Plasma Membrane and Water Potential
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Plasma Membrane
A barrier composed of phospholipids and proteins.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads.
Fluid Mosaic Model (Singer + Nicolson)
Phospholipid bilayer with proteins partially or fully imbedded, electron micrographs of freeze-fractured membrane
Robert Hooke
First to describe cells in 1665.
Charles Overton
Proposed membrane composed of lipids in 1895.
E. Gorter and G. Grendel
Identified phospholipid bilayer structure in 1925.
Sandwich Model (Danielli + Davson)
Plasma membrane model where 2 layers of globular proteins with phospholipid inside to make a layer and then join 2 layers together to make a channel for molecules to pass
Unit Membrane Model (Robertson)
Outer layer of protein with phospholipid bilayer inside, believed that all cells are the same composition, does not explain how some molecules pass through or use the proteins with nonpolar parts, used transmission electron microscopy
Cholesterol
Regulates membrane fluidity at varying temperatures.
Transport Proteins
Facilitate movement of substances across the membrane.
Isotonic Solution
Equal solute concentration inside and outside the cell.
Hypotonic Solution
Lower solute concentration outside, causing cell swelling.
Hypertonic Solution
Higher solute concentration outside, causing cell shrinkage.
Plasmolysis
Cell shrinkage due to water loss in hypertonic solution.
A plant wilts (sags) in a hypertonic environment, since the water in the cells diffuses out and turgor pressure is lost
Exocytosis
Movement of large molecules bound in the vesicles out of the cell with the aid of ATP energy
Vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane to eject macromolecules
Endocytosis
Movement of large molecules bound in the vesicles into the cell with the aid of ATP energy
Phagocytosis
Cellular eating; engulfing large particles or cells.
Pinocytosis
Cellular drinking; engulfing liquids and small solutes.
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Specific uptake of molecules via receptor binding.
Cotransport
Active transport of one solute drives another's transport.
Active Transport
Molecules from from low to high concentration gradient using ATP energy
Membrane Potential
Voltage difference across a cell membrane.
Water Potential (ΨW)
Potential energy of water; quantitative description of free energy in water
Pressure Potential (ΨP)
Pressure exerted by water in plant cells.
Osmotic Potential (ΨS)
Effect of solutes on water potential, always negative.
Membrane Potential (ΨM)
Influence of membranes on water potential.
tendency to bump into other things that depresses movement
Sandwich model
Unit Membrane model
Fluid Mosaic model
What are the 3 plasma membrane models?
Basic Tenets of the Fluid Mosaic Model
Hydrophilic lipid heads face outwards and hydrophobic lipid tails face inward
The “fluid” part is attributed to the sideway movements of phospholipids
Membrane proteins define the “mosaic” part
Biological model by Singer-Nicolson that describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components that gives the membrane a fluid character.
The cell membrane is heterogeneous and patchy due to the nature of proteins which diffuse or remain attached to its neighbors.
Phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol
Proteins
Cytoskeletal filaments
Carbohydrate chain
The plasma membrane contains what?
Transmembrane/Intrinsic/Integral: fully embedded in bilayer
Peripheral/Extrinsic: outer of inner surface of the bilayer
What are the two types of proteins?
Transport proteins
Receptor proteins
Enzymatic proteins
Cell Recognition proteins
Attachment proteins
Intercellular Junction proteins
What are the 6 membrane functions of the proteins in the plasma membrane?
Carrier Protein - possess configurations for certain
molecules to pass through the membrane
Channel Protein - allows materials to pass through the
membrane; acts as a tunnel
2 types of transport proteins
Receptor proteins
Recognize and receive chemical signals
Enzymatic proteins
Serve as enzymes or the venue for certain cellular reactions
Cell recognition proteins
Possess structures (e.g., carbohydrate chain) that can be used to interact with other cells
Attachment proteins
Have cytoskeletal structures attached to them, allowing the protein to attach to other structures
Intercellular Junction Proteins
Serve as a junction between other cells
Through the plasma membrane, some move between the phospholipids or through the proteins
How do materials move into and out of the cell?
No, because proteins are randomly distributed in each phospholipid bilayer where some are organized into lipid drafts or microdomains
Do all plasma membranes look the same?
Plasma/cell membrane
What cell structure is common to all living things that acts as a selective barrier to passage of materials into and out of the cell?
Plasmodesmata vs pits
Plasmodesmata: gaps
Pits: depression only
But these both serve the same purpose
Thin areas on the secondary cell walls of plants. They look like depressions on the walls. Also, they aid in the transport of minerals and water between the cells
What are pits?
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
3 membrane transport mechanisms of passive transport
Diffusion
Molecules move directly through the lipid bilayer
Net movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration until equilibrium is reached
Gases (O, C, D), water molecules (slow rate due to polarity), lipids (steroid hormones), lipid-soluble molecules (hydrocarbons, alcohols, some vitamins), small uncharged molecules (NH3)
What materials pass through the plasma membrane by diffusion?
temperature, pressure, state of matter, size of concentration gradient, and surface area of membrane
Diffusion rate is related to…
Facilitated Diffusion
Net movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration with the aid of a channel of carrier proteins
Ions, sugars, amino acids, small water-soluble molecules, water (faster than diffusion)
What materials pass through the plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion?
Channel proteins: ions, small solutes, and water to pass
Carrier proteins: glucose and amino acids
How does facilitated diffusion work?
Osmosis
movement of water through the plasma membrane, form high to low concentration gradient
Tonicity
Measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient
Total solute concentration of the solution outside the cell
Isotonic
■ Concentration: outside = inside
Hypertonic
■ Concentration: outside > inside
■ net movement of water will be out of the body and into the solution
Hypotonic
■ Concentration: outside < inside
■ net movement of water will be into the body from the solution
Differentiate isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic from each other
Plants use osmosis in hypotonic soil
How to maintain rigidity
plasmolyzed/shriveled
Water leaving the cell will make the cells
Turgid
Water entering the cell will make it
Turgor pressure
Pressure of water molecules against the cell wall; cell swelling stops when the expanding membrane hits the cell wall
Cell wall
What keeps plant cells from bursting?
Active transport
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
3 types of active transport
Pumps
Protein carriers in active transport are called
Needed for the constant supply of raw materials and to get rid of unwanted molecules
Maintains internal conditions different from the environment
Regulates the volume of cells by controlling osmotic potential
Functions of active transport
Class of cellular structures consisting of multi-protein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between the cell and extracellular matrix of animals
Define cell junctions
Plasmodesmata, like xylem and phloem
Cell junctions in plants
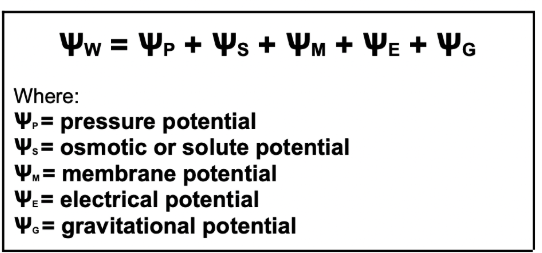
Ѱs = the more solute, the less the water potential; always negative
Ѱp = the more water flowing inside denotes higher pressure potential, thus higher Ѱw
Ѱm = the higher the membrane potential, the lesser the water potential
Ѱe and Ѱg can be ignored
What is the full equation of water potential?
Ѱs = negative
Ѱm = negative
Ѱp = positive
Pure water means Ѱw = 0
Conditions in water potential
negative
Plant cells usually have a _______ Ѱw
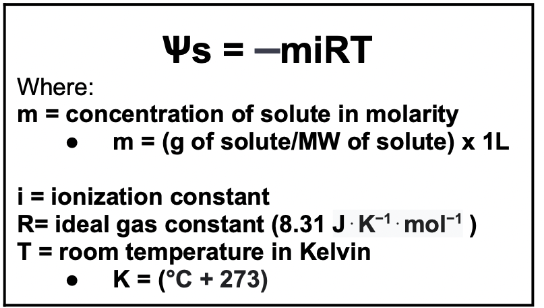
How to calculate Ѱs?
Pressure
Concentration
Electrical
Gravity
Ѱw can be affected by:

In the case of a tree, the soil outside the roots must have greater water potential. How does this happen?
If there is higher water potential inside, water will leave which will make it wilt. To revive it, just water it again
Why does a plant become wilted?