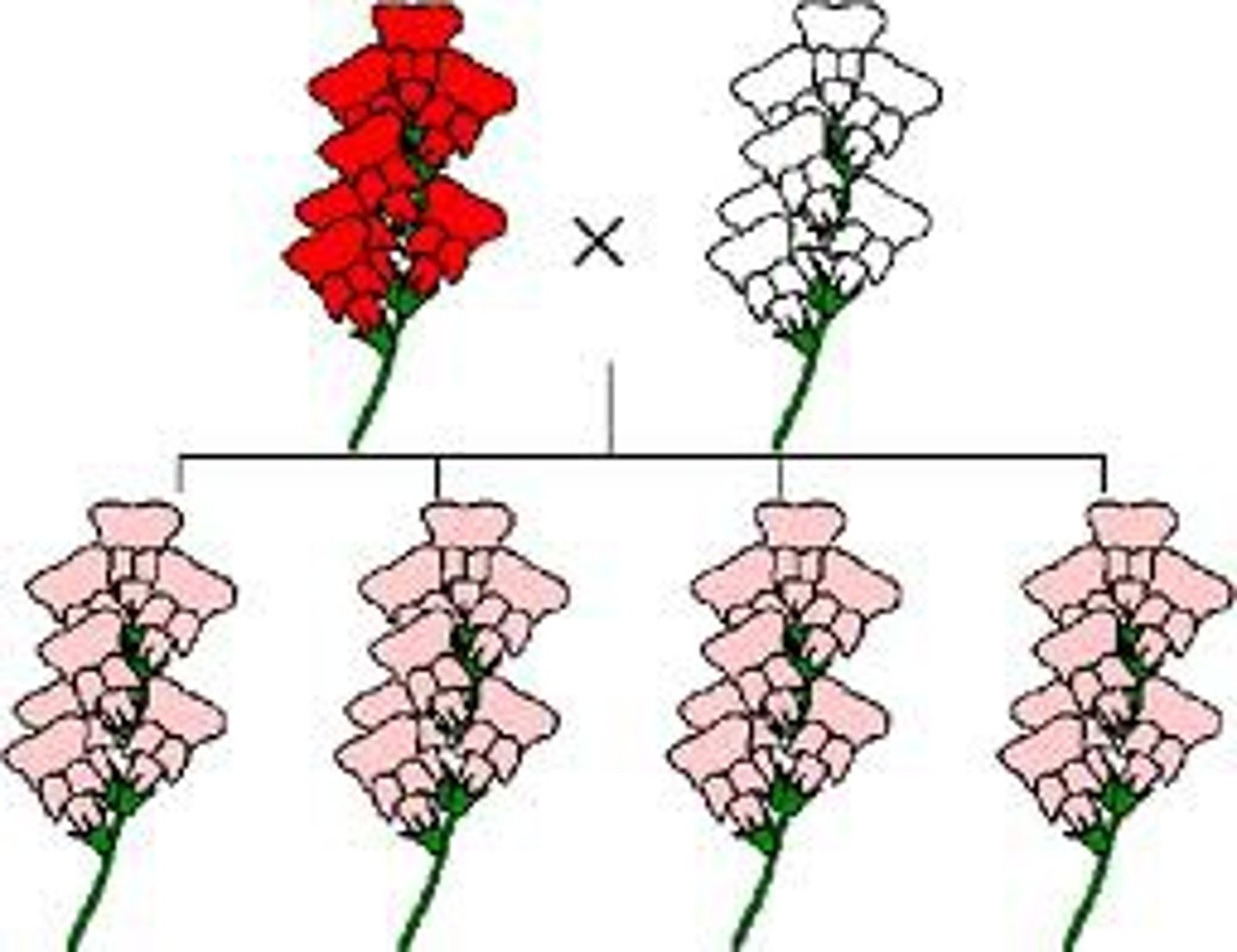
Is this incomplete dominance or codominance?

What is Codominance?
When both traits are fully expressed
Describe the difference between incomplete dominance and codominance.
Incomplete dominance, the offsprings are a blend. In codominance, both traits are expressed.
What does it mean to have "multiple alleles?"
To have more that 2 alleles.
What is the most common display of multiple alleals?
Codominance
What is a good example of multiple allele inheritance?
Blood type, there are 4 possible phenotypes
What are the 4 types of blood?
A, B, AB, O
What defines each type of blood?
Surface antigens
What makes blood type O different?
It has no surface antigens.
What are the 3 alleles for blood type?
I^A, I^B, i
What does genotype I^A I^A result in?
Blood type A
What does genotype I^A i result in?
Blood type A
What does genotype I^B I^B result in?
Blood type B
What does genotype I^A I^B result in?
Blood type AB, universal recipitant
What does genotype ii result in?
Blood type O, universal donor
What is the most common blood type?
O+
What is the 2nd most common blood type?
A+
What determines whether blood type is positive or negative?
Antigen D
What are traits controlled by 2 or more genes called?
Polygenic traits
Where can polygenic genes be located?
Along the same chromosome or on a different chromosome
What is skin color in humans controlled by?
Polygenic trait controlled by more than 4 genes
How are differences in genetics portrayed?
Shape of eyes, shape of nose, hair color, and the resemblance of your parents. These are called traits.
How many chromosomes does a fruit fly have?
8
What is the symbol for males?
♂
What is the symbol for females?
♀
What are homologous chromosomes?
2 sets or one pair of chromosomes that are genetically identical
What is a cell containing both sets of homologous chromosomes called?
diploid
What is the symbol for a a diploid?
2n
What are haploids?
Cells that only have one set of chromosomes
What is the symbol for haploids?
n
What are gamates?
Sex cells
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes with half the normal amount of chromosomes (n)
How many cells does meiosis produce?
4 cells
What happens before meiosis?
The chromosomes are replicated (S Phase)
What are the 2 parts of meiosis?
Meiosis I and Meiosis II
What is a tetrad?
2 pairs of homologous chromosomes attached to one another, so 4 chromatids total
What happens in Prophase I?
Each chromosome joins with its homologous pair to form a tetrad, then they exchange their chromatids in a process called crossing-over
What are chromosomes called after they cross over?
They are called alleles.
What is a tetrad of alleles called? (When chromatids have crossed over but they are still together)
Recumbent chromosomes
What happens in Metaphase I?
Pairs of homologous chromosomes randomly line up along the middle of the equator and connect to spindle fibers. This mixes up the chromosome combinations.
What happens in Anaphase I?
The spindle fibers pull the homologous chromosomes of the tetrad toward the opposite side end of the cell, but the sister chromatids stay attached to one another. (One chromosome gets transferred to each cell)
What happens in Telophase I and cytokenesis?
Nuclear membranes form, the cell separates into 2 cells, and the 2 cells made by meiosis I have different chromosome alleles that are different from each other.
What happens after Telophase I and cytokenesis?
The cell does not go through interphase again because they have all the chromosomes needed to divide again.
What happens in Metaphase II?
The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell
What happens in Anaphase II?
Sister chromatids are separated and move to other ends of the cell.
What happenes in Telophase II and cytokenesis?
Meiosis results in 4 haploid (n) daughter cells.
What does meiosis produce for male animals?
4 equal sized gametes called sperms
How does a sperm move?
Flagellum tail
What are the parts of a sperm?
The head, where there is tightly packed DNA, and the tail, which is powered by its own mitochondria in the middle piece.
What does meiosis produce in most female animals?
4 eggs, one egg is kept where most of the organelles, cytoplasm, and nutrients are sent. The other 3 are called polar bodies and are eventually broken down
How is meiosis different from mitosis?
Mitosis results in 2 genetically identical diploid cells. Meiosis produces 4 genetically different haploid cells.
Where is meiosis used?
How sexually reproducing organisms produce gametes
Where is mitosis used?
Asexual reproduction
What are somatic cells?
Body cells, diploids
What are all sex cells?
Haploids
List the type of cell (diploid, haploid): Liver cell
diploid, somatic cell
List the type of cell (diploid, haploid): Egg cell
haploid, gamete
List the type of cell (diploid, haploid): Sperm Cell
haploid, gamate
List the type of cell (diploid, haploid): Lung cell
diploid, somatic cell
Who started the study of heredity?
An Australian Monk named Gregor Mendel
What is the process where sperm and egg cells join together?
Fertilization
What is the product of fertilization?
New cell (diploid)
What are most plants? (Hint: Eggs and sperms in same flower)
Self-polinating
What is produced by self-polination?
Seeds that inherit all of the characteristics from the plant that bore them
What does true-breeding mean?
parents produce offsprings that are identical to themselves
What is the P Generation?
The parental generation, the original pair of true-breeding plants
What is the F1 Generation?
The first filial, or the offsprings of the parental generation.
What is the first concept mendel made to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern?
Alternate versions of genes account of variation in inherited characteristics (new alternates are called alleales)
What does each gene reside at?
A specific locus on a specific chromosome
What is the 2nd concept mendel made to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern?
For each characteristic an organism inherits, there are 2 alleles, one from each parent.
How many alleles do you need for 1 trait?
2 alleles
Why do you need 2 alleles for one trait?
One from mom, one from dad
What is the 3rd concept mendel made to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern?
If 2 alleles at a locus differ, then one (dominant allele) determines the organism's appearance and the other (recessive) has no noticeable effect on appearance.
What is the 4 concept mendel made to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern?
Known as the law of segregation, it states that the 2 alleles for a heritable character separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes. This happens during anaphase.
What are homozygous alleles?
2 identical alleles (TT, tt)
What are heterozygous alleles?
2 different alleles (Tt), they are hybrid for a particular trait
What is a genotype?
The set of alleles that an individual has for a trait
What is a phenotype?
The physical appearance of a character/trait, think physical, phenotype
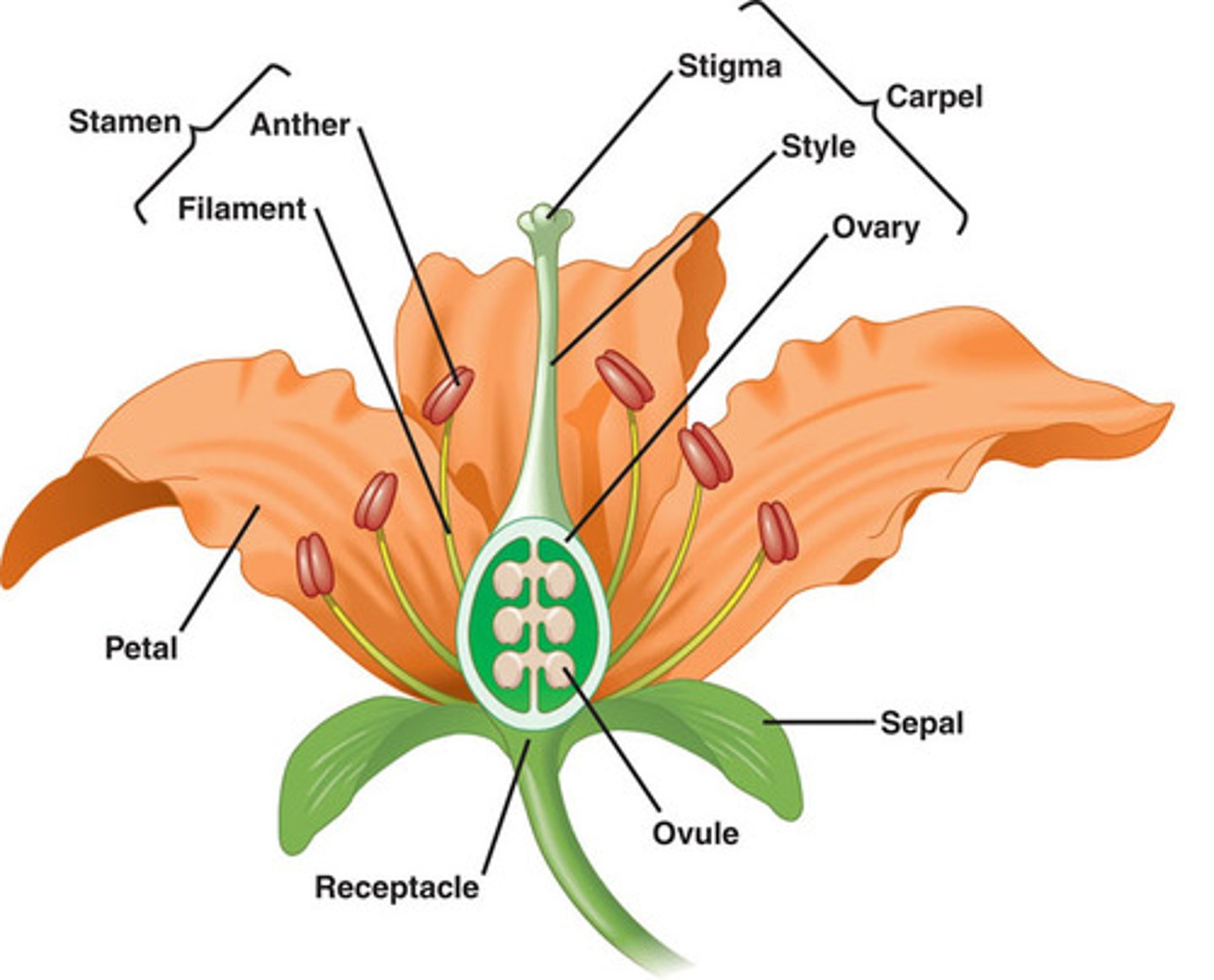
Be able to label a flower, including its male and female parts.
What is cross-polination?
Cut away male parts from the plant and dust a different color flower with the pollen
Why did Mendel cross-polinate?
So that he could produce plants that had 2 different color parents
What is cross breeding?
Producing an offspring with 2 genetically different parents
Gametes are formed by the process of what?
Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces...
Gamates
A sperm cell of a species of insect has 22 chromosomes, what is the diploid chromosome number for this species?
44
What can be said about a pair of chromosomes if they are the same length, contain the same genes, and the centromere is located in the same place?
homologous
How many chromosomes are in the body cells of an organism that has a haploid number of 8?
16
When does crossing over occur?
Prophase 1
During meiosis 1 spindle fibers extending from the centrioles attach to what?
centromeres
A haploid cell that is unable to be fertilized is called...
Polar body
During crossing over, genetic material is exchanged between...
non-sister chromatids
Mitosis involves the separation of only sister chromatids while meiosis involves...
Separation of homologous chromosomes as well as sister chromatids
Multicellular organisms like animals use mitosis for growth development, and...
repair
3 multiple choice options
If 2n has a total on 22 chromosomes how many daughter cells will have 11 chromosomes?
None
What 2 parts of the flower are involved in pollination
Stigma and anther
Fertilization is a result of...
When a 2n and a haploid are joined together