WGU D322
1/488
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
489 Terms
Information Technology
The technology used in creating, maintaining, and making information accessible.
IT Professional Roles
Administration and Support
System Administrator
responsible for providing technical support for hardware and software issues end users encounter, such as log-in issues
Network Administrator
is responsible for designing, planning, setting up, and maintaining an organization's network
Database Administrator
is responsible for installing and configuring databases. This position also fixes database errors and creates user accounts.
Security Administrator
is responsible for installing, administering, and troubleshooting network security issues
Web Administrator
is responsible for troubleshooting error messages employees encounter when attempting to access their organization's website. The web administrator is also responsible for tracking, compiling, and analyzing website usage data. This role reports security breaches to appropriate personnel.
Support IT Professionals
Help desk and training.
Information
collection of processed data from a variety of sources
DIKW Hierarchy
Defines the transition of data to information from knowledge to wisdom. (Data Information Knowledge Wisdom)
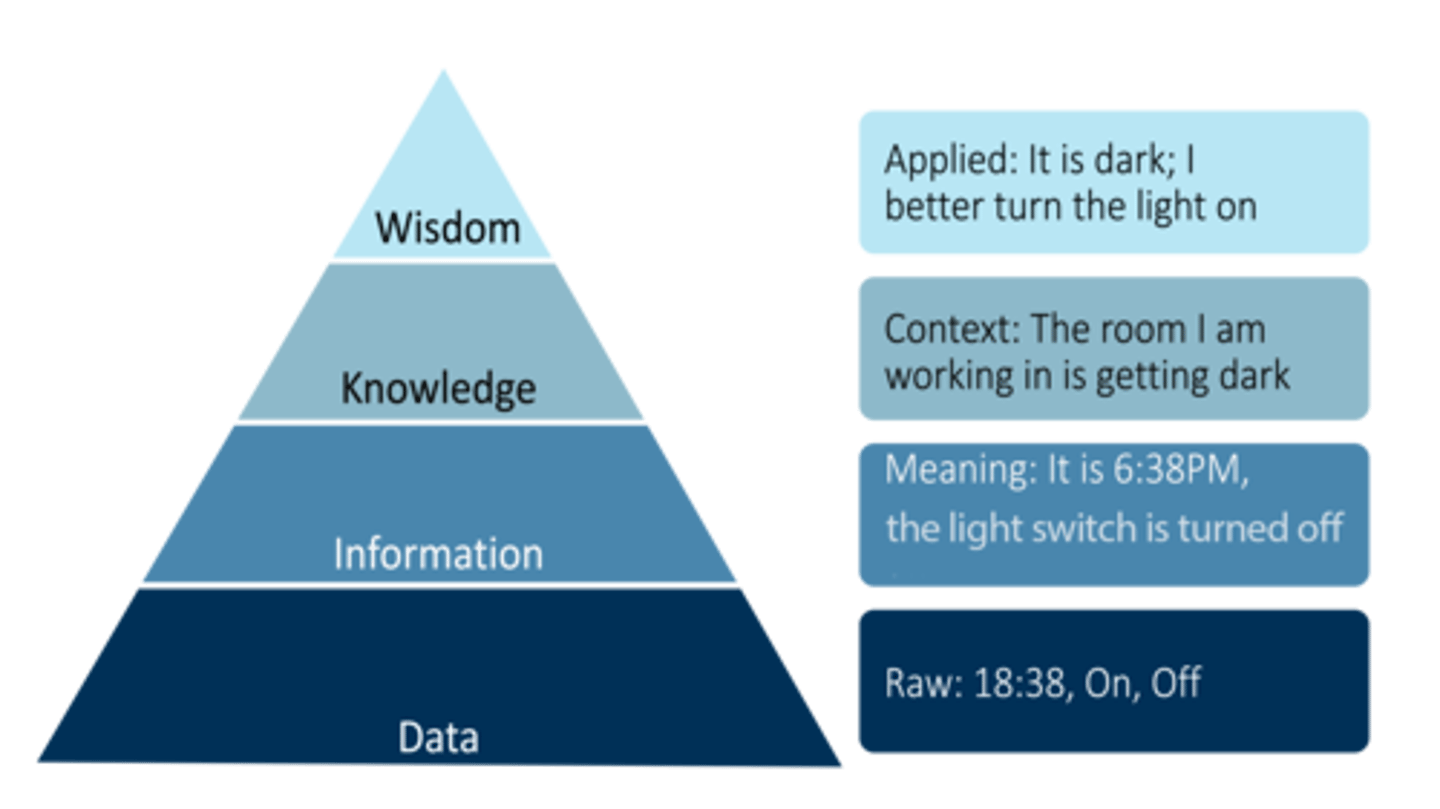
Data in DIKW
The input directly received by the user (or computer). It is generally not usable until it has been converted into a relevant form.
Information in DIKW
Having been inferred from data; one or more processes have been applied to the data to transform it into a more useful form.
Knowledge in DIKW
Information that has been put to use; information placed into a context. Refined information such that the user of the knowledge is able to call forth only relevant portions of information when needed. KNOWING THR RIGHT THING TO DO
Wisdom in DIKW
Provides a social setting to knowledge; an understanding of the "why". Can only come by having both knowledge and experience.
Information Systems
A collection of data and information used to support the management of an organization. Also refers to the technical components and human resources that enable the assembly, storage, and processing of data and the delivery of information. This has existed for a lot longer than computers.
Characteristics of Quality Data
Relevance - the data being used must apply directly to the decision being made
Timely - data must be efficient and must be provided in a timely manner
Thorough - the data must be complete
Accurate - data should be captured only once, where possible and should be captured as close to the point of activity as possible.
Reliable - data should reflect stable and consistent data collection processes across collections points and over time
Structured data
is coded in a way that makes it easy to convert into a form usable for analysis.
Examples of structured data
contact information such as first name, last name, email address, and phone number. In addition, quantitative fields like date of birth, date of transaction, and the amount received or amount due are forms of structured data.
Unstructured data
refers to data that is more complex and possibly stored in a format that is not easily decoded.
Examples of unstructured data
include data stored in text or video format, comments on a web page, text messages, and videos of presentations or conferences.
To begin analyzing business processes
a business must first collect data from multiple platforms and portals.
Data in businesses comes from various activities like
sales and marketing, finance, customer service, and relationship management.
Companies store data in multiple systems like
customer relationship management (CRM) system and sales records, finance, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and customer applications. each has data on every customer
Data Hygiene
refers to the processes of ensuring the cleanliness of data (i.e., that the data is relatively error-free)
Data scrubbing
the process of amending or removing data in a database that is incorrect, incomplete, improperly formatted, or duplicated.
Quality data
defined as data that is precise, valid, reliable, timely, and complete.
Good data enables businesses to do the following:
*Analyze the current financial state of the organization in terms of net profits, revenues, cash flow, assets, and liabilities
*Increase revenues through better targeting of products and increased customer satisfaction
*Examine existing production processes to take corrective action, improve efficiency, and lower costs
*Develop new, automated processes that integrate harmoniously into existing workflows and reduce demands on labor
*Gather competitive information on product and pricing decisions to stay ahead of competitors
*Make evidence-based decisions that utilize verifiable data to maximize profits and efficiency
*Understand business value by exploiting rapid changes in information and generating insights from diverse data sources to widen the competitive differentiation gap
Types of bad data
*Duplicate data: Two or more identical records
*Conflicting data: The same records with differing attributes
*Incomplete data: Missing attributes
*Invalid data: Attributes not conforming to standardization
*Unsynchronized data: Data not appropriately shared between two systems
three general steps for transforming institutional knowledge into implementable data solutions:
capturing, analyzing, and using.
IPO
The input-process-output
4 main functions of a computer
Input, processing, Output, Storage
Input
Raw data is entered by the user.
Processing
actoins computer takes to execute commands. Raw data is organized or structured for usefulness.
Output
Information is given out so users can see results. results provided by the computer after processing
Storage
Processed information is stored for permanent record.
Computer System
A collection of components that work together to meet the needs of the user; typically categorized as either hardware, software, networks, or users.
The most important element of a computer system is?
its users, sometimes called liveware
Hardware
Physical components of a computer system which include the system unit and its components and peripheral devices; tangible aspects of the computer. Motherboards, graphics cards, central processing units (CPUs), and power supply
Middleware
allows the hardware and software to communicate with each other, enabling data to move between computer system components
Software
a collection of instructions that enable a user to interact with a computer to perform tasks. Internet browsers, text editing tools, and spreadsheets are examples of computer software
Types of system software
Windows, Mac, or Linux
Word processing applications
allow users to type letters, complete assignments, and produce any other written artifact.
Spreadsheet applications
Spreadsheet applications help create charts and complete complex calculations.
Email applications
allow a user to receive and send email communications.
Web browsers
allow a user to access the content of web pages on various sites.
The Motherboard
is at the center of what makes a computer work. It houses the CPU and serves as the brain of the system allocating resources, such as power, and communicating with all other components.
The CPU
processes the data from the programs your computer runs.
Random-access memory (RAM)
occupies the memory slots of the CPU and keeps that data immediately accessible.
The hard drive
is a storage device that permanently stores data, or temporarily stores data in a paging file system.
This paging
a built-in mechanism available with most operating systems that permit data to be moved from RAM to the hard drive when the amount of memory in use exceeds the memory available on the computer system.
Network
A collection of computers and resources connected by various media so that they can communicate with each other.
3 common types of network
local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) and Personal area network (PAN)
LAN
consist of a collection of computers in a single building or building complex. such as homes, schools or a manufacturing building
WAN
reach across cities, states, or even across the world. The internet is the world's largest public wide area network.
PAN
is normally used for short-range communications, within a few feet, such as wireless headphones to a smartphone or a wireless mouse to a PC.
open network vs closed/proprietary network
the network's internal workings are based on designs that are in the public domain (open network) or on designs owned or controlled by third parties (closed or proprietary networks). Open network designs are freely circulated and are often more popular than proprietary designs that are restricted by license fees and contracts
example of an open network
The internet
User
Those who use a computer.
What is the world largest area network?
The Internet
2 types of network design includes
client-to-server and peer-to-peer
client-to-server
a popular convention used for interprocess communication. The basic roles played by the processes are categorized as either a client making requests or a server satisfying client requests.
peer-to-peer Network
another model for interprocess communication. In this model, processers both request and provide service to each other. Instant messaging and interactive games played by users on multiple machines are both examples of the P2P model.
BitTorrent
used commonly for distributing large video files, employs a "swarm" model, whereby files are downloaded in simultaneous pieces from multiple host computers
The Gnutella protocol
operates without any centralized server and allows for numerous software clients to be used for access, which makes it nearly impossible to shut down.
There are several types of distributed systems
Cluster computing, Grid computing, Cloud computing
Cluster computing
uses many independent computers to provide computation or services comparable to those of a larger machine. The cost of several individual machines can be less than a higher-priced supercomputer, with comparable performance. Cluster computing provides high availability as it is likely that at least one computer in the cluster will be able to answer a request even when others in the cluster are unavailable or broken down. In addition, clusters can balance loads by automatically shifting requests among the cluster members
Grid computing
is a type of distributed system that is more loosely coupled than clusters but still works together as a system to complete large tasks. Grid computing typically includes specialized software to make it easier to distribute the workload and data among the machines in the grid
Cloud computing
provides large pools of shared computers that can be allocated to clients as needed. Services such as Amazon's Elastic Compute Cloud allow clients to rent virtual computers by the hour no matter where the associated computer hardware is located. Services such as Google Cloud and Google Apps allow users to collaborate or build web services without needing to know how many computers are working on the problem or where the relevant data is stored. Cloud computing provides reasonable guarantees for reliability and scalability while raising concerns about security and privacy.
A transmission medium
A transmission medium (the singular form of the word "media") is simply a component that carries data from one network device to another. There are two types of transmission media: wired and wireless.
wired networks
Twisted pair cables, coaxial cable, and optical fiber cables are common network media.
Twisted pair cables are the most widely used type of transmission media. Two common types of twisted pair cables are unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). STP cables consist of two separately insulated copper wires wound around each other, making them more expensive than UTP cables.
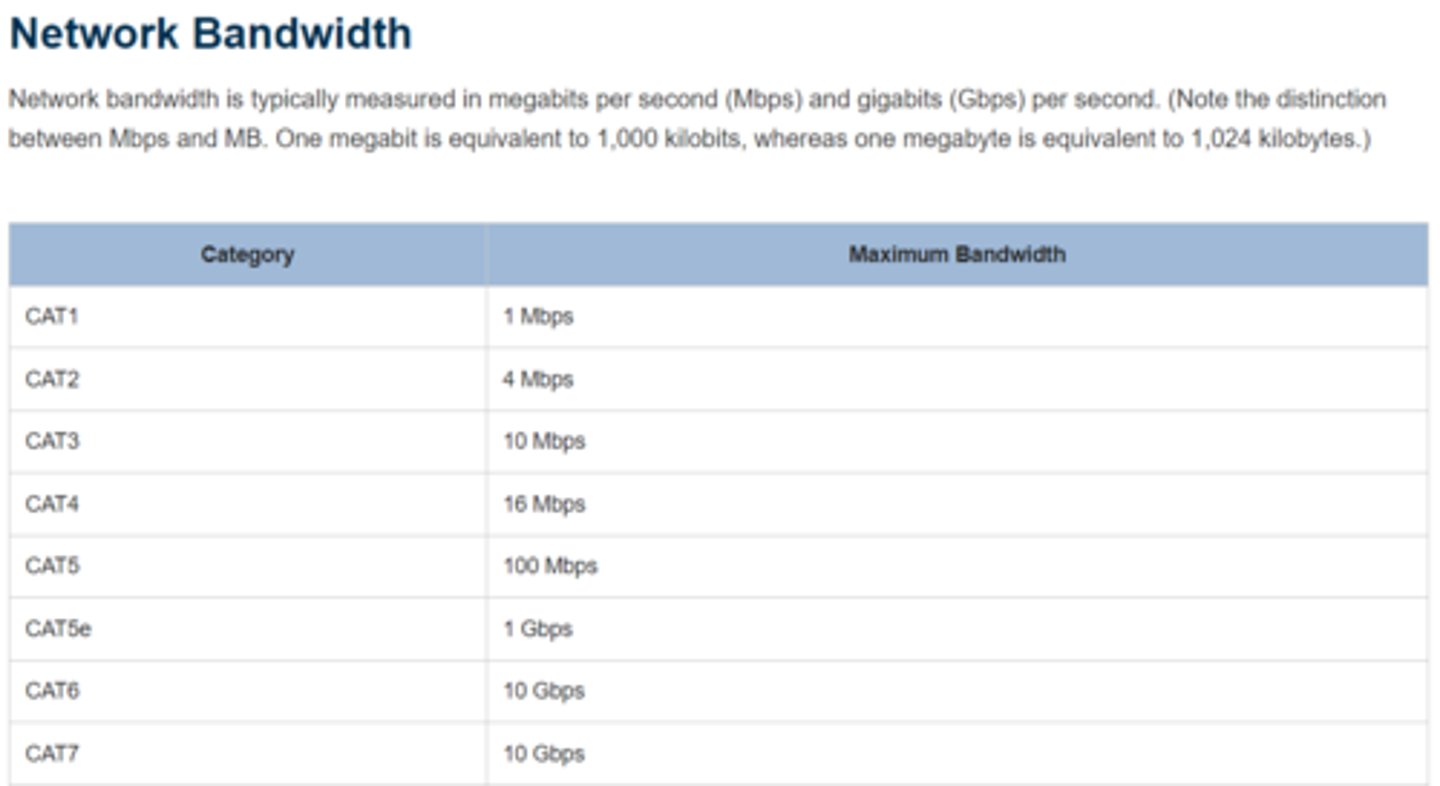
Network bandwidth is measured in:
measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and gigabits (Gbps) per second
Coaxial Cables
(often referred to as "coax") have an outer plastic that is used in computer networks and to deliver cable TV services. First used commercially used in the 1940s, it is used for both baseband and broadband data communication services. The bandwidth of coaxial cables is about 80 times the bandwidth of twisted wires. Cable modems and televisions typically use coaxial cables.
Baseband
is a signal at a very narrow frequency range on which data or information is superimposed and then transmitted. Examples include Ethernet LANs and serial cables.
Broadband
is considered high-capacity transmission technologies that are used to transmit data, voice, and video across long distances and at high speeds. Examples include coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, and radio waves.
Fiber-Optic Cable
uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. Fiber-optic cable are able to transmit large volumes of data. Their bandwidth can provide up to 26,000 times the bandwidth of the twisted pair wires, at the time of this writing.
Bluetooth vs WiFi
Bluetooth supports distances shorter than 30 feet, while Wi-Fi devices can be accessed up to 300 feet away.
wireless networks
use radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
The following devices can be used to connect networks:
Repeaters, bridges, switches, routers
Repeaters
extend the range of cabling types so connections can be made by increasing the strength of the network signal. For example, if two twisted pair cabling networks are 500 feet apart, a repeater can be used to extend the 300 feet range of twisted pair cabling to 500 feet. Repeaters can be used on fiber and coaxial also.
Bridges
are used to connect to different types of network and provide management of the message. For example, a bridge can connect a twisted pair and coaxial network. The bridge analyzes the network message and will only bridge the network if a message is addressed to a device on the other side.
Switches
are used on LANs to reduce network traffic by management of network messages. Older devices would broadcast all messages to all devices on the LAN. For example, on a 100-device network, a switch would only send one message to the destination device. This management example would create 99% less traffic.
Routers
are the device that makes the internet possible. A router connected to your LAN acts as gateway to the internet. (This device on your LAN can be also be called a Gateway.) Routers manage network traffic by having a routing table of know devices. If a destination address is unknown to the Router, it will forward the message to another router. This analyze and forward process continues until the message reaches the correct address.
Most common network topologies are
bus, star, ring, and mesh.
Software Categories
Systems Software and Applications Software
Evolution of Users
First users were the engineers who built and programmed computers, then employees who had received specialized training were users, and now today, anyone and everyone can be a user.
Protocol
Rules provided by which networks communicate with each other OR Languages supporting data exchange between computers (textbook definition)
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. Most commonly used protocol; is required of all computers that communicate over the Internet. found in internet and home network
Special-purpose computer systems include
network routers, access points, and switches. These devices, along with cable media such as fiber optic and Ethernet, make it possible for devices to communicate with each other.
Protocol Stack
A collection of protocols. TCP/IP is an example.
One of the earliest computing devices was?
The Abacus, probably first used in China and then by the early Greek and Roman civilizations
Leibniz machine
the gears of the machine are initially mechanically set in a position that represents the input, and their final state represents the output of the calculations.
Who is considered the world's first programmer?
Ada Lovelace
Components of a Computer
CPU, Memory and Storage, Peripheral Devices
Memory
Stores the programs being executed and the data they are using.
input/output....I/O Subsystem
All peripheral devices where long term storage devices are used. Provides efficient mode of communication btw the central system and the outside environment
Bus or Bus lines
wires that serve as electrical roadways, transmitting information between the CPU and other components.
3 types of buses
1) Address bus: Carries the destination address of where the data is assigned to be processed
2) Data bus: Carries data between the processor, the memory unit, and the input/output devices
3)Control bus: Carries control signals (commands) from the CPU (and status signals from devices); controls and coordinates all activities within the computer system
System Unit
Critical component of all computer based systems; consists of most of the hardware the computer needs in order to run; comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. also known as a tower or chassis
Internal Components of the System Unit
Case, Internal Bays, Buses, Ports, Hard Drive, Motherboard, CPU, CPU Cooler(heat sink), Memory Module (RAM), Power Supply Unit (PSU), Expansion Slots/Cards
Parts of the CPU
Control Unit (CU) - retrieves the instructions and the raw data that is input and coordinates or controls the sending of those instructions and data to the ALU
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) - does the actual processing of the data; completing mathematical calculations and logical operations to process the data and converting the input of the keyboard text entry to output displayed on the screen